



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (02): 361-370.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.016
张金龙1( ), 潘志龙1(
), 潘志龙1( ), 张运强2, 张欢1, 侯德华1, 石光耀3
), 张运强2, 张欢1, 侯德华1, 石光耀3
出版日期:2025-04-10
发布日期:2025-05-08
通信作者:
潘志龙,男,正高级工程师,1983年出生,资源勘查工程专业,主要从事第四纪地质与区域地质研究工作。Email:15304570@qq.com。作者简介:张金龙,男,工程师,1989年出生,资源勘查工程专业,主要从事第四纪地质与区域地质研究工作。Email:562278395@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Jinlong1( ), PAN Zhilong1(
), PAN Zhilong1( ), ZHANG Yunqiang2, ZHANG Huan1, HOU Dehua1, SHI Guangyao3
), ZHANG Yunqiang2, ZHANG Huan1, HOU Dehua1, SHI Guangyao3
Published:2025-04-10
Online:2025-05-08
摘要:
河北平原区第四纪地层沉积格架构建是区域地层对比和沉积环境研究的基础。为进一步探明河北平原北部大厂凹陷内第四纪松散沉积物的沉积特征,本文在廊坊市三河地区第四纪标准孔(叁9)研究成果基础上,又补充了沉积物粒度分析和古地磁等方面的研究工作,并分别对大厂凹陷内沿北北东方向分布的8个第四纪钻孔进行了地层划分、沉积相分析和联孔剖面的绘制等工作,并对凹陷内的第四纪三维地质结构、河流与洪积扇的迁移进行了综合研究。结果表明,区内第四纪沉积物主要是由鲍丘河、泃河及段甲岭洪积扇共同作用的结果;其中,标准孔(叁9)揭示了该区域在早更新世以洪积扇沉积环境为主;进入中更新世,区域气候相对较暖,水系较发育,主要以河流相沉积和局部洪积扇沉积作用为主;至晚更新世,随着区内南北地势的差异逐渐减小,洪积扇沉积逐渐收缩,该时期的沉积物多以古泃河与古鲍丘河的洪泛平原沉积为主;全新世以来,区内气候转暖,水系较发育,以古鲍丘河的明显下切为主要特征。最后,鲍丘河、泃河及东北部段甲岭一带的洪积扇均进入稳定期,形成现今地貌特征。
中图分类号:
张金龙, 潘志龙, 张运强, 张欢, 侯德华, 石光耀. 河北平原北部大厂凹陷第四纪沉积物的充填过程[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(02): 361-370.
ZHANG Jinlong, PAN Zhilong, ZHANG Yunqiang, ZHANG Huan, HOU Dehua, SHI Guangyao. Sedimentary Filling Processes of Quaternary Deposits in the Dachang Depression, North Hebei Plain[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(02): 361-370.
| 样品 编号 | 中值粒径 (Md) | 平均粒径 (Mz) | 标准偏差 (δ) | 偏态 (Sk) | 峰态 (Ku) | 样品 编号 | 中值粒径 (Md) | 平均粒径 (Mz) | 标准偏差 (δ) | 偏态 (Sk) | 峰态 (Ku) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD-1 | 5.72 | 5.95 | 3.76 | 0.09 | 0.19 | LD-59 | 6.44 | 6.43 | 4.00 | 0.03 | 0.15 |
| LD-2 | 5.44 | 5.75 | 4.23 | 0.07 | 0.15 | LD-60 | 5.95 | 6.04 | 4.36 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
| LD-3 | 4.86 | 5.36 | 4.46 | 0.09 | 0.15 | LD-61 | 3.81 | 4.59 | 5.74 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| LD-4 | 5.78 | 6.03 | 4.01 | 0.07 | 0.16 | LD-62 | 4.05 | 4.62 | 5.76 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| LD-5 | 5.54 | 5.88 | 3.95 | 0.08 | 0.18 | LD-63 | 5.90 | 6.06 | 3.67 | 0.06 | 0.18 |
| LD-6 | 5.88 | 6.09 | 3.87 | 0.07 | 0.17 | LD-64 | 6.64 | 6.51 | 4.43 | 0.00 | 0.12 |
| LD-7 | 4.58 | 5.01 | 3.45 | 0.19 | 0.36 | LD-65 | 6.21 | 6.40 | 3.12 | 0.10 | 0.29 |
| LD-8 | 6.93 | 6.94 | 3.18 | 0.01 | 0.28 | LD-66 | 3.04 | 3.91 | 5.65 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| LD-9 | 5.70 | 6.06 | 4.21 | 0.07 | 0.14 | LD-67 | 4.73 | 5.23 | 4.73 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| LD-10 | 7.12 | 7.26 | 2.54 | 0.11 | 0.40 | LD-68 | 1.19 | 1.69 | 4.04 | 0.28 | 0.49 |
| LD-11 | 6.79 | 6.71 | 3.96 | 0.01 | 0.15 | LD-69 | 2.94 | 3.84 | 7.17 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| LD-12 | 6.37 | 6.44 | 4.04 | 0.03 | 0.15 | LD-70 | 4.32 | 4.71 | 4.93 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| LD-13 | 6.31 | 6.35 | 4.55 | 0.02 | 0.11 | LD-71 | 5.83 | 6.03 | 3.16 | 0.12 | 0.29 |
| LD-14 | 6.68 | 6.59 | 4.16 | 0.01 | 0.13 | LD-72 | 2.62 | 3.38 | 5.59 | 0.09 | 0.12 |
| LD-15 | 5.39 | 5.67 | 5.26 | 0.03 | 0.09 | LD-73 | 3.51 | 4.21 | 8.36 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| LD-16 | 7.08 | 7.10 | 2.84 | 0.05 | 0.31 | LD-74 | 1.38 | 2.17 | 5.75 | 0.14 | 0.17 |
| LD-17 | 6.46 | 6.47 | 4.29 | 0.02 | 0.13 | LD-75 | 1.58 | 2.78 | 7.92 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| LD-18 | 5.83 | 6.08 | 3.80 | 0.08 | 0.18 | LD-76 | 1.56 | 2.22 | 4.70 | 0.21 | 0.30 |
| LD-19 | 3.98 | 4.54 | 3.68 | 0.20 | 0.32 | LD-77 | 4.51 | 4.60 | 9.65 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| LD-20 | 6.06 | 6.18 | 3.01 | 0.11 | 0.38 | LD-78 | 3.39 | 4.11 | 4.90 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
| LD-21 | 7.35 | 7.31 | 2.76 | 0.00 | 0.37 | LD-79 | 2.71 | 3.71 | 8.44 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| LD-22 | 6.84 | 6.82 | 3.63 | 0.03 | 0.18 | LD-80 | 5.84 | 6.14 | 3.72 | 0.08 | 0.20 |
| LD-23 | 4.66 | 5.27 | 3.99 | 0.14 | 0.22 | LD-81 | 2.01 | 3.29 | 7.94 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| LD-24 | 6.00 | 6.22 | 3.88 | 0.07 | 0.17 | LD-82 | 2.13 | 3.42 | 8.34 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| LD-25 | 4.28 | 4.87 | 6.73 | 0.03 | 0.05 | LD-83 | 6.78 | 6.80 | 3.53 | 0.03 | 0.19 |
| LD-26 | 5.68 | 6.04 | 3.45 | 0.12 | 0.26 | LD-84 | 1.66 | 2.36 | 5.11 | 0.18 | 0.24 |
| LD-27 | 2.00 | 2.49 | 3.92 | 0.27 | 0.46 | LD-85 | 1.79 | 2.45 | 4.77 | 0.19 | 0.27 |
| LD-28 | 1.44 | 1.87 | 3.53 | 0.41 | 0.80 | LD-86 | 3.16 | 3.59 | 3.35 | 0.29 | 0.52 |
| LD-29 | 2.33 | 2.67 | 2.86 | 0.53 | 1.18 | LD-87 | 3.20 | 3.88 | 4.87 | 0.13 | 0.18 |
| LD-30 | 6.03 | 5.80 | 6.84 | -0.01 | 0.05 | LD-88 | 2.34 | 2.69 | 2.84 | 0.50 | 1.13 |
| LD-31 | 1.92 | 2.43 | 3.85 | 0.29 | 0.50 | LD-89 | 2.63 | 3.20 | 4.05 | 0.22 | 0.35 |
| LD-32 | 1.86 | 2.25 | 3.44 | 0.38 | 0.75 | LD-90 | 2.97 | 3.76 | 7.42 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| LD-33 | 5.08 | 5.39 | 5.31 | 0.03 | 0.10 | LD-91 | 5.04 | 5.61 | 3.99 | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| LD-34 | 6.38 | 6.51 | 3.48 | 0.07 | 0.21 | LD-92 | 7.66 | 7.59 | 2.47 | -0.10 | 0.69 |
| LD-35 | 7.80 | 7.71 | 2.67 | -0.12 | 0.61 | LD-93 | 5.05 | 5.38 | 4.25 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
| LD-36 | 5.53 | 5.82 | 4.73 | 0.05 | 0.11 | LD-94 | 3.45 | 4.04 | 6.70 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| LD-37 | 5.19 | 5.14 | 7.59 | 0.01 | 0.03 | LD-95 | 6.48 | 6.07 | 6.56 | -0.03 | 0.06 |
| LD-38 | 4.44 | 5.09 | 5.23 | 0.07 | 0.10 | LD-96 | 6.88 | 6.77 | 3.64 | 0.00 | 0.18 |
| LD-39 | 3.81 | 4.43 | 5.69 | 0.07 | 0.09 | LD-97 | 5.91 | 6.10 | 3.71 | 0.06 | 0.18 |
| LD-40 | 4.24 | 4.72 | 9.82 | 0.01 | 0.02 | LD-98 | 5.73 | 5.93 | 4.02 | 0.06 | 0.15 |
| LD-41 | 1.33 | 2.61 | 8.85 | 0.05 | 0.04 | LD-99 | 5.42 | 5.79 | 4.91 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| LD-42 | 2.04 | 3.21 | 7.65 | 0.06 | 0.05 | LD-100 | 4.56 | 4.91 | 4.70 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| LD-43 | 0.97 | 1.64 | 5.44 | 0.16 | 0.22 | LD-101 | 6.66 | 6.70 | 3.50 | 0.03 | 0.20 |
| LD-44 | 5.82 | 6.10 | 3.96 | 0.07 | 0.17 | LD-102 | 5.76 | 5.95 | 4.00 | 0.06 | 0.15 |
| LD-45 | 6.63 | 6.71 | 3.37 | 0.01 | 0.29 | LD-103 | 6.72 | 6.84 | 2.81 | 0.10 | 0.33 |
| LD-46 | 4.76 | 5.17 | 7.15 | 0.02 | 0.04 | LD-104 | 5.91 | 6.19 | 3.24 | 0.12 | 0.27 |
| LD-47 | 4.47 | 4.91 | 9.08 | 0.01 | 0.02 | LD-105 | 3.20 | 3.86 | 4.20 | 0.16 | 0.24 |
| LD-48 | 1.86 | 3.08 | 8.02 | 0.05 | 0.05 | LD-106 | 1.92 | 2.65 | 4.96 | 0.16 | 0.22 |
| LD-49 | 2.46 | 3.35 | 5.51 | 0.10 | 0.13 | LD-107 | 2.39 | 3.44 | 6.76 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| LD-50 | 1.76 | 3.16 | 8.61 | 0.04 | 0.04 | LD-108 | 3.15 | 3.84 | 4.58 | 0.14 | 0.20 |
| LD-51 | 3.08 | 4.07 | 6.34 | 0.06 | 0.07 | LD-109 | 4.05 | 4.60 | 4.24 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| LD-52 | 5.66 | 5.96 | 4.28 | 0.06 | 0.13 | LD-110 | 3.30 | 3.91 | 5.78 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| LD-53 | 4.28 | 4.99 | 4.58 | 0.11 | 0.15 | LD-111 | 2.35 | 3.37 | 6.71 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| LD-54 | 6.46 | 6.38 | 4.66 | 0.01 | 0.10 | LD-112 | 3.54 | 4.05 | 3.95 | 0.17 | 0.27 |
| LD-55 | 4.45 | 5.16 | 4.74 | 0.09 | 0.13 | LD-113 | 4.96 | 5.40 | 4.71 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| LD-56 | 4.49 | 5.07 | 3.64 | 0.20 | 0.31 | LD-114 | 2.25 | 3.36 | 7.64 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| LD-57 | 3.97 | 4.41 | 2.75 | 0.43 | 0.83 | LD-115 | 2.56 | 3.33 | 5.18 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| LD-58 | 6.08 | 6.34 | 3.45 | 0.09 | 0.21 | LD-116 | 3.64 | 4.23 | 7.60 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
表1 叁9孔粒度样品测试信息
Table 1 Test information of particle size sample from borehole San 9
| 样品 编号 | 中值粒径 (Md) | 平均粒径 (Mz) | 标准偏差 (δ) | 偏态 (Sk) | 峰态 (Ku) | 样品 编号 | 中值粒径 (Md) | 平均粒径 (Mz) | 标准偏差 (δ) | 偏态 (Sk) | 峰态 (Ku) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LD-1 | 5.72 | 5.95 | 3.76 | 0.09 | 0.19 | LD-59 | 6.44 | 6.43 | 4.00 | 0.03 | 0.15 |
| LD-2 | 5.44 | 5.75 | 4.23 | 0.07 | 0.15 | LD-60 | 5.95 | 6.04 | 4.36 | 0.04 | 0.12 |
| LD-3 | 4.86 | 5.36 | 4.46 | 0.09 | 0.15 | LD-61 | 3.81 | 4.59 | 5.74 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| LD-4 | 5.78 | 6.03 | 4.01 | 0.07 | 0.16 | LD-62 | 4.05 | 4.62 | 5.76 | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| LD-5 | 5.54 | 5.88 | 3.95 | 0.08 | 0.18 | LD-63 | 5.90 | 6.06 | 3.67 | 0.06 | 0.18 |
| LD-6 | 5.88 | 6.09 | 3.87 | 0.07 | 0.17 | LD-64 | 6.64 | 6.51 | 4.43 | 0.00 | 0.12 |
| LD-7 | 4.58 | 5.01 | 3.45 | 0.19 | 0.36 | LD-65 | 6.21 | 6.40 | 3.12 | 0.10 | 0.29 |
| LD-8 | 6.93 | 6.94 | 3.18 | 0.01 | 0.28 | LD-66 | 3.04 | 3.91 | 5.65 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| LD-9 | 5.70 | 6.06 | 4.21 | 0.07 | 0.14 | LD-67 | 4.73 | 5.23 | 4.73 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| LD-10 | 7.12 | 7.26 | 2.54 | 0.11 | 0.40 | LD-68 | 1.19 | 1.69 | 4.04 | 0.28 | 0.49 |
| LD-11 | 6.79 | 6.71 | 3.96 | 0.01 | 0.15 | LD-69 | 2.94 | 3.84 | 7.17 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| LD-12 | 6.37 | 6.44 | 4.04 | 0.03 | 0.15 | LD-70 | 4.32 | 4.71 | 4.93 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| LD-13 | 6.31 | 6.35 | 4.55 | 0.02 | 0.11 | LD-71 | 5.83 | 6.03 | 3.16 | 0.12 | 0.29 |
| LD-14 | 6.68 | 6.59 | 4.16 | 0.01 | 0.13 | LD-72 | 2.62 | 3.38 | 5.59 | 0.09 | 0.12 |
| LD-15 | 5.39 | 5.67 | 5.26 | 0.03 | 0.09 | LD-73 | 3.51 | 4.21 | 8.36 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| LD-16 | 7.08 | 7.10 | 2.84 | 0.05 | 0.31 | LD-74 | 1.38 | 2.17 | 5.75 | 0.14 | 0.17 |
| LD-17 | 6.46 | 6.47 | 4.29 | 0.02 | 0.13 | LD-75 | 1.58 | 2.78 | 7.92 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| LD-18 | 5.83 | 6.08 | 3.80 | 0.08 | 0.18 | LD-76 | 1.56 | 2.22 | 4.70 | 0.21 | 0.30 |
| LD-19 | 3.98 | 4.54 | 3.68 | 0.20 | 0.32 | LD-77 | 4.51 | 4.60 | 9.65 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| LD-20 | 6.06 | 6.18 | 3.01 | 0.11 | 0.38 | LD-78 | 3.39 | 4.11 | 4.90 | 0.11 | 0.15 |
| LD-21 | 7.35 | 7.31 | 2.76 | 0.00 | 0.37 | LD-79 | 2.71 | 3.71 | 8.44 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| LD-22 | 6.84 | 6.82 | 3.63 | 0.03 | 0.18 | LD-80 | 5.84 | 6.14 | 3.72 | 0.08 | 0.20 |
| LD-23 | 4.66 | 5.27 | 3.99 | 0.14 | 0.22 | LD-81 | 2.01 | 3.29 | 7.94 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| LD-24 | 6.00 | 6.22 | 3.88 | 0.07 | 0.17 | LD-82 | 2.13 | 3.42 | 8.34 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| LD-25 | 4.28 | 4.87 | 6.73 | 0.03 | 0.05 | LD-83 | 6.78 | 6.80 | 3.53 | 0.03 | 0.19 |
| LD-26 | 5.68 | 6.04 | 3.45 | 0.12 | 0.26 | LD-84 | 1.66 | 2.36 | 5.11 | 0.18 | 0.24 |
| LD-27 | 2.00 | 2.49 | 3.92 | 0.27 | 0.46 | LD-85 | 1.79 | 2.45 | 4.77 | 0.19 | 0.27 |
| LD-28 | 1.44 | 1.87 | 3.53 | 0.41 | 0.80 | LD-86 | 3.16 | 3.59 | 3.35 | 0.29 | 0.52 |
| LD-29 | 2.33 | 2.67 | 2.86 | 0.53 | 1.18 | LD-87 | 3.20 | 3.88 | 4.87 | 0.13 | 0.18 |
| LD-30 | 6.03 | 5.80 | 6.84 | -0.01 | 0.05 | LD-88 | 2.34 | 2.69 | 2.84 | 0.50 | 1.13 |
| LD-31 | 1.92 | 2.43 | 3.85 | 0.29 | 0.50 | LD-89 | 2.63 | 3.20 | 4.05 | 0.22 | 0.35 |
| LD-32 | 1.86 | 2.25 | 3.44 | 0.38 | 0.75 | LD-90 | 2.97 | 3.76 | 7.42 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| LD-33 | 5.08 | 5.39 | 5.31 | 0.03 | 0.10 | LD-91 | 5.04 | 5.61 | 3.99 | 0.12 | 0.19 |
| LD-34 | 6.38 | 6.51 | 3.48 | 0.07 | 0.21 | LD-92 | 7.66 | 7.59 | 2.47 | -0.10 | 0.69 |
| LD-35 | 7.80 | 7.71 | 2.67 | -0.12 | 0.61 | LD-93 | 5.05 | 5.38 | 4.25 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
| LD-36 | 5.53 | 5.82 | 4.73 | 0.05 | 0.11 | LD-94 | 3.45 | 4.04 | 6.70 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| LD-37 | 5.19 | 5.14 | 7.59 | 0.01 | 0.03 | LD-95 | 6.48 | 6.07 | 6.56 | -0.03 | 0.06 |
| LD-38 | 4.44 | 5.09 | 5.23 | 0.07 | 0.10 | LD-96 | 6.88 | 6.77 | 3.64 | 0.00 | 0.18 |
| LD-39 | 3.81 | 4.43 | 5.69 | 0.07 | 0.09 | LD-97 | 5.91 | 6.10 | 3.71 | 0.06 | 0.18 |
| LD-40 | 4.24 | 4.72 | 9.82 | 0.01 | 0.02 | LD-98 | 5.73 | 5.93 | 4.02 | 0.06 | 0.15 |
| LD-41 | 1.33 | 2.61 | 8.85 | 0.05 | 0.04 | LD-99 | 5.42 | 5.79 | 4.91 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| LD-42 | 2.04 | 3.21 | 7.65 | 0.06 | 0.05 | LD-100 | 4.56 | 4.91 | 4.70 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| LD-43 | 0.97 | 1.64 | 5.44 | 0.16 | 0.22 | LD-101 | 6.66 | 6.70 | 3.50 | 0.03 | 0.20 |
| LD-44 | 5.82 | 6.10 | 3.96 | 0.07 | 0.17 | LD-102 | 5.76 | 5.95 | 4.00 | 0.06 | 0.15 |
| LD-45 | 6.63 | 6.71 | 3.37 | 0.01 | 0.29 | LD-103 | 6.72 | 6.84 | 2.81 | 0.10 | 0.33 |
| LD-46 | 4.76 | 5.17 | 7.15 | 0.02 | 0.04 | LD-104 | 5.91 | 6.19 | 3.24 | 0.12 | 0.27 |
| LD-47 | 4.47 | 4.91 | 9.08 | 0.01 | 0.02 | LD-105 | 3.20 | 3.86 | 4.20 | 0.16 | 0.24 |
| LD-48 | 1.86 | 3.08 | 8.02 | 0.05 | 0.05 | LD-106 | 1.92 | 2.65 | 4.96 | 0.16 | 0.22 |
| LD-49 | 2.46 | 3.35 | 5.51 | 0.10 | 0.13 | LD-107 | 2.39 | 3.44 | 6.76 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| LD-50 | 1.76 | 3.16 | 8.61 | 0.04 | 0.04 | LD-108 | 3.15 | 3.84 | 4.58 | 0.14 | 0.20 |
| LD-51 | 3.08 | 4.07 | 6.34 | 0.06 | 0.07 | LD-109 | 4.05 | 4.60 | 4.24 | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| LD-52 | 5.66 | 5.96 | 4.28 | 0.06 | 0.13 | LD-110 | 3.30 | 3.91 | 5.78 | 0.07 | 0.10 |
| LD-53 | 4.28 | 4.99 | 4.58 | 0.11 | 0.15 | LD-111 | 2.35 | 3.37 | 6.71 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| LD-54 | 6.46 | 6.38 | 4.66 | 0.01 | 0.10 | LD-112 | 3.54 | 4.05 | 3.95 | 0.17 | 0.27 |
| LD-55 | 4.45 | 5.16 | 4.74 | 0.09 | 0.13 | LD-113 | 4.96 | 5.40 | 4.71 | 0.06 | 0.12 |
| LD-56 | 4.49 | 5.07 | 3.64 | 0.20 | 0.31 | LD-114 | 2.25 | 3.36 | 7.64 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| LD-57 | 3.97 | 4.41 | 2.75 | 0.43 | 0.83 | LD-115 | 2.56 | 3.33 | 5.18 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| LD-58 | 6.08 | 6.34 | 3.45 | 0.09 | 0.21 | LD-116 | 3.64 | 4.23 | 7.60 | 0.03 | 0.04 |

图4 洪积扇相的扇中、扇端和扇前洼地沉积环境特征 1. 砂砾石;2.泥砾石;3.砂;4.粉砂;5.黏土;6.淤泥质黏土;7.平行层理;8.水平层理;9.粒序层理;10.脉状层理;11.板状交错层理
Fig.4 Characteristics of sedimentary environment in mid-fan, end-fan and pre-fan depressions of diluvial fan facies

图5 辫状河相的心滩和河漫滩沉积环境特征 1. 砾石;2.含砾砂;3.砂;4.粉砂;5.黏土;6.平行层理;7.粒序层理;8.槽状交错层理;9.板状交错层理
Fig.5 Sedimentary environment characteristics of the central and floodplain of braided fluvial facies

图6 曲流河边滩微相沉积环境特征 1. 粗砂;2.中砂;3.细砂;4.含黏粉砂;5.黏土质粉砂;6.黏土;7.平行层理;8.水平层理;9.脉状层理;10.板状交错层理
Fig.6 Characteristics of microfacies sedimentary environment in meandering river bank
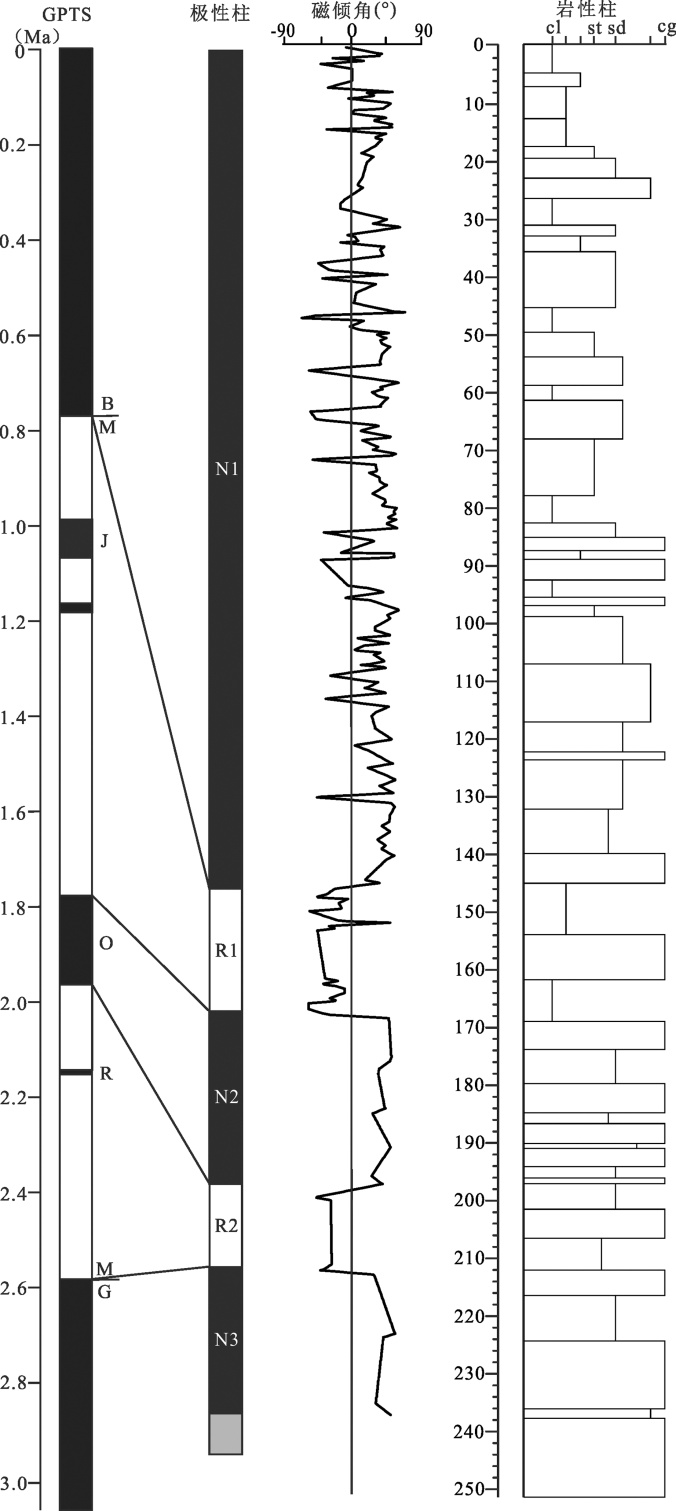
图7 叁9孔磁性地层与标准极性柱对比图(据文献[14]改编) cl.黏土;st.粉砂;sd.砂;cg.粗砾石
Fig.7 Comparison diagram of magnetostratigraphy for borehole San 9 with polarity zones(modified from reference [14])

图9 三河地区大厂凹陷构造单元内北东东走向钻孔剖面图(剖面位置见图1)
Fig.9 Borehole profile in the NEE direction of the Dachang depression structural unit in the Sanhe area (Profile location shown in Fig.1)
| [1] | 杨旭. 廊坊盆地更新世以来沉积相精细分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012. |
| [2] | 中国科学院贵阳地球化学研究所华北平原研究组. 河北平原东部第四纪地层及其特征的初步研究[J]. 地球化学, 1978, 7(3): 169-178. |
| [3] | 陈望和, 倪明云, 等. 河北第四纪地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 8-47. |
| [4] | 刘立军, 徐海振, 崔秋苹, 等. 河北平原第四纪地层划分研究[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2010, 26(2): 54-57. |
| [5] | 余中元, 潘华, 沈军, 等. 夏垫断裂荣家堡探槽揭示的断裂活动特征及未来地震危险性概率评价[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 688-702. |
| [6] | 徐锡伟, 计凤桔, 于贵华, 等. 用钻孔地层剖面记录恢复古地震序列: 河北夏垫断裂古地震研究[J]. 地震地质, 2000, 22(1): 9-19. |
| [7] | 高景华, 徐明才, 荣立新, 等. 探测城市断裂活动性的浅层地震方法技术[J]. 物探与化探, 2007, 31(S1): 4-8. |
| [8] | 刘智荣, 沈军, 黄静宜, 等. 河北三河晚更新世地层粒度特征分析[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(5): 997-1005. |
| [9] | 刘丹. 廊坊市第四纪沉积物粒度特征及沉积环境分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012. |
| [10] | 杨旭, 白志强, 陈建强, 等. 廊坊地区中晚更新世以来沉积地层与环境演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 60-64, 81. |
| [11] | 河北省区域地质调查院. 河北1:5万大厂回族自治县等三幅第四系覆盖区地质填图报告[M]. 2019: 33-113. |
| [12] |
李德生. 渤海湾含油气盆地的地质和构造特征[J]. 石油学报, 1980, 1(1): 6-20.
DOI |
| [13] | 地质矿产部航空物探总队九零三队. 冀中坳陷北部地区高精度航磁测量成果报告[M]. 1987: 52-88. |
| [14] | 石光耀, 潘志龙, 张欢, 等. 河北平原三河S9孔岩心特征及第四纪地层划分研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(5): 1332-1342. |
| [15] | 朱筱敏. 沉积岩石学[M]. 4版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 64-79. |
| [16] | 何幼斌, 王文广. 沉积岩与沉积相[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2007: 158-181. |
| [17] | 张运强. 京津冀山前冲洪积平原区1: 50000填图方法指南[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 92-97. |
| [18] | 王强. 渤海西岸全新世早期基底泥炭堆积时间域初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 1999, 19(1): 91-99. |
| [19] | 王强, 张玉发, 袁桂邦, 等. MIS 3阶段以来河北黄骅北部地区海侵与气候期对比[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(1): 79-95. |
| [20] | 邵时雄, 安仲元, 韩书华. 河北平原新构造运动主要特征的分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(4): 67-77. |
| [21] | 陈望和, 等. 河北地下水[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999: 1-539. |
| [22] | 李海君, 张耀文, 孟健. 华北平原地面沉降新构造运动影响特征[J]. 能源与环保, 2017, 39(6): 57-62, 66. |
| [23] | 许炯心. 基于大样本14C测年资料的华北平原沉积速率研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(3): 437-443. |
| [24] | 吴忱, 张秀清, 马永红. 太行山、燕山主要隆起于第四纪[J]. 华北地震科学, 1999, 17(3): 1-7. |
| [25] | 高秀林, 王强, 李玉德, 等. 从天津P8孔看中更新世末期以来海侵期、气候期对比问题[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(1): 53-64, 131. |
| [26] |
赵勇, 王强, 李瑞杰, 等. 北京平原区南部PGZ01孔第四纪地层划分及其环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(2): 337-348.
DOI |
| [1] | 石光耀, 潘志龙, 张欢, 吕可欣, 张金龙, 张运强, 李庆喆, 张鹏程. 河北平原三河S9孔岩心特征及第四纪地层划分研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1332-1342. |
| [2] | 赵建鹏, 崔利凯, 陈惠, 李宁, 王自亮, 马瑶, 杜贵超. 基于CT扫描数字岩心的岩石微观结构定量表征方法[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1205-1213. |
| [3] | 郑德顺, 杨东亮, 杨文涛, 李雨. 豫西鲁山地区寒武系辛集组沉积环境及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 604-614. |
| [4] | 孙军, 杨慧良, 何磊, 褚宏宪, 路月, 李攀峰, 刘长春, 祁江豪, 强小科. 渤海海峡BHS01孔沉积物磁性地层学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 315-324. |
| [5] | 陈碧珊, 陈诗敏, 何炽鹏. 雷州半岛红树林湿地表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 198-205. |
| [6] | 赵勇, 李瑞杰, 魏波, 王纯君, 孙永华, 方同明. 北京大兴凸起南部PGZ05钻孔剖面第四纪磁性地层学[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 56-62. |
| [7] | 白凌燕, 李潇, 秦浩敏, 张晓亮, 张悦泽. 北京平原南口—孙河断裂南段第四纪活动性及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(02): 270-278. |
| [8] | 郑建彬, 陈建强. 河南新乡第四纪地层划分与沉积环境分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 81-91. |
| [9] | 张皓月 ,张绪教 ,李成路 ,何泽新 ,叶培盛 ,叶梦旎. 内蒙古河套平原塔尔湖地区湖泊成因[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1170-. |
| [10] | 冯军,张彬,黄骁,孙进忠,柏永亮,霍东平. 北京延庆新城规划区场地动力响应数值模拟[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1252-1259. |
| [11] | 白凌燕,张磊,蔡向民,王继明,杨天水,吴怀春,何静,张晓亮,赵勇. 磁性地层年代对北京平原顺义断裂第四纪活动性的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1234-1242. |
| [12] | 袁胜元,李长安. 基于因子分析的江汉盆地第四纪沉积物源讨论[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(5): 980-985. |
| [13] | 王丽媛,程捷,辛蔚,昝立宏. 腾格里沙漠西北缘青土湖中更新世晚期以来沉积环境变迁[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 949-958. |
| [14] | 刘亚雷,齐英敏,刘云翔,王月然,赵岩,张强等. 塔里木盆地阿恰构造带断裂构造分析[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(1): 158-164. |
| [15] | 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 李军, 李随民, 宋泽峰. 河北平原土壤元素评价[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(3): 569-574. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||