



Geoscience ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (02): 353-374.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.062
• Petrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
LOU Yuanlin1,2,3( ), CHENG Ming1, TANG Yao1, ZHANG Chaoming1, LAN Jingzhou1, YUAN Yongsheng4, YANG Tao5
), CHENG Ming1, TANG Yao1, ZHANG Chaoming1, LAN Jingzhou1, YUAN Yongsheng4, YANG Tao5
Received:2022-03-04
Revised:2022-09-29
Online:2023-04-10
Published:2023-05-23
CLC Number:
LOU Yuanlin, CHENG Ming, TANG Yao, ZHANG Chaoming, LAN Jingzhou, YUAN Yongsheng, YANG Tao. Geochemical Characteristics,Tectonic Setting, and Mineralization of Magmatic Rocks in Gudui Area, Southern Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 353-374.

Fig.1 Sketch map showing the distribution of magmatic rocks and structures (a) and ore deposits (b) in the Gudui area, southern Tibet (modified after ref.[8])
| 样品类型 | 样品时代 | 采样位置 | 岩性(个数) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 侵入岩 | 早白垩世 | 江拉、哲古 | 辉长岩(5),辉绿岩(2),闪长岩(1) |
| 始新世 | 达拉、恰嘎 | 绢英岩化斑状花岗岩(2),斑状花岗岩(1),斑状二长花岗岩(1) | |
| 火山岩 | 晚三叠世 | 拉九 | 玄武岩(3) |
| 中侏罗世 | 古堆、杀渔朗 | 玄武岩(2),英安岩(6) | |
| 晚侏罗世—早白垩世 | 夏瓦 | 玄武岩(5) | |
| 脉岩 | 侏罗纪 | 古堆、恰嘎 | 煌斑岩(8) |
Table 1 Statistics of magmatic rocks in the Gudui area, southern Tibet
| 样品类型 | 样品时代 | 采样位置 | 岩性(个数) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 侵入岩 | 早白垩世 | 江拉、哲古 | 辉长岩(5),辉绿岩(2),闪长岩(1) |
| 始新世 | 达拉、恰嘎 | 绢英岩化斑状花岗岩(2),斑状花岗岩(1),斑状二长花岗岩(1) | |
| 火山岩 | 晚三叠世 | 拉九 | 玄武岩(3) |
| 中侏罗世 | 古堆、杀渔朗 | 玄武岩(2),英安岩(6) | |
| 晚侏罗世—早白垩世 | 夏瓦 | 玄武岩(5) | |
| 脉岩 | 侏罗纪 | 古堆、恰嘎 | 煌斑岩(8) |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | Mg# | A/CNK | AR | σ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM4QY002 | 辉长岩 | 52.14 | 3.64 | 13.96 | 3.02 | 7.48 | 0.15 | 3.54 | 6.52 | 3.84 | 1.63 | 0.66 | 2.89 | 99.47 | 5.47 | 0.42 | 46.00 | 0.70 | 1.73 | 3.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM101 | 49.85 | 2.93 | 14.68 | 3.24 | 8.59 | 0.17 | 3.53 | 7.51 | 3.82 | 1.37 | 0.53 | 2.69 | 98.91 | 5.19 | 0.36 | 42.52 | 0.69 | 1.61 | 3.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM102 | 48.76 | 2.84 | 13.86 | 2.70 | 8.56 | 0.16 | 6.36 | 8.90 | 3.07 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 3.19 | 98.86 | 3.19 | 0.04 | 57.22 | 0.65 | 1.33 | 1.77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM301 | 49.18 | 4.13 | 14.36 | 2.32 | 8.91 | 0.15 | 4.48 | 6.79 | 4.39 | 1.15 | 0.47 | 2.52 | 98.85 | 5.54 | 0.26 | 47.51 | 0.69 | 1.71 | 4.97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM302 | 48.14 | 2.51 | 12.88 | 2.92 | 8.14 | 0.17 | 3.63 | 6.66 | 2.83 | 0.91 | 0.51 | 9.66 | 98.96 | 3.74 | 0.32 | 44.53 | 0.73 | 1.47 | 2.72 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q6 | 辉绿岩 | 51.70 | 2.42 | 14.36 | 2.12 | 7.95 | 0.16 | 5.33 | 7.65 | 2.74 | 1.44 | 0.29 | 2.02 | 98.18 | 4.18 | 0.53 | 54.69 | 0.72 | 1.47 | 2.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q8 | 50.61 | 2.22 | 15.34 | 1.86 | 7.34 | 0.15 | 5.42 | 8.50 | 2.46 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 2.49 | 97.96 | 3.77 | 0.53 | 57.07 | 0.73 | 1.38 | 1.87 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q14 | 闪长岩 | 55.40 | 2.08 | 13.13 | 2.98 | 7.79 | 0.14 | 2.54 | 5.30 | 2.80 | 2.66 | 0.86 | 2.40 | 98.08 | 5.46 | 0.95 | 36.98 | 0.77 | 1.84 | 2.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM3 | 恰嘎 花岗岩 | 74.91 | 0.05 | 15.08 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.99 | 3.86 | 2.32 | 0.10 | 1.91 | 100.12 | 6.18 | 0.60 | — | 1.41 | 2.25 | 1.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM4 | 71.85 | 0.28 | 15.30 | 1.89 | 1.00 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 2.45 | 3.24 | 3.08 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 100.83 | 6.32 | 0.95 | — | 1.17 | 2.11 | 1.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM2 | 达拉 花岗岩 | 75.39 | 0.07 | 14.61 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.97 | 3.59 | 2.38 | 0.07 | 2.10 | 100.19 | 5.97 | 0.66 | — | 1.43 | 2.24 | 1.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | 68.17 | 0.28 | 16.27 | 0.38 | 1.39 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 2.83 | 3.93 | 3.01 | 0.10 | 1.91 | 99.19 | 6.94 | 0.77 | — | 1.09 | 2.14 | 1.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Cr | Ni | Co | V | Rb | Sr | Ba | Sc | Nb | Ta | Li | Zr | Hf | U | Th | W | Sn | Cu | Pb | Zn | Au | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM4QY002 | 辉长岩 | 12.20 | 17.60 | 40.80 | 237.8 | 22.2 | 441.6 | 433.0 | 19.60 | 61.70 | 3.54 | 17.2 | 914.8 | 12.80 | 1.06 | 3.64 | 0.68 | 8.30 | 27.00 | 13.8 | 119.8 | <0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM101 | 37.50 | 18.10 | 24.20 | 139.7 | 125.3 | 128.9 | 501.5 | 17.60 | 27.20 | 1.69 | 39.8 | 387.8 | 10.20 | 2.43 | 23.60 | 2.64 | 3.74 | 11.40 | 26.0 | 99.7 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM102 | 132.60 | 49.60 | 45.50 | 271.4 | 5.0 | 121.7 | 155.7 | 26.80 | 18.20 | 0.97 | 35.7 | 332.1 | 5.40 | 0.28 | 1.40 | 0.91 | 3.92 | 20.10 | 5.7 | 100.9 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM301 | 18.80 | 18.70 | 52.20 | 312.0 | 20.4 | 183.8 | 205.8 | 23.60 | 42.00 | 2.54 | 31.5 | 598.3 | 6.80 | 0.69 | 3.00 | 0.62 | 2.35 | 18.80 | 13.7 | 103.0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM302 | 11.80 | 2.00 | 36.50 | 256.4 | 26.1 | 127.3 | 201.8 | 16.70 | 29.20 | 1.45 | 74.1 | 175.3 | 7.30 | 0.43 | 4.87 | 0.41 | 5.00 | 6.00 | 20.9 | 110.5 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q6 | 辉绿岩 | 131.70 | 20.30 | 43.80 | 273.2 | 50.3 | 394.3 | 355.4 | 26.30 | 26.40 | 0.72 | 36.9 | 273.6 | 07.21 | 0.61 | 5.80 | 2.11 | 2.82 | — | 21.7 | 100.5 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q8 | 115.80 | 24.00 | 41.67 | 257.3 | 49.9 | 412.3 | 279.4 | 25.40 | 28.60 | 0.63 | 25.7 | 216.3 | 10.80 | 0.81 | 5.61 | 1.59 | 2.07 | — | 24.8 | 95.4 | 0.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q14 | 闪长岩 | 102.10 | 1.68 | 35.40 | 140.5 | 69.3 | 448.6 | 516.0 | 18.90 | 35.30 | 1.81 | 26.1 | 603.5 | 28.10 | 1.46 | 6.01 | 1.26 | 3.52 | — | 21.5 | 158.3 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM3 | 恰嘎 花岗岩 | 2.52 | 0.92 | 04.94 | 025.6 | 237.5 | 114.3 | 044.0 | 06.90 | 07.21 | 1.45 | 101.5 | 100.5 | 05.04 | 7.43 | 6.80 | 48.10 | 19.80 | 2.72 | 126.8 | 31.3 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM4 | 6.22 | 4.39 | 15.10 | 042.1 | 164.8 | 352.2 | 473.9 | 08.61 | 09.44 | 1.27 | 059.3 | 019.0 | 00.82 | 1.48 | 12.70 | 146.00 | 3.66 | 4.27 | 60.0 | 58.9 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM2 | 达拉 花岗岩 | 2.56 | 1.57 | 3.09 | 020.2 | 213.2 | 050.4 | 034.0 | 11.0 | 06.55 | 1.49 | 054.5 | 092.8 | 04.63 | 5.82 | 03.91 | 28.30 | 20.30 | 1.59 | 126.5 | 35.6 | 1.35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | — | — | — | — | 149.8 | 373.0 | 483.4 | — | 07.96 | 0.15 | — | 092.3 | 03.91 | 1.79 | 11.60 | — | — | — | 47.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | LaN/ YbN | Eu* | Ce* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM4QY002 | 辉长岩 | 48.98 | 57.72 | 119.20 | 15.94 | 75.72 | 14.45 | 4.45 | 11.96 | 2.08 | 10.39 | 2.04 | 5.38 | 0.73 | 4.74 | 0.69 | 325.49 | 287.48 | 38.01 | 7.56 | 8.73 | 1.03 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM101 | 34.71 | 10.69 | 44.51 | 6.37 | 32.31 | 7.58 | 2.43 | 6.68 | 1.37 | 7.13 | 1.47 | 3.76 | 0.52 | 3.23 | 0.48 | 128.53 | 103.89 | 24.64 | 4.22 | 2.37 | 1.04 | 1.32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM102 | 35.19 | 38.74 | 94.78 | 13.70 | 69.13 | 13.58 | 5.85 | 11.28 | 1.90 | 8.67 | 1.59 | 3.70 | 0.41 | 2.28 | 0.31 | 265.92 | 235.78 | 30.14 | 7.82 | 12.19 | 1.45 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM301 | 36.53 | 24.02 | 65.64 | 9.15 | 45.03 | 9.56 | 3.32 | 8.25 | 1.53 | 7.69 | 1.57 | 4.02 | 0.55 | 3.38 | 0.49 | 184.20 | 156.72 | 27.48 | 5.70 | 5.10 | 1.14 | 1.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM302 | 42.41 | 37.03 | 85.91 | 11.56 | 54.38 | 11.13 | 3.19 | 9.64 | 1.83 | 9.14 | 1.83 | 4.76 | 0.64 | 3.73 | 0.54 | 235.31 | 203.20 | 32.11 | 6.33 | 7.12 | 0.94 | 1.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | LaN/ YbN | Eu* | Ce* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q6 | 辉绿岩 | 55.17 | 37.34 | 78.77 | 10.23 | 43.64 | 10.34 | 4.38 | 9.35 | 1.72 | 10.39 | 2.05 | 5.45 | 0.86 | 5.05 | 0.74 | 220.31 | 184.70 | 35.61 | 5.19 | 5.30 | 1.36 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q8 | 49.69 | 32.84 | 68.17 | 8.78 | 37.50 | 8.86 | 3.86 | 8.17 | 1.49 | 9.08 | 1.83 | 4.91 | 0.79 | 4.63 | 0.72 | 191.63 | 160.01 | 31.62 | 5.06 | 5.09 | 1.39 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q14 | 闪长岩 | 91.36 | 81.52 | 204.60 | 22.63 | 97.61 | 22.92 | 10.08 | 19.68 | 3.15 | 18.80 | 3.34 | 9.20 | 1.43 | 8.93 | 1.39 | 505.28 | 439.36 | 65.92 | 6.67 | 6.55 | 1.45 | 1.17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM3 | 恰嘎 花岗岩 | 9.42 | 11.16 | 22.73 | 2.51 | 9.08 | 2.71 | 0.37 | 2.30 | 0.39 | 1.76 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 54.68 | 48.56 | 6.12 | 7.94 | 14.82 | 0.45 | 1.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM4 | 6.53 | 33.03 | 64.14 | 7.25 | 27.21 | 4.95 | 1.25 | 3.66 | 0.40 | 1.59 | 0.26 | 0.62 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 144.86 | 137.83 | 7.03 | 19.62 | 65.81 | 0.90 | 1.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM2 | 达拉 花岗岩 | 5.96 | 4.68 | 10.45 | 1.27 | 4.06 | 1.46 | 0.33 | 1.41 | 0.27 | 1.33 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 26.70 | 22.25 | 4.45 | 5.01 | 6.85 | 0.70 | 1.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | 8.12 | 36.50 | 71.10 | 7.81 | 29.06 | 5.73 | 1.74 | 4.22 | 0.46 | 1.75 | 0.27 | 0.72 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 160.24 | 151.94 | 8.30 | 18.31 | 63.86 | 1.08 | 1.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2 Major (%), trace (10-6) and rare earth element (10-6) contents of intrusive rocks in the Gudui area, southern Tibet
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | Mg# | A/CNK | AR | σ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM4QY002 | 辉长岩 | 52.14 | 3.64 | 13.96 | 3.02 | 7.48 | 0.15 | 3.54 | 6.52 | 3.84 | 1.63 | 0.66 | 2.89 | 99.47 | 5.47 | 0.42 | 46.00 | 0.70 | 1.73 | 3.27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM101 | 49.85 | 2.93 | 14.68 | 3.24 | 8.59 | 0.17 | 3.53 | 7.51 | 3.82 | 1.37 | 0.53 | 2.69 | 98.91 | 5.19 | 0.36 | 42.52 | 0.69 | 1.61 | 3.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM102 | 48.76 | 2.84 | 13.86 | 2.70 | 8.56 | 0.16 | 6.36 | 8.90 | 3.07 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 3.19 | 98.86 | 3.19 | 0.04 | 57.22 | 0.65 | 1.33 | 1.77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM301 | 49.18 | 4.13 | 14.36 | 2.32 | 8.91 | 0.15 | 4.48 | 6.79 | 4.39 | 1.15 | 0.47 | 2.52 | 98.85 | 5.54 | 0.26 | 47.51 | 0.69 | 1.71 | 4.97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM302 | 48.14 | 2.51 | 12.88 | 2.92 | 8.14 | 0.17 | 3.63 | 6.66 | 2.83 | 0.91 | 0.51 | 9.66 | 98.96 | 3.74 | 0.32 | 44.53 | 0.73 | 1.47 | 2.72 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q6 | 辉绿岩 | 51.70 | 2.42 | 14.36 | 2.12 | 7.95 | 0.16 | 5.33 | 7.65 | 2.74 | 1.44 | 0.29 | 2.02 | 98.18 | 4.18 | 0.53 | 54.69 | 0.72 | 1.47 | 2.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q8 | 50.61 | 2.22 | 15.34 | 1.86 | 7.34 | 0.15 | 5.42 | 8.50 | 2.46 | 1.31 | 0.26 | 2.49 | 97.96 | 3.77 | 0.53 | 57.07 | 0.73 | 1.38 | 1.87 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q14 | 闪长岩 | 55.40 | 2.08 | 13.13 | 2.98 | 7.79 | 0.14 | 2.54 | 5.30 | 2.80 | 2.66 | 0.86 | 2.40 | 98.08 | 5.46 | 0.95 | 36.98 | 0.77 | 1.84 | 2.40 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM3 | 恰嘎 花岗岩 | 74.91 | 0.05 | 15.08 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.99 | 3.86 | 2.32 | 0.10 | 1.91 | 100.12 | 6.18 | 0.60 | — | 1.41 | 2.25 | 1.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM4 | 71.85 | 0.28 | 15.30 | 1.89 | 1.00 | 0.03 | 0.88 | 2.45 | 3.24 | 3.08 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 100.83 | 6.32 | 0.95 | — | 1.17 | 2.11 | 1.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM2 | 达拉 花岗岩 | 75.39 | 0.07 | 14.61 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.97 | 3.59 | 2.38 | 0.07 | 2.10 | 100.19 | 5.97 | 0.66 | — | 1.43 | 2.24 | 1.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | 68.17 | 0.28 | 16.27 | 0.38 | 1.39 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 2.83 | 3.93 | 3.01 | 0.10 | 1.91 | 99.19 | 6.94 | 0.77 | — | 1.09 | 2.14 | 1.91 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Cr | Ni | Co | V | Rb | Sr | Ba | Sc | Nb | Ta | Li | Zr | Hf | U | Th | W | Sn | Cu | Pb | Zn | Au | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM4QY002 | 辉长岩 | 12.20 | 17.60 | 40.80 | 237.8 | 22.2 | 441.6 | 433.0 | 19.60 | 61.70 | 3.54 | 17.2 | 914.8 | 12.80 | 1.06 | 3.64 | 0.68 | 8.30 | 27.00 | 13.8 | 119.8 | <0.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM101 | 37.50 | 18.10 | 24.20 | 139.7 | 125.3 | 128.9 | 501.5 | 17.60 | 27.20 | 1.69 | 39.8 | 387.8 | 10.20 | 2.43 | 23.60 | 2.64 | 3.74 | 11.40 | 26.0 | 99.7 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM102 | 132.60 | 49.60 | 45.50 | 271.4 | 5.0 | 121.7 | 155.7 | 26.80 | 18.20 | 0.97 | 35.7 | 332.1 | 5.40 | 0.28 | 1.40 | 0.91 | 3.92 | 20.10 | 5.7 | 100.9 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM301 | 18.80 | 18.70 | 52.20 | 312.0 | 20.4 | 183.8 | 205.8 | 23.60 | 42.00 | 2.54 | 31.5 | 598.3 | 6.80 | 0.69 | 3.00 | 0.62 | 2.35 | 18.80 | 13.7 | 103.0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM302 | 11.80 | 2.00 | 36.50 | 256.4 | 26.1 | 127.3 | 201.8 | 16.70 | 29.20 | 1.45 | 74.1 | 175.3 | 7.30 | 0.43 | 4.87 | 0.41 | 5.00 | 6.00 | 20.9 | 110.5 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q6 | 辉绿岩 | 131.70 | 20.30 | 43.80 | 273.2 | 50.3 | 394.3 | 355.4 | 26.30 | 26.40 | 0.72 | 36.9 | 273.6 | 07.21 | 0.61 | 5.80 | 2.11 | 2.82 | — | 21.7 | 100.5 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q8 | 115.80 | 24.00 | 41.67 | 257.3 | 49.9 | 412.3 | 279.4 | 25.40 | 28.60 | 0.63 | 25.7 | 216.3 | 10.80 | 0.81 | 5.61 | 1.59 | 2.07 | — | 24.8 | 95.4 | 0.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q14 | 闪长岩 | 102.10 | 1.68 | 35.40 | 140.5 | 69.3 | 448.6 | 516.0 | 18.90 | 35.30 | 1.81 | 26.1 | 603.5 | 28.10 | 1.46 | 6.01 | 1.26 | 3.52 | — | 21.5 | 158.3 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM3 | 恰嘎 花岗岩 | 2.52 | 0.92 | 04.94 | 025.6 | 237.5 | 114.3 | 044.0 | 06.90 | 07.21 | 1.45 | 101.5 | 100.5 | 05.04 | 7.43 | 6.80 | 48.10 | 19.80 | 2.72 | 126.8 | 31.3 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM4 | 6.22 | 4.39 | 15.10 | 042.1 | 164.8 | 352.2 | 473.9 | 08.61 | 09.44 | 1.27 | 059.3 | 019.0 | 00.82 | 1.48 | 12.70 | 146.00 | 3.66 | 4.27 | 60.0 | 58.9 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM2 | 达拉 花岗岩 | 2.56 | 1.57 | 3.09 | 020.2 | 213.2 | 050.4 | 034.0 | 11.0 | 06.55 | 1.49 | 054.5 | 092.8 | 04.63 | 5.82 | 03.91 | 28.30 | 20.30 | 1.59 | 126.5 | 35.6 | 1.35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | — | — | — | — | 149.8 | 373.0 | 483.4 | — | 07.96 | 0.15 | — | 092.3 | 03.91 | 1.79 | 11.60 | — | — | — | 47.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | LaN/ YbN | Eu* | Ce* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM4QY002 | 辉长岩 | 48.98 | 57.72 | 119.20 | 15.94 | 75.72 | 14.45 | 4.45 | 11.96 | 2.08 | 10.39 | 2.04 | 5.38 | 0.73 | 4.74 | 0.69 | 325.49 | 287.48 | 38.01 | 7.56 | 8.73 | 1.03 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM101 | 34.71 | 10.69 | 44.51 | 6.37 | 32.31 | 7.58 | 2.43 | 6.68 | 1.37 | 7.13 | 1.47 | 3.76 | 0.52 | 3.23 | 0.48 | 128.53 | 103.89 | 24.64 | 4.22 | 2.37 | 1.04 | 1.32 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM102 | 35.19 | 38.74 | 94.78 | 13.70 | 69.13 | 13.58 | 5.85 | 11.28 | 1.90 | 8.67 | 1.59 | 3.70 | 0.41 | 2.28 | 0.31 | 265.92 | 235.78 | 30.14 | 7.82 | 12.19 | 1.45 | 1.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM301 | 36.53 | 24.02 | 65.64 | 9.15 | 45.03 | 9.56 | 3.32 | 8.25 | 1.53 | 7.69 | 1.57 | 4.02 | 0.55 | 3.38 | 0.49 | 184.20 | 156.72 | 27.48 | 5.70 | 5.10 | 1.14 | 1.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11PM302 | 42.41 | 37.03 | 85.91 | 11.56 | 54.38 | 11.13 | 3.19 | 9.64 | 1.83 | 9.14 | 1.83 | 4.76 | 0.64 | 3.73 | 0.54 | 235.31 | 203.20 | 32.11 | 6.33 | 7.12 | 0.94 | 1.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/ HREE | LaN/ YbN | Eu* | Ce* | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q6 | 辉绿岩 | 55.17 | 37.34 | 78.77 | 10.23 | 43.64 | 10.34 | 4.38 | 9.35 | 1.72 | 10.39 | 2.05 | 5.45 | 0.86 | 5.05 | 0.74 | 220.31 | 184.70 | 35.61 | 5.19 | 5.30 | 1.36 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q8 | 49.69 | 32.84 | 68.17 | 8.78 | 37.50 | 8.86 | 3.86 | 8.17 | 1.49 | 9.08 | 1.83 | 4.91 | 0.79 | 4.63 | 0.72 | 191.63 | 160.01 | 31.62 | 5.06 | 5.09 | 1.39 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11Q14 | 闪长岩 | 91.36 | 81.52 | 204.60 | 22.63 | 97.61 | 22.92 | 10.08 | 19.68 | 3.15 | 18.80 | 3.34 | 9.20 | 1.43 | 8.93 | 1.39 | 505.28 | 439.36 | 65.92 | 6.67 | 6.55 | 1.45 | 1.17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM3 | 恰嘎 花岗岩 | 9.42 | 11.16 | 22.73 | 2.51 | 9.08 | 2.71 | 0.37 | 2.30 | 0.39 | 1.76 | 0.29 | 0.66 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.08 | 54.68 | 48.56 | 6.12 | 7.94 | 14.82 | 0.45 | 1.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM4 | 6.53 | 33.03 | 64.14 | 7.25 | 27.21 | 4.95 | 1.25 | 3.66 | 0.40 | 1.59 | 0.26 | 0.62 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 144.86 | 137.83 | 7.03 | 19.62 | 65.81 | 0.90 | 1.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QM2 | 达拉 花岗岩 | 5.96 | 4.68 | 10.45 | 1.27 | 4.06 | 1.46 | 0.33 | 1.41 | 0.27 | 1.33 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.06 | 26.70 | 22.25 | 4.45 | 5.01 | 6.85 | 0.70 | 1.05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q7 | 8.12 | 36.50 | 71.10 | 7.81 | 29.06 | 5.73 | 1.74 | 4.22 | 0.46 | 1.75 | 0.27 | 0.72 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 160.24 | 151.94 | 8.30 | 18.31 | 63.86 | 1.08 | 1.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | SI | AR | σ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 48.06 | 1.49 | 12.91 | 1.35 | 8.62 | 0.13 | 7.62 | 7.22 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 9.34 | 99.30 | 2.22 | 0.14 | 0.78 | 38.47 | 1.25 | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 47.70 | 1.77 | 12.70 | 1.37 | 8.16 | 0.18 | 7.39 | 7.97 | 1.60 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 9.81 | 99.29 | 1.94 | 0.21 | 0.73 | 39.18 | 1.21 | 0.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 50.57 | 2.28 | 13.26 | 1.23 | 8.96 | 0.18 | 7.13 | 5.71 | 1.70 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 7.89 | 99.48 | 1.94 | 0.14 | 0.99 | 37.02 | 1.23 | 0.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 50.31 | 3.75 | 13.47 | 2.11 | 8.78 | 0.15 | 6.47 | 7.14 | 3.99 | 1.21 | 0.48 | 1.78 | 99.64 | 5.20 | 0.30 | 0.65 | 29.27 | 1.67 | 3.36 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 52.32 | 4.08 | 13.58 | 2.11 | 9.22 | 0.16 | 5.03 | 6.77 | 2.54 | 1.73 | 0.51 | 1.57 | 99.62 | 4.27 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 24.99 | 1.53 | 1.83 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 70.16 | 0.89 | 13.17 | 1.38 | 3.08 | 0.06 | 1.38 | 1.09 | 3.28 | 2.99 | 0.32 | 1.89 | 99.69 | 6.27 | 0.91 | 1.24 | 11.48 | 2.57 | 1.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 70.55 | 0.81 | 13.32 | 1.42 | 2.90 | 0.06 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 3.01 | 3.29 | 0.31 | 1.76 | 99.74 | 6.30 | 1.09 | 1.29 | 10.90 | 2.45 | 1.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 69.22 | 0.82 | 12.82 | 2.48 | 3.28 | 0.09 | 1.45 | 1.36 | 1.97 | 3.47 | 0.29 | 2.33 | 99.58 | 5.44 | 1.76 | 1.35 | 11.51 | 1.77 | 1.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 68.68 | 0.92 | 13.27 | 1.83 | 3.78 | 0.08 | 1.63 | 1.21 | 4.53 | 1.29 | 0.32 | 2.15 | 99.69 | 5.82 | 0.28 | 1.20 | 12.58 | 2.34 | 1.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 72.45 | 0.64 | 12.59 | 0.63 | 2.74 | 0.05 | 1.14 | 1.10 | 1.65 | 4.85 | 0.33 | 1.48 | 99.65 | 6.50 | 2.94 | 1.26 | 10.45 | 2.81 | 1.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 68.37 | 0.77 | 14.20 | 1.40 | 4.06 | 0.06 | 1.50 | 0.82 | 4.24 | 1.97 | 0.32 | 2.05 | 99.76 | 6.21 | 0.46 | 1.34 | 11.51 | 2.41 | 1.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 49.36 | 4.57 | 13.11 | 6.76 | 6.17 | 0.19 | 4.51 | 6.11 | 3.91 | 2.21 | 0.64 | 1.22 | 98.76 | 6.12 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 19.26 | 1.93 | 5.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 49.47 | 4.98 | 12.93 | 5.11 | 8.10 | 0.19 | 5.08 | 5.99 | 3.33 | 0.83 | 0.41 | 2.36 | 98.78 | 4.16 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 22.64 | 1.56 | 2.24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 52.84 | 3.92 | 12.51 | 3.64 | 7.65 | 0.16 | 5.56 | 5.29 | 4.54 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 2.07 | 98.91 | 4.82 | 0.06 | 0.72 | 25.66 | 1.74 | 2.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 51.68 | 3.91 | 13.52 | 3.50 | 6.20 | 0.14 | 5.07 | 7.68 | 2.93 | 1.10 | 0.57 | 2.42 | 98.72 | 4.03 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 26.97 | 1.47 | 1.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 53.32 | 4.00 | 15.63 | 5.74 | 0.96 | 0.11 | 2.92 | 4.22 | 5.17 | 1.64 | 0.61 | 3.27 | 97.59 | 6.81 | 0.32 | 0.87 | 18.07 | 2.04 | 3.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Cr | Ni | Co | V | Rb | Sr | Ba | Sc | Nb | Ta | Li | Zr | Hf | U | Th | W | Sn | Cu | Pb | Zn | Au | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 413.00 | 69.05 | 43.68 | 249.20 | 13.47 | 207.40 | 127.00 | 22.37 | 8.25 | 0.92 | 117.20 | 223.00 | 1.87 | 0.58 | 3.83 | 2.44 | 1.96 | 24.73 | 9.45 | 102.60 | 1.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 329.90 | 53.24 | 34.76 | 246.10 | 16.57 | 146.80 | 87.72 | 20.27 | 9.52 | 1.26 | 100.10 | 217.00 | 1.73 | 0.61 | 3.70 | 3.67 | 1.56 | 22.41 | 4.33 | 99.47 | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 317.50 | 60.72 | 41.36 | 255.80 | 14.28 | 127.50 | 44.41 | 22.20 | 11.81 | 1.30 | 123.20 | 231.00 | 2.72 | 0.72 | 4.05 | 2.78 | 1.70 | 30.25 | 7.62 | 108.10 | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 172.10 | 93.33 | 40.25 | 301.70 | 45.47 | 383.20 | 262.40 | 28.41 | 16.16 | 1.37 | 16.42 | 274.00 | 4.96 | 0.67 | 2.70 | 5.84 | 2.40 | 60.80 | 7.33 | 143.60 | 0.57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 46.16 | 30.20 | 36.95 | 272.60 | 50.71 | 430.90 | 370.50 | 25.06 | 34.84 | 2.48 | 17.70 | 322.00 | 7.06 | 0.87 | 3.97 | 17.73 | 2.50 | 53.15 | 9.21 | 151.50 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 11.35 | 7.77 | 13.26 | 46.03 | 161.30 | 149.50 | 643.10 | 11.00 | 23.03 | 1.56 | 27.81 | 525.00 | 4.61 | 3.74 | 29.09 | 79.69 | 5.27 | 14.96 | 25.65 | 56.07 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 13.47 | 8.38 | 14.54 | 47.56 | 164.40 | 124.40 | 645.40 | 11.95 | 24.38 | 2.14 | 27.06 | 497.00 | 4.77 | 3.78 | 29.83 | 84.24 | 5.03 | 14.63 | 21.60 | 41.97 | 0.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 28.15 | 8.75 | 13.10 | 52.88 | 159.80 | 180.60 | 978.30 | 12.54 | 22.74 | 1.47 | 23.27 | 487.00 | 4.38 | 3.49 | 28.28 | 75.43 | 5.06 | 14.06 | 20.44 | 42.82 | 0.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 16.39 | 9.84 | 16.79 | 54.13 | 79.22 | 165.30 | 479.20 | 11.99 | 25.94 | 1.88 | 16.01 | 526.00 | 2.86 | 3.17 | 29.37 | 96.21 | 5.52 | 19.82 | 25.49 | 71.88 | 0.55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 16.66 | 9.12 | 9.88 | 55.74 | 194.30 | 101.80 | 844.80 | 6.51 | 22.26 | 1.52 | 29.56 | 362.00 | 1.98 | 2.71 | 26.64 | 61.52 | 5.19 | 17.28 | 28.69 | 54.80 | 0.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 20.91 | 9.00 | 10.78 | 57.43 | 65.94 | 91.36 | 717.10 | 11.02 | 22.66 | 1.49 | 24.71 | 300.00 | 1.85 | 2.53 | 30.00 | 47.03 | 6.60 | 14.10 | 22.33 | 68.89 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 66.39 | 52.38 | 60.87 | 344.40 | 30.49 | 573.70 | 3399.00 | 24.08 | 65.02 | 7.62 | 13.28 | 388.15 | 18.26 | 1.06 | 4.39 | 3.71 | 3.78 | 43.29 | 17.12 | 131.40 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 30.58 | 20.49 | 52.24 | 243.10 | 13.19 | 505.80 | 372.90 | 23.02 | 29.19 | 3.46 | 28.32 | 319.70 | 10.99 | 0.70 | 2.86 | 18.18 | 7.57 | 42.35 | 27.54 | 149.80 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 43.24 | 33.64 | 54.94 | 287.60 | 4.04 | 245.00 | 634.50 | 24.04 | 22.03 | 2.59 | 19.29 | 283.59 | 10.36 | 0.60 | 2.40 | 1.62 | 2.21 | 23.19 | 17.02 | 123.70 | 0.57 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 91.56 | 60.88 | 50.10 | 268.10 | 14.87 | 612.00 | 2552.00 | 20.68 | 36.46 | 4.47 | 26.52 | 395.19 | 17.06 | 0.82 | 3.49 | 3.99 | 2.47 | 33.51 | 27.00 | 108.00 | 0.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 53.09 | 32.26 | 48.63 | 277.60 | 15.68 | 128.40 | 356.10 | 21.19 | 36.49 | 4.92 | 21.60 | 396.30 | 13.77 | 0.80 | 4.08 | 5.15 | 2.54 | 17.51 | 15.58 | 122.40 | 0.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 38.86 | 22.57 | 046.68 | 06.61 | 29.67 | 07.16 | 1.69 | 06.21 | 1.13 | 06.41 | 1.43 | 3.10 | 0.48 | 2.23 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 40.19 | 22.72 | 046.89 | 06.61 | 29.61 | 07.28 | 2.10 | 06.30 | 1.18 | 06.80 | 1.48 | 3.11 | 0.50 | 2.37 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 40.69 | 23.76 | 049.91 | 06.93 | 31.49 | 07.47 | 2.24 | 06.65 | 1.18 | 06.69 | 1.50 | 3.26 | 0.51 | 2.36 | 0.35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 45.23 | 27.17 | 058.28 | 08.59 | 39.55 | 09.89 | 3.12 | 08.65 | 1.60 | 09.14 | 1.86 | 4.79 | 0.76 | 3.96 | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 45.76 | 38.28 | 077.10 | 10.74 | 47.38 | 11.07 | 3.61 | 09.35 | 1.68 | 09.46 | 1.91 | 5.01 | 0.78 | 4.03 | 0.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 55.48 | 88.21 | 163.89 | 18.88 | 71.58 | 13.74 | 2.46 | 11.70 | 1.96 | 10.70 | 2.23 | 6.26 | 1.05 | 5.86 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 56.86 | 84.56 | 152.14 | 18.76 | 71.10 | 13.55 | 2.42 | 11.38 | 1.87 | 10.46 | 2.26 | 6.29 | 1.05 | 5.98 | 0.99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 56.26 | 88.42 | 158.89 | 19.45 | 73.55 | 13.97 | 2.65 | 11.89 | 1.95 | 10.72 | 2.22 | 6.16 | 1.04 | 5.66 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 54.73 | 93.11 | 166.56 | 20.68 | 79.42 | 15.36 | 2.71 | 12.84 | 2.06 | 10.76 | 2.22 | 5.94 | 0.94 | 5.18 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 41.67 | 71.16 | 129.86 | 15.88 | 59.89 | 11.81 | 2.06 | 09.76 | 1.62 | 08.34 | 1.67 | 4.59 | 0.68 | 3.84 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 36.95 | 91.24 | 162.47 | 19.63 | 73.82 | 13.72 | 2.55 | 11.24 | 1.64 | 07.96 | 1.56 | 3.99 | 0.57 | 3.04 | 0.51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 50.26 | 47.05 | 98.01 | 13.30 | 57.43 | 12.51 | 6.09 | 10.79 | 1.89 | 10.71 | 2.06 | 5.43 | 0.78 | 4.27 | 0.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 36.06 | 25.49 | 55.78 | 7.94 | 36.04 | 8.34 | 2.67 | 7.20 | 1.32 | 7.64 | 1.48 | 3.87 | 0.52 | 2.83 | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 33.59 | 23.70 | 52.80 | 7.80 | 35.26 | 8.42 | 2.72 | 7.08 | 1.27 | 7.06 | 1.35 | 3.55 | 0.49 | 2.62 | 0.39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 39.39 | 32.90 | 70.63 | 9.80 | 43.80 | 10.05 | 4.53 | 8.27 | 1.47 | 8.50 | 1.68 | 4.29 | 0.62 | 3.41 | 0.52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 35.04 | 43.31 | 90.33 | 11.71 | 49.92 | 10.90 | 3.42 | 8.82 | 1.49 | 7.86 | 1.49 | 3.84 | 0.56 | 2.98 | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | CeN/YbN | LaN/SmN | GdN/YbN | Eu* | Ce* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 135.68 | 114.37 | 21.31 | 5.37 | 7.25 | 5.81 | 2.03 | 2.30 | 0.77 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 137.28 | 115.22 | 22.07 | 5.22 | 6.88 | 5.50 | 2.01 | 2.20 | 0.95 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 144.31 | 121.81 | 22.50 | 5.41 | 7.21 | 5.87 | 2.05 | 2.33 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 177.97 | 146.60 | 31.37 | 4.67 | 4.92 | 4.09 | 1.77 | 1.81 | 1.03 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 221.05 | 188.18 | 32.87 | 5.72 | 6.81 | 5.31 | 2.23 | 1.92 | 1.08 | 0.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 399.48 | 358.76 | 40.72 | 8.81 | 10.8 | 7.77 | 4.14 | 1.65 | 0.59 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 382.81 | 342.53 | 40.28 | 8.50 | 10.14 | 7.07 | 4.03 | 1.57 | 0.60 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 397.52 | 356.93 | 40.59 | 8.79 | 11.21 | 7.80 | 4.09 | 1.74 | 0.63 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 418.60 | 377.84 | 40.76 | 9.27 | 12.89 | 8.93 | 3.91 | 2.05 | 0.59 | 0.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 321.76 | 290.66 | 31.10 | 9.35 | 13.29 | 9.39 | 3.89 | 2.10 | 0.59 | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 393.94 | 363.43 | 30.51 | 11.91 | 21.53 | 14.85 | 4.29 | 3.06 | 0.63 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 270.94 | 234.39 | 36.55 | 6.41 | 7.90 | 6.37 | 2.42 | 2.09 | 1.60 | 0.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 161.54 | 136.26 | 25.28 | 5.39 | 6.46 | 5.47 | 1.97 | 2.10 | 1.05 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 154.51 | 130.70 | 23.81 | 5.49 | 6.49 | 5.59 | 1.81 | 2.23 | 1.08 | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 200.47 | 171.71 | 28.76 | 5.97 | 6.92 | 5.75 | 2.11 | 2.01 | 1.52 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 237.05 | 209.59 | 27.46 | 7.63 | 10.42 | 8.42 | 2.56 | 2.44 | 1.07 | 0.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3 Major (%), trace (10-6) and rare earth element (10-6) contents of extrusive rocks in the Gudui area, southern Tibet
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI | Total | K2O+Na2O | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | SI | AR | σ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 48.06 | 1.49 | 12.91 | 1.35 | 8.62 | 0.13 | 7.62 | 7.22 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 9.34 | 99.30 | 2.22 | 0.14 | 0.78 | 38.47 | 1.25 | 0.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 47.70 | 1.77 | 12.70 | 1.37 | 8.16 | 0.18 | 7.39 | 7.97 | 1.60 | 0.34 | 0.31 | 9.81 | 99.29 | 1.94 | 0.21 | 0.73 | 39.18 | 1.21 | 0.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 50.57 | 2.28 | 13.26 | 1.23 | 8.96 | 0.18 | 7.13 | 5.71 | 1.70 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 7.89 | 99.48 | 1.94 | 0.14 | 0.99 | 37.02 | 1.23 | 0.37 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 50.31 | 3.75 | 13.47 | 2.11 | 8.78 | 0.15 | 6.47 | 7.14 | 3.99 | 1.21 | 0.48 | 1.78 | 99.64 | 5.20 | 0.30 | 0.65 | 29.27 | 1.67 | 3.36 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 52.32 | 4.08 | 13.58 | 2.11 | 9.22 | 0.16 | 5.03 | 6.77 | 2.54 | 1.73 | 0.51 | 1.57 | 99.62 | 4.27 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 24.99 | 1.53 | 1.83 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 70.16 | 0.89 | 13.17 | 1.38 | 3.08 | 0.06 | 1.38 | 1.09 | 3.28 | 2.99 | 0.32 | 1.89 | 99.69 | 6.27 | 0.91 | 1.24 | 11.48 | 2.57 | 1.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 70.55 | 0.81 | 13.32 | 1.42 | 2.90 | 0.06 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 3.01 | 3.29 | 0.31 | 1.76 | 99.74 | 6.30 | 1.09 | 1.29 | 10.90 | 2.45 | 1.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 69.22 | 0.82 | 12.82 | 2.48 | 3.28 | 0.09 | 1.45 | 1.36 | 1.97 | 3.47 | 0.29 | 2.33 | 99.58 | 5.44 | 1.76 | 1.35 | 11.51 | 1.77 | 1.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 68.68 | 0.92 | 13.27 | 1.83 | 3.78 | 0.08 | 1.63 | 1.21 | 4.53 | 1.29 | 0.32 | 2.15 | 99.69 | 5.82 | 0.28 | 1.20 | 12.58 | 2.34 | 1.30 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 72.45 | 0.64 | 12.59 | 0.63 | 2.74 | 0.05 | 1.14 | 1.10 | 1.65 | 4.85 | 0.33 | 1.48 | 99.65 | 6.50 | 2.94 | 1.26 | 10.45 | 2.81 | 1.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 68.37 | 0.77 | 14.20 | 1.40 | 4.06 | 0.06 | 1.50 | 0.82 | 4.24 | 1.97 | 0.32 | 2.05 | 99.76 | 6.21 | 0.46 | 1.34 | 11.51 | 2.41 | 1.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 49.36 | 4.57 | 13.11 | 6.76 | 6.17 | 0.19 | 4.51 | 6.11 | 3.91 | 2.21 | 0.64 | 1.22 | 98.76 | 6.12 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 19.26 | 1.93 | 5.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 49.47 | 4.98 | 12.93 | 5.11 | 8.10 | 0.19 | 5.08 | 5.99 | 3.33 | 0.83 | 0.41 | 2.36 | 98.78 | 4.16 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 22.64 | 1.56 | 2.24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 52.84 | 3.92 | 12.51 | 3.64 | 7.65 | 0.16 | 5.56 | 5.29 | 4.54 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 2.07 | 98.91 | 4.82 | 0.06 | 0.72 | 25.66 | 1.74 | 2.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 51.68 | 3.91 | 13.52 | 3.50 | 6.20 | 0.14 | 5.07 | 7.68 | 2.93 | 1.10 | 0.57 | 2.42 | 98.72 | 4.03 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 26.97 | 1.47 | 1.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 53.32 | 4.00 | 15.63 | 5.74 | 0.96 | 0.11 | 2.92 | 4.22 | 5.17 | 1.64 | 0.61 | 3.27 | 97.59 | 6.81 | 0.32 | 0.87 | 18.07 | 2.04 | 3.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Cr | Ni | Co | V | Rb | Sr | Ba | Sc | Nb | Ta | Li | Zr | Hf | U | Th | W | Sn | Cu | Pb | Zn | Au | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 413.00 | 69.05 | 43.68 | 249.20 | 13.47 | 207.40 | 127.00 | 22.37 | 8.25 | 0.92 | 117.20 | 223.00 | 1.87 | 0.58 | 3.83 | 2.44 | 1.96 | 24.73 | 9.45 | 102.60 | 1.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 329.90 | 53.24 | 34.76 | 246.10 | 16.57 | 146.80 | 87.72 | 20.27 | 9.52 | 1.26 | 100.10 | 217.00 | 1.73 | 0.61 | 3.70 | 3.67 | 1.56 | 22.41 | 4.33 | 99.47 | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 317.50 | 60.72 | 41.36 | 255.80 | 14.28 | 127.50 | 44.41 | 22.20 | 11.81 | 1.30 | 123.20 | 231.00 | 2.72 | 0.72 | 4.05 | 2.78 | 1.70 | 30.25 | 7.62 | 108.10 | 0.54 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 172.10 | 93.33 | 40.25 | 301.70 | 45.47 | 383.20 | 262.40 | 28.41 | 16.16 | 1.37 | 16.42 | 274.00 | 4.96 | 0.67 | 2.70 | 5.84 | 2.40 | 60.80 | 7.33 | 143.60 | 0.57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 46.16 | 30.20 | 36.95 | 272.60 | 50.71 | 430.90 | 370.50 | 25.06 | 34.84 | 2.48 | 17.70 | 322.00 | 7.06 | 0.87 | 3.97 | 17.73 | 2.50 | 53.15 | 9.21 | 151.50 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 11.35 | 7.77 | 13.26 | 46.03 | 161.30 | 149.50 | 643.10 | 11.00 | 23.03 | 1.56 | 27.81 | 525.00 | 4.61 | 3.74 | 29.09 | 79.69 | 5.27 | 14.96 | 25.65 | 56.07 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 13.47 | 8.38 | 14.54 | 47.56 | 164.40 | 124.40 | 645.40 | 11.95 | 24.38 | 2.14 | 27.06 | 497.00 | 4.77 | 3.78 | 29.83 | 84.24 | 5.03 | 14.63 | 21.60 | 41.97 | 0.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 28.15 | 8.75 | 13.10 | 52.88 | 159.80 | 180.60 | 978.30 | 12.54 | 22.74 | 1.47 | 23.27 | 487.00 | 4.38 | 3.49 | 28.28 | 75.43 | 5.06 | 14.06 | 20.44 | 42.82 | 0.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 16.39 | 9.84 | 16.79 | 54.13 | 79.22 | 165.30 | 479.20 | 11.99 | 25.94 | 1.88 | 16.01 | 526.00 | 2.86 | 3.17 | 29.37 | 96.21 | 5.52 | 19.82 | 25.49 | 71.88 | 0.55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 16.66 | 9.12 | 9.88 | 55.74 | 194.30 | 101.80 | 844.80 | 6.51 | 22.26 | 1.52 | 29.56 | 362.00 | 1.98 | 2.71 | 26.64 | 61.52 | 5.19 | 17.28 | 28.69 | 54.80 | 0.61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 20.91 | 9.00 | 10.78 | 57.43 | 65.94 | 91.36 | 717.10 | 11.02 | 22.66 | 1.49 | 24.71 | 300.00 | 1.85 | 2.53 | 30.00 | 47.03 | 6.60 | 14.10 | 22.33 | 68.89 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 66.39 | 52.38 | 60.87 | 344.40 | 30.49 | 573.70 | 3399.00 | 24.08 | 65.02 | 7.62 | 13.28 | 388.15 | 18.26 | 1.06 | 4.39 | 3.71 | 3.78 | 43.29 | 17.12 | 131.40 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 30.58 | 20.49 | 52.24 | 243.10 | 13.19 | 505.80 | 372.90 | 23.02 | 29.19 | 3.46 | 28.32 | 319.70 | 10.99 | 0.70 | 2.86 | 18.18 | 7.57 | 42.35 | 27.54 | 149.80 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 43.24 | 33.64 | 54.94 | 287.60 | 4.04 | 245.00 | 634.50 | 24.04 | 22.03 | 2.59 | 19.29 | 283.59 | 10.36 | 0.60 | 2.40 | 1.62 | 2.21 | 23.19 | 17.02 | 123.70 | 0.57 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 91.56 | 60.88 | 50.10 | 268.10 | 14.87 | 612.00 | 2552.00 | 20.68 | 36.46 | 4.47 | 26.52 | 395.19 | 17.06 | 0.82 | 3.49 | 3.99 | 2.47 | 33.51 | 27.00 | 108.00 | 0.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 53.09 | 32.26 | 48.63 | 277.60 | 15.68 | 128.40 | 356.10 | 21.19 | 36.49 | 4.92 | 21.60 | 396.30 | 13.77 | 0.80 | 4.08 | 5.15 | 2.54 | 17.51 | 15.58 | 122.40 | 0.79 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 38.86 | 22.57 | 046.68 | 06.61 | 29.67 | 07.16 | 1.69 | 06.21 | 1.13 | 06.41 | 1.43 | 3.10 | 0.48 | 2.23 | 0.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 40.19 | 22.72 | 046.89 | 06.61 | 29.61 | 07.28 | 2.10 | 06.30 | 1.18 | 06.80 | 1.48 | 3.11 | 0.50 | 2.37 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 40.69 | 23.76 | 049.91 | 06.93 | 31.49 | 07.47 | 2.24 | 06.65 | 1.18 | 06.69 | 1.50 | 3.26 | 0.51 | 2.36 | 0.35 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 45.23 | 27.17 | 058.28 | 08.59 | 39.55 | 09.89 | 3.12 | 08.65 | 1.60 | 09.14 | 1.86 | 4.79 | 0.76 | 3.96 | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 45.76 | 38.28 | 077.10 | 10.74 | 47.38 | 11.07 | 3.61 | 09.35 | 1.68 | 09.46 | 1.91 | 5.01 | 0.78 | 4.03 | 0.65 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 55.48 | 88.21 | 163.89 | 18.88 | 71.58 | 13.74 | 2.46 | 11.70 | 1.96 | 10.70 | 2.23 | 6.26 | 1.05 | 5.86 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 56.86 | 84.56 | 152.14 | 18.76 | 71.10 | 13.55 | 2.42 | 11.38 | 1.87 | 10.46 | 2.26 | 6.29 | 1.05 | 5.98 | 0.99 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 56.26 | 88.42 | 158.89 | 19.45 | 73.55 | 13.97 | 2.65 | 11.89 | 1.95 | 10.72 | 2.22 | 6.16 | 1.04 | 5.66 | 0.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 54.73 | 93.11 | 166.56 | 20.68 | 79.42 | 15.36 | 2.71 | 12.84 | 2.06 | 10.76 | 2.22 | 5.94 | 0.94 | 5.18 | 0.82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 41.67 | 71.16 | 129.86 | 15.88 | 59.89 | 11.81 | 2.06 | 09.76 | 1.62 | 08.34 | 1.67 | 4.59 | 0.68 | 3.84 | 0.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 36.95 | 91.24 | 162.47 | 19.63 | 73.82 | 13.72 | 2.55 | 11.24 | 1.64 | 07.96 | 1.56 | 3.99 | 0.57 | 3.04 | 0.51 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Y | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 50.26 | 47.05 | 98.01 | 13.30 | 57.43 | 12.51 | 6.09 | 10.79 | 1.89 | 10.71 | 2.06 | 5.43 | 0.78 | 4.27 | 0.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 36.06 | 25.49 | 55.78 | 7.94 | 36.04 | 8.34 | 2.67 | 7.20 | 1.32 | 7.64 | 1.48 | 3.87 | 0.52 | 2.83 | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 33.59 | 23.70 | 52.80 | 7.80 | 35.26 | 8.42 | 2.72 | 7.08 | 1.27 | 7.06 | 1.35 | 3.55 | 0.49 | 2.62 | 0.39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 39.39 | 32.90 | 70.63 | 9.80 | 43.80 | 10.05 | 4.53 | 8.27 | 1.47 | 8.50 | 1.68 | 4.29 | 0.62 | 3.41 | 0.52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 35.04 | 43.31 | 90.33 | 11.71 | 49.92 | 10.90 | 3.42 | 8.82 | 1.49 | 7.86 | 1.49 | 3.84 | 0.56 | 2.98 | 0.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | LaN/YbN | CeN/YbN | LaN/SmN | GdN/YbN | Eu* | Ce* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-2-Q | 玄武岩 | 135.68 | 114.37 | 21.31 | 5.37 | 7.25 | 5.81 | 2.03 | 2.30 | 0.77 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-7-Q | 137.28 | 115.22 | 22.07 | 5.22 | 6.88 | 5.50 | 2.01 | 2.20 | 0.95 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM12-13-Q | 144.31 | 121.81 | 22.50 | 5.41 | 7.21 | 5.87 | 2.05 | 2.33 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-6-Q1 | 玄武岩 | 177.97 | 146.60 | 31.37 | 4.67 | 4.92 | 4.09 | 1.77 | 1.81 | 1.03 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-10-Q1 | 221.05 | 188.18 | 32.87 | 5.72 | 6.81 | 5.31 | 2.23 | 1.92 | 1.08 | 0.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-3-Q1 | 英安岩 | 399.48 | 358.76 | 40.72 | 8.81 | 10.8 | 7.77 | 4.14 | 1.65 | 0.59 | 0.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-4-Q1 | 382.81 | 342.53 | 40.28 | 8.50 | 10.14 | 7.07 | 4.03 | 1.57 | 0.60 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-7-Q1 | 397.52 | 356.93 | 40.59 | 8.79 | 11.21 | 7.80 | 4.09 | 1.74 | 0.63 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-8-Q1 | 418.60 | 377.84 | 40.76 | 9.27 | 12.89 | 8.93 | 3.91 | 2.05 | 0.59 | 0.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-9-Q1 | 321.76 | 290.66 | 31.10 | 9.35 | 13.29 | 9.39 | 3.89 | 2.10 | 0.59 | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM18-11-Q1 | 393.94 | 363.43 | 30.51 | 11.91 | 21.53 | 14.85 | 4.29 | 3.06 | 0.63 | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-100 | 玄武岩 | 270.94 | 234.39 | 36.55 | 6.41 | 7.90 | 6.37 | 2.42 | 2.09 | 1.60 | 0.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM1-101 | 161.54 | 136.26 | 25.28 | 5.39 | 6.46 | 5.47 | 1.97 | 2.10 | 1.05 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-102 | 154.51 | 130.70 | 23.81 | 5.49 | 6.49 | 5.59 | 1.81 | 2.23 | 1.08 | 0.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-103 | 200.47 | 171.71 | 28.76 | 5.97 | 6.92 | 5.75 | 2.11 | 2.01 | 1.52 | 0.96 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PM22-104 | 237.05 | 209.59 | 27.46 | 7.63 | 10.42 | 8.42 | 2.56 | 2.44 | 1.07 | 0.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
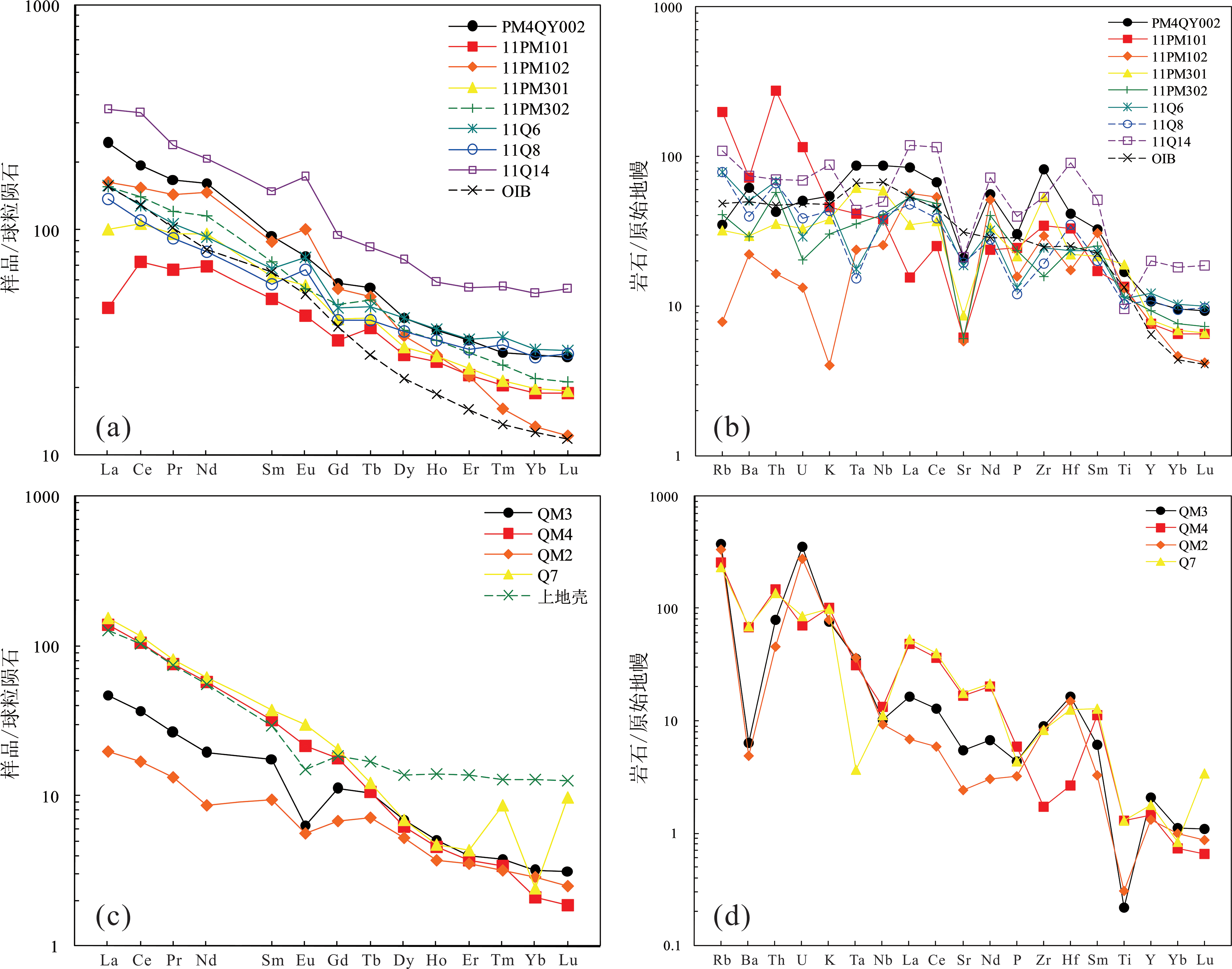
Fig.5 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns ((a),(c)), and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spider diagrams ((b),(d)) of intrusive rocks in the Gudui area, southern Tibet (normalizing values from ref. [27])

Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns ((a),(c),(e)), and primitive mantle-normalized multi-element spider diagram ((b),(d),(f)) of extrusive rocks in the Gudui area, southern Tibet (normalizing values from ref.[27])
| [1] | 王广耀, 许培春. 新疆阿尔泰地区岩浆岩的特征及其与成矿关系[J]. 西北地质, 1983, 16(1):8-9,11-21. |
| [2] |
WANG Q, XU J F, JIAN P, et al. Petrogenesis of adakitic porphyries in an extensional tectonic setting, Dexing, South China: implications for the genesis of porphyry copper mineralization[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47: 119-144.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 赖杨, 周清, 秦建华, 等. 藏南扎西康整装勘查区岩浆岩地质特征及研究意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(1):31-42. |
| [4] | 张刚阳. 藏南金锑多金属成矿带成矿模式与找矿前景研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2012. |
| [5] | 于淼. 藏南扎西康锑铅锌银矿床地质及成矿流体特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [6] | 张建芳, 郑有业, 张刚阳, 等. 西藏北喜马拉雅马扎拉金锑矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 黄金, 2011, 32(1):20-24. |
| [7] | 董富权, 胡可卫, 李武毅, 等. 西藏隆子县恰嘎村辉锑矿地质特征及找矿潜力[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2015, 30(1):98-102. |
| [8] | 娄元林, 陈武, 陈东太, 等. 西藏隆子县恰嘎锑矿4号脉原生晕特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 西北地质, 2016, 49(4):146-164. |
| [9] | 陈东太, 陈武, 胡可卫, 等. 西藏隆子县邦卓玛金矿床地质特征及地球化学异常特征[J]. 黄金, 2016, 37(8):25-28. |
| [10] | 杨竹森, 侯增谦, 高伟, 等. 藏南拆离系锑金成矿特征与成因模式[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(9):1377-1391. |
| [11] | 戚学祥, 曾令森, 孟祥金, 等. 特提斯喜马拉雅打拉花岗岩的SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(7):1501-1508. |
| [12] | 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等. 西藏冈底斯带侏罗纪岩浆作用的时空分布及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(4):458-468. |
| [13] | 周雄, 温春齐, 张贻, 等. 西藏冈底斯东段侵入岩岩石化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, 31(增1):1085-1086. |
| [14] | 娄元林. 西藏哲古—古堆地区地球化学特征及找矿前景分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [15] | 吕晓春, 任冲, 武睿, 等. 藏南隆子地区早白垩世双峰式火山岩的发现——来自SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学的证据[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(4):945-954. |
| [16] | 丁枫, 高建国, 徐琨智. 西藏南部绒布地区基性岩脉岩石地球化学、年代学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(2):391-408. |
| [17] | 许云鹏. 藏南古堆地区金锑多金属矿床形成深度及找矿潜力分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2021, 35(2):202-210. |
| [18] | 潘桂棠, 王立全, 张万平, 等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书(1:150 万)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013:24-105. |
| [19] | 胡可卫, 陈武, 董富权, 等. 西藏古堆地区成矿系列、成矿谱系研究及其找矿意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 2016, 30(5):761-767. |
| [20] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 胡朋, 等. 藏南基性岩墙群的地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(1):60-71. |
| [21] | 童劲松, 刘俊, 钟华明, 等. 藏南洛扎地区基性岩墙群锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 26(12):1655-1664. |
| [22] |
ZHU D C, CHUNG S L, MO X X, et al. The 132 Ma Comei-Bunbury large igneous province: Remnants identified in present-day southeastern Tibet and southwestern Australia[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(7):583-586.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 杨超, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝, 等. 藏南扎西康锌多金属矿床辉绿岩锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学特征研究[J]. 有色金属(矿山部分), 2014, 66(5):30-37. |
| [24] | 任冲, 刘顺, 朱利东, 等. 藏南哲古基性岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 四川地质学报, 2014, 34(4):496-500. |
| [25] | 任冲, 马飞宙, 朱振华, 等. 藏南哲古基性岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4):881-890. |
| [26] | 黎彤, 袁怀雨, 吴胜昔. 中国花岗岩类和世界花岗岩类平均化学成分的对比研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1998, 22(1):29-34. |
| [27] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and Isotope Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[M]//SAUNDERS A D,NORRY M J. Magmatism in ocean Basins. London,Geological Society Publication, 1989: 313-345. |
| [28] |
FREY F A, GREEN D H, ROY S D. Integrated models of basalts petrogenesis: a study of quartz tholeiites to olivine melilitites from South Eastern Australia utilizing geochemical experimental petrological data[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1978, 19:463-513.
DOI URL |
| [29] | HESS P C. Phase equilibria constrains on the origin of ocean floor basalts[J]. Geophysical Monograph, 1992, 71:67-102. |
| [30] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 1-312. |
| [31] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1971, 8(5):523-548.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MORRISON G W. Characteristics and tectonic setting of the shoshonite rock association[J]. Lithos, 1980, 13(1):97-108.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WINCHESTER J A, FLOYD P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20: 325-342.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WRIHGT J B. A simple alkalinity ratio and its application to questions of non-orogenic granite genesis[J]. Geological Magazine, 1969, 106(4):370-384.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 张志平, 钟康惠, 董瀚, 等. 西藏桑日县帕南岩体岩石学、地球化学、地质年代学研究及构造背景探讨[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(2):52-64. |
| [38] | RUDNICK R L, GAO S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3(12):1-64. |
| [39] | WILSON M. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach[M]. London: Unwin Hyman, 1989: 1-466. |
| [40] |
WEAVER B L. The origin of ocean island basalt end-member compositions: trace element and isotopic constrains[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104(2/4): 381-397.
DOI URL |
| [41] | LASSITER J C, DE PAOLO D J. Plume /lithosphere interaction in the generation of continental and oceanic flood basalts: chemical and isotopic constrains[J]. American Geophysical Union Monograph, 2000, 100: 335-355. |
| [42] | 盖辰星, 齐祥春, 鲁星凯, 等. 藏南古堆地区煌斑岩地球化学特征及构造环境[J]. 现代矿业, 2016, 32(10):131-132,151. |
| [43] | 袁和, 罗先熔, 李武毅, 等. 西藏古堆地区煌斑岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(2):300-309. |
| [44] | 朱弟成, 王立全, 潘桂棠, 等. 藏南特提斯喜马拉雅带中段中侏罗统遮拉组OIB型玄武岩浆的识别及其意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2004, 23(3):15-24. |
| [45] | 夏瑛, 朱第成, 赵志丹, 等. 藏东南措美大火成岩省中OIB型镁铁质岩的全岩地球化学和锆石Hf同位素[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(5):1588-1602. |
| [46] | PEARCE J A. Role of the Sub-Continental Lithosphere in Magma Genesis at Active Continental Margins[M]// HAWKESWORTH C J,NORRY M J. Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths[J]. Nantwich: Shiva, 1983: 230-249. |
| [47] |
PEARCE J A, NORRY M J. Petrogenetic implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb Variations in Volcanic rocks[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1979, 69(1): 33-37.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 钟华明, 童劲松, 夏军, 等. 藏南羊卓雍错南部桑秀组火山岩的特征及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(1):72-79. |
| [49] | 钟华明, 夏军, 童劲松, 等. 洛扎县幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(5/6):451-457. |
| [50] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
MESCHEDE M. A method of discriminating between different type of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56: 207-218.
DOI URL |
| [52] | PEARCE J A, CANN J R. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analysis[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 12: 290-300. |
| [53] | 陈澍民. 西藏古堆地区金锑多金属矿床地球化学特征及成矿模式[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017. |
| [54] | 娄元林, 陈武, 杨桃. 西藏隆子县邦卓玛金矿床成矿模式与找矿模型[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(2):449-461. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||