



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (02): 362-372.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.065
收稿日期:2023-01-06
修回日期:2023-08-08
出版日期:2024-04-10
发布日期:2024-05-22
通讯作者:
邹华耀,男,1963年出生,教授,石油地质学专业,主要从事油气成藏机理教学与科研工作。Email: huayaozou@cup.edu.cn。
作者简介:蒋代琴,女,1994年出生,博士研究生,地质资源与地质工程专业,主要从事页岩油气成藏研究。Email: jiangdq728@163.com。
基金资助:
JIANG Daiqin( ), LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao(
), LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao( )
)
Received:2023-01-06
Revised:2023-08-08
Online:2024-04-10
Published:2024-05-22
摘要:
川东北元坝地区陆相页岩中天然裂缝发育,是影响页岩油气富集和保存的关键因素。本文依据岩心、镜下薄片和扫描电镜等资料研究该区侏罗系大安寨段和千佛崖组页岩层系天然裂缝的发育分布特征,探讨裂缝对页岩油气富集和保存的影响。结果表明,侏罗系页岩中主要发育构造裂缝、层理缝、穿层水力破裂缝和收缩缝,其中构造裂缝包括穿层剪切缝、顺层剪切缝和层内张开缝,层理缝是页岩中最为发育的天然裂缝,线密度介于66~357条/m之间,平均为188条/m。层理缝和收缩缝既是页岩油气的储集空间也是运移通道,改善了页岩的储集性能,有利于页岩油气的富集。构造裂缝、穿层水力破裂缝与层理缝相互连通形成的宏观裂缝网络是页岩油气排放的通道,对大安寨段页岩气的逸散影响较大,对千佛崖组页岩油的保存条件影响较小。研究成果可为四川盆地陆相页岩油气勘探开发提供基础性参考依据。
中图分类号:
蒋代琴, 李平平, 邹华耀. 川东北元坝地区侏罗系陆相页岩天然裂缝发育特征及其对页岩油气富集和保存的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 362-372.
JIANG Daiqin, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao. Characteristics of Natural Fractures and Their Influence on Oil and Gas Enrichment and Preservation of the Jurassic Continental Shale in the Yuanba Area, Northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 362-372.

图1 元坝地区构造位置图(a)、下侏罗统自流井组断层平面分布图(b)、构造剖面图(c)和地层岩性剖面图(d) J2s. 中侏罗统上沙溪庙组;J2x. 中侏罗统下沙溪庙组;J2q. 中侏罗统千佛崖组;J1z4. 下侏罗统自流井组大安寨段;J1z1—J1z3. 下侏罗统自流井组珍珠冲段、东岳庙段和马鞍山段;T3x. 上三叠统须家河组
Fig.1 Tectonic location (a), fault distribution (b), structural profile (c), and stratigraphic profile (d) in Yuanba

图2 元坝地区侏罗系页岩构造裂缝特征 (a) 泥质粉砂岩,高角度微断层、张开缝(黄色箭头)和层理缝,YY2井千佛崖组,3722.86 m;(b) 泥岩,高角度穿层剪切缝,YY3井千佛崖组,3510.51 m;(c) 页岩,低角度穿层剪切缝和层理缝,YY3井千佛崖组,3583.52 m;(d) 灰岩,低角度穿层剪切缝被方解石充填(左侧为岩心侧面,右侧为岩心断面),YL175井大安寨段,3948.2 m;(e) 页岩,顺层剪切缝,YL30大安寨段,3996.78 m;(f) 页岩,顺层剪切缝,YY2井千佛崖组,3765.41 m
Fig.2 Characteristics of tectonic fractures from the cores of the Jurassic shale in Yuanba

图3 元坝地区侏罗系页岩岩心非构造裂缝特征 (a) 页岩,层理缝,YY2井大安寨段,3910.88 m;(b) 页岩,层理缝和纤维状方解石脉,YY2井千佛崖组,3728.14 m;(c) 页岩,层理缝和纤维状方解石脉,YY2井大安寨段,3905.7 m;(d) 页岩,顺层和穿层水力破裂缝被沥青充填,沥青与围岩之间充填方解石,YY2井千佛崖组,3718.67 m;(e) 页岩,穿层水力破裂缝被沥青充填,YY3井千佛崖组,3574.71 m;(f) 泥岩,网状收缩缝,YY2千佛崖组,3728.14 m
Fig.3 Characteristics of nontectonic fractures from the cores of the Jurassic shale in Yuanba

图4 元坝地区侏罗系页岩薄片非构造裂缝特征 (a) 页岩,层理缝,YY2井千佛崖组,3770.9 m;(b) 页岩,层理缝,YY2井大安寨段,3908.79 m;(c) 含介壳页岩,层理缝、介壳边缘缝及其延展缝,YY2井大安寨段,3884.68 m;(d) 页岩,被沥青充填的层理缝,YY2井大安寨段,3911.89 m;(e) 页岩,顺层脉状裂缝与纤维状方解石脉,YY2井大安寨段,3885.31 m;(f) 纤维状方解石脉中暗色泥质条纹,YY2井大安寨段,3884.36 m;(g) 粉砂岩,被沥青充填的层理缝,YY3井千佛崖组,3535.56 m;(h) 泥岩,网状收缩缝,YY3井千佛崖组,3505.37 m;(i) 介壳灰岩,被沥青充填的缝合线,YY2井大安寨段,3889.4 m
Fig.4 Characteristics of nontectonic fractures from the thin sections of the Jurassic shale in Yuanba

图5 元坝地区侏罗系页岩扫描电镜下非构造裂缝特征 (a) 层理缝,YY2井大安寨段,3887.35 m;(b) 黏土矿物收缩缝,YL4井大安寨段,3753.38 m;(c) 黏土矿物收缩缝,YY2井大安寨段,3887.35 m;(d) 有机质收缩缝,YY2井大安寨段,3887.35 m;(e) 有机质收缩缝,YY2井大安寨段,3890.95 m;(f) 方解石内部解理缝,YY2井大安寨段,3907.15 m
Fig.5 Characteristics of microfractures from the FE-SEM images of the Jurassic shale in Yuanba
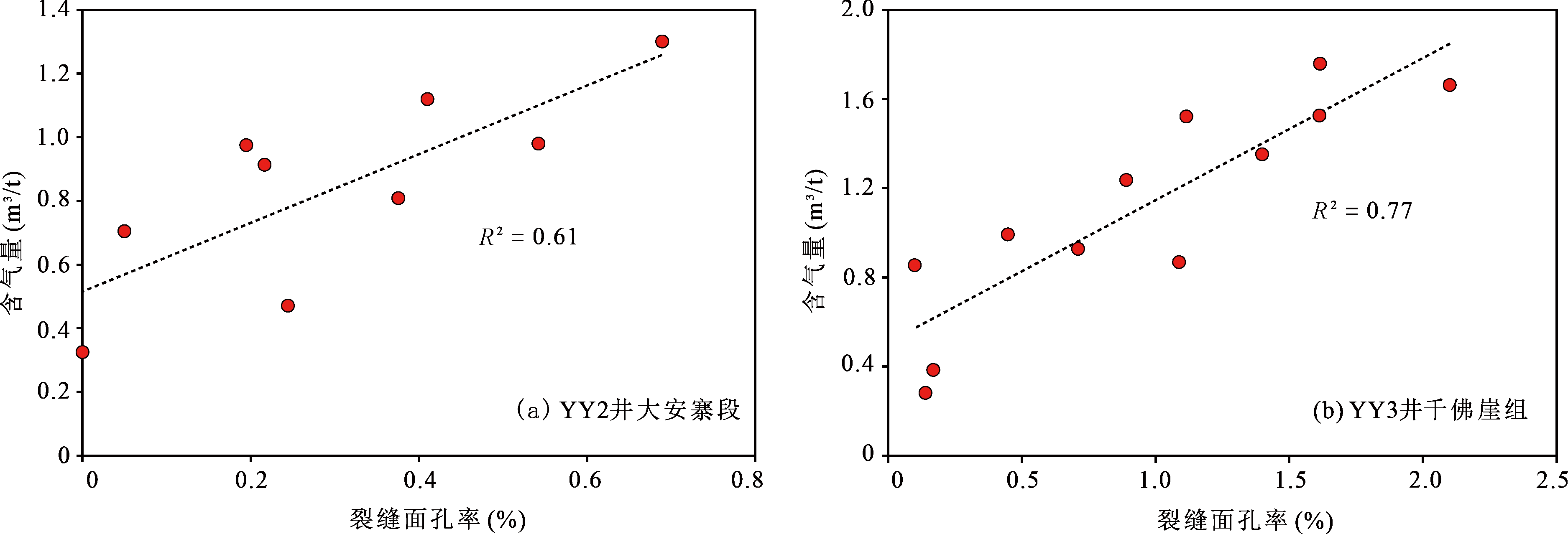
图7 元坝地区大安寨段(a)和千佛崖组页岩(b)含气量与裂缝面孔率相关关系图
Fig.7 Diagrams of relationship between gas content and fracture surface porosity of the Da’anzhai shale and Qianfoya shale in Yuanba

图8 元坝地区侏罗系页岩油气显示 (a) 黑灰色页岩,针状-粒状气泡断续从层理缝中冒出,YY2井大安寨段,3905.89 m;(b) 黑色页岩,大量呈排线状气泡连续从层理缝中冒出,YY3井千佛崖组,3570.96 m;(c) 灰色厚层介壳灰岩,针状-粒状气泡断续冒出,YY2井大安寨段,3897.81 m;(d) 灰色粉砂岩,层理缝中见原油渗出,YY3井千佛崖组,3535.56 m
Fig.8 Display of oil and gas in the Jurassic shale from Yuanba

图9 元坝地区侏罗系页岩油气运聚和排放模式 (a)-(c) 页岩油气微观运聚模式;(d) 大安寨段页岩排烃模式;(e) 千佛崖组页岩排烃模式;有机质生烃作用形成的页岩油气在异常高压驱动下运移至收缩缝、溶蚀缝等微裂缝中并逐渐向更大尺度的裂缝中汇聚,进一步通过层理缝、构造裂缝和穿层水力破裂缝运移并被排出至近源的介壳灰岩和粉砂岩中
Fig.9 Migration, accumulation, and emission model of the Jurassic shale oil and gas in Yuanba
| [1] | CURTIS J B. Fractured shale-gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938. |
| [2] | 黎茂稳, 马晓潇, 蒋启贵, 等. 北美海相页岩油形成条件、富集特征与启示[J]. 油气地质与采收率. 2019, 26(1):13-28. |
| [3] | ZENG L B, LYU W Y, LI J, et al. Natural fractures and their influence on shale gas enrichment in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2016, 30:1-9. |
| [4] |
董大忠, 施振生, 孙莎莎, 等. 黑色页岩微裂缝发育控制因素——以长宁双河剖面五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5):763-774.
DOI |
| [5] | GALE J F W, REED R M, HOLDER J. Natural fractures in the Barnett Shale and their importance for hydraulic fracture treatments[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):603-622. |
| [6] | 谭鹏, 金衍, 陈刚. 四川盆地不同埋深龙马溪页岩水力裂缝缝高延伸形态及差异分析[J]. 石油科学通报, 2022, 7(1):61-70. |
| [7] | 李浩, 陆建林, 王保华, 等. 陆相页岩油富集高产关键因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(4):837-848. |
| [8] | 丁文龙, 许长春, 久凯, 等. 泥页岩裂缝研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(2):135-144. |
| [9] | 田鹤, 曾联波, 徐翔, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区海相页岩天然裂缝特征及对页岩气的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3):474-483. |
| [10] | GALE J F W, LAUBACH S E, OLSON J E, et al. Natural fractures in shale: A review and new observations[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(11):2165-2216. |
| [11] | 李长海, 赵伦, 刘波, 等. 微裂缝研究进展、意义及发展趋势[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(3):402-416. |
| [12] | 张琴, 刘畅, 梅啸寒, 等. 页岩气储层微观储集空间研究现状及展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(4):666-674. |
| [13] | 王艿川, 赵靖舟, 丁文龙, 等. 渝东南地区龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(4):760-770. |
| [14] |
曾联波, 吕文雅, 徐翔, 等. 典型致密砂岩与页岩层理缝的发育特征、形成机理及油气意义[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(2):180-191.
DOI |
| [15] | 曾联波, 肖淑蓉. 低渗透储集层中的泥岩裂缝储集体[J]. 石油实验地质, 1999, 21(3):266-269. |
| [16] | ANDERS M H, LAUBACH S E, SCHOLZ C H. Microfractures: A review[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2014, 69:377-394. |
| [17] | 汪吉林, 朱炎铭, 宫云鹏, 等. 重庆南川地区龙马溪组页岩微裂缝发育影响因素及程度预测[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(8):1579-1586. |
| [18] | 丁文龙, 李超, 李春燕, 等. 页岩裂缝发育主控因素及其对含气性的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(2):212-220. |
| [19] | 袁余洋, 李虎, 王瑛, 等. 页岩岩相类型对裂缝形成及演化的影响研究——以黔西北地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(1):82-97. |
| [20] | 郑荣才, 郭春利, 梁西文, 等. 四川盆地大安寨段非常规储层的储集空间类型与评价[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(1):16-29. |
| [21] |
刘红岐, 李博, 王拥军, 等. 川中大安寨段致密油储层储集特征研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(6):47-55.
DOI |
| [22] |
周德华, 孙川翔, 刘忠宝, 等. 川东北地区大安寨段陆相页岩气藏地质特征[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(5):32-42.
DOI |
| [23] | 郭旭升, 赵永强, 张文涛, 等. 四川盆地元坝地区千佛崖组页岩油气富集特征与主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5):749-757. |
| [24] | 郭正吾. 四川盆地形成与演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996:15-89. |
| [25] | 刘昭茜, 罗开平, 唐永, 等. 四川盆地元坝—通南巴地区关键构造期构造特征及陆相致密砂岩天然气成藏响应[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3):756-772. |
| [26] | 汪泽成, 赵文智, 徐安娜, 等. 四川盆地北部大巴山山前带构造样式与变形机制[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(3):429-435. |
| [27] | 于冬冬, 汤良杰, 余一欣, 等. 川西和川东北地区差异构造演化及其对陆相层系天然气成藏的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5):1085-1095. |
| [28] | 郑荣才, 何龙, 梁西文, 等. 川东地区下侏罗统大安寨段页岩气(油)成藏条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2013, 33(12):30-40. |
| [29] | COSGROVE J W. Hydraulic fracturing during the formation and deformation of a basin: A factor in the dewatering of low-permeability sediments[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2001, 85(4):737-748. |
| [30] | 骆杨, 赵彦超, 陈红汉, 等. 构造应力-流体压力耦合作用下的裂缝发育特征——以渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷柳屯洼陷裂缝性泥页岩“油藏”为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(2):177-185. |
| [31] | 袁玉松, 周雁, 邱登峰, 等. 泥页岩非构造裂缝形成机制及特征[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(1):155-162. |
| [32] |
王淼, 陈勇, 徐兴友, 等. 泥质岩中纤维状结构脉体成因机制及其与油气活动关系研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(10):1107-1118.
DOI |
| [33] | 黄伟林, 冯明友, 刘小洪, 等. 渝东石柱地区龙马溪组页岩纤维状脉体成因[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3):160-169. |
| [34] | 邹华耀, 郝芳, 李平平, 等. 四川元坝地区须家河组沥青发育分布特征及其烃源岩排烃通道标志[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2018, 40(1):1-10. |
| [35] | LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098. |
| [36] | 张金川, 刘树根, 魏晓亮, 等. 页岩含气量评价方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(1):28-40. |
| [37] | BOWKER K A. Barnett shale gas production, Fort Worth Basin: Issues and discussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):523-533. |
| [38] | ENGELDER T, LASH G G, UZCÁTEGUI R S. Joint sets that enhance production from Middle and Upper Devonian gas shales of the Appalachian Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(7):857-889. |
| [39] |
黄东, 段勇, 李育聪, 等. 淡水湖相页岩油气有机碳含量下限研究——以四川盆地侏罗系大安寨段为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(6):38-45.
DOI |
| [40] | 何志勇, 刘海涛, 肖伟, 等. 四川盆地元坝地区下侏罗统介壳灰岩储层分布预测[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(1):142-149. |
| [41] | 柳广弟. 石油地质学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009:184-185. |
| [1] | 邓毅, 高崇龙, 王剑, 刘明, 孟元林, 任影, 刘可, 王柯. 准噶尔盆地南缘西段齐古组深层储层特征及物性控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 335-349. |
| [2] | 王爱, 肖开华, 刘忠群, 黄彦庆, 乔大伟. 川东北元坝西部须二段—须三段沉积相及其对储层控制作用[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 350-361. |
| [3] | 王爱, 钟大康, 刘忠群, 王威, 杜红权, 周志恒, 唐自成. 川东北元坝西地区须三段钙屑致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1193-1204. |
| [4] | 何志勇, 刘海涛, 肖伟, 杜红权. 四川盆地元坝地区下侏罗统介壳灰岩储层分布预测[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 142-149. |
| [5] | 于冬冬 , 汤良杰 , 余一欣 , 陈茜. 川西和川东北地区差异构造演化及其对陆相层系天然气成藏的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1085-1095. |
| [6] | 黄仁春. 川东北元坝地区雷口坡组天然气来源与成藏分析[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 412-418. |
| [7] | 李锟,于炳松,王黎栋,潘莹露. 塔里木盆地东南地区侏罗系低孔渗砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 388-395. |
| [8] | 郭继刚,李建华,庞雄奇,向才富,姜福杰,王鹏威. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系烃源岩排烃效率研究[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1081-1088. |
| [9] | 龙华山,王绪龙,向才富,雷德文,郭继刚,阿布力米提,郑金海,王力宏,庞雄奇. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系烃源岩评价[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1070-1080. |
| [10] | 冯冲,郭彤楼,邹华耀,成晓啭. 川东北地区飞仙关组—长兴组天然气富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 907-914. |
| [11] | 唐洪,吴斌,张婷,曹刚,罗韧. 川东北铁山-龙会地区长兴组礁滩相储层特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 644-652. |
| [12] | 周新平, 徐怀民, 王仁冲, 刘桠颖, 苏芮. 准噶尔盆地侏罗系不整合复合体及其岩性地层油气藏[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(3): 581-588. |
| [13] | 胡望水, 曾涛, 周亚丽, 姚乾坤, 汤济广. 含滑脱层剖面的分层平衡恢复技术在川东北构造演化研究中的运用[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(5): 896-901. |
| [14] | 赵彦德, 刘显阳, 张雪峰, 张忠义, 李程善, 齐亚林. 鄂尔多斯盆地天环坳陷南段侏罗系原油油源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(1): 85-93. |
| [15] | 赵文光, 郭彤楼, 蔡忠贤, 黄仁春, 杨博, 段金宝. 川东北地区二叠系长兴组生物礁类型及控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(5): 951-956. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||