



现代地质 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (04): 772-782.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.04.08
许胜超1( ), 肖高强1(
), 肖高强1( ), 龚庆杰2, 刘宁强2, 杨天仪1, 刀艳1, 向龙洲1, 李忠1
), 龚庆杰2, 刘宁强2, 杨天仪1, 刀艳1, 向龙洲1, 李忠1
收稿日期:2019-03-20
修回日期:2019-05-08
出版日期:2019-08-20
发布日期:2019-09-05
通讯作者:
肖高强
作者简介:肖高强,男,硕士,1983年出生,地球化学专业,主要从事勘查地球化学及土地质量地球化学调查工作。Email: 13057980@qq.com。基金资助:
XU Shengchao1( ), XIAO Gaoqiang1(
), XIAO Gaoqiang1( ), GONG Qingjie2, LIU Ningqiang2, YANG Tianyi1, DAO Yan1, XIANG Longzhou1, LI Zhong1
), GONG Qingjie2, LIU Ningqiang2, YANG Tianyi1, DAO Yan1, XIANG Longzhou1, LI Zhong1
Received:2019-03-20
Revised:2019-05-08
Online:2019-08-20
Published:2019-09-05
Contact:
XIAO Gaoqiang
摘要:
西南三江中段兰坪盆地是著名的金属成矿区,区内矿产资源丰富,以铜、铅、锌、银为主。2012—2016年云南省地质调查院完成了1∶25万丽江市幅水系沉积物测量工作,平均采样密度为1.02个/km2,采样介质为代表汇水域基岩成分的岩屑,样品粒级为-10~+60目。以兰坪盆地内的1∶25万水系沉积物测量成果为基础,首先分析了盆地内微量元素的地球化学特征,指出仅从元素富集系数的大小来判断研究区内有利矿种的方法欠妥;进而为消除元素的风化富集效应而采用变值七级异常划分方案绘制了该区地球化学异常图,并对区内的主要成矿元素进行异常圈定和分级评价。结果表明所圈定的异常区不仅与该区典型矿床在空间上相吻合,而且单元素异常级别或平均异常强度也与矿床的规模相一致,已知矿床均位于平均异常强度达3级以上的异常区。除典型已知矿区外,区域地球化学异常特征显示兰坪盆地东北部老君山地区和盆地中南部白洋厂南部地区是盆地内寻找多金属矿床的有利地段。
中图分类号:
许胜超, 肖高强, 龚庆杰, 刘宁强, 杨天仪, 刀艳, 向龙洲, 李忠. 兰坪盆地区域地球化学异常特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 772-782.
XU Shengchao, XIAO Gaoqiang, GONG Qingjie, LIU Ningqiang, YANG Tianyi, DAO Yan, XIANG Longzhou, LI Zhong. Anomalies and Prospecting Directions of Regional Geochemistry Survey in the Lanping Basin of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(04): 772-782.
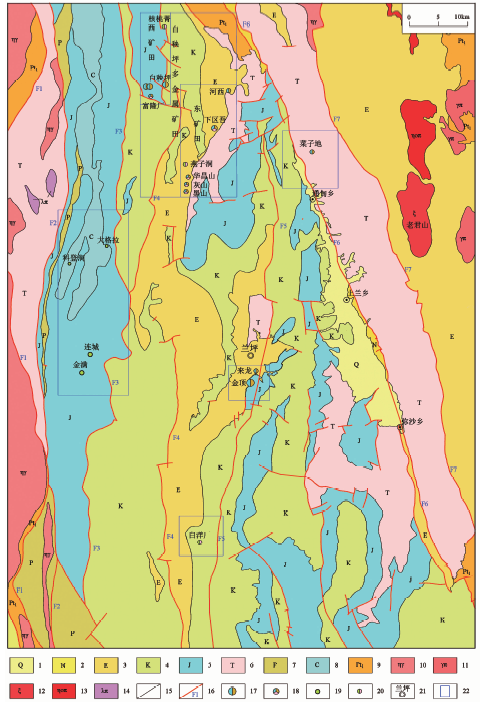
图1 兰坪盆地区域地质图据苏学军等[22]修编 1.第四系砂、泥、黏土冲积物;2.新近系粗面质火山角砾岩、集块岩、凝灰岩;3.古近系砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩;4.白垩系石英砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩;5.侏罗系泥岩、粉砂岩、细砂岩;6.三叠系砂岩、粉砂岩、页岩、灰岩及中酸性火山岩;7.二叠系砂岩、泥岩、板岩、千枚岩;8.石炭系玄武岩、凝灰岩及生物碎屑灰岩;9.古元古界变粒岩、片岩;10.二长花岗岩;11.花岗斑岩;12.正长岩;13.石英二长斑岩;14.石英闪长岩;15.岩性界线;16.断层及编号;17.铅锌矿床;18.铅-锌-银多金属矿床;19.铜矿床;20.铜、银多金属矿床;21.地名;22.矿田/矿区
Fig.1 Regional geological map in the Lanping basin of Yunnan province, China (modified after Su et al. [22])
| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素和氧化物 | 分析方法 | 检出限 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | ES | 20 | Cu | ICP-OES | 1 | Pb | XRF | 2 | Y | XRF | 1 |
| As | AFS | 1 | F | ISE | 100 | Rb | XRF | 3 | Zn | XRF | 4 |
| Au | ICP-MS | 0.3 | Hg | AFS | 0.003 | Sb | AFS | 0.05 | Zr | XRF | 2 |
| B | ES | 1 | La | ICP-OES | 2 | Sn | ES | 0.5 | SiO2 | XRF | 0.1 |
| Ba | ICP-OES | 10 | Li | ICP-OES | 1 | Sr | XRF | 4 | Al2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Be | ICP-OES | 0.3 | Mn | ICP-OES | 5 | Th | XRF | 2 | TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Bi | AFS | 0.05 | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.2 | Ti | XRF | 10 | K2O | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cd | ICP-MS | 0.03 | Nb | XRF | 2 | U | ICP-MS | 0.1 | Na2O | XRF | 0.1 |
| Co | ICP-OES | 0.5 | Ni | ICP-OES | 1.5 | V | ICP-OES | 3 | CaO | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cr | XRF | 2.5 | P | XRF | 10 | W | POL | 0.3 | MgO | XRF | 0.05 |
表1 39种元素和氧化物分析方法及检出限
Table 1 Analytical methods and detection limits for 39 elements or major oxides
| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素和氧化物 | 分析方法 | 检出限 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | ES | 20 | Cu | ICP-OES | 1 | Pb | XRF | 2 | Y | XRF | 1 |
| As | AFS | 1 | F | ISE | 100 | Rb | XRF | 3 | Zn | XRF | 4 |
| Au | ICP-MS | 0.3 | Hg | AFS | 0.003 | Sb | AFS | 0.05 | Zr | XRF | 2 |
| B | ES | 1 | La | ICP-OES | 2 | Sn | ES | 0.5 | SiO2 | XRF | 0.1 |
| Ba | ICP-OES | 10 | Li | ICP-OES | 1 | Sr | XRF | 4 | Al2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Be | ICP-OES | 0.3 | Mn | ICP-OES | 5 | Th | XRF | 2 | TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Bi | AFS | 0.05 | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.2 | Ti | XRF | 10 | K2O | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cd | ICP-MS | 0.03 | Nb | XRF | 2 | U | ICP-MS | 0.1 | Na2O | XRF | 0.1 |
| Co | ICP-OES | 0.5 | Ni | ICP-OES | 1.5 | V | ICP-OES | 3 | CaO | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cr | XRF | 2.5 | P | XRF | 10 | W | POL | 0.3 | MgO | XRF | 0.05 |
| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 富集系数 | 西南三江水系 沉积物背景值 | 边界品位/ 10-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 22 800 | 31 | 83 | 254 | 993 | 3.30 | 77 | 40 000 |
| As | 2 146 | 2.06 | 12.6 | 28.2 | 90 | 2.41 | 11.7 | 13 100 |
| Au | 57.7 | 0.15 | 0.93 | 1.10 | 2.23 | 0.87 | 1.27 | 1 000 |
| B | 300 | 5.04 | 66 | 68.3 | 31.7 | 1.22 | 56.2 | 9 316 |
| Ba | 13 895 | 73.8 | 440 | 562 | 596 | 1.44 | 389 | 139 172 |
| Be | 12.80 | 0.30 | 2.23 | 2.20 | 0.67 | 1.08 | 2.04 | 144.00 |
| Bi | 182 | 0.064 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 5.58 | 2.73 | 0.33 | 500 |
| Cd | 301 | 0.038 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 10.4 | 6.67 | 0.15 | 100 |
| Co | 175 | 2.09 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 7.46 | 1.07 | 12.4 | 200 |
| Cr | 568 | 4.3 | 74.2 | 72.6 | 32.0 | 1.22 | 59.4 | 171 000 |
| Cu | 6 544 | 1.07 | 22.0 | 46.5 | 231 | 2.00 | 23.2 | 2 000 |
| F | 1 743 | 108 | 593 | 593 | 155 | 1.16 | 510 | 97 311 |
| Hg | 165 | 0.003 | 0.040 | 0.40 | 4.21 | 13.3 | 0.030 | 400 |
| La | 130 | 3.92 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 8.25 | 0.98 | 35.6 | 853 |
| Li | 283 | 8.36 | 46.4 | 51.5 | 27.7 | 1.49 | 34.5 | 1 858 |
| Mo | 18.7 | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 1.23 | 0.65 | 300 |
| Nb | 42.3 | 2.5 | 15.1 | 14.9 | 3.93 | 0.96 | 15.5 | 350 |
| Ni | 189 | 2.24 | 30.7 | 29.7 | 13.4 | 1.13 | 26.4 | 2 000 |
| Pb | 16 382 | 4.26 | 25.8 | 118 | 833 | 5.06 | 23.3 | 3 000 |
| Sb | 793 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 5.20 | 34.4 | 6.05 | 0.86 | 5 000 |
| Sn | 42 | 0.99 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 1.16 | 1.02 | 2.94 | 1 000 |
| Sr | 3 206 | 13.8 | 92.3 | 137 | 176 | 1.49 | 92 | 47 701 |
| Th | 65.6 | 2.3 | 13.1 | 13.1 | 4.68 | 1.20 | 10.9 | 879 |
| U | 9.66 | 0.46 | 2.68 | 2.80 | 0.85 | 1.27 | 2.20 | 300 |
| V | 200 | 13.6 | 97.4 | 93.0 | 30.8 | 1.09 | 85.5 | 2 801 |
| W | 181 | 0.15 | 1.72 | 1.90 | 3.93 | 1.12 | 1.70 | 507 |
| Y | 208 | 4.4 | 22.9 | 23.4 | 10.6 | 0.98 | 23.8 | 394 |
| Zn | 44 331 | 4.1 | 75 | 192 | 1 388 | 2.69 | 71.5 | 5 000 |
| Zr | 1 451 | 66 | 187 | 193 | 74 | 0.83 | 233 | 2 221 |
| SiO2 | 93.9 | 20.4 | 67.5 | 67.9 | 6.70 | 1.06 | 64.0 | |
| Al2O3 | 20.9 | 2.24 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 2.35 | 1.08 | 13.1 | |
| TFe2O3 | 16.3 | 0.05 | 5.48 | 5.30 | 1.54 | 1.08 | 4.90 | |
| MgO | 10.9 | 0.08 | 1.46 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.18 | 1.27 | |
| CaO | 44.2 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 2.82 | 2.15 | 0.79 | |
| Na2O | 5.85 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 1.14 | 0.79 | |
| K2O | 6.63 | 0.41 | 3.06 | 3.10 | 0.81 | 1.27 | 2.45 | |
| Ti | 8 373 | 978 | 4 022 | 3 827 | 920 | 0.97 | 3 959 | |
| Mn | 12 265 | 128 | 630 | 687 | 397 | 1.00 | 684 | |
| P | 1 959 | 134 | 495 | 508 | 136 | 0.85 | 599 |
表2 兰坪盆地研究区1:25万水系沉积物元素含量统计参数
Table 2 Statistical parameters of elemental contents in stream sediments in the Lanping basin
| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 富集系数 | 西南三江水系 沉积物背景值 | 边界品位/ 10-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 22 800 | 31 | 83 | 254 | 993 | 3.30 | 77 | 40 000 |
| As | 2 146 | 2.06 | 12.6 | 28.2 | 90 | 2.41 | 11.7 | 13 100 |
| Au | 57.7 | 0.15 | 0.93 | 1.10 | 2.23 | 0.87 | 1.27 | 1 000 |
| B | 300 | 5.04 | 66 | 68.3 | 31.7 | 1.22 | 56.2 | 9 316 |
| Ba | 13 895 | 73.8 | 440 | 562 | 596 | 1.44 | 389 | 139 172 |
| Be | 12.80 | 0.30 | 2.23 | 2.20 | 0.67 | 1.08 | 2.04 | 144.00 |
| Bi | 182 | 0.064 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 5.58 | 2.73 | 0.33 | 500 |
| Cd | 301 | 0.038 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 10.4 | 6.67 | 0.15 | 100 |
| Co | 175 | 2.09 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 7.46 | 1.07 | 12.4 | 200 |
| Cr | 568 | 4.3 | 74.2 | 72.6 | 32.0 | 1.22 | 59.4 | 171 000 |
| Cu | 6 544 | 1.07 | 22.0 | 46.5 | 231 | 2.00 | 23.2 | 2 000 |
| F | 1 743 | 108 | 593 | 593 | 155 | 1.16 | 510 | 97 311 |
| Hg | 165 | 0.003 | 0.040 | 0.40 | 4.21 | 13.3 | 0.030 | 400 |
| La | 130 | 3.92 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 8.25 | 0.98 | 35.6 | 853 |
| Li | 283 | 8.36 | 46.4 | 51.5 | 27.7 | 1.49 | 34.5 | 1 858 |
| Mo | 18.7 | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 1.23 | 0.65 | 300 |
| Nb | 42.3 | 2.5 | 15.1 | 14.9 | 3.93 | 0.96 | 15.5 | 350 |
| Ni | 189 | 2.24 | 30.7 | 29.7 | 13.4 | 1.13 | 26.4 | 2 000 |
| Pb | 16 382 | 4.26 | 25.8 | 118 | 833 | 5.06 | 23.3 | 3 000 |
| Sb | 793 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 5.20 | 34.4 | 6.05 | 0.86 | 5 000 |
| Sn | 42 | 0.99 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 1.16 | 1.02 | 2.94 | 1 000 |
| Sr | 3 206 | 13.8 | 92.3 | 137 | 176 | 1.49 | 92 | 47 701 |
| Th | 65.6 | 2.3 | 13.1 | 13.1 | 4.68 | 1.20 | 10.9 | 879 |
| U | 9.66 | 0.46 | 2.68 | 2.80 | 0.85 | 1.27 | 2.20 | 300 |
| V | 200 | 13.6 | 97.4 | 93.0 | 30.8 | 1.09 | 85.5 | 2 801 |
| W | 181 | 0.15 | 1.72 | 1.90 | 3.93 | 1.12 | 1.70 | 507 |
| Y | 208 | 4.4 | 22.9 | 23.4 | 10.6 | 0.98 | 23.8 | 394 |
| Zn | 44 331 | 4.1 | 75 | 192 | 1 388 | 2.69 | 71.5 | 5 000 |
| Zr | 1 451 | 66 | 187 | 193 | 74 | 0.83 | 233 | 2 221 |
| SiO2 | 93.9 | 20.4 | 67.5 | 67.9 | 6.70 | 1.06 | 64.0 | |
| Al2O3 | 20.9 | 2.24 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 2.35 | 1.08 | 13.1 | |
| TFe2O3 | 16.3 | 0.05 | 5.48 | 5.30 | 1.54 | 1.08 | 4.90 | |
| MgO | 10.9 | 0.08 | 1.46 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.18 | 1.27 | |
| CaO | 44.2 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 2.82 | 2.15 | 0.79 | |
| Na2O | 5.85 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 1.14 | 0.79 | |
| K2O | 6.63 | 0.41 | 3.06 | 3.10 | 0.81 | 1.27 | 2.45 | |
| Ti | 8 373 | 978 | 4 022 | 3 827 | 920 | 0.97 | 3 959 | |
| Mn | 12 265 | 128 | 630 | 687 | 397 | 1.00 | 684 | |
| P | 1 959 | 134 | 495 | 508 | 136 | 0.85 | 599 |
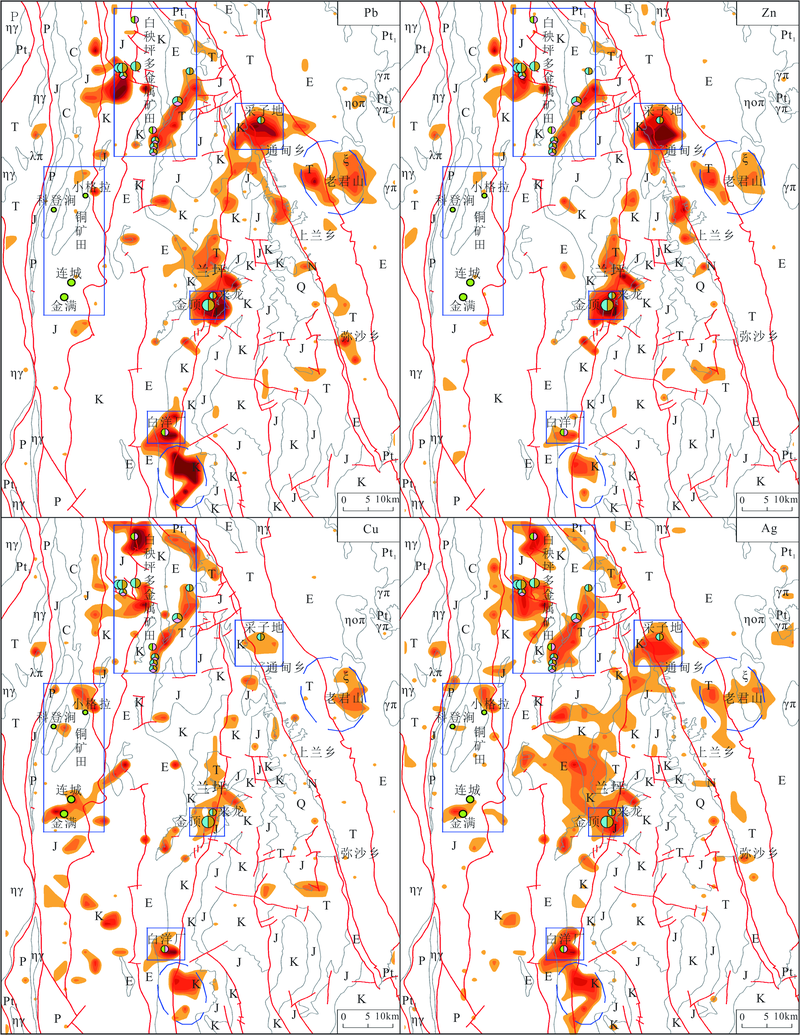
图2 兰坪盆地Pb、Zn、Cu、Ag区域地球化学异常图
Fig.2 The geochemical anomaly maps of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Ag determined on the method of seven levels’ classification in the Lanping basin of Yunnan province, China

图3 兰坪盆地As、Sb、Bi、B区域地球化学异常图
Fig.3 (The geochemical anomaly maps of As, Sb, Bi, and B determined on the method of seven levels’ classification in the Lanping basin of Yunnan province, China
| 矿田/矿区 | Pb | Zn | Cu | Ag | As | Sb | Bi | B | 异常平均强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白秧坪多金属矿田 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5.9 |
| 金顶铅多金属矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 菜子地铅锌矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 中西部铜矿田 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3.8 |
| 白洋厂铜银矿区 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4.6 |
| 老君山预测区 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3.1 |
| 白洋厂南预测区 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4.0 |
表3 兰坪盆地1:25万区域化探元素异常分级
Table 3 Anomaly levels of 8 elements on regional geochemistry survey in Lanping basin
| 矿田/矿区 | Pb | Zn | Cu | Ag | As | Sb | Bi | B | 异常平均强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白秧坪多金属矿田 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5.9 |
| 金顶铅多金属矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 菜子地铅锌矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 中西部铜矿田 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3.8 |
| 白洋厂铜银矿区 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4.6 |
| 老君山预测区 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3.1 |
| 白洋厂南预测区 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4.0 |
| [1] | 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 杨建民, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地构造体制和成矿背景分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2002,21(1):36-44. |
| [2] | 徐启东, 李建威. 云南兰坪北部铜多金属矿化成矿流体流动与矿化分带:流体包裹体和稳定同位素依据[J]. 矿床地质, 2003,22(4):365-376. |
| [3] | 杨伟光, 喻学惠, 李文昌, 等. 云南白秧坪银多金属矿集区成矿流体特征及成矿机制[J]. 现代地质, 2003,17(1):27-33. |
| [4] | 朱志军, 郭福生, 宋玉财, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地古近系构造-沉积演化与成矿的关系[J]. 沉积学报, 2014,32(6):997-1006. |
| [5] | 沈青强, 曹凯, 王国灿, 等. 剑川—兰坪盆地古近系沉积-构造变革及其区域构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017,41(1):23-41. |
| [6] | 王安建, 曹殿华, 高兰, 等. 论云南兰坪金顶超大型铅锌矿床的成因[J]. 地质学报, 2009,83(1):43-54. |
| [7] | 黄玉凤, 曹殿华, 王志军, 等. 云南兰坪盆地北部东缘铅锌矿床喷流沉积成因的厘定:来自矿物学和硫同位素证据[J]. 地质力学学报, 2011,17(1):91-102. |
| [8] | 李小明. 滇西金满铜矿床成矿年龄测定[J]. 现代地质, 2001,15(4):405-408. |
| [9] | 王晓虎, 宋玉财, 张洪瑞, 等. 白秧坪铅锌多金属矿集区东矿带成矿地球化学作用与成矿年龄[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016,22(2):294-309. |
| [10] | 徐墨寒, 薛传东, 杨天南, 等. 兰坪盆地西缘大宗铜矿区容矿火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016,35(5):735-750. |
| [11] | 朱华平, 范文玉, 高大发, 等. 西南三江成矿带中南段铅锌矿床成矿系列[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2008,28(4):62-68. |
| [12] | 朱多录. 云南兰坪矿集区成矿系列及成矿规律[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2013,28(2):224-229. |
| [13] | 江彪, 邓军, 张长青. 西南三江地区沉积岩容矿型铅锌矿成矿特征和成矿规律[J]. 地质学报, 2014,88(12):2532-2544. |
| [14] | 肖高强, 张小兵, 李忠, 等. 因子分析在1∶25万丽江市幅区域地球化学数据解释中的应用[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,29(S2):175-179. |
| [15] | 徐志刚, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 中国成矿区带划分方案[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 1-138. |
| [16] | 张锦让, 温汉捷, 裘愉卓, 等. 兰坪盆地西缘沉积岩容矿脉状Cu-Ag(±Pb-Zn)多金属矿床成矿流体特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2015,34(3):497-520. |
| [17] | 赵海滨. 滇西兰坪盆地中北部铜多金属矿床成矿特征及地质条件[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2006: 11. |
| [18] | 牟传龙, 王剑, 余谦, 等. 兰坪中新生代沉积盆地演化[J]. 矿物岩石, 1999,19(3):30-36. |
| [19] | 付修根. 兰坪陆相盆地演化与金属矿床的形成[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2005,27(2):26-32. |
| [20] | 刘俊来, 王安建, 曹殿华, 等. 三江造山带后碰撞断裂构造带的结构与演化:以新生代剑川—兰坪盆地为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2004,10(4):488-499. |
| [21] | 张乾, 绍树勋, 刘家军, 等. 兰坪盆地大型矿集区多金属矿床的铅同位素组成及铅的来源[J]. 矿物学报, 2002,22(2):147-154. |
| [22] | 苏学军, 张家云, 肖玲, 等. 1∶25万福贡县幅、丽江市幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质调查院, 2008: 1-314. |
| [23] | 陈开旭, 何龙清, 杨振强, 等. 云南兰坪三山—白秧坪铜银多金属成矿富集区的碳氧同位素地球化学[J]. 华南地质与成矿, 2000(4):1-8. |
| [24] | 何龙清, 陈开旭, 魏君奇. 云南白秧坪地区东成矿带矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2005,24(1):61-70. |
| [25] | 刘家军, 翟德高, 李志明, 等. 兰坪盆地白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区中银、钴、铋、镍的赋存状态与成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(6):1646-1660. |
| [26] | 王晓虎, 侯增谦, 宋玉财, 等. 兰坪盆地白秧坪铅锌铜银多金属矿床:成矿年代及区域成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(9):2625-2634. |
| [27] | 王光辉, 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 等. 兰坪盆地连城脉状铜矿床辉钼矿Re-Os定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2009,28(4):413-424. |
| [28] | 刘家军, 李志明, 刘玉平, 等. 滇西金满脉状铜矿床成矿年龄讨论[J]. 现代地质, 2003,17(1):34-39. |
| [29] | 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 滇西北金顶和白秧坪矿床:地质和He,Ne,Xe同位素组成及成矿时代[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2003,33(4):315-322. |
| [30] | 牟传龙, 余谦. 金顶铅锌矿床相关地质问题及成因探讨[J]. 矿物岩石, 2004,24(1):48-51. |
| [31] | 史长义, 梁萌, 冯斌. 中国水系沉积物39种元素系列背景值[J]. 地球科学, 2016,41(2):234-251. |
| [32] |
GONG Q J, LI J Z, XIANG Y C, et al. Determination and classification of geochemical anomalies based on backgrounds and cutoff grades of trace elements: A case study in South Nanling Range, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018,194:44-51.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
GONG Q J, DENG J, WANG C M, et al. Element behaviors due to rock weathering and its implication to geochemical anomaly re-cognition: A case study on Linglong biotite granite in Jiaodong peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013,128:14-24.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 马云涛, 龚庆杰, 韩东昱, 等. 安山岩风化过程中元素行为——以豫西熊耳山地区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015,51(3):545-554. |
| [35] |
LI J Z, GONG Q J, YAN T T, et al. Quantitative description of geochemical backgrounds of gold due to rock weathering in Jiao-dong peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018,192:155-162.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 向运川, 牟绪赞, 任天祥, 等. 全国矿产资源潜力评价化探资料应用研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 1-445. |
| [37] | 许胜超. 南岭东段区域化探异常分析[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2016: 5. |
| [38] |
GONG Q J, DENG J, JIA Y J, et al. Empirical equations to describe trace element behaviors due to rock weathering in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015,152:110-117.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张伟, 安茂国, 王志鹏, 杨启, 陈怀鑫, 马晓峰, 支成龙, 邢其涛, 裴长世, 王娜, 刘铭. 青海省那陵格勒河中游地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 690-707. |
| [2] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [3] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [4] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [5] | 李超, 罗先熔, 邱炜, 王宇慧, 赵欣怡, 郑超杰, 刘攀峰. 青海省都兰县金水口地区水系沉积物地球化学异常特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1397-1410. |
| [6] | 曾凯, 刘海, 黄德将, 郭威, 漆双林, 斯小华, 杨育振. 云南勐翁地区1:5万水系沉积物测量异常特征及找矿效果分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(01): 270-280. |
| [7] | 黄永高, 熊昌利, 罗改, 张彤, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 叶春林, 王燚. 滇西北香格里拉翁水地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 897-907. |
| [8] | 柳坤峰, 冯昌荣, 翟黎明, 徐磊, 张嘉升, 王少华, 寇昕. 新疆乌恰县吾合沙鲁地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(04): 759-771. |
| [9] | 韦彬, 侯青叶, 唐志敏, 宗庆霞, 闫帅, 何海云. 珠江水系沉积物重金属元素背景值估算及污染特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 293-304. |
| [10] | 王涛, 张静, 佟子达, 李腾建. 滇西莲花山富碱斑岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 438-452. |
| [11] | 高永伟, 郭周平, 赵辛敏, 王育习, 李向民, 薛宝林. 青海北祁连冷龙岭地区水系沉积物元素地球化学特征及异常圈定[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 468-480. |
| [12] | 胡兆国, 张少鹏, 连国建, 王磊, 李绪蛟, 李仕远, 张之武, 杨生飞, 胡加斌, 王小玉, 赵晓博, 张扬. 青海省纳日宗地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 481-492. |
| [13] | 王磊,杨建国,王小红,齐琦,张洲远, 张乐,谢燮,杨涛,杨生飞,胡兆国. 甘肃北山炭山子—黄草泉一带水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1276-1284. |
| [14] | 杨帆,宋云涛,张舜尧,郝志红,郭志娟,王成文,岑况. 内蒙古大石寨地区稀土元素的区域分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(4): 802-810. |
| [15] | 李小聪,王安东,万建军,李全忠,林乐夫. 赣江流域(南昌段)水系沉积物物源示踪研究:来自锆石U-Pb同位素证据的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3): 514-527. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||