



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 1059-1067.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.056
赵超1( ), 魏翔2,*(
), 魏翔2,*( ), 孙建伟1, 龚文强1, 赵浩1, 李晓明1, 郑俭峰1, 赵立磊1
), 孙建伟1, 龚文强1, 赵浩1, 李晓明1, 郑俭峰1, 赵立磊1
出版日期:2025-08-10
发布日期:2025-08-27
通信作者:
*魏翔,男,副研究员,1976年出生,主要从事区域成矿、矿产勘查研究和地调项目管理工作。Email:weix@mail.cgs.gov.cn。作者简介:赵超,男,工程师,1992年出生,主要从事矿床学和环境演变方面研究工作。Email:zhaochao199205@126.com。
基金资助:
ZHAO Chao1( ), WEI Xiang2,*(
), WEI Xiang2,*( ), SUN Jianwei1, GONG Wenqiang1, ZHAO Hao1, LI Xiaoming1, ZHENG Jianfeng1, ZHAO Lilei1
), SUN Jianwei1, GONG Wenqiang1, ZHAO Hao1, LI Xiaoming1, ZHENG Jianfeng1, ZHAO Lilei1
Published:2025-08-10
Online:2025-08-27
摘要:
第四纪处于气候的快速波动期,黄土记录了丰富的古气候信息。为探讨汉江上游地区晚更新世以来气候变化过程,对汉江上游洋县境内汉江Ⅰ级河流阶地朱家村剖面沉积特征、常量元素分布、地球化学参数及形成时代进行研究。结果表明:汉江上游Ⅰ级河流阶地形成于50 ka BP前后;剖面由下到上具有典型黄土(L1)→古土壤(S0)→全新世黄土(L0)→表层土(TS)的地层序列;剖面主要化学成分为SiO2、Al2O3和Fe2O3,化学风化过程中Ca、Na元素迁移淋失程度较高,K、Mg元素迁移淋失程度相对较低;剖面化学风化程度呈现从典型黄土(L1)→古土壤(S0)逐渐增强,到全新世黄土(L0)层又略降低的规律,记录了该区域气候在50~11 ka BP干燥寒冷,由11.00 ka BP开始逐渐增温增湿,2.50 ka BP到达最暖湿,2.50~0 ka BP持续降温变干的演变过程。研究成果可为我国北亚热带古气候重建提供数据参考。
中图分类号:
赵超, 魏翔, 孙建伟, 龚文强, 赵浩, 李晓明, 郑俭峰, 赵立磊. 汉江上游晚更新世以来气候演变特征:来自朱家村剖面土壤地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 1059-1067.
ZHAO Chao, WEI Xiang, SUN Jianwei, GONG Wenqiang, ZHAO Hao, LI Xiaoming, ZHENG Jianfeng, ZHAO Lilei. Climatic Evolution Characteristics in the Upper Hanjiang River Since the Late Pleistocene: Evidence from Soil Geochemistry of the Zhujia Village Section[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(04): 1059-1067.
| 样品编号 | 深度(cm) | U(10-6) | Th(10-6) | K(%) | 环境剂量(Gy/ka) | 等效剂量(Gy) | 实测年龄(ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSG-1 | 450~460 | 1.40±0.17 | 13.00±1.04 | 2.16±0.11 | 3.65±0.17 | 174.35±4.37 | 47.75±2.47 |
| GSG-2 | 330~340 | 1.39±0.16 | 13.86±0.97 | 2.28±0.09 | 3.86±0.16 | 143.61±4.90 | 37.21±2.02 |
| GSG-3 | 270~280 | 1.50±0.18 | 14.74±1.18 | 2.19±0.04 | 3.92±0.16 | 80.53±2.27 | 20.53±1.01 |
| GSG-4 | 140~150 | 1.90±0.25 | 13.60±0.82 | 1.82±0.10 | 3.68±0.16 | 7.70±0.09 | 2.09±0.10 |
表1 朱家村剖面OSL测年结果
Table 1 OSL dating results of the Zhujiacun profile
| 样品编号 | 深度(cm) | U(10-6) | Th(10-6) | K(%) | 环境剂量(Gy/ka) | 等效剂量(Gy) | 实测年龄(ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSG-1 | 450~460 | 1.40±0.17 | 13.00±1.04 | 2.16±0.11 | 3.65±0.17 | 174.35±4.37 | 47.75±2.47 |
| GSG-2 | 330~340 | 1.39±0.16 | 13.86±0.97 | 2.28±0.09 | 3.86±0.16 | 143.61±4.90 | 37.21±2.02 |
| GSG-3 | 270~280 | 1.50±0.18 | 14.74±1.18 | 2.19±0.04 | 3.92±0.16 | 80.53±2.27 | 20.53±1.01 |
| GSG-4 | 140~150 | 1.90±0.25 | 13.60±0.82 | 1.82±0.10 | 3.68±0.16 | 7.70±0.09 | 2.09±0.10 |
| 样品编号 | 地层单元 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJC-1 | TS | 71.35 | 11.78 | 5.05 | 0.62 | 1.05 | 2.23 | 1.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| ZJC-2 | 72.59 | 11.95 | 3.64 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 2.38 | 1.13 | 0.06 | 0.04 | |
| ZJC-3 | 74.69 | 12.32 | 3.87 | 0.45 | 0.82 | 1.90 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| ZJC-4 | 70.14 | 13.15 | 5.55 | 0.52 | 0.95 | 2.22 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.04 | |
| ZJC-5 | L0 | 62.33 | 14.77 | 6.23 | 0.73 | 1.46 | 2.67 | 0.95 | 0.11 | 0.17 |
| ZJC-6 | 63.34 | 14.99 | 5.96 | 0.73 | 1.44 | 2.52 | 0.96 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-7 | S0 | 62.95 | 15.20 | 6.02 | 0.77 | 1.60 | 2.61 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| ZJC-8 | 63.28 | 15.07 | 5.90 | 0.77 | 1.62 | 2.63 | 0.89 | 0.12 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-9 | 63.48 | 14.45 | 5.96 | 0.81 | 1.52 | 2.73 | 1.03 | 0.11 | 0.13 | |
| ZJC-10 | 64.40 | 15.08 | 5.75 | 0.74 | 1.56 | 2.51 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-11 | L1 | 63.56 | 14.57 | 6.03 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 2.74 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| ZJC-12 | 63.90 | 14.43 | 5.93 | 0.79 | 1.47 | 2.68 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-13 | 63.48 | 14.87 | 6.06 | 0.80 | 1.52 | 2.70 | 0.99 | 0.12 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-14 | 64.48 | 14.53 | 5.90 | 0.83 | 1.46 | 2.66 | 0.99 | 0.11 | 0.09 | |
| ZJC-15 | 64.11 | 14.58 | 5.65 | 0.85 | 1.51 | 2.78 | 1.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 | |
| ZJC-16 | 64.72 | 14.18 | 5.78 | 0.85 | 1.40 | 2.69 | 1.07 | 0.10 | 0.14 | |
| ZJC-17 | 66.07 | 14.12 | 5.08 | 0.84 | 1.30 | 2.73 | 1.16 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-18 | 67.45 | 14.75 | 5.19 | 0.70 | 1.15 | 2.29 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-19 | 67.16 | 14.82 | 5.11 | 0.72 | 1.17 | 2.29 | 0.98 | 0.08 | 0.10 | |
| ZJC-20 | 66.13 | 14.87 | 5.43 | 0.73 | 1.25 | 2.33 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-21 | 65.89 | 14.12 | 5.34 | 0.88 | 1.20 | 2.67 | 1.20 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-22 | 66.03 | 14.82 | 5.50 | 0.86 | 1.19 | 2.48 | 1.15 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| ZJC-23 | 66.42 | 15.00 | 5.43 | 0.86 | 1.18 | 2.40 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| 平均值 | 66.00 | 14.28 | 5.49 | 0.75 | 1.32 | 2.52 | 1.02 | 0.10 | 0.11 | |
| 变异系数(CV) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.16 | |
| 上陆壳(UCC)[ | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 4.20 | 2.20 | 3.40 | 3.90 | 0.50 | 0.06 | |
表2 朱家村剖面常量元素氧化物含量(%)
Table 2 Contents of major element oxides in the Zhujiacun profile (%)
| 样品编号 | 地层单元 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | MnO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJC-1 | TS | 71.35 | 11.78 | 5.05 | 0.62 | 1.05 | 2.23 | 1.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| ZJC-2 | 72.59 | 11.95 | 3.64 | 0.56 | 1.00 | 2.38 | 1.13 | 0.06 | 0.04 | |
| ZJC-3 | 74.69 | 12.32 | 3.87 | 0.45 | 0.82 | 1.90 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| ZJC-4 | 70.14 | 13.15 | 5.55 | 0.52 | 0.95 | 2.22 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.04 | |
| ZJC-5 | L0 | 62.33 | 14.77 | 6.23 | 0.73 | 1.46 | 2.67 | 0.95 | 0.11 | 0.17 |
| ZJC-6 | 63.34 | 14.99 | 5.96 | 0.73 | 1.44 | 2.52 | 0.96 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-7 | S0 | 62.95 | 15.20 | 6.02 | 0.77 | 1.60 | 2.61 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| ZJC-8 | 63.28 | 15.07 | 5.90 | 0.77 | 1.62 | 2.63 | 0.89 | 0.12 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-9 | 63.48 | 14.45 | 5.96 | 0.81 | 1.52 | 2.73 | 1.03 | 0.11 | 0.13 | |
| ZJC-10 | 64.40 | 15.08 | 5.75 | 0.74 | 1.56 | 2.51 | 0.88 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-11 | L1 | 63.56 | 14.57 | 6.03 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 2.74 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 0.13 |
| ZJC-12 | 63.90 | 14.43 | 5.93 | 0.79 | 1.47 | 2.68 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 0.12 | |
| ZJC-13 | 63.48 | 14.87 | 6.06 | 0.80 | 1.52 | 2.70 | 0.99 | 0.12 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-14 | 64.48 | 14.53 | 5.90 | 0.83 | 1.46 | 2.66 | 0.99 | 0.11 | 0.09 | |
| ZJC-15 | 64.11 | 14.58 | 5.65 | 0.85 | 1.51 | 2.78 | 1.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 | |
| ZJC-16 | 64.72 | 14.18 | 5.78 | 0.85 | 1.40 | 2.69 | 1.07 | 0.10 | 0.14 | |
| ZJC-17 | 66.07 | 14.12 | 5.08 | 0.84 | 1.30 | 2.73 | 1.16 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-18 | 67.45 | 14.75 | 5.19 | 0.70 | 1.15 | 2.29 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-19 | 67.16 | 14.82 | 5.11 | 0.72 | 1.17 | 2.29 | 0.98 | 0.08 | 0.10 | |
| ZJC-20 | 66.13 | 14.87 | 5.43 | 0.73 | 1.25 | 2.33 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-21 | 65.89 | 14.12 | 5.34 | 0.88 | 1.20 | 2.67 | 1.20 | 0.08 | 0.11 | |
| ZJC-22 | 66.03 | 14.82 | 5.50 | 0.86 | 1.19 | 2.48 | 1.15 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| ZJC-23 | 66.42 | 15.00 | 5.43 | 0.86 | 1.18 | 2.40 | 1.13 | 0.09 | 0.09 | |
| 平均值 | 66.00 | 14.28 | 5.49 | 0.75 | 1.32 | 2.52 | 1.02 | 0.10 | 0.11 | |
| 变异系数(CV) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.16 | |
| 上陆壳(UCC)[ | 66.00 | 15.20 | 5.00 | 4.20 | 2.20 | 3.40 | 3.90 | 0.50 | 0.06 | |
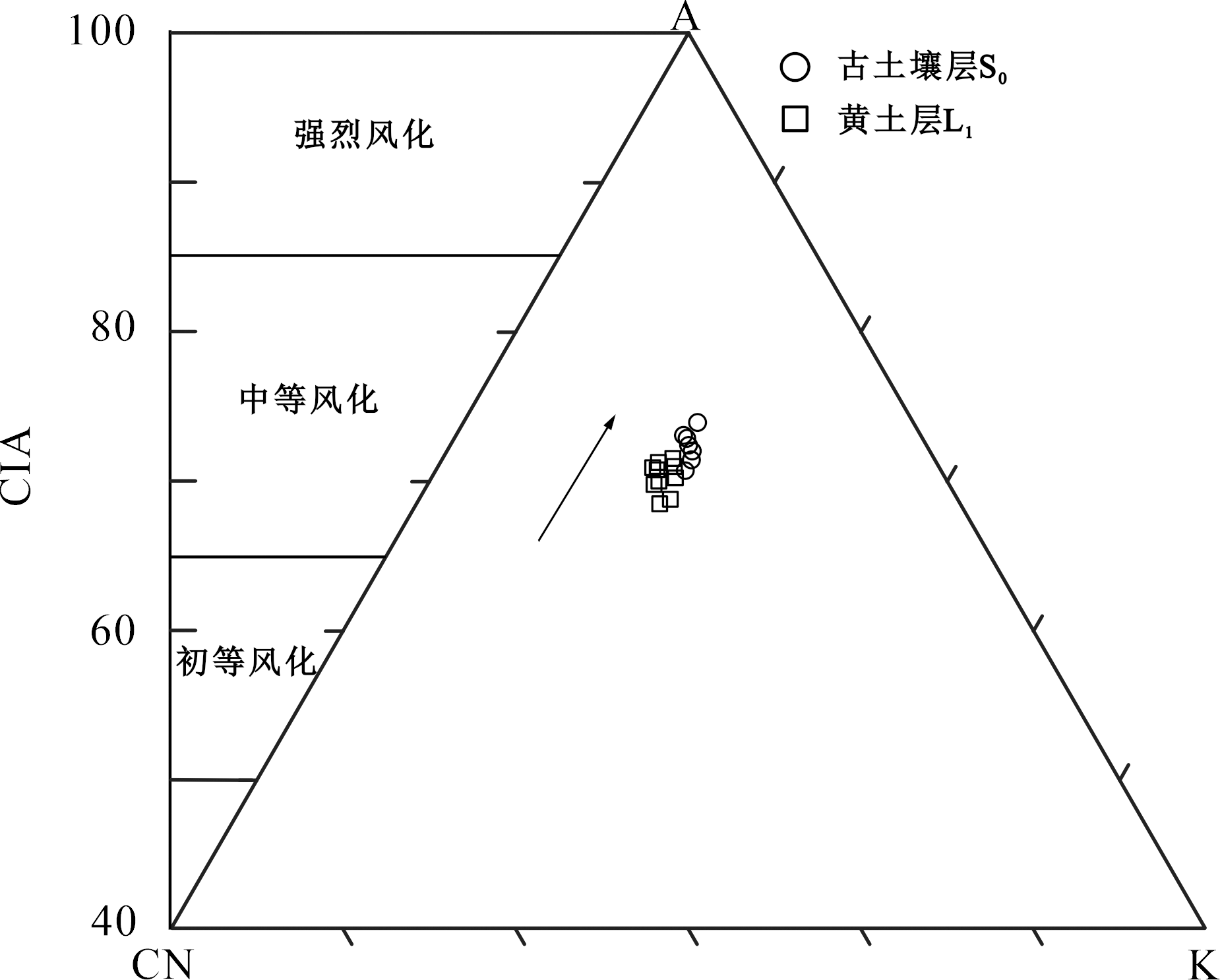
图6 朱家村剖面A-CN-K三角图(箭头指示化学风化趋势) A= Al2O3;CN=CaO*+Na2O;K=K2O
Fig.6 A-CN-K ternary diagram of the Zhujiacun profile (arrows indicate chemical weathering trends)
| [1] | 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985. |
| [2] | GALLET S, JAHN B M, TORII M. Geochemical characterization of the Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence, China, and paleoclimatic implications[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 133(1/4): 67-88. |
| [3] | 刘晓鸿. 克什克腾世界地质公园晚第四纪黄土沉积特征及其古气候意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(3): 821-833. |
| [4] |
胡梦珺, 许澳康, 孙文丽, 等. 青海湖湖东地区近32 ka BP以来风沙沉积的粒度端元特征及环境意义[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02):487-496.
DOI |
| [5] | HUANG C, PANG J, ZHOU Q Y, et al. Holocene pedogenic change and the emergence and decline of rain-fed cereal agriculture on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(23/24): 2525-2535. |
| [6] | 唐克丽, 贺秀斌. 黄土高原全新世黄土-古土壤演替及气候演变的再研讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(2): 129-139, 245. |
| [7] | 祝婷, 何政伟, 杨振京, 等. 川西阿坝盆地南缘阿柯河Ⅲ级阶地晚更新世中期的孢粉记录[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(4): 870-880. |
| [8] |
李佩, 张春霞, 罗浩, 等. 青藏高原东南缘昭通盆地晚中新世到上新世古环境演化过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(4): 326-339.
DOI |
| [9] | 孔凡彪, 徐树建, 贾广菊. 山东淄博佛村黄土沉积多指标记录的气候环境演变过程[J]. 地球环境学报, 2017, 8(5): 407-418. |
| [10] |
陈豆, 肖奇立, 张玉柱, 等. 黄河源玛曲段全新世风成黄土-古土壤序列风化成壤特征以及古气候演变[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41(8): 2277-2294.
DOI |
| [11] | 田庆春, 郝晓龙, 韩军青, 等. 临汾盆地黄土沉积微量元素地球化学特征及其气候意义[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(5): 87-93. |
| [12] | 赵庆, 王辉, 郑祥民, 等. 末次冰期东海嵊山岛黄土元素地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地球与环境, 2023, 51(1): 17-26. |
| [13] | 丁敏, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 关中东部全新世黄土古土壤序列常量元素地球化学特性研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(4): 862-867. |
| [14] | 杨瑞霞, 李志飞, 张莉, 等. 河南嵩山东麓邓家剖面元素的地球化学特征及环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(2): 129-134. |
| [15] | 熊平生. 红土和黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征及其对比[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(4): 160-164. |
| [16] | 裘湧泉, 刘丹, 杨海明. 结合多源遥感数据的青海省碾伯镇黄土滑坡信息提取研究[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 48(1): 73-83. |
| [17] | 陈渠, 吕镔, 刘秀铭, 等. 伊犁典型黄土磁学与常量元素地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2021, 41(6): 1632-1644. |
| [18] | AN Z S, LIU T S, LU Y C, et al. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990(7/8): 91-95. |
| [19] | 刘鑫, 覃泽华, 汪潇杰, 等. 循环荷载下饱和黄土的剪切特性与破坏模式[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2024, 54(5): 1604-1614. |
| [20] | 孙斌, 郭正堂, 尹秋珍, 等. 西宁第四纪黄土-古土壤序列中的可溶盐、来源及环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [21] | 李拓宇, 莫多闻, 朱高儒, 等. 晋南全新世黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 地理研究, 2013, 32(8): 1411-1420. |
| [22] | 雷祥义. 秦岭黄土-古土壤发育时的植被与环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20(1): 73-79. |
| [23] | 何报寅, 张穗, 蔡述明. 近2600年神农架大九湖泥炭的气候变化记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(2): 109-115. |
| [24] |
毛沛妮, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游黄土常量元素地球化学特征及区域对比[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(2): 279-291.
DOI |
| [25] | 庞奖励, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 汉江上游谷地全新世风成黄土及其成壤改造特征[J]. 地理学报, 2011, 66(11): 1562-1573. |
| [26] | 赵艳雷, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游前坊村黄土剖面化学风化程度及其环境意义[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(8): 1166-1172. |
| [27] | 朱震达. 汉江上游丹江口至白河间的河谷地貌[J]. 地理学报, 1955, 10(3): 259-271. |
| [28] | 沈玉昌. 汉水河谷的地貌及其发育史[J]. 地理学报, 1956, 11(4): 296-323. |
| [29] | 庞奖励, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 汉江上游Ⅰ级河流阶地形成及对东亚季风变化的响应[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(5): 1076-1084. |
| [30] | STARKEL L. Climatically controlled terraces in uplifting mountain areas[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22(20): 2189-2198. |
| [31] | 潘保田, 苏怀, 刘小丰, 等. 兰州东盆地最近1.2 Ma的黄河阶地序列与形成原因[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(2): 172-180. |
| [32] |
庞奖励, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 郧县盆地风成黄土-古土壤与汉江I级阶地形成年龄研究[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70(1): 63-72.
DOI |
| [33] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. London: Blackwell, 1985. |
| [34] | NESBITT H W, MARKOVICS G, PRICE R C. Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(11): 1659-1666. |
| [35] | HU X F, DU Y, GUAN C L, et al. Color variations of the Quaternary Red Clay in Southern China and its paleoclimatic implications[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2014, 303: 15-25. |
| [36] |
王千锁, 宋友桂, 李吉均, 等. 末次冰期-间冰期旋回朝那黄土颜色特征及古气候意义[J]. 地理科学, 2015, 35(11): 1489-1494.
DOI |
| [37] | 王海燕, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 等. 郧西县庹家湾黄土剖面色度参数特征及其古气候重建[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(2): 151-156. |
| [38] |
杨宇哲, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 等. 毛乌素沙地东南缘L3、S3黄土-古土壤色度特征及古气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 176-186.
DOI |
| [39] | NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. |
| [40] | MCLENNAN S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(2): 295-303. |
| [41] | 李徐生, 韩志勇, 杨守业, 等. 镇江下蜀土剖面的化学风化强度与元素迁移特征[J]. 地理学报, 2007, 62(11): 1174-1184. |
| [42] |
张晓娟, 季宏兵, 冯晓静, 等. 岩溶盆地红土风化剖面的元素地球化学研究[J]. 地理科学, 2017, 37(6): 944-951.
DOI |
| [43] | 张晶, 柴波, 邵长生, 等. 宜昌市龙潭河阶地的沉积特征及其环境指示[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(4): 183-193. |
| [44] | 陈骏, 安芷生, 刘连文, 等. 最近2.5 Ma以来黄土高原风尘化学组成的变化与亚洲内陆的化学风化[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2001, 31(2): 136-145. |
| [1] | 姚瑞晨, 郝仕龙, 李秀萍, 侯佳成, 陈浩源, 张岩. 1982—2020年黄河流域(河南段)NDVI动态演变及其与气候变化响应研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 612-623. |
| [2] | 张伟, 安茂国, 王志鹏, 杨启, 陈怀鑫, 马晓峰, 支成龙, 邢其涛, 裴长世, 王娜, 刘铭. 青海省那陵格勒河中游地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 690-707. |
| [3] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [4] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [5] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [6] | 朱英海, 施泽明, 王新宇, 张凯亮, 朱伯丞. 攀西大梁子铅锌矿区水系沉积物重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 923-932. |
| [7] | 安国英, 郭兆成, 叶佩. 云南大理地区1989—2019年期间气候变化及对洱海水质的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 406-417. |
| [8] | 孙爽, 胡克, 李琰, 杨俊鹏. 我国沿海不同气候带山溪性河流沉积物输运特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 68-76. |
| [9] | 远继东, 姜正龙, 代友旭, 郝连成, 张健康, 张德程, 郑立龙. 湛江湾海域表层沉积物稀土元素特征及其物源指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 77-87. |
| [10] | 王雪木, 瞿洪宝, 熊元凯, 吕琳, 胡克. 海南昌化江入海口底表沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 88-95. |
| [11] | 魏定邦, 杨强, 夏建新. 深海沉积物贯入阻力影响因素及其变化规律[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1871-1879. |
| [12] | 许可可, 杨振京, 宁凯, 韩强强, 毕志伟, 赵楠楠. 基于端元法的银川盆地MIS6—MIS5气候变化探究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1311-1322. |
| [13] | 王香莲, 黄庭, 肖河, 吴代赦, 张小龙, 程胜高, 毛绪美. 东北哈尼泥炭沉积物磁化率特征及古气候意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1323-1331. |
| [14] | 李超, 罗先熔, 邱炜, 王宇慧, 赵欣怡, 郑超杰, 刘攀峰. 青海省都兰县金水口地区水系沉积物地球化学异常特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1397-1410. |
| [15] | 李金哲, 刘宁强, 龚庆杰, 李承柱. 广东汕头市内海湾沉积物重金属环境质量调查与评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1441-1449. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||