



Geoscience ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (03): 801-813.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.043
• Energy Geology and Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
DENG Shuo1,2( ), LI Sumei1,2,*(
), LI Sumei1,2,*( ), LIU Jia1,2
), LIU Jia1,2
Online:2025-06-10
Published:2025-07-03
Contact:
LI Sumei
CLC Number:
DENG Shuo, LI Sumei, LIU Jia. Distribution Characteristics and Geochemical Significances of the Individual Hydrocarbon Sulfur Isotopes of Crude Oils in the Liaohe Western Depression[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(03): 801-813.

Fig.1 Structural location map of the Liaohe Western Depression (a), planar schematic diagram of oil reservoir distribution in different structural units (b) and structural and oil reservoir distribution profile diagram (c)
| 井号 | 油田 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | 密度 (g/cm3) | 黏度 (mPa·s) | 凝固点 (℃) | 含蜡量 (%) | 含硫量 (%) | 饱和烃 (%) | 芳烃 (%) | 非烃+沥 青质(%) | 饱 芳比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 潜山 | 1786.80 | 0.82 | 3.73 | 32.00 | 14.99 | - | 72.70 | 15.70 | 11.60 | 4.63 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1199.50 | 0.91 | 258.07 | 16.00 | 10.52 | - | 40.60 | 23.40 | 35.90 | 1.74 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1307.35 | 0.88 | 120.00 | 24.00 | 15.44 | - | 51.70 | 25.20 | 23.10 | 2.05 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | Es4 | 1093.05 | 0.93 | 1539.30 | 15.50 | 5.09 | - | 38.20 | 30.50 | 31.40 | 1.25 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | Ng | 654.00 | 1.00 | 664977.30 | 46.00 | 1.28 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1753.00 | 0.89 | 414.20 | 31.00 | 11.45 | 0.48 | 35.90 | 20.70 | 43.50 | 1.73 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1641.95 | 0.93 | 2585.00 | 9.00 | - | 0.51 | 24.00 | 19.60 | 56.40 | 1.22 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1788.00 | 0.94 | 3524.00 | 6.00 | 5.10 | 0.53 | 27.50 | 21.10 | 51.40 | 1.30 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | Es4下 | 1909.55 | 0.88 | 1178.00 | 39.00 | 13.43 | 0.40 | 37.80 | 17.20 | 45.00 | 2.20 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | Es3 | 2483.90 | 0.80 | 2.47 | 9.00 | 19.57 | - | 72.60 | 15.00 | 12.40 | 4.84 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | Mz | - | 0.81 | 6.10 | 25.00 | 17.89 | - | 68.70 | 14.10 | 17.20 | 4.87 |
Table 1 Physical properties and group composition for the oils from the Liaohe Western Depression
| 井号 | 油田 | 层位 | 深度 (m) | 密度 (g/cm3) | 黏度 (mPa·s) | 凝固点 (℃) | 含蜡量 (%) | 含硫量 (%) | 饱和烃 (%) | 芳烃 (%) | 非烃+沥 青质(%) | 饱 芳比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 潜山 | 1786.80 | 0.82 | 3.73 | 32.00 | 14.99 | - | 72.70 | 15.70 | 11.60 | 4.63 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1199.50 | 0.91 | 258.07 | 16.00 | 10.52 | - | 40.60 | 23.40 | 35.90 | 1.74 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | Es4 | 1307.35 | 0.88 | 120.00 | 24.00 | 15.44 | - | 51.70 | 25.20 | 23.10 | 2.05 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | Es4 | 1093.05 | 0.93 | 1539.30 | 15.50 | 5.09 | - | 38.20 | 30.50 | 31.40 | 1.25 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | Ng | 654.00 | 1.00 | 664977.30 | 46.00 | 1.28 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | Es4中 | 1753.00 | 0.89 | 414.20 | 31.00 | 11.45 | 0.48 | 35.90 | 20.70 | 43.50 | 1.73 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1641.95 | 0.93 | 2585.00 | 9.00 | - | 0.51 | 24.00 | 19.60 | 56.40 | 1.22 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | Es3下 | 1788.00 | 0.94 | 3524.00 | 6.00 | 5.10 | 0.53 | 27.50 | 21.10 | 51.40 | 1.30 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | Es4下 | 1909.55 | 0.88 | 1178.00 | 39.00 | 13.43 | 0.40 | 37.80 | 17.20 | 45.00 | 2.20 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | Es3 | 2483.90 | 0.80 | 2.47 | 9.00 | 19.57 | - | 72.60 | 15.00 | 12.40 | 4.84 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | Mz | - | 0.81 | 6.10 | 25.00 | 17.89 | - | 68.70 | 14.10 | 17.20 | 4.87 |
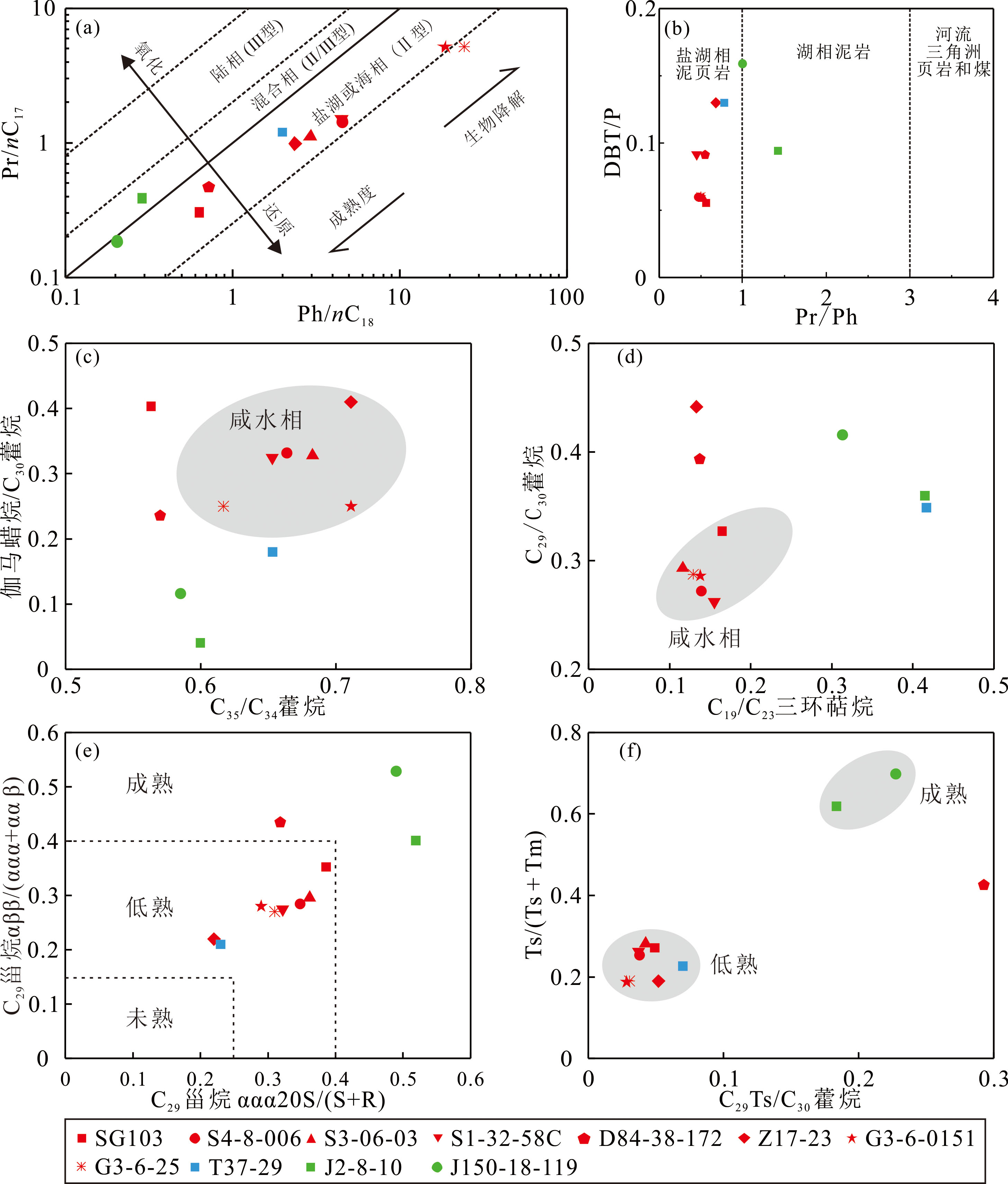
Fig.4 Cross plots of biomarker parameters of oils from the Liaohe Western Depression oils (Base figure (a) is based on Connan et al.[36], and base figure (b) is based on Hughes et al.[32])
| 井号 | 油田 | Pr/ Ph | Pr/ nC17 | Ph/ nC18 | G/ C30H | C35/ C34H | C19/ C23TT | C29/ C30H | S/R | αββ | C29Ts/ C30H | Ts/ (Ts+Tm) | DBT/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | 0.47 | 1.46 | 4.48 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | 0.53 | 1.12 | 2.92 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.06 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 4.52 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.09 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.09 |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 18.77 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 24.29 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | 0.78 | 1.22 | 1.98 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.13 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | 1.42 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 0.09 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.58 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.16 |
Table 2 Basic geochemical parameters of the oils
| 井号 | 油田 | Pr/ Ph | Pr/ nC17 | Ph/ nC18 | G/ C30H | C35/ C34H | C19/ C23TT | C29/ C30H | S/R | αββ | C29Ts/ C30H | Ts/ (Ts+Tm) | DBT/P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG103 | 曙光 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.06 |
| S4-8-006 | 曙光 | 0.47 | 1.46 | 4.48 | 0.33 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| S3-06-03 | 曙光 | 0.53 | 1.12 | 2.92 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.28 | 0.06 |
| S1-32-58C | 曙光 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 4.52 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.09 |
| D84-38-172 | 曙光 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.09 |
| Z17-23 | 高升 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 2.35 | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| G3-6-0151 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 18.77 | 0.25 | 0.71 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| G3-6-25 | 高升 | 0.50 | 5.22 | 24.29 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.06 |
| T37-29 | 牛心坨 | 0.78 | 1.22 | 1.98 | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.13 |
| J2-8-10 | 锦州 | 1.42 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 0.09 |
| J150-18-119 | 锦州 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.58 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.16 |
| [1] | CAI C, AMRANI A, WORDEN R H, et al. Sulfur isotopic compositions of individual organosulfur compounds and their genetic links in the Lower Paleozoic petroleum pools of the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 182: 88-108. |
| [2] | GREENWOOD P F, MOHAMMED L, GRICE K, et al. The application of compound-specific sulfur isotopes to the oil-source rock correlation of Kurdistan petroleum[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 117: 22-30. |
| [3] | KE C W, LI S M, ZHANG H G, et al. Compound specific sulfur isotopes of saline lacustrine oils from the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 195: 104361. |
| [4] | ELLIS G S, SAID-AHMAD W, LILLIS P G, et al. Effects of thermal maturation and thermochemical sulfate reduction on compound-specific sulfur isotopic compositions of organosulfur compounds in Phosphoria oils from the Bighorn Basin, USA[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 103: 63-78. |
| [5] | ROSENBERG Y O, MESHOULAM A, SAID-AHMAD W, et al. Study of thermal maturation processes of sulfur-rich source rock using compound specific sulfur isotope analysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 112: 59-74. |
| [6] | HE N, GRICE K, GREENWOOD P F. The distribution and δ34S values of organic sulfur compounds in biodegraded oils from Peace River (Alberta Basin, western Canada)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2019, 128: 16-25. |
| [7] | AMRANI A, DEEV A, SESSIONS A L, et al. The sulfur-isotopic compositions of benzothiophenes and dibenzothiophenes as a proxy for thermochemical sulfate reduction[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 84: 152-164. |
| [8] | GVIRTZMAN Z, SAID-AHMAD W, ELLIS G S, et al. Compound-specific sulfur isotope analysis of thiadiamondoids of oils from the Smackover Formation, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 167: 144-161. |
| [9] | 赵雪培, 张霞, 林春明, 等. 辽河拗陷滩海东部沙河街组低渗透砂岩储层成岩作用特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 196-204. |
| [10] | 蔡国刚, 鞠俊成. 辽河西部凹陷稠油成藏机制及深化勘探方法探讨[J]. 特种油气藏, 2010, 17(4): 35-38. |
| [11] | 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 高先志, 等. 辽河西部凹陷稠油成因机制[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2008, (S1): 138-149. |
| [12] | 惠沙沙, 庞雄奇, 柳广弟, 等. 辽河西部凹陷沙河街组烃源岩特征及油源精细对比[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(8): 3081-3098. |
| [13] | 毛俊莉, 张金川, 丁江辉, 等. 辽河坳陷清水洼陷沙三段页岩气富集条件[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(6): 1252-1262. |
| [14] | 邓硕, 李素梅, 曹敬涛, 等. 辽河西部凹陷低熟油的高分辨质谱特征及其成因机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5): 1354-1369. |
| [15] | LI S M, PANG X Q, LIU K Y, et al. Formation mechanisms of heavy oils in the Liaohe Western Depression, Bohai Gulf Basin[J]. Science in China Series D-Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(2): 156-169. |
| [16] | HUANG H, BOWLER B F J, OLDENBURG T B P, et al. The effect of biodegradation on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in reservoired oils from the Liaohe basin, NE China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2004, 35(11): 1619-1634. |
| [17] | HUANG H, BOWLER B F J, ZHANG Z, et al. Influence of biodegradation on carbazole and benzocarbazole distributions in oil columns from the Liaohe basin, NE China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(7): 951-969. |
| [18] | SONGNIAN L, WEI H, HAIPING H. The geochemical characteristics of heavy oil and its recovery in Liaohe Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1990, 16(1): 437-449. |
| [19] | 徐二社, 黄娟, 鹿坤, 等. 致密油运聚动力研究:以渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷Wg4井沙三中致密油为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(1): 17-24. |
| [20] | 漆家福, 李晓光, 于福生, 等. 辽河西部凹陷新生代构造变形及“郯庐断裂带”的表现[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(8): 1324-1337. |
| [21] | 单俊峰, 陈振岩, 张卓, 等. 辽河坳陷西部凹陷西斜坡古潜山的油气运移条件[J]. 现代地质, 2005, (2): 274-278. |
| [22] | 冷济高, 庞雄奇, 李晓光, 等. 辽河断陷西部凹陷油气成藏主控因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2008, (5): 473-480. |
| [23] |
王延山, 胡英杰, 黄双泉, 等. 渤海湾盆地辽河坳陷天然气地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(10): 1422-1432.
DOI |
| [24] | 陈星州, 邵建欣, 孙转, 等. 渤海湾盆地辽河坳陷稠油分布特征及主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 317-326. |
| [25] | 周晓龙. 辽河西部凹陷雷家—高升地区原油物性特征及影响因素[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2017, 31(1): 22-5+131-2. |
| [26] | 朱芳冰. 辽河盆地西部凹陷源岩特征及低熟油分布规律研究[J]. 地球科学, 2002, (1): 25-29. |
| [27] |
AMRANI A, SESSIONS A L, ADKINS J F. Compound-specific delta34S analysis of volatile organics by coupled GC/multicollector-ICPMS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(21): 9027-9034.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | PETERS K E, PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, et al. The biomarker guide[M]. Cambridge university press, 2005. |
| [29] | GRANTHAM P J. The occurence of unusual C27 and C29 sterane predominances in two types of Oman crude oil[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(1): 1-10. |
| [30] | VOLKMAN J K. A review of sterol markers for marine and terrigenous organic matter[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 9(2): 83-99. |
| [31] | DERENNE S, LARGEAU C, BERKALOFF C, et al. Non-hydrolysable macromolecular constituents from outer walls of Chlorella fusca and Nanochlorum eucaryotum[J]. Phytochemistry, 1992, 31(6): 1923-1929. |
| [32] | HUGHES W B, HOLBA A G, DZOU L I P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3581-3598. |
| [33] |
SINNINGHE DAMSTé J S, KENIG F, KOOPMANS M P, et al. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column stratification[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(9): 1895-1900.
PMID |
| [34] | AZEVEDO D A, AQUINO NETO F R, SIMONEIT B R T, et al. Novel series of tricyclic aromatic terpanes characterized in Tasmanian tasmanite[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 18(1): 9-16. |
| [35] | DIFAN H, JINCHAO L, DAJIANG Z. Maturation sequence of continental crude oils in hydrocarbon basins in China and its significance[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1990, 16(1): 521-529. |
| [36] | CONNAN J, CASSOU A M. Properties of gases and petroleum liquids derived from terrestrial kerogen at various maturation levels[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(1): 1-23. |
| [37] | FEDORAK P M, WESTLAKE D W S. Microbial degradation of organic sulfur compounds in Prudhoe Bay crude oil[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 1983, 29(3): 291-296. |
| [38] | AMRANI A. Organosulfur Compounds: Molecular and Isotopic Evolution from Biota to Oil and Gas[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2014, 42(1): 733-768. |
| [39] | 包建平, 王培荣, 朱翠山, 等. 有机硫化合物组成特征与热稳定性研究——以约旦油页岩和页岩油为例[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1990, 3: 1-8. |
| [40] | 杨华敏, 王萍, 陶成, 等. 天然气中硫化氢含量及硫同位素联测方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 166-172. |
| [41] |
高文强, 夏燕青, 马素萍, 等. 烃源岩和油气中有机含硫化合物的生成、分布及应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(11): 1615-1627.
DOI |
| [42] | 李素梅, 张宝收, 张海祖, 等. 塔中原油超高二苯并噻吩硫特征及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(6): 1108-1120. |
| [43] | 肖飞, 包建平, 张文艳, 等. 烷基二苯并噻吩类化合物研究进展[J]. 广东石油化工学院学报, 2012, 22(6): 16-9+22. |
| [44] | KE C, LI S, GREENWOOD P, et al. Maturity and depositional controls on compound-specific sulfur isotope values of saline lacustrine source rocks in the north Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 212: 110286. |
| [45] | RADKE M. Application of aromatic compounds as maturity indicators in source rocks and crude oils[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1988, 5(3): 224-236. |
| [46] | RADKE M, WILLSCH H. Extractable alkyldibenzothiophenes in Posidonia Shale (Toarcian) source rocks: Relationship of yields to petroleum formation and expulsion[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(23): 5223-5244. |
| [47] | 柯昌炜, 李素梅, 张洪安, 等. 东濮凹陷盐湖相烃源岩有机硫同位素分布特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 301-314. |
| [48] |
蔡春芳. 有机硫同位素组成应用于油气来源和演化研究进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(2): 159-167.
DOI |
| [49] | AMRANI A, LEWAN M D, AIZENSHTAT Z. Stable sulfur isotope partitioning during simulated petroleum formation as determined by hydrous pyrolysis of Ghareb Limestone, Israel[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(22): 5317-5331. |
| [50] | XUE C, CHI G, LI Z, et al. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Cretaceous and Paleocene sandstone- and conglomerate-hosted Uragen Zn-Pb deposit, Xinjiang, China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 63: 328-342. |
| [51] | ZHANG S, ZHU G, LIANG Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Zhaolanzhuang sour gas accumulation and thermochemical sulfate reduction in the Jixian Sag of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(12): 1717-1730. |
| [52] |
CANFIELD D E, HABICHT K S, THAMDRUP B. The Archean Sulfur Cycle and the Early History of Atmospheric Oxygen[J]. Science, 2000, 288: 658-661.
PMID |
| [53] | FIKE D A, GROTZINGER J P, PRATT L M, et al. Oxidation of the Ediacaran Ocean[J]. Nature, 2006, 444: 744-747. |
| [54] | SUN Y, CHEN Z, XU S, et al. Stable carbon and hydrogen isotopic fractionation of individual n-alkanes accompanying biodegradation: evidence from a group of progressively biodegraded oils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(2): 225-238. |
| [55] | KINNAMAN F S, VALENTINE D L, TYLER S C. Carbon and hydrogen isotope fractionation associated with the aerobic microbial oxidation of methane, ethane, propane and butane[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(2): 271-283. |
| [56] | ASIF M, GRICE K, FAZEELAT T. Assessment of petroleum biodegradation using stable hydrogen isotopes of individual saturated hydrocarbon and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distributions in oils from the Upper Indus Basin, Pakistan[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(3): 301-311. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||