



Geoscience ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (05): 1345-1357.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.049
• Petroleum Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zhipeng1,2( ), YU Qiling1,2(
), YU Qiling1,2( ), ZAN Lin3, YU Wenduan3, ZHANG Zhihuan1,2
), ZAN Lin3, YU Wenduan3, ZHANG Zhihuan1,2
Received:2022-10-12
Revised:2023-06-15
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-11-14
CLC Number:
LI Zhipeng, YU Qiling, ZAN Lin, YU Wenduan, ZHANG Zhihuan. Geochemical Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Generation Potential of Different Lithologic Source Rocks in the Second Member of Funing Formation in Qintong Sag, Subei Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357.

Fig.1 Regional geological structure map of Qintong Sag, Subei Basin and stratigraphic map of the second member of Funing Formation ((c) modified from reference[1])
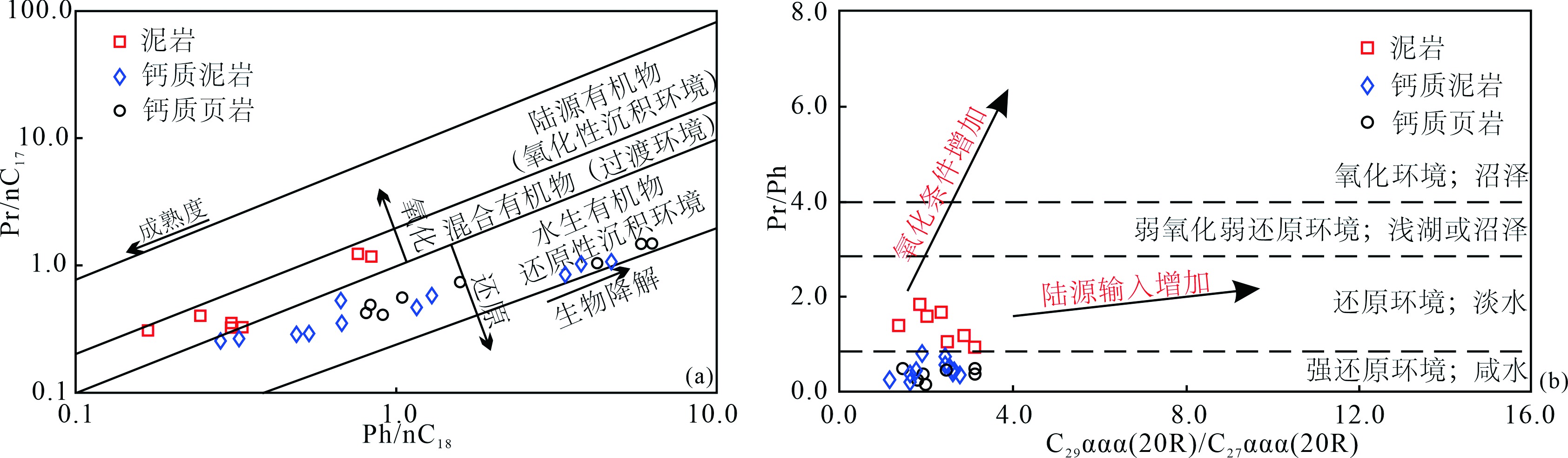
Fig.10 Plots of Ph/nC18 versus Pr/n C 17 [ 23 - 25 ] (a) and C29ααα(20R)/C27ααα(20R) versus Pr/Ph [25?-27] (b) of different source rock samples from the second member of Funing Formation, Qintong Sag
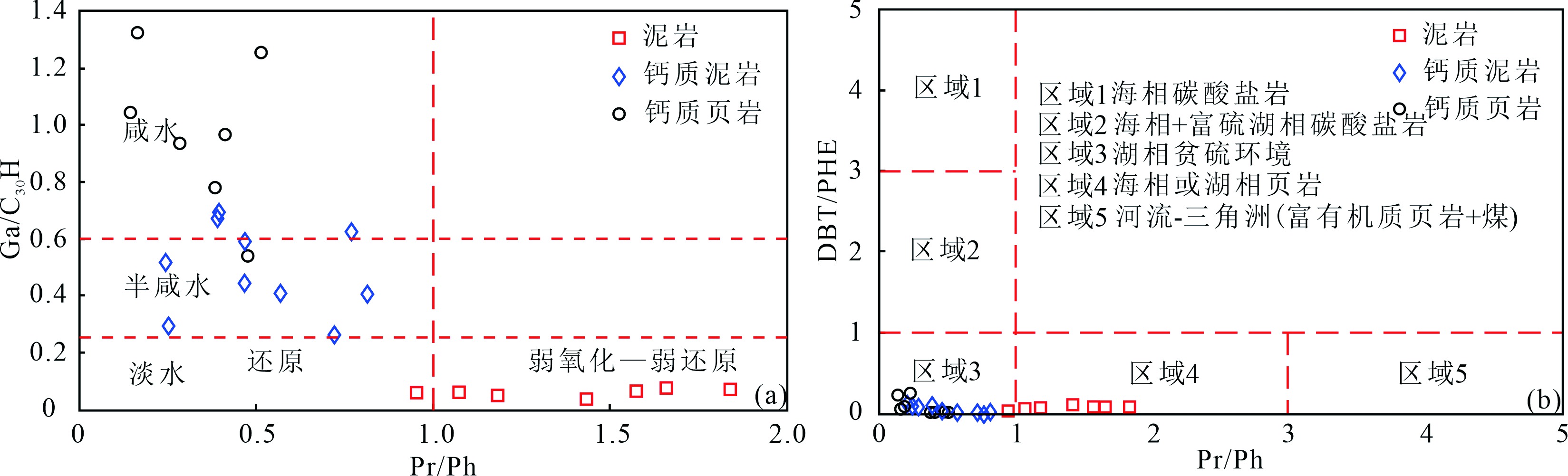
Fig.12 Plots of Pr/Ph verses Ga/C30 hopene[36] (a)and Pr/Ph verses DBT/PHE[37-38] (b) of different types of source rocks in the second member of Funing Formation, Qintong Sag
| [1] | 昝灵, 骆卫峰, 马晓东. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段烃源岩生烃潜力及形成环境[J]. 非常规油气, 2016, 3(3): 1-8. |
| [2] | 昝灵, 柴方园, 印燕铃. 溱潼凹陷斜坡带原油物性和地化特征及成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(5): 1068-1077. |
| [3] | 昝灵, 骆卫峰, 印燕铃, 等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷古近系阜宁组二段页岩油形成条件及有利区评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 233-241. |
| [4] | 刘世丽, 段宏亮, 章亚, 等. 苏北盆地阜二段陆相页岩油气勘探潜力分析[J]. 海洋石油, 2014, 34(3): 27-33. |
| [5] | 彭金宁, 邱岐, 王东燕, 等. 苏北盆地古近系阜宁组致密油赋存状态与可动用性[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 53-59. |
| [6] | 芮晓庆, 周圆圆, 李志明, 等. 苏北盆地阜宁组源储特征及页岩油勘探方向探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(6): 133-145. |
| [7] | 郑开富, 彭霞玲. 苏北盆地上白垩统—第三系页岩油气成藏层位及有利区带[J]. 地质学刊, 2013, 37(1): 147-154. |
| [8] | 张航国, 昝灵. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷西斜坡阜宁组三段油气富集规律[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 35(13): 13-17, 3. |
| [9] | 董清源, 章亚, 刘世丽. 苏北盆地阜二段页岩油生烃潜力评价及有利区预测[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2020, 46(4): 104-110. |
| [10] | 方朝合, 张枝焕, 王义凤, 等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷第三系烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 23(6): 1-5, 117. |
| [11] | 姚红生, 昝灵, 高玉巧, 等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷古近系阜宁组二段页岩油富集高产主控因素与勘探重大突破[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 776-783. |
| [12] | 江夏, 周荔青. 苏北盆地富油气凹陷形成与分布特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(4): 319-325. |
| [13] | 段宏亮, 刘世丽, 付茜. 苏北盆地古近系阜宁组二段富有机质页岩特征与沉积环境[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(4): 612-617. |
| [14] | 邱旭明, 钱诗友, 于雯泉, 等. 苏北盆地“十二五”油气勘探主要成果、新认识和技术进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(3): 62-73. |
| [15] | 王红伟. 盐城凹陷阜二段页岩油形成条件及富集规律研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2017. |
| [16] | 王旭影, 姜在兴. 苏北盆地古近系阜三段沉积体系特征与模式[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6): 1132-1143. |
| [17] | 中国石油天然气总公司. 陆相烃源岩地球化学评价方法: SY/T 5735—1995[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996. |
| [18] | 唐建云, 宋红霞, 陈玉宝, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地富黄探区延长组烃源岩评价[J]. 煤炭技术, 2016, 35(6): 110-112. |
| [19] | 刘亚洲. 湖相烃源岩非均质性研究及生烃潜力评价: 以盐池—定边地区长7烃源岩为例[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018. |
| [20] | 可行, 赵青芳, 吴飘, 等. 胶莱盆地东北部白垩系烃源岩特征与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2022, https://doi.org/10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.083. |
| [21] | 卢双舫, 张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008. |
| [22] |
SEIFERT W K, MOLDOWAN J M. The effect of thermal stress on source-rock quality as measured byhopane stereochemistry[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 1980, 12: 229-237.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CONNAN J, CASSOU A M. Properties of gases and petroleum liquids derived from terrestrial kerogen at various maturation levels[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(1): 1-23.
DOI URL |
| [24] | SHANMUGAM G. Significance of coniferous rain forests and related organic matter in generating commercial quantities of oil, gippsland basin, Australia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69 (8): 1241-1254. |
| [25] |
GAO G, YANG S R, ZHANG W W, et al. Organic geochemistry of the lacustrine shales from the Cretaceous Taizhou Formation in the Gaoyou sag, northern Jiangsu Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 89: 594-603.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
HUANG W Y, MEINSCHEIN W G. Sterols as ecological indicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(5): 739-745.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
VOLKMAN J K, BARRETT S M, BLACKBURN S I, et al. Microalgal biomarkers: A review of recent research developments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(5/6/7): 1163-1179.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MACKENZIE A S, HOFFMANN C F, MAXWELL J R. Molecular parameters of maturation in the Toarcian shales, Paris Basin, France—III.Changes in aromatic steroid hydrocarbons[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(8): 1345-1355.
DOI URL |
| [29] | YUREWICZ D A, ADVOCATE D M, LO H B, et al. Source rocks and oil families, southwest Maracaibo Basin (Catatumbo Subbasin), Colombia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82 (7): 1329-1352. |
| [30] | 卢晓林, 石宁, 李美俊, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷原油双杜松烷分布特征及地球化学意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 560-568. |
| [31] | 包建平, 朱翠山, 倪春华. 北部湾盆地不同凹陷原油生物标志物分布与组成特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(4): 646-652. |
| [32] | 席胜利, 刚文哲, 杨清宇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地盐池—定边地区长7烃源岩有机地球化学特征及沉积环境研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4): 890-901. |
| [33] |
ADEGOKE A K, ABDULLAH W H, HAKIMI M H, et al. Geochemicalcharacterisation of Fika Formation in the Chad (Bornu) Basin, northeastern Nigeria: Implications for depositional environment and tectonic setting[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 43: 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 梅博文, 刘希江. 我国原油中异戊间二烯烷烃的分布及其与地质环境的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1980, 1(2): 99-115. |
| [35] |
DIDYK B M, SIMONEIT B R T, BRASSELL S C, et al. Organic geochemical indicators ofpalaeoenvironmental conditions of sedimentation[J]. Nature, 1978, 272: 216-222.
DOI |
| [36] | 马立元, 尹航, 陈纯芳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田原油地球化学特征及油源分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(2): 416-425. |
| [37] |
QIAO J Q, BANIASAD A, ZIEGER L, et al. Paleo-depositional environment, origin and characteristics of organic matter of the Triassic Chang 7 Member of the Yanchang Formation throughout the mid-western part of the Ordos Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2021, 237: 103636.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
HUGHES W B, HOLBA A G, DZOU L I P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3581-3598.
DOI URL |
| [1] | LUO Haiyi, LUO Xianrong, LIU Panfeng, MA Mingliang, LU Xiansheng, JIANG Xiaoming, BAO Guangui, JIANG Yuxiong. Soil Geochemical Characteristics in the Naqu Area,Chongzuo City, Guangxi,and Their Mineral Prospecting Applications [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | NI Minjie, ZHU Hexuan, HE Wenjun, YANG Sen, ZOU Yang, ZHANG Yuanyuan. Depositional Environment and Sedimentary Model of the Fengcheng Formation in Mahu sag, Junggar Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1194-1207. |
| [3] | ZHANG Wei, AN Maoguo, WANG Zhipeng, YANG Qi, CHEN Huaixin, MA Xiaofeng, ZHI Chenglong, XING Qitao, PEI Changshi, WANG Na, LIU Ming. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting in the Middle Reach of the Nalinggele River, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 690-707. |
| [4] | LIANG Dong, HUA Bei, ZHAO Dehuai, WU Hao, WAN Shengnan, TAN Chaoxin, ZHAO Xiaojian, YANG Zhipeng. Geochemical Characteristics of River Sediment and Ore Prediction in the Malashan Area of the Karakoram Region [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [5] | LOU Yuanlin, CHENG Ming, TANG Yao, ZHANG Chaoming, LAN Jingzhou, YUAN Yongsheng, YANG Tao. Geochemical Characteristics,Tectonic Setting, and Mineralization of Magmatic Rocks in Gudui Area, Southern Tibet [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [6] | CHEN Shiming, YANG Zhenxi, LEI Ziqiang, KANG Weiliang, ZHANG Jing, ZHAO Qinghu. Geochemical Characteristics and Prospecting on Stream Sediment Survey in Qianhongquan Area of Beishan in Gansu Province, China [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [7] | WANG Kai, LIU Huichuan, REN Weiwei, LI Wenqi, YU Zhiqi. Influence of Cenozoic Diabase Intrusion on Reservoir Properties of Mudstone Wallrocks in the Yangxin Sub-depression, Subei Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(06): 1563-1573. |
| [8] | LIU Tong, LIU Chuanpeng, KANG Pengyu, ZHAO Xiufang, DENG Jun, WANG Kaikai. Geochemical Characteristics and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soils of Eastern Yinan, Shandong Province [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [9] | LIU Yang, LI Xianqing, ZHAO Guangjie, LIU Mancang, DONG Caiyuan, LI Jin, XIAO Zhongyao. Geochemical Characteristics of Natural Gas and Hydrocarbon Charging History of the Tugeerming Area in the Eastern Kuqa Depression [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [10] | WANG Bin, REN Tao, SONG Yiwei, YANG Ke, WANG Zhanbin, SUN Yake. Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Stream Sediments in Changjiashan Region, Western Qinling Orogen [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [11] | LIU Yang, JIANG Bing, ZHANG Hairui, SUN Zengbing, WANG Songtao. Geochemical Characteristics of Selenium in Surface Soil of Qingzhou, Shandong [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 933-940. |
| [12] | WANG Meihua. Geochemical Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Selenium-enriched Soils in Cultivated Land Around Typical Stone Coal Mines in Western Zhejiang [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [13] | CAO Lanzhu, WU Piao, HOU Dujie, WEI Xiuli, ZHEN Ronghua. Classification of Sub-sags in the Erlian Basin and Its Petroleum Prospecting Significance [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 719-728. |
| [14] | ZHU Biqing, CHEN Shijia, BAI Yanjun, LEI Junjie, YIN Xiangdong. Geochemical Characteristics and Source of Crude Oil in Chang 8 Member of Yanchang Formation, Ganquan Area, Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 742-754. |
| [15] | GAO Yinhu, YIN Gang, GONG Zeqiang, GUO Mingchun. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Xiangtanzi Gold Deposit in Liangdang County, Gansu Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||