



现代地质 ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (02): 233-243.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.02.02
杨培奇1,2( ), 刘敬党1, 张艳飞4, 梁帅3, 刘淑梅4
), 刘敬党1, 张艳飞4, 梁帅3, 刘淑梅4
收稿日期:2019-07-04
修回日期:2020-02-26
出版日期:2020-05-25
发布日期:2020-05-25
作者简介:杨培奇,男,1982年出生,高级工程师,地质工程专业,从事矿床学、地球化学方面研究。Email: yangpeiqi19821013@163.com。
基金资助:
YANG Peiqi1,2( ), LIU Jingdang1, ZHANG Yangfei4, LIANG Shuai3, LIU Shumei4
), LIU Jingdang1, ZHANG Yangfei4, LIANG Shuai3, LIU Shumei4
Received:2019-07-04
Revised:2020-02-26
Online:2020-05-25
Published:2020-05-25
摘要:
辽宁北镇杜屯石墨矿矿体赋存于中元古界高于庄组,通过对矿区含矿岩石地球化学特征及碎屑锆石的SHRIMP U-Pb年代学开展系统研究,探讨了石墨矿床的形成时代及构造环境。地球化学特征表明,含矿岩石稀土元素含量较高,并富集Rb、Ba、K、Sr等大离子亲石元素;反映出原岩(沉积物质)主要来源于陆源碎屑物质,并有少量海源物质混入,为缺氧沉积环境。锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年结果显示:碎屑锆石表面平均年龄为(2535.64±25.59) Ma,代表含矿层原岩沉积上限晚于早元古代早期;重结晶锆石表面年龄为(1216.75±12.33)~(1675.70±17.46) Ma,代表含矿层的沉积下限不晚于中元古代晚期;自生锆石表面平均年龄为(212.53±3.69) Ma,显示晚三叠世岩浆-构造热事件对晶质石墨的重结晶、富集成矿起到重要的控矿作用。因此杜屯石墨矿床成因归结为中元古代浅海环境沉积富含有机质的黑色岩系,在后期变质作用和晚三叠世岩浆活动影响下,黑色岩系碳质重结晶形成浅变质石墨矿床。
中图分类号:
杨培奇, 刘敬党, 张艳飞, 梁帅, 刘淑梅. 辽宁北镇石墨矿含矿岩石地球化学及SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(02): 233-243.
YANG Peiqi, LIU Jingdang, ZHANG Yangfei, LIANG Shuai, LIU Shumei. Geochemisty and SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Chronology of Ore-bearing Rocks from Graphite Deposit in Beizhen County, Liaoning Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(02): 233-243.
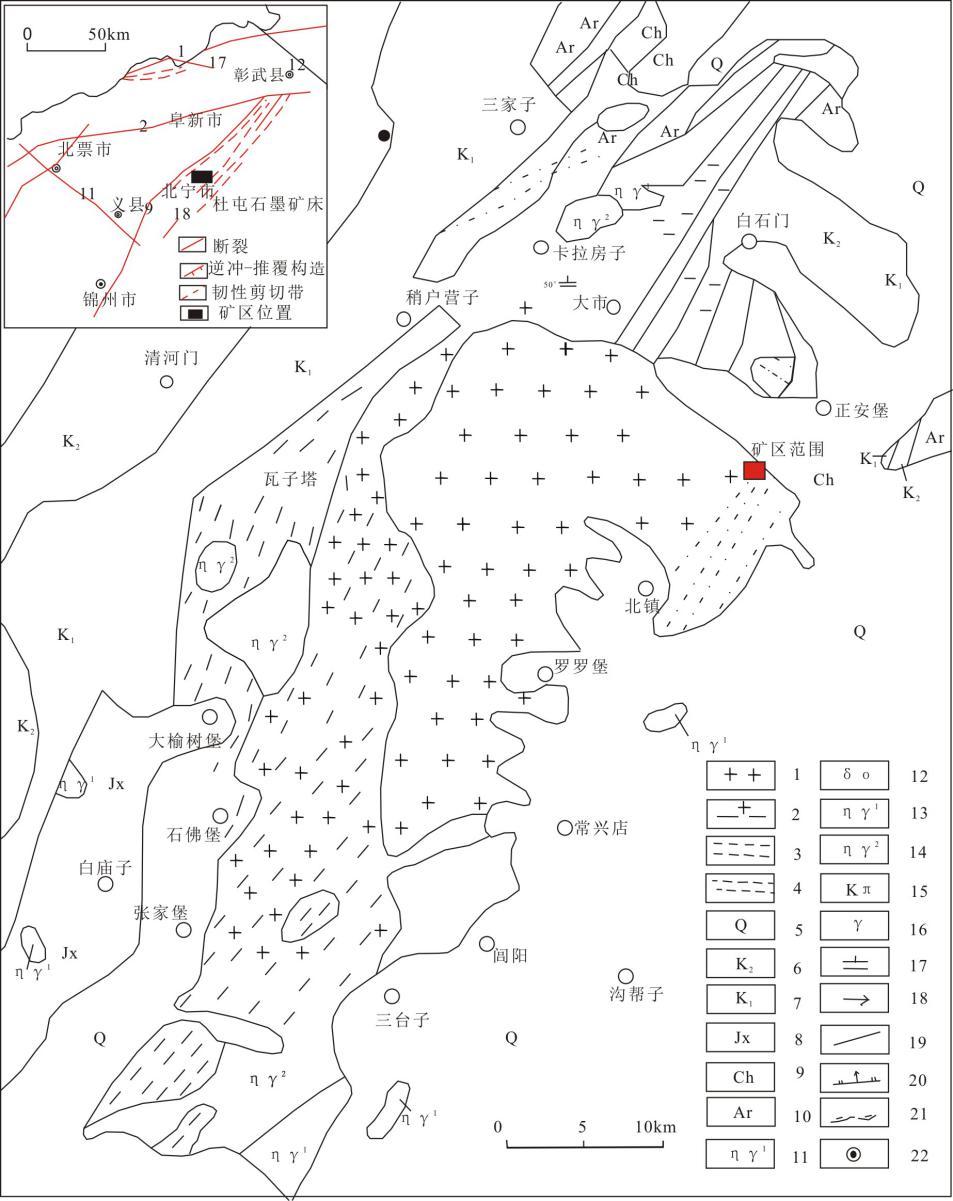
图1 区域构造图及区域地质图(据文献[14,15,16]) 1.第四系;2.上白垩统;3.下白垩统;4.蓟县系;5.长城系;6.太古宇;7.燕山早期二长花岗岩;8.正长斑岩;9.燕山晚期花岗岩;10.燕山晚期二长花岗岩;11.医巫闾山花岗岩体;12.华里西晚期二长花岗岩;13.石英闪长岩;14.中新元古界岩石糜棱岩带; 15.太古宇岩石糜棱岩带;16.花岗岩与糜棱岩互层带;17.糜棱岩片理产状;18.糜棱岩线理产状;19.断层;20.正断层;21.拆离断层;22.矿区位置。
Fig. 1 Map showing regional tectonics and regional geology of the study area (after reference [14-16])

图2 矿区石墨绢云绿泥石英片岩野外和显微照片 a.厚层石墨绢云绿泥石英片岩剖面上针状红柱石定向排列;b.石墨片岩层面上针状红柱石呈交织状分布;c.石墨片岩中针状红柱石,显微照片,单偏光;d.石墨片岩中针状红柱石,一级灰干涉色,显微照片,正交偏光;e.石墨片岩中微晶石墨沿片理定向分布,显微照片,反射光;f.石墨与绢云母聚合成相间条带定向排列,石英聚合形成眼球构造,显微照片,正交偏光; Ad. 红柱石;Gph. 石墨;Ser. 绢云母;Mu.白云母;Qz.石英。
Fig. 2 Field photos and photomicrographs of the graphite-sericite-chlorite-quartz schist in the Dutun mining area
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 主要矿物 | 结构构造 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BZ-01 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | 鳞片变晶结构,片状构造 |
| BZ-02 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-05 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-11 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-13 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-16 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-21 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-24 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-18 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-19 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-20 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-23 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-22 | 大理岩 | 方解石、白云石、蛇纹石,少量绢云母、石英 | 粒状变晶结构,块状构造 |
表1 含矿岩石样品的岩相学特征
Table1 Petrographical characteristics of ore-bearing rocks in the Dutun deposit
| 样品号 | 岩性 | 主要矿物 | 结构构造 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BZ-01 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | 鳞片变晶结构,片状构造 |
| BZ-02 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-05 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-11 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-13 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-16 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-21 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-24 | 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、红柱石 | |
| BZ-18 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-19 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-20 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-23 | 绢云绿泥石英片岩 | 石英、斜长石、石墨、绢云母、绿泥石、透闪石、少量红柱石 | |
| BZ-22 | 大理岩 | 方解石、白云石、蛇纹石,少量绢云母、石英 | 粒状变晶结构,块状构造 |
| 岩石 名称 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 有机碳 | Na2O+ K2O | K2O/ Na2O | MgO/ CaO | A/CNK | A/NK | Rb | Sr | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红柱石绢 云绿泥石 英片岩 | BZ-01 | 53.49 | 0.55 | 16.21 | 0.74 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 1.20 | 0.55 | 3.83 | 0.05 | 20.44 | 15.05 | 4.39 | 6.93 | 0.81 | 2.24 | 3.20 | 114 | 183 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-02 | 69.80 | 0.42 | 15.28 | 1.17 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 3.86 | 0.02 | 6.87 | 4.38 | 4.81 | 4.04 | 1.77 | 2.43 | 2.65 | 94 | 105 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-05 | 62.21 | 0.52 | 19.49 | 1.01 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.21 | 0.66 | 5.29 | 0.02 | 9.31 | 6.14 | 5.94 | 8.01 | 2.52 | 2.71 | 2.86 | 128 | 88 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-11 | 68.33 | 0.65 | 16.23 | 2.20 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 1.01 | 3.45 | 0.03 | 6.27 | 3.23 | 4.46 | 3.40 | 1.91 | 2.69 | 3.00 | 76 | 141 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-13 | 62.23 | 0.66 | 21.78 | 1.29 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 6.74 | 0.01 | 5.50 | 2.35 | 6.94 | 33.80 | 6.55 | 2.78 | 2.85 | 128 | 42 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-16 | 67.88 | 0.54 | 17.81 | 0.51 | 0.91 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.95 | 4.64 | 0.02 | 5.62 | 3.12 | 5.59 | 4.86 | 1.28 | 2.46 | 2.70 | 82 | 82 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-21 | 55.70 | 0.78 | 16.95 | 1.87 | 5.25 | 0.13 | 4.28 | 4.24 | 3.60 | 2.53 | 0.29 | 4.20 | 0.64 | 6.13 | 0.70 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.95 | 132 | 394 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-24 | 62.14 | 0.77 | 20.30 | 0.61 | 3.34 | 0.05 | 1.38 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 5.36 | 0.21 | 4.31 | 1.82 | 6.16 | 6.75 | 2.57 | 2.51 | 2.85 | 109 | 106 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 62.72 | 0.61 | 18.01 | 1.18 | 1.66 | 0.05 | 1.19 | 0.91 | 1.09 | 4.46 | 0.08 | 7.81 | 4.59 | 5.55 | 8.56 | 2.30 | 2.35 | 2.76 | 107.71 | 142.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 69.80 | 0.78 | 21.78 | 2.20 | 5.25 | 0.13 | 4.28 | 4.24 | 3.60 | 6.74 | 0.29 | 20.44 | 15.05 | 6.94 | 33.80 | 6.55 | 2.78 | 3.20 | 131.50 | 393.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 53.49 | 0.42 | 15.28 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 2.53 | 0.01 | 4.20 | 0.64 | 4.39 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 1.03 | 1.95 | 76.30 | 41.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 绢云绿泥 石英片岩 | BZ-18 | 75.16 | 0.03 | 14.28 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 4.78 | 3.76 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 8.53 | 0.79 | 0.18 | 1.14 | 1.20 | 197 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-19 | 73.71 | 0.29 | 14.09 | 1.55 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.96 | 4.91 | 2.70 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 7.61 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 68 | 276 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-20 | 73.53 | 0.07 | 14.28 | 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 1.04 | 4.42 | 4.02 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 0.21 | 8.44 | 0.91 | 0.15 | 1.06 | 1.23 | 147 | 126 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-23 | 67.15 | 0.39 | 11.73 | 0.11 | 2.91 | 0.42 | 3.32 | 4.79 | 0.21 | 6.33 | 0.14 | 2.36 | 1.16 | 6.54 | 30.19 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 1.63 | 132 | 242 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 72.39 | 0.20 | 13.59 | 0.58 | 1.10 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 1.78 | 3.58 | 4.20 | 0.10 | 1.11 | 0.42 | 7.78 | 8.11 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 1.33 | 135.90 | 165.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 75.16 | 0.39 | 14.28 | 1.55 | 2.91 | 0.42 | 3.32 | 4.79 | 4.91 | 6.33 | 0.14 | 2.36 | 1.16 | 8.53 | 30.19 | 0.69 | 1.14 | 1.63 | 196.80 | 275.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 67.15 | 0.03 | 11.73 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 2.70 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 6.54 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.74 | 1.20 | 67.60 | 17.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 大理岩 | BZ-22 | 9.18 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 9.39 | 42.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 38.22 | 9.60 | 0.06 | 2.00 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 4.19 | 2 | 217 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石名称 | 样号 | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | Cr | Ni | Co | V | F | Cl | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | V/Cr | V/(Ni+V) | Zr/Y | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 红柱石绢 云绿泥石 英片岩 | BZ-01 | 1 005 | 166 | 3.91 | 6.91 | 3.08 | 32.05 | 6.80 | 0.36 | 72.20 | 16.21 | 6.91 | 112.90 | 475 | 61 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 2.24 | 1.56 | 0.87 | 5.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-02 | 765 | 121 | 3.26 | 6.06 | 0.81 | 13.44 | 11.09 | 0.77 | 25.40 | 7.62 | 2.74 | 59.50 | 237 | 27 | 0.89 | 0.14 | 7.48 | 2.34 | 0.89 | 8.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-05 | 1 112 | 169 | 4.78 | 7.05 | 0.98 | 17.22 | 12.97 | 0.87 | 36.90 | 9.03 | 3.24 | 89.70 | 342 | 34 | 1.45 | 0.08 | 7.20 | 2.43 | 0.91 | 9.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-11 | 897 | 174 | 4.87 | 5.83 | 1.04 | 16.58 | 12.74 | 0.81 | 55.50 | 20.38 | 6.44 | 72.30 | 279 | 38 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 5.61 | 1.30 | 0.78 | 10.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-13 | 1 530 | 141 | 4.08 | 5.90 | 0.87 | 9.76 | 15.63 | 1.13 | 39.20 | 6.35 | 2.08 | 97.50 | 387 | 33 | 3.05 | 0.03 | 6.79 | 2.49 | 0.94 | 14.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-16 | 1 295 | 123 | 3.76 | 6.25 | 0.83 | 15.75 | 14.33 | 0.97 | 35.60 | 10.63 | 5.12 | 68.10 | 303 | 59 | 1.00 | 0.06 | 7.54 | 1.91 | 0.86 | 7.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-21 | 500 | 59 | 2.02 | 3.21 | 1.53 | 14.27 | 12.08 | 1.27 | 126.50 | 42.14 | 22.19 | 195.60 | 1 264 | 32 | 0.33 | 0.79 | 2.09 | 1.55 | 0.82 | 4.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-24 | 1 083 | 164 | 4.76 | 7.93 | 1.48 | 19.62 | 16.93 | 1.16 | 55.70 | 18.36 | 13.32 | 114.90 | 475 | 104 | 1.03 | 0.10 | 5.37 | 2.06 | 0.86 | 8.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 1 023.29 | 139.46 | 3.93 | 6.14 | 1.33 | 17.34 | 12.82 | 0.92 | 55.88 | 16.34 | 7.76 | 101.31 | 470.22 | 48.30 | 1.11 | 0.19 | 5.54 | 1.96 | 0.87 | 8.64 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 1 530.10 | 173.70 | 4.87 | 7.93 | 3.08 | 32.05 | 16.93 | 1.27 | 126.50 | 42.14 | 22.19 | 195.60 | 1 263.59 | 104.00 | 3.05 | 0.79 | 7.54 | 2.49 | 0.94 | 14.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 499.70 | 58.70 | 2.02 | 3.21 | 0.81 | 9.76 | 6.80 | 0.36 | 25.40 | 6.35 | 2.08 | 59.50 | 237.20 | 26.80 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 2.09 | 1.30 | 0.78 | 4.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石名称 | 样号 | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | Cr | Ni | Co | V | F | Cl | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | V/Cr | V/(Ni+V) | Zr/Y | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 绢云绿泥 石英片岩 | BZ-18 | 54 | 27 | 1.95 | 0.48 | 2.12 | 10.89 | 48.07 | 5.68 | 5.90 | 2.56 | 0.81 | 7.50 | 515 | 35 | 11.25 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 1.27 | 0.75 | 2.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-19 | 1 024 | 108 | 3.09 | 15.96 | 2.27 | 35.20 | 6.28 | 0.53 | 14.20 | 15.08 | 13.50 | 35.20 | 372 | 29 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 7.03 | 2.48 | 0.70 | 3.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-20 | 243 | 30 | 1.69 | 1.23 | 1.58 | 11.09 | 32.17 | 3.07 | 5.70 | 2.69 | 0.97 | 8.50 | 387 | 38 | 1.17 | 0.52 | 0.78 | 1.49 | 0.76 | 2.68 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-23 | 1 227 | 166 | 5.68 | 14.59 | 4.13 | 14.14 | 12.57 | 1.13 | 43.90 | 18.61 | 9.58 | 51.00 | 989 | 41 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 3.53 | 1.16 | 0.73 | 11.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 637.05 | 82.70 | 3.10 | 8.06 | 2.52 | 17.83 | 24.77 | 2.60 | 17.43 | 9.73 | 6.21 | 25.55 | 565.69 | 35.63 | 3.30 | 0.33 | 2.89 | 1.60 | 0.73 | 4.99 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 1 226.60 | 166.20 | 5.68 | 15.96 | 4.13 | 35.20 | 48.07 | 5.68 | 43.90 | 18.61 | 13.50 | 51.00 | 989.21 | 40.60 | 11.25 | 0.52 | 7.03 | 2.48 | 0.76 | 11.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 54.40 | 26.50 | 1.69 | 0.48 | 1.58 | 10.89 | 6.28 | 0.53 | 5.70 | 2.56 | 0.81 | 7.50 | 371.56 | 28.60 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 1.16 | 0.70 | 2.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 大理岩 | BZ-22 | 19 | 3 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 2.25 | 1.32 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 7.32 | 1.19 | 5.50 | 316 | 30 | 0.01 | 11.35 | 1.89 | 275.00 | 0.43 | 1.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石名称 | 样号 | Nb/Ta | F/Cl | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE/ HREE | δCe | δEu | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 红柱石绢 云绿泥石 英片岩 | BZ-01 | 18.69 | 7.84 | 47.80 | 102.71 | 12.02 | 46.33 | 8.24 | 1.85 | 6.92 | 1.03 | 5.73 | 1.11 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 3.30 | 0.52 | 241.21 | 9.83 | 1.03 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-02 | 14.40 | 8.85 | 20.83 | 38.28 | 6.55 | 23.88 | 4.25 | 0.97 | 2.97 | 0.47 | 2.58 | 0.50 | 1.45 | 0.23 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 104.82 | 9.43 | 0.79 | 0.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-05 | 14.87 | 10.19 | 26.40 | 65.60 | 8.28 | 30.76 | 5.59 | 1.15 | 4.11 | 0.62 | 3.34 | 0.63 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 2.08 | 0.35 | 151.05 | 10.38 | 1.07 | 0.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-11 | 15.68 | 7.29 | 23.56 | 51.62 | 6.52 | 23.68 | 4.15 | 0.96 | 3.29 | 0.50 | 2.89 | 0.57 | 1.69 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.28 | 121.81 | 9.76 | 1.00 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-13 | 13.85 | 11.87 | 8.39 | 13.75 | 2.64 | 9.88 | 1.78 | 0.39 | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.69 | 0.36 | 1.11 | 0.20 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 43.58 | 5.47 | 0.70 | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-16 | 14.82 | 5.15 | 22.40 | 37.70 | 6.82 | 25.58 | 4.67 | 1.05 | 3.47 | 0.56 | 3.11 | 0.60 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 1.74 | 0.28 | 109.88 | 8.41 | 0.73 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-21 | 9.54 | 39.74 | 12.74 | 33.71 | 4.37 | 17.91 | 3.68 | 0.85 | 2.89 | 0.47 | 2.72 | 0.51 | 1.53 | 0.25 | 1.71 | 0.27 | 83.61 | 7.08 | 1.09 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-24 | 14.54 | 4.56 | 34.78 | 86.15 | 9.06 | 32.47 | 5.50 | 1.21 | 4.30 | 0.65 | 3.62 | 0.70 | 2.10 | 0.33 | 2.17 | 0.34 | 183.37 | 11.92 | 1.17 | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 14.55 | 11.94 | 24.61 | 53.69 | 7.03 | 26.31 | 4.73 | 1.06 | 3.67 | 0.57 | 3.21 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 0.29 | 1.99 | 0.32 | 129.92 | 9.03 | 0.95 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 18.69 | 39.74 | 47.80 | 102.71 | 12.02 | 46.33 | 8.24 | 1.85 | 6.92 | 1.03 | 5.73 | 1.11 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 3.30 | 0.52 | 241.21 | 11.92 | 1.17 | 0.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 9.54 | 4.56 | 8.39 | 13.75 | 2.64 | 9.88 | 1.78 | 0.39 | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.69 | 0.36 | 1.11 | 0.20 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 43.58 | 5.47 | 0.70 | 0.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 绢云绿泥 石英片岩 | BZ-18 | 8.46 | 14.59 | 3.29 | 7.08 | 0.88 | 3.17 | 0.96 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.32 | 1.02 | 0.17 | 1.25 | 0.19 | 21.41 | 2.60 | 1.00 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-19 | 11.95 | 12.99 | 87.00 | 173.60 | 19.66 | 70.63 | 11.77 | 1.60 | 9.50 | 1.30 | 6.75 | 1.23 | 3.46 | 0.48 | 3.08 | 0.47 | 390.54 | 13.86 | 1.01 | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-20 | 10.48 | 10.19 | 9.78 | 18.32 | 2.07 | 7.12 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.36 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.32 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 45.08 | 6.42 | 0.98 | 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-23 | 11.14 | 24.36 | 28.45 | 62.64 | 6.99 | 25.33 | 4.24 | 0.87 | 3.44 | 0.50 | 2.62 | 0.49 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.52 | 0.25 | 139.04 | 12.21 | 1.07 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 10.51 | 15.53 | 32.13 | 65.41 | 7.40 | 26.56 | 4.61 | 0.69 | 3.82 | 0.58 | 3.22 | 0.59 | 1.72 | 0.26 | 1.74 | 0.27 | 149.02 | 8.77 | 1.01 | 0.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 11.95 | 24.36 | 87.00 | 173.60 | 19.66 | 70.63 | 11.77 | 1.60 | 9.50 | 1.30 | 6.75 | 1.23 | 3.46 | 0.48 | 3.08 | 0.47 | 390.54 | 13.86 | 1.07 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 8.46 | 10.19 | 3.29 | 7.08 | 0.88 | 3.17 | 0.96 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.32 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 21.41 | 2.60 | 0.98 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 大理岩 | BZ-22 | 42.62 | 10.38 | 2.62 | 4.77 | 0.55 | 1.96 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 11.42 | 9.44 | 0.96 | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||
表2 含矿岩石主量元素(%)和微量元素(10-6)组成
Table 2 Compositions of major elements (%) and trace elements (10-6) of the ore-bearing rocks
| 岩石 名称 | 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 有机碳 | Na2O+ K2O | K2O/ Na2O | MgO/ CaO | A/CNK | A/NK | Rb | Sr | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红柱石绢 云绿泥石 英片岩 | BZ-01 | 53.49 | 0.55 | 16.21 | 0.74 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 1.20 | 0.55 | 3.83 | 0.05 | 20.44 | 15.05 | 4.39 | 6.93 | 0.81 | 2.24 | 3.20 | 114 | 183 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-02 | 69.80 | 0.42 | 15.28 | 1.17 | 0.55 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 3.86 | 0.02 | 6.87 | 4.38 | 4.81 | 4.04 | 1.77 | 2.43 | 2.65 | 94 | 105 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-05 | 62.21 | 0.52 | 19.49 | 1.01 | 0.51 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.21 | 0.66 | 5.29 | 0.02 | 9.31 | 6.14 | 5.94 | 8.01 | 2.52 | 2.71 | 2.86 | 128 | 88 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-11 | 68.33 | 0.65 | 16.23 | 2.20 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 1.01 | 3.45 | 0.03 | 6.27 | 3.23 | 4.46 | 3.40 | 1.91 | 2.69 | 3.00 | 76 | 141 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-13 | 62.23 | 0.66 | 21.78 | 1.29 | 0.48 | 0.03 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 6.74 | 0.01 | 5.50 | 2.35 | 6.94 | 33.80 | 6.55 | 2.78 | 2.85 | 128 | 42 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-16 | 67.88 | 0.54 | 17.81 | 0.51 | 0.91 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.36 | 0.95 | 4.64 | 0.02 | 5.62 | 3.12 | 5.59 | 4.86 | 1.28 | 2.46 | 2.70 | 82 | 82 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-21 | 55.70 | 0.78 | 16.95 | 1.87 | 5.25 | 0.13 | 4.28 | 4.24 | 3.60 | 2.53 | 0.29 | 4.20 | 0.64 | 6.13 | 0.70 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 1.95 | 132 | 394 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-24 | 62.14 | 0.77 | 20.30 | 0.61 | 3.34 | 0.05 | 1.38 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 5.36 | 0.21 | 4.31 | 1.82 | 6.16 | 6.75 | 2.57 | 2.51 | 2.85 | 109 | 106 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 62.72 | 0.61 | 18.01 | 1.18 | 1.66 | 0.05 | 1.19 | 0.91 | 1.09 | 4.46 | 0.08 | 7.81 | 4.59 | 5.55 | 8.56 | 2.30 | 2.35 | 2.76 | 107.71 | 142.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 69.80 | 0.78 | 21.78 | 2.20 | 5.25 | 0.13 | 4.28 | 4.24 | 3.60 | 6.74 | 0.29 | 20.44 | 15.05 | 6.94 | 33.80 | 6.55 | 2.78 | 3.20 | 131.50 | 393.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 53.49 | 0.42 | 15.28 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 2.53 | 0.01 | 4.20 | 0.64 | 4.39 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 1.03 | 1.95 | 76.30 | 41.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 绢云绿泥 石英片岩 | BZ-18 | 75.16 | 0.03 | 14.28 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 4.78 | 3.76 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 8.53 | 0.79 | 0.18 | 1.14 | 1.20 | 197 | 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-19 | 73.71 | 0.29 | 14.09 | 1.55 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.96 | 4.91 | 2.70 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 7.61 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 68 | 276 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-20 | 73.53 | 0.07 | 14.28 | 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 1.04 | 4.42 | 4.02 | 0.07 | 0.99 | 0.21 | 8.44 | 0.91 | 0.15 | 1.06 | 1.23 | 147 | 126 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-23 | 67.15 | 0.39 | 11.73 | 0.11 | 2.91 | 0.42 | 3.32 | 4.79 | 0.21 | 6.33 | 0.14 | 2.36 | 1.16 | 6.54 | 30.19 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 1.63 | 132 | 242 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 72.39 | 0.20 | 13.59 | 0.58 | 1.10 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 1.78 | 3.58 | 4.20 | 0.10 | 1.11 | 0.42 | 7.78 | 8.11 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 1.33 | 135.90 | 165.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 75.16 | 0.39 | 14.28 | 1.55 | 2.91 | 0.42 | 3.32 | 4.79 | 4.91 | 6.33 | 0.14 | 2.36 | 1.16 | 8.53 | 30.19 | 0.69 | 1.14 | 1.63 | 196.80 | 275.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 67.15 | 0.03 | 11.73 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.33 | 0.21 | 2.70 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 6.54 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.74 | 1.20 | 67.60 | 17.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 大理岩 | BZ-22 | 9.18 | 0.01 | 0.32 | 0.11 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 9.39 | 42.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 38.22 | 9.60 | 0.06 | 2.00 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 4.19 | 2 | 217 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石名称 | 样号 | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | Cr | Ni | Co | V | F | Cl | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | V/Cr | V/(Ni+V) | Zr/Y | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 红柱石绢 云绿泥石 英片岩 | BZ-01 | 1 005 | 166 | 3.91 | 6.91 | 3.08 | 32.05 | 6.80 | 0.36 | 72.20 | 16.21 | 6.91 | 112.90 | 475 | 61 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 2.24 | 1.56 | 0.87 | 5.18 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-02 | 765 | 121 | 3.26 | 6.06 | 0.81 | 13.44 | 11.09 | 0.77 | 25.40 | 7.62 | 2.74 | 59.50 | 237 | 27 | 0.89 | 0.14 | 7.48 | 2.34 | 0.89 | 8.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-05 | 1 112 | 169 | 4.78 | 7.05 | 0.98 | 17.22 | 12.97 | 0.87 | 36.90 | 9.03 | 3.24 | 89.70 | 342 | 34 | 1.45 | 0.08 | 7.20 | 2.43 | 0.91 | 9.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-11 | 897 | 174 | 4.87 | 5.83 | 1.04 | 16.58 | 12.74 | 0.81 | 55.50 | 20.38 | 6.44 | 72.30 | 279 | 38 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 5.61 | 1.30 | 0.78 | 10.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-13 | 1 530 | 141 | 4.08 | 5.90 | 0.87 | 9.76 | 15.63 | 1.13 | 39.20 | 6.35 | 2.08 | 97.50 | 387 | 33 | 3.05 | 0.03 | 6.79 | 2.49 | 0.94 | 14.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-16 | 1 295 | 123 | 3.76 | 6.25 | 0.83 | 15.75 | 14.33 | 0.97 | 35.60 | 10.63 | 5.12 | 68.10 | 303 | 59 | 1.00 | 0.06 | 7.54 | 1.91 | 0.86 | 7.82 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-21 | 500 | 59 | 2.02 | 3.21 | 1.53 | 14.27 | 12.08 | 1.27 | 126.50 | 42.14 | 22.19 | 195.60 | 1 264 | 32 | 0.33 | 0.79 | 2.09 | 1.55 | 0.82 | 4.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-24 | 1 083 | 164 | 4.76 | 7.93 | 1.48 | 19.62 | 16.93 | 1.16 | 55.70 | 18.36 | 13.32 | 114.90 | 475 | 104 | 1.03 | 0.10 | 5.37 | 2.06 | 0.86 | 8.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 1 023.29 | 139.46 | 3.93 | 6.14 | 1.33 | 17.34 | 12.82 | 0.92 | 55.88 | 16.34 | 7.76 | 101.31 | 470.22 | 48.30 | 1.11 | 0.19 | 5.54 | 1.96 | 0.87 | 8.64 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 1 530.10 | 173.70 | 4.87 | 7.93 | 3.08 | 32.05 | 16.93 | 1.27 | 126.50 | 42.14 | 22.19 | 195.60 | 1 263.59 | 104.00 | 3.05 | 0.79 | 7.54 | 2.49 | 0.94 | 14.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 499.70 | 58.70 | 2.02 | 3.21 | 0.81 | 9.76 | 6.80 | 0.36 | 25.40 | 6.35 | 2.08 | 59.50 | 237.20 | 26.80 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 2.09 | 1.30 | 0.78 | 4.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石名称 | 样号 | Ba | Zr | Hf | Th | U | Y | Nb | Ta | Cr | Ni | Co | V | F | Cl | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba | Th/U | V/Cr | V/(Ni+V) | Zr/Y | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 绢云绿泥 石英片岩 | BZ-18 | 54 | 27 | 1.95 | 0.48 | 2.12 | 10.89 | 48.07 | 5.68 | 5.90 | 2.56 | 0.81 | 7.50 | 515 | 35 | 11.25 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 1.27 | 0.75 | 2.43 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-19 | 1 024 | 108 | 3.09 | 15.96 | 2.27 | 35.20 | 6.28 | 0.53 | 14.20 | 15.08 | 13.50 | 35.20 | 372 | 29 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 7.03 | 2.48 | 0.70 | 3.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-20 | 243 | 30 | 1.69 | 1.23 | 1.58 | 11.09 | 32.17 | 3.07 | 5.70 | 2.69 | 0.97 | 8.50 | 387 | 38 | 1.17 | 0.52 | 0.78 | 1.49 | 0.76 | 2.68 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-23 | 1 227 | 166 | 5.68 | 14.59 | 4.13 | 14.14 | 12.57 | 1.13 | 43.90 | 18.61 | 9.58 | 51.00 | 989 | 41 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 3.53 | 1.16 | 0.73 | 11.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 637.05 | 82.70 | 3.10 | 8.06 | 2.52 | 17.83 | 24.77 | 2.60 | 17.43 | 9.73 | 6.21 | 25.55 | 565.69 | 35.63 | 3.30 | 0.33 | 2.89 | 1.60 | 0.73 | 4.99 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 1 226.60 | 166.20 | 5.68 | 15.96 | 4.13 | 35.20 | 48.07 | 5.68 | 43.90 | 18.61 | 13.50 | 51.00 | 989.21 | 40.60 | 11.25 | 0.52 | 7.03 | 2.48 | 0.76 | 11.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 54.40 | 26.50 | 1.69 | 0.48 | 1.58 | 10.89 | 6.28 | 0.53 | 5.70 | 2.56 | 0.81 | 7.50 | 371.56 | 28.60 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 1.16 | 0.70 | 2.43 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 大理岩 | BZ-22 | 19 | 3 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 2.25 | 1.32 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 7.32 | 1.19 | 5.50 | 316 | 30 | 0.01 | 11.35 | 1.89 | 275.00 | 0.43 | 1.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩石名称 | 样号 | Nb/Ta | F/Cl | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | REE | LREE/ HREE | δCe | δEu | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 红柱石绢 云绿泥石 英片岩 | BZ-01 | 18.69 | 7.84 | 47.80 | 102.71 | 12.02 | 46.33 | 8.24 | 1.85 | 6.92 | 1.03 | 5.73 | 1.11 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 3.30 | 0.52 | 241.21 | 9.83 | 1.03 | 0.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-02 | 14.40 | 8.85 | 20.83 | 38.28 | 6.55 | 23.88 | 4.25 | 0.97 | 2.97 | 0.47 | 2.58 | 0.50 | 1.45 | 0.23 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 104.82 | 9.43 | 0.79 | 0.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-05 | 14.87 | 10.19 | 26.40 | 65.60 | 8.28 | 30.76 | 5.59 | 1.15 | 4.11 | 0.62 | 3.34 | 0.63 | 1.86 | 0.29 | 2.08 | 0.35 | 151.05 | 10.38 | 1.07 | 0.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-11 | 15.68 | 7.29 | 23.56 | 51.62 | 6.52 | 23.68 | 4.15 | 0.96 | 3.29 | 0.50 | 2.89 | 0.57 | 1.69 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.28 | 121.81 | 9.76 | 1.00 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-13 | 13.85 | 11.87 | 8.39 | 13.75 | 2.64 | 9.88 | 1.78 | 0.39 | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.69 | 0.36 | 1.11 | 0.20 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 43.58 | 5.47 | 0.70 | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-16 | 14.82 | 5.15 | 22.40 | 37.70 | 6.82 | 25.58 | 4.67 | 1.05 | 3.47 | 0.56 | 3.11 | 0.60 | 1.65 | 0.26 | 1.74 | 0.28 | 109.88 | 8.41 | 0.73 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-21 | 9.54 | 39.74 | 12.74 | 33.71 | 4.37 | 17.91 | 3.68 | 0.85 | 2.89 | 0.47 | 2.72 | 0.51 | 1.53 | 0.25 | 1.71 | 0.27 | 83.61 | 7.08 | 1.09 | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-24 | 14.54 | 4.56 | 34.78 | 86.15 | 9.06 | 32.47 | 5.50 | 1.21 | 4.30 | 0.65 | 3.62 | 0.70 | 2.10 | 0.33 | 2.17 | 0.34 | 183.37 | 11.92 | 1.17 | 0.76 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 14.55 | 11.94 | 24.61 | 53.69 | 7.03 | 26.31 | 4.73 | 1.06 | 3.67 | 0.57 | 3.21 | 0.62 | 1.82 | 0.29 | 1.99 | 0.32 | 129.92 | 9.03 | 0.95 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 18.69 | 39.74 | 47.80 | 102.71 | 12.02 | 46.33 | 8.24 | 1.85 | 6.92 | 1.03 | 5.73 | 1.11 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 3.30 | 0.52 | 241.21 | 11.92 | 1.17 | 0.83 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 9.54 | 4.56 | 8.39 | 13.75 | 2.64 | 9.88 | 1.78 | 0.39 | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.69 | 0.36 | 1.11 | 0.20 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 43.58 | 5.47 | 0.70 | 0.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 绢云绿泥 石英片岩 | BZ-18 | 8.46 | 14.59 | 3.29 | 7.08 | 0.88 | 3.17 | 0.96 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.32 | 1.02 | 0.17 | 1.25 | 0.19 | 21.41 | 2.60 | 1.00 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-19 | 11.95 | 12.99 | 87.00 | 173.60 | 19.66 | 70.63 | 11.77 | 1.60 | 9.50 | 1.30 | 6.75 | 1.23 | 3.46 | 0.48 | 3.08 | 0.47 | 390.54 | 13.86 | 1.01 | 0.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-20 | 10.48 | 10.19 | 9.78 | 18.32 | 2.07 | 7.12 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.36 | 0.28 | 1.76 | 0.32 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 45.08 | 6.42 | 0.98 | 0.49 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BZ-23 | 11.14 | 24.36 | 28.45 | 62.64 | 6.99 | 25.33 | 4.24 | 0.87 | 3.44 | 0.50 | 2.62 | 0.49 | 1.49 | 0.23 | 1.52 | 0.25 | 139.04 | 12.21 | 1.07 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 平均 | 10.51 | 15.53 | 32.13 | 65.41 | 7.40 | 26.56 | 4.61 | 0.69 | 3.82 | 0.58 | 3.22 | 0.59 | 1.72 | 0.26 | 1.74 | 0.27 | 149.02 | 8.77 | 1.01 | 0.47 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最高 | 11.95 | 24.36 | 87.00 | 173.60 | 19.66 | 70.63 | 11.77 | 1.60 | 9.50 | 1.30 | 6.75 | 1.23 | 3.46 | 0.48 | 3.08 | 0.47 | 390.54 | 13.86 | 1.07 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 最低 | 8.46 | 10.19 | 3.29 | 7.08 | 0.88 | 3.17 | 0.96 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.25 | 1.76 | 0.32 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 1.13 | 0.17 | 21.41 | 2.60 | 0.98 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 大理岩 | BZ-22 | 42.62 | 10.38 | 2.62 | 4.77 | 0.55 | 1.96 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 11.42 | 9.44 | 0.96 | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||
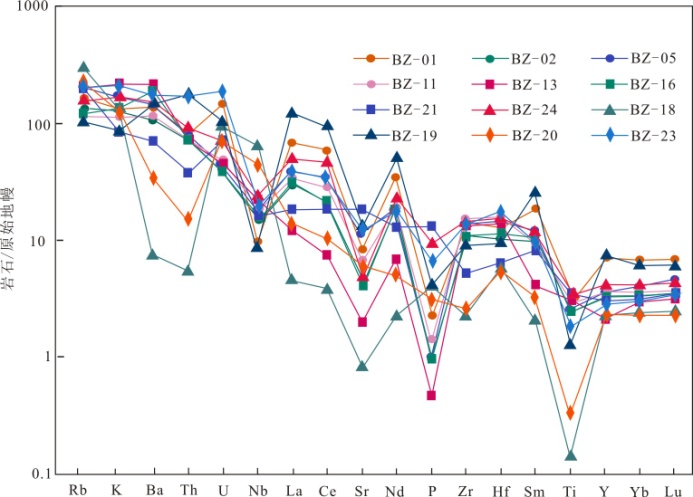
图3 含矿岩石微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(原始地幔据文献[18])
Fig. 3 Primitive mantle normalized trace elements patterns of ore-bearing rocks (primitive mantle values after reference[18])

图4 红柱石绢云绿泥石英片岩稀土元素配分曲线图(球粒陨石据文献[19])
Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of andalusite-sericite chlorite quartz schists (Chondrite values after reference[19])
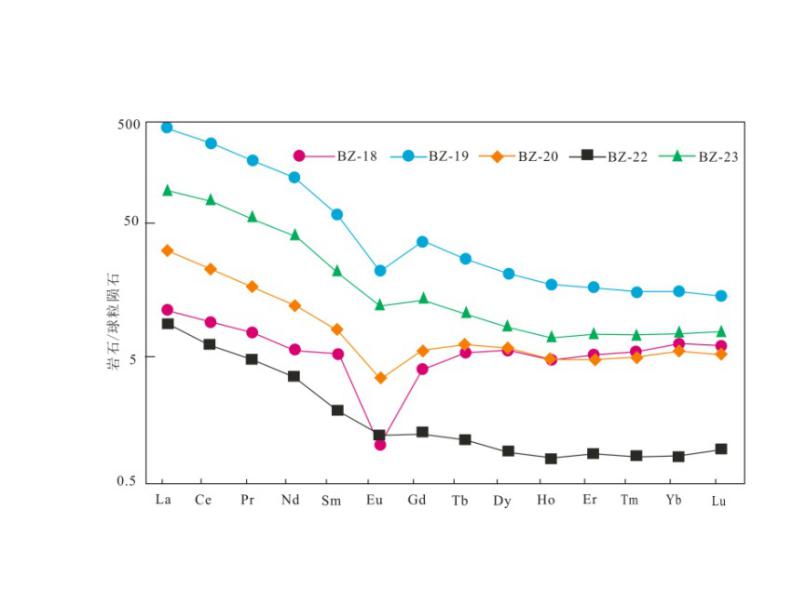
图5 绢云绿泥石英片岩和大理岩稀土元素配分曲线图(球粒陨石据文献[19])
Fig. 5 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of sericite chlorite quartz schist and marble (Chondrite values after reference[19])
| 样品 编号 | 测试值/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 表面年龄(Ma) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | 206Pb* | 232Th/238U | 207Pb*/235U | ±σ/% | 206Pb*/238U | ±σ/% | 207Pb*/206Pb* | ±σ/% | 206Pb/238U | ±σ | 207Pb/206Pb | ±σ | 208Pb/232Th | ±σ | |
| BZ-04-6c | 166.18 | 116.79 | 69.49 | 0.73 | 11.18 | 1.41 | 0.49 | 1.26 | 0.17 | 0.62 | 2553.15 | 26.62 | 2527.03 | 10.40 | 2388.84 | 38.29 |
| BZ-04-10c | 179.57 | 107.67 | 75.56 | 0.62 | 11.18 | 1.40 | 0.49 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 2566.80 | 26.40 | 2514.84 | 10.85 | 2463.48 | 39.53 |
| BZ-04-13c | 272.43 | 260.24 | 112.36 | 0.99 | 11.05 | 1.29 | 0.48 | 1.20 | 0.17 | 0.48 | 2523.03 | 25.07 | 2530.83 | 8.13 | 2513.35 | 35.15 |
| BZ-07-9c | 379.56 | 284.20 | 154.64 | 0.77 | 10.82 | 1.23 | 0.47 | 1.17 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 2499.59 | 24.25 | 2515.11 | 6.31 | 2452.16 | 31.53 |
| 平均 | 249.44 | 192.22 | 103.01 | 0.78 | 11.06 | 1.33 | 0.48 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 2535.64 | 25.59 | 2521.95 | 8.92 | 2454.46 | 36.13 |
| BZ-04-2m | 482.57 | 530.79 | 125.92 | 1.14 | 6.42 | 2.02 | 0.29 | 1.18 | 0.16 | 1.64 | 1675.70 | 17.46 | 2422.64 | 27.75 | 1142.64 | 46.50 |
| BZ-07-4m | 1177.93 | 300.28 | 212.12 | 0.26 | 4.18 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 1.11 | 0.15 | 0.55 | 1216.75 | 12.33 | 2299.23 | 9.38 | 1131.56 | 37.97 |
| BZ-04-1r | 1042.07 | 379.49 | 37.66 | 0.38 | 0.30 | 3.22 | 0.04 | 1.15 | 0.05 | 3.01 | 263.73 | 2.96 | 259.19 | 69.15 | 247.74 | 8.65 |
| BZ-04-3r | 504.15 | 468.92 | 12.85 | 0.96 | 0.21 | 8.57 | 0.03 | 1.36 | 0.05 | 8.46 | 183.61 | 2.46 | 267.46 | 194.00 | 185.76 | 8.59 |
| BZ-04-4r | 307.78 | 178.83 | 13.21 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 3.95 | 0.05 | 1.26 | 0.05 | 3.74 | 312.26 | 3.84 | 244.41 | 86.25 | 302.88 | 10.73 |
| BZ-04-5r | 400.69 | 275.01 | 10.25 | 0.71 | 0.23 | 10.23 | 0.03 | 1.43 | 0.06 | 10.13 | 185.75 | 2.63 | 498.96 | 223.09 | 202.20 | 12.68 |
| BZ-04-7r | 390.02 | 728.62 | 10.57 | 1.93 | 0.23 | 10.39 | 0.03 | 1.45 | 0.05 | 10.29 | 195.67 | 2.80 | 342.49 | 232.85 | 183.90 | 5.57 |
| BZ-04-8r | 149.22 | 135.76 | 3.97 | 0.94 | 0.29 | 3.89 | 0.03 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 3.49 | 195.58 | 3.30 | 912.74 | 71.92 | 202.96 | 6.58 |
| BZ-04-9r | 1258.68 | 672.23 | 46.76 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 2.52 | 0.04 | 1.13 | 0.05 | 2.25 | 271.17 | 3.00 | 236.66 | 52.02 | 260.24 | 5.72 |
| BZ-04-11r | 380.77 | 300.50 | 11.33 | 0.82 | 0.25 | 13.43 | 0.03 | 1.55 | 0.06 | 13.34 | 208.87 | 3.19 | 455.41 | 296.03 | 248.15 | 17.73 |
| BZ-04-12r | 113.92 | 159.95 | 3.04 | 1.45 | 0.21 | 22.38 | 0.03 | 2.07 | 0.05 | 22.28 | 191.15 | 3.89 | 232.26 | 514.44 | 176.11 | 13.01 |
| BZ-07-1r | 197.91 | 216.35 | 6.86 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 9.12 | 0.04 | 1.65 | 0.08 | 8.97 | 249.12 | 4.03 | 1129.71 | 178.56 | 273.17 | 13.98 |
| BZ-07-2r | 170.99 | 325.89 | 4.31 | 1.97 | 0.19 | 16.98 | 0.03 | 2.32 | 0.05 | 16.82 | 184.28 | 4.21 | 16.21 | 404.18 | 173.44 | 7.43 |
| BZ-07-3r | 176.74 | 235.24 | 4.48 | 1.38 | 0.17 | 18.42 | 0.03 | 1.68 | 0.04 | 18.35 | 183.51 | 3.03 | -250.32 | 464.32 | 171.50 | 9.07 |
| BZ-07-5r | 467.75 | 316.63 | 13.66 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 35.57 | 0.03 | 1.87 | 0.05 | 35.52 | 200.87 | 3.70 | 1.05 | 856.00 | 213.87 | 29.06 |
| BZ-07-6r | 437.74 | 470.61 | 11.44 | 1.11 | 0.18 | 14.39 | 0.03 | 1.46 | 0.04 | 14.31 | 185.54 | 2.67 | -79.00 | 350.21 | 191.95 | 9.98 |
| BZ-07-7r | 368.41 | 411.33 | 10.68 | 1.15 | 0.21 | 34.73 | 0.02 | 2.32 | 0.05 | 34.66 | 186.85 | 4.27 | 269.47 | 794.75 | 201.77 | 24.73 |
| BZ-07-8r | 209.66 | 140.96 | 5.77 | 0.69 | 0.18 | 25.13 | 0.03 | 2.88 | 0.05 | 32.18 | 179.97 | 5.10 | 187.59 | 3.96 | 114.58 | 46.47 |
| BZ-07-10r | 184.57 | 139.65 | 6.69 | 0.78 | 0.26 | 42.34 | 0.04 | 3.02 | 0.05 | 42.23 | 223.40 | 6.64 | 334.51 | 957.22 | 218.66 | 56.33 |
| BZ-07-11r | 448.39 | 264.79 | 12.33 | 0.61 | 0.15 | 34.88 | 0.03 | 2.18 | 0.04 | 34.81 | 174.85 | 3.77 | -452.81 | 917.69 | 163.25 | 40.18 |
| BZ-07-12r | 100.48 | 44.51 | 3.94 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 22.50 | 0.04 | 1.95 | 0.05 | 22.41 | 281.17 | 5.36 | 16.48 | 538.59 | 260.99 | 50.71 |
| BZ-07-13r | 195.81 | 232.74 | 5.25 | 1.23 | 0.17 | 17.03 | 0.03 | 1.59 | 0.04 | 16.96 | 193.17 | 3.03 | -377.97 | 440.32 | 165.75 | 9.34 |
| 平均 | 375.29 | 304.90 | 11.75 | 0.98 | 0.24 | 17.08 | 0.03 | 1.80 | 0.05 | 16.95 | 212.53 | 3.69 | 212.22 | 382.28 | 207.94 | 19.33 |
| 最大 | 1258.68 | 728.62 | 46.76 | 1.97 | 0.42 | 42.34 | 0.05 | 3.02 | 0.08 | 42.23 | 312.26 | 6.64 | 1129.71 | 957.22 | 302.88 | 56.33 |
| 最小 | 100.48 | 44.51 | 3.04 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 2.52 | 0.03 | 1.13 | 0.04 | 2.25 | 174.85 | 2.46 | -452.81 | 3.96 | 114.58 | 5.57 |
表3 北镇石墨矿床红柱石绢云绿泥片岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄数据
Table 3 SHRIMP U-Pb dating results of zircons from andalusite sericite schist in graphite deposit in Beizhen County
| 样品 编号 | 测试值/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 表面年龄(Ma) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | 206Pb* | 232Th/238U | 207Pb*/235U | ±σ/% | 206Pb*/238U | ±σ/% | 207Pb*/206Pb* | ±σ/% | 206Pb/238U | ±σ | 207Pb/206Pb | ±σ | 208Pb/232Th | ±σ | |
| BZ-04-6c | 166.18 | 116.79 | 69.49 | 0.73 | 11.18 | 1.41 | 0.49 | 1.26 | 0.17 | 0.62 | 2553.15 | 26.62 | 2527.03 | 10.40 | 2388.84 | 38.29 |
| BZ-04-10c | 179.57 | 107.67 | 75.56 | 0.62 | 11.18 | 1.40 | 0.49 | 1.25 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 2566.80 | 26.40 | 2514.84 | 10.85 | 2463.48 | 39.53 |
| BZ-04-13c | 272.43 | 260.24 | 112.36 | 0.99 | 11.05 | 1.29 | 0.48 | 1.20 | 0.17 | 0.48 | 2523.03 | 25.07 | 2530.83 | 8.13 | 2513.35 | 35.15 |
| BZ-07-9c | 379.56 | 284.20 | 154.64 | 0.77 | 10.82 | 1.23 | 0.47 | 1.17 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 2499.59 | 24.25 | 2515.11 | 6.31 | 2452.16 | 31.53 |
| 平均 | 249.44 | 192.22 | 103.01 | 0.78 | 11.06 | 1.33 | 0.48 | 1.22 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 2535.64 | 25.59 | 2521.95 | 8.92 | 2454.46 | 36.13 |
| BZ-04-2m | 482.57 | 530.79 | 125.92 | 1.14 | 6.42 | 2.02 | 0.29 | 1.18 | 0.16 | 1.64 | 1675.70 | 17.46 | 2422.64 | 27.75 | 1142.64 | 46.50 |
| BZ-07-4m | 1177.93 | 300.28 | 212.12 | 0.26 | 4.18 | 1.24 | 0.21 | 1.11 | 0.15 | 0.55 | 1216.75 | 12.33 | 2299.23 | 9.38 | 1131.56 | 37.97 |
| BZ-04-1r | 1042.07 | 379.49 | 37.66 | 0.38 | 0.30 | 3.22 | 0.04 | 1.15 | 0.05 | 3.01 | 263.73 | 2.96 | 259.19 | 69.15 | 247.74 | 8.65 |
| BZ-04-3r | 504.15 | 468.92 | 12.85 | 0.96 | 0.21 | 8.57 | 0.03 | 1.36 | 0.05 | 8.46 | 183.61 | 2.46 | 267.46 | 194.00 | 185.76 | 8.59 |
| BZ-04-4r | 307.78 | 178.83 | 13.21 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 3.95 | 0.05 | 1.26 | 0.05 | 3.74 | 312.26 | 3.84 | 244.41 | 86.25 | 302.88 | 10.73 |
| BZ-04-5r | 400.69 | 275.01 | 10.25 | 0.71 | 0.23 | 10.23 | 0.03 | 1.43 | 0.06 | 10.13 | 185.75 | 2.63 | 498.96 | 223.09 | 202.20 | 12.68 |
| BZ-04-7r | 390.02 | 728.62 | 10.57 | 1.93 | 0.23 | 10.39 | 0.03 | 1.45 | 0.05 | 10.29 | 195.67 | 2.80 | 342.49 | 232.85 | 183.90 | 5.57 |
| BZ-04-8r | 149.22 | 135.76 | 3.97 | 0.94 | 0.29 | 3.89 | 0.03 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 3.49 | 195.58 | 3.30 | 912.74 | 71.92 | 202.96 | 6.58 |
| BZ-04-9r | 1258.68 | 672.23 | 46.76 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 2.52 | 0.04 | 1.13 | 0.05 | 2.25 | 271.17 | 3.00 | 236.66 | 52.02 | 260.24 | 5.72 |
| BZ-04-11r | 380.77 | 300.50 | 11.33 | 0.82 | 0.25 | 13.43 | 0.03 | 1.55 | 0.06 | 13.34 | 208.87 | 3.19 | 455.41 | 296.03 | 248.15 | 17.73 |
| BZ-04-12r | 113.92 | 159.95 | 3.04 | 1.45 | 0.21 | 22.38 | 0.03 | 2.07 | 0.05 | 22.28 | 191.15 | 3.89 | 232.26 | 514.44 | 176.11 | 13.01 |
| BZ-07-1r | 197.91 | 216.35 | 6.86 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 9.12 | 0.04 | 1.65 | 0.08 | 8.97 | 249.12 | 4.03 | 1129.71 | 178.56 | 273.17 | 13.98 |
| BZ-07-2r | 170.99 | 325.89 | 4.31 | 1.97 | 0.19 | 16.98 | 0.03 | 2.32 | 0.05 | 16.82 | 184.28 | 4.21 | 16.21 | 404.18 | 173.44 | 7.43 |
| BZ-07-3r | 176.74 | 235.24 | 4.48 | 1.38 | 0.17 | 18.42 | 0.03 | 1.68 | 0.04 | 18.35 | 183.51 | 3.03 | -250.32 | 464.32 | 171.50 | 9.07 |
| BZ-07-5r | 467.75 | 316.63 | 13.66 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 35.57 | 0.03 | 1.87 | 0.05 | 35.52 | 200.87 | 3.70 | 1.05 | 856.00 | 213.87 | 29.06 |
| BZ-07-6r | 437.74 | 470.61 | 11.44 | 1.11 | 0.18 | 14.39 | 0.03 | 1.46 | 0.04 | 14.31 | 185.54 | 2.67 | -79.00 | 350.21 | 191.95 | 9.98 |
| BZ-07-7r | 368.41 | 411.33 | 10.68 | 1.15 | 0.21 | 34.73 | 0.02 | 2.32 | 0.05 | 34.66 | 186.85 | 4.27 | 269.47 | 794.75 | 201.77 | 24.73 |
| BZ-07-8r | 209.66 | 140.96 | 5.77 | 0.69 | 0.18 | 25.13 | 0.03 | 2.88 | 0.05 | 32.18 | 179.97 | 5.10 | 187.59 | 3.96 | 114.58 | 46.47 |
| BZ-07-10r | 184.57 | 139.65 | 6.69 | 0.78 | 0.26 | 42.34 | 0.04 | 3.02 | 0.05 | 42.23 | 223.40 | 6.64 | 334.51 | 957.22 | 218.66 | 56.33 |
| BZ-07-11r | 448.39 | 264.79 | 12.33 | 0.61 | 0.15 | 34.88 | 0.03 | 2.18 | 0.04 | 34.81 | 174.85 | 3.77 | -452.81 | 917.69 | 163.25 | 40.18 |
| BZ-07-12r | 100.48 | 44.51 | 3.94 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 22.50 | 0.04 | 1.95 | 0.05 | 22.41 | 281.17 | 5.36 | 16.48 | 538.59 | 260.99 | 50.71 |
| BZ-07-13r | 195.81 | 232.74 | 5.25 | 1.23 | 0.17 | 17.03 | 0.03 | 1.59 | 0.04 | 16.96 | 193.17 | 3.03 | -377.97 | 440.32 | 165.75 | 9.34 |
| 平均 | 375.29 | 304.90 | 11.75 | 0.98 | 0.24 | 17.08 | 0.03 | 1.80 | 0.05 | 16.95 | 212.53 | 3.69 | 212.22 | 382.28 | 207.94 | 19.33 |
| 最大 | 1258.68 | 728.62 | 46.76 | 1.97 | 0.42 | 42.34 | 0.05 | 3.02 | 0.08 | 42.23 | 312.26 | 6.64 | 1129.71 | 957.22 | 302.88 | 56.33 |
| 最小 | 100.48 | 44.51 | 3.04 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 2.52 | 0.03 | 1.13 | 0.04 | 2.25 | 174.85 | 2.46 | -452.81 | 3.96 | 114.58 | 5.57 |
| [1] | 赵光慧, 关玉波, 赵建军, 等. 辽宁板块构造特征及大地构造单元划分[J]. 地质与资源, 2011,20(2):101-106. |
| [2] | 辽宁省地质矿产局. 辽宁省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 659-663. |
| [3] | 宋鸿林. 燕山式板内造山带基本特征与动力学探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 1999,6(4):307-316. |
| [4] | 王伟锋, 陆诗阔, 孙月平. 辽西地区构造演化与盆地成因类型研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 1997,3(3):81-89. |
| [5] | 洪作民, 白尚金, 全秀杰, 等. 辽西地区逆冲断层和推覆构造[J]. 辽宁地质, 1985,( 1):1-12. |
| [6] | 王根厚, 张长厚, 王果胜, 等. 辽西地区中生代构造格局及其形成演化[J]. 现代地质, 2001,15(1):1-7. |
| [7] | 和政军, 李锦轶, 牛宝贵, 等. 燕山—阴山地区晚侏罗世强烈推覆-隆升事件及沉积响应[J]. 地质论评, 1998,44(4):407-418. |
| [8] | 江淑娥, 张国仁, 潘玉启. 辽西中生代板内造山带构造基本特征及构造演化[J]. 吉林地质, 2010,29(1):29-35. |
| [9] | 贾三石. 辽西钼多金属矿床遥感影像模型及远景区预测[D]. 沈阳:东北大学, 2008: 83-87. |
| [10] | 王东坡, 薛林福, 许敏, 等. 下辽河盆地外围深部构造特征及中生代构造演化模式[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1997,27(4):369-374. |
| [11] | 杨占兴. 辽宁省成矿系列与成矿区带研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2006: 105-116. |
| [12] | 刘艳青, 杨忠芳, 赖木收, 等. 辽西中生代沉积岩稀土、微量元素地球化学特征及其构造背景[J]. 地质论评, 2006,52(4):450-458. |
| [13] | 张璟. 辽西地区金矿成矿规律及成矿预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012: 97-101. |
| [14] | 李刚. 辽西医巫闾山变质核杂岩的形成过程及其区域地质意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2013: 142-156. |
| [15] | 朱大岗, 孟宪刚, 马寅生. 辽西医巫闾山变质核杂岩构造特征及其对金矿床的控制作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2002,26(2):156-161. |
| [16] | 林晓辉, 秦正永. 对燕山辽西地区构造格局的认识和讨论[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2003,25(1):5-12. |
| [17] | 郝增元, 牛永峰, 陈萌超, 等. 内蒙古石哈河地区黑云母二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2016,43(1):72-80. |
| [18] | TAYLOR H P, SHEPPARD S M F. Igneous Rocks:I. Process of isotopic fractionation and isotope systematics[M]//VALLEY J W,TAYLOR H P,O’NEIL J R. Stable Isotopes in High Temperature Geological Processes. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1986,16:227. |
| [19] | 周新, 倪志耀, 石楠. 冀北崇礼红旗营子黑云斜长片麻岩的地质地球化学特征[J]. 西南科技大学学报, 2013,28(4):23-30. |
| [20] | WILLIAMS I S, CLAESSON S. Isotope evidence for the Precambrian province and Caledonian metamorphism of high grade paragneiss from the Seve Nappes,Scandinavian Caledonides, Ⅱ: Ion microprobe Zircon U-Th-Pb[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,97:205-217. |
| [21] | 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(10):2595-2604. |
| [22] | 侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009,28(4):481-492. |
| [23] | LUDWIG K R. Using Isoplot/Ex (version 3.0): A Geochronological Tool kit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley :Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2001: 40-43. |
| [24] | 杜建军, 马寅生, 赵越. 辽西医巫闾山花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2007,34(1):26-33. |
| [25] | 马光, 刘继顺, 宫丽, 等. 辽宁省早前寒武纪两类不同花岗质岩石元素地球化学模型及意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2004,40(1):50-54. |
| [26] | 李怀坤, 朱士兴, 相振群, 等. 北京延庆高于庄组凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb定年研究及其对华北北部中元古界划分新方案的进一步约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(7):2131-2140. |
| [1] | 罗海怡, 罗先熔, 刘攀峰, 马明亮, 陆显盛, 蒋小明, 鲍官桂, 蒋羽雄. 广西崇左市那渠地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿前景[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1553-1566. |
| [2] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [3] | 梁东, 华北, 赵德怀, 吴浩, 万生楠, 谭朝欣, 赵晓健, 杨志鹏. 喀喇昆仑麦拉山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [4] | 娄元林, 成明, 唐侥, 张潮明, 蓝景周, 袁永盛, 杨桃. 藏南古堆地区岩浆岩岩石地球化学特征、构造环境分析及成矿响应[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 353-374. |
| [5] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| [6] | 夏锦胜, 孙莉, 张鹏, 陈昌阔, 汪君珠, 司江福. 四川坪河晶质石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1486-1496. |
| [7] | 陈世明, 杨镇熙, 雷自强, 康维良, 张晶, 赵青虎. 甘肃北山前红泉地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [8] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [9] | 刘洋, 李贤庆, 赵光杰, 刘满仓, 董才源, 李谨, 肖中尧. 库车坳陷东部吐格尔明地区天然气地球化学特征及油气充注史[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 988-997. |
| [10] | 王斌, 任涛, 宋伊圩, 杨可, 王占彬, 孙亚柯. 西秦岭常家山地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [11] | 刘阳, 姜冰, 张海瑞, 孙增兵, 王松涛. 山东省青州市表层土壤硒元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 933-940. |
| [12] | 王美华. 浙西典型石煤矿山周边耕地富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(03): 941-952. |
| [13] | 杨培奇, 刘敬党, 刘淑梅, 杨飞, 杨孝伟. 内蒙古乌拉特中旗大乌淀石墨矿床石英片岩地球化学特征与SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 672-681. |
| [14] | 朱必清, 陈世加, 白艳军, 雷俊杰, 尹相东. 鄂尔多斯盆地甘泉地区延长组长8段原油地球化学特征及来源[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 742-754. |
| [15] | 高银虎, 尹刚, 龚泽强, 郭明春. 甘肃两当湘潭子金矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(06): 1523-1535. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||