



Geoscience ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (05): 1258-1269.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.103
• Oil and Gas Exploration in Sedimentary Basin and Key Techniques • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAI Zhenzhong1( ), XU Fan2,3, YANG Guo1, LI Hao2, HU Fangjie1, LIN Changsong2(
), XU Fan2,3, YANG Guo1, LI Hao2, HU Fangjie1, LIN Changsong2( )
)
Online:2024-10-10
Published:2024-11-13
Contact:
LIN Changsong
CLC Number:
CAI Zhenzhong, XU Fan, YANG Guo, LI Hao, HU Fangjie, LIN Changsong. Sedimentary Characteristics of the Lower Cambrian Yuertusi Formation and the Organic Matter Enrichment Model in the Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1258-1269.
| 岩相 组合 | 岩相类型 | 岩相描述 | 沉积相 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fa1 | 粉砂岩+泥质粉砂岩/(粉砂质)泥岩+云质粉砂岩+灰色含泥白云岩 | 成分成熟度高,分选性差,白云岩中含粉砂石英 | 混积潮坪 |
| Fa2 | 深灰色含泥白云岩+颗粒白云岩 | 发育泥质纹层和粉砂级石英颗粒,含海绵骨针 | 浅水陆棚 |
| Fa3 | 深灰色泥质灰岩+灰色含泥灰岩/灰岩 | 发育水平层理,含少量钙质海绵骨针和石英颗粒 | 浅水陆棚 |
| Fa4 | 黑色硅质岩+黄色磷质岩+黑色页岩 | 硅质岩与磷质岩混杂堆积,呈厚板状,页岩段较薄 | 深水陆棚,具热液和上升流活动 |
| Fa5 | 黑色硅质岩+黑色页岩 | 硅质岩呈薄板状,页岩段厚,含黄铁矿、生物碎屑 | 深水陆棚,具热液沉积 |
| Fa6 | 灰黑色泥岩/深灰色含灰泥岩+灰色含泥灰岩 | 含硅质放射虫和海绵骨针 | 深水陆棚 |
| Fa7 | 黑色泥岩+泥质灰岩 | 泥岩厚度较大,含黄铁矿颗粒,夹薄层泥质灰岩 | 深水盆地 |
Table 1 Facies associations and sedimentary facies of the Yuertusi Formation
| 岩相 组合 | 岩相类型 | 岩相描述 | 沉积相 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fa1 | 粉砂岩+泥质粉砂岩/(粉砂质)泥岩+云质粉砂岩+灰色含泥白云岩 | 成分成熟度高,分选性差,白云岩中含粉砂石英 | 混积潮坪 |
| Fa2 | 深灰色含泥白云岩+颗粒白云岩 | 发育泥质纹层和粉砂级石英颗粒,含海绵骨针 | 浅水陆棚 |
| Fa3 | 深灰色泥质灰岩+灰色含泥灰岩/灰岩 | 发育水平层理,含少量钙质海绵骨针和石英颗粒 | 浅水陆棚 |
| Fa4 | 黑色硅质岩+黄色磷质岩+黑色页岩 | 硅质岩与磷质岩混杂堆积,呈厚板状,页岩段较薄 | 深水陆棚,具热液和上升流活动 |
| Fa5 | 黑色硅质岩+黑色页岩 | 硅质岩呈薄板状,页岩段厚,含黄铁矿、生物碎屑 | 深水陆棚,具热液沉积 |
| Fa6 | 灰黑色泥岩/深灰色含灰泥岩+灰色含泥灰岩 | 含硅质放射虫和海绵骨针 | 深水陆棚 |
| Fa7 | 黑色泥岩+泥质灰岩 | 泥岩厚度较大,含黄铁矿颗粒,夹薄层泥质灰岩 | 深水盆地 |

Fig.4 Seismic profile (a) and interpretation (b) ofthe bottom truncation and top downlap of the Yuertusi Formation in the Tarim Basin (see Fig.1 for profile location)
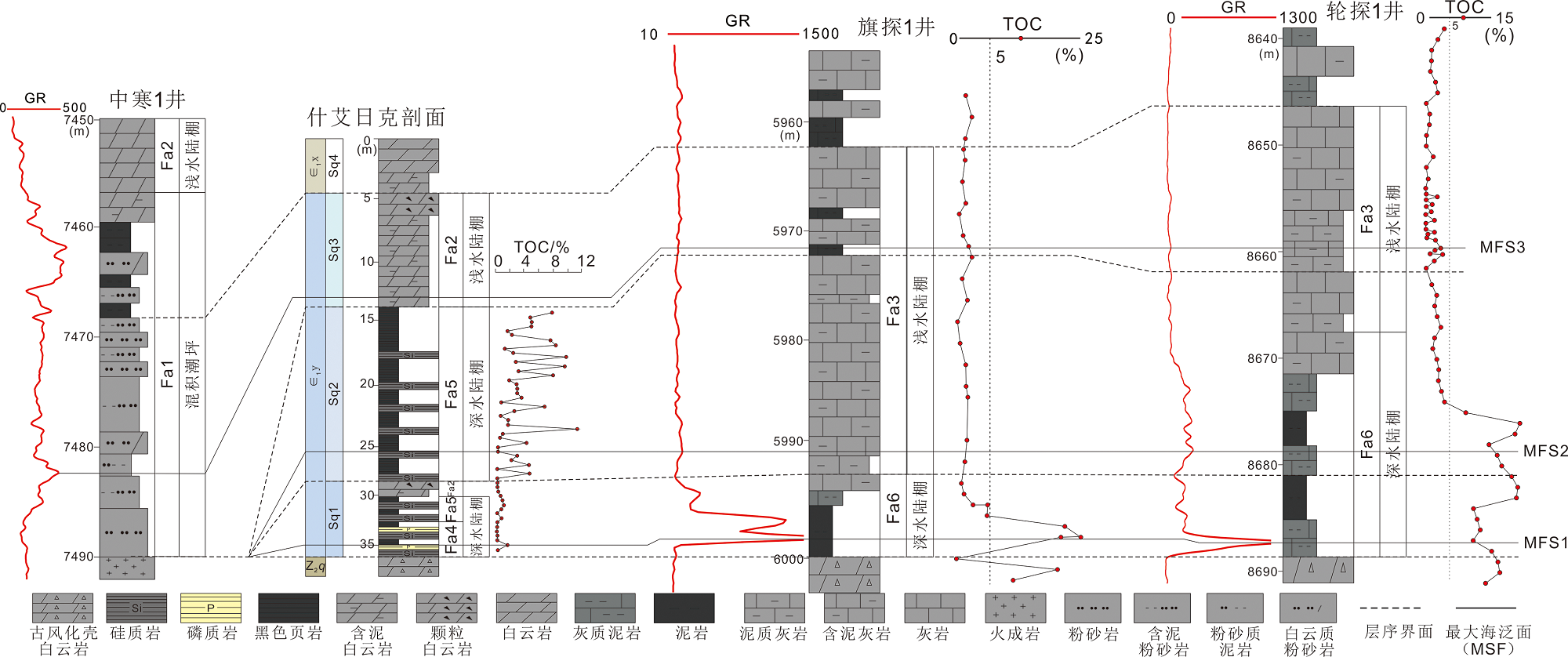
Fig.5 Changes of sequence-sedimentary microfacies and total organic carbon (TOC) content in the Yuertusi Formation, Tarim Basin (see Fig.1 for profile location)

Fig.8 Vertical variations in element abundance, U/Th ratios, paleotemperature, and TOC values in the Yuertusi Formation of QT1 (Organic matter is more abundant in the deep shelf zone compared to the shallow shelf; Palaeotemperatures are estimated from bulk oxygen isotopes)
| 深度 (m) | δCVPDB (‰) | δOVPDB (‰) | 深度 (m) | δCVPDB (‰) | δOVPDB (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5955 | -0.6 | -9.3 | 5978 | -1.2 | -8.8 |
| 5957 | -0.1 | -9 | 5980 | -1.6 | -8.7 |
| 5959 | -0.7 | -8.5 | 5982 | -1.6 | -9.3 |
| 5961 | 0.2 | -8.9 | 5984 | -1.5 | -10.3 |
| 5962 | 0.1 | -9.6 | 5986 | -1.7 | -8.9 |
| 5964 | 0.1 | -8.8 | 5989 | -1.9 | -10.2 |
| 5966 | -0.9 | -8.8 | 5991 | -2.5 | -9.1 |
| 5968 | -1.4 | -8.8 | 5993 | -2.1 | -9.7 |
| 5970 | -1.2 | -8.5 | 5995 | 2.0 | -14.1 |
| 5972 | -1.0 | -8.5 | 5997 | -0.3 | -8.6 |
| 5974 | -0.7 | -8.2 | 5999 | 0.9 | -7.5 |
| 5976 | -1.6 | -8.8 | 6000 | 1.7 | -7.9 |
Table 2 C-O composition of the Yuertusi Formation in well QT1
| 深度 (m) | δCVPDB (‰) | δOVPDB (‰) | 深度 (m) | δCVPDB (‰) | δOVPDB (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5955 | -0.6 | -9.3 | 5978 | -1.2 | -8.8 |
| 5957 | -0.1 | -9 | 5980 | -1.6 | -8.7 |
| 5959 | -0.7 | -8.5 | 5982 | -1.6 | -9.3 |
| 5961 | 0.2 | -8.9 | 5984 | -1.5 | -10.3 |
| 5962 | 0.1 | -9.6 | 5986 | -1.7 | -8.9 |
| 5964 | 0.1 | -8.8 | 5989 | -1.9 | -10.2 |
| 5966 | -0.9 | -8.8 | 5991 | -2.5 | -9.1 |
| 5968 | -1.4 | -8.8 | 5993 | -2.1 | -9.7 |
| 5970 | -1.2 | -8.5 | 5995 | 2.0 | -14.1 |
| 5972 | -1.0 | -8.5 | 5997 | -0.3 | -8.6 |
| 5974 | -0.7 | -8.2 | 5999 | 0.9 | -7.5 |
| 5976 | -1.6 | -8.8 | 6000 | 1.7 | -7.9 |
| [1] | 王招明, 谢会文, 陈永权, 等. 塔里木盆地中深1井寒武系盐下白云岩原生油气藏的发现与勘探意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(2): 1-13. |
| [2] |
杨海军, 陈永权, 田军, 等. 塔里木盆地轮探1井超深层油气勘探重大发现与意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(2): 62-72.
DOI |
| [3] | 张宝民, 张水昌, 边立曾, 等. 浅析中国新元古—下古生界海相烃源岩发育模式[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(增): 58-69. |
| [4] | 张水昌, 高志勇, 李建军, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武系—奥陶系海相烃源岩识别与分布预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(3): 285-294. |
| [5] |
潘文庆, 陈永权, 熊益学, 等. 塔里木盆地下寒武统烃源岩沉积相研究及其油气勘探指导意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(7): 1224-1232.
DOI |
| [6] | 陈强路, 储呈林, 胡广, 等. 塔里木盆地柯坪地区寒武系玉尔吐斯组沉积环境分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(3): 311-317, 326. |
| [7] | ZHU G Y, LI T T, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Distribution and geodynamic setting of the Late Neoproterozoic-Early Cambrian hydrocarbon source rocks in the South China and Tarim Blocks[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 201: 104504. |
| [8] | 樊奇, 樊太亮, 李一凡, 等. 塔里木地台北缘早寒武世古海洋氧化-还原环境与优质海相烃源岩发育模式[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1): 285-302. |
| [9] | 江维, 高志前, 胡宗全, 等. 塔里木盆地玉尔吐斯组高频层序沉积充填演化特征及控烃作用[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 349-364. |
| [10] | 杨宗玉, 罗平, 刘波, 等. 塔里木盆地阿克苏地区下寒武统玉尔吐斯组两套黑色岩系的差异及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(6): 1893-1918. |
| [11] |
张春宇, 管树巍, 吴林, 等. 塔西北地区早寒武世玉尔吐斯组热液作用及沉积模式[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 202-211.
DOI |
| [12] | 王志宏, 丁伟铭, 李剑, 等. 塔里木盆地西缘下寒武统玉尔吐斯组沉积地球化学及有机质富集机制研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 56(4): 667-678. |
| [13] | KAUFMAN A J, JACOBSEN S B, KNOLL A H. The Vendian record of Sr and C isotopic variations in seawater: Implications for tectonics and paleoclimate[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 120(3/4): 409-430. |
| [14] | SCHRODER S, GROTZINGER J P. Evidence for anoxia at the Ediacaran-Cambrian boundary: The record of redox-sensitive trace elements and rare earth elements in Oman[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1): 175-187. |
| [15] | YU B S, DONG H L, WIDOM E, et al. Geochemistry of basal Cambrian black shales and cherts from the Northern Tarim Basin, Northwest China: Implications for depositional setting and tectonic history[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 418-436. |
| [16] | SHU D G, ISOZAKI Y, ZHANG X L, et al. Birth and early evolution of metazoans[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(3): 884-895. |
| [17] | VEIZER J, PROKOPH A. Temperatures and oxygen isotopic composition of Phanerozoic Oceans[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 146: 92-104. |
| [18] |
王洪浩, 李江海, 周肖贝, 等. 塔里木陆块在Rodinia超大陆中位置的新认识: 来自地层对比和古地磁的制约[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(2): 589-600.
DOI |
| [19] | YOU X L, WU S N, XU F. The characteristics and main control factors of hydrocarbon accumulation of ultra-deep marine carbonates in the Tarim Basin, nw China: A review[J]. Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 13(1): 135-146. |
| [20] | ZHANG C L, ZOU H B, LI H K, et al. Tectonic framework and evolution of the Tarim Block in NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4): 1306-1315. |
| [21] | 林畅松, 李思田, 刘景彦, 等. 塔里木盆地古生代重要演化阶段的古构造格局与古地理演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 210-218. |
| [22] | 贾承造. 中国塔里木盆地构造特征与油气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997. |
| [23] | TURNER S A. Sedimentary record of Late Neoproterozoic rifting in the NW Tarim Basin, China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 181(1/2/3/4): 85-96. |
| [24] | HOFFMAN P F, LI Z X. A palaeogeographic context for Neoproterozoic glaciation[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2009, 277(3/4): 158-172. |
| [25] | 朱茂炎, 杨爱华, 袁金良, 等. 中国寒武纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2019, 49(1): 26-65. |
| [26] | FLÜGEL E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Interpretation and Application[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2010. |
| [27] | 张水昌, 张宝民, 边立曾, 等. 河北张家口下花园青白口系下马岭组 “红藻石” 的发现[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2005, 22(2): 121-126. |
| [28] | 边立曾, 张水昌, 张宝民, 等. 河北张家口下花园地区新元古代下马岭组油页岩中的红藻化石[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2005, 22(3): 209-216. |
| [29] | BAK K. Organic-rich and manganese sedimentation during the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event in the Outer Carpathian Basins: a new record from the Skole Nappe, Poland[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 256(1/2): 21-46. |
| [30] | MARTINEZ-RUIZ F, KASTNER M, PAYTAN A, et al. Geochemical evidence for enhanced productivity during S1 sapropel deposition in the eastern Mediterranean[J]. Paleoceanography, 2000, 15(2): 200-209. |
| [31] | MARTÍNEZ-RUIZ F, PAYTAN A, KASTNER M, et al. A comparative study of the geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of the S1 sapropel in the western and eastern Mediterranean[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2003, 190: 23-37. |
| [32] | 东野脉兴. 上升洋流与陆缘坻[J]. 化工矿产地质, 1996, 18(3): 156-162. |
| [33] | 密文天, 林丽. 海相磷块岩沉积事件研究: 以新元古代末—寒武纪成磷事件为例[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(4): 26-31, 54. |
| [34] | GANESHRAM R S, PEDERSEN T F, CALVERT S, et al. Reduced nitrogen fixation in the glacial ocean inferred from changes in marine nitrogen and phosphorus inventories[J]. Nature, 2002, 415: 156-159. |
| [35] | SANDERS C J, CALDEIRA P P, SMOAK J M, et al. Recent organic carbon accumulation (-100 years) along the Cabo Frio, Brazil upwelling region[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 75: 68-75. |
| [36] | 汤冬杰, 史晓颖, 赵相宽, 等. Mo-U共变作为古沉积环境氧化还原条件分析的重要指标: 进展、问题与展望[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(1): 1-13. |
| [37] | LEHMANN B, NÄGLER T F, HOLLAND H D, et al. Highly metalliferous carbonaceous shale and Early Cambrian seawater[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(5): 403. |
| [38] | CHEN D Z, WANG J G, QING H R, et al. Hydrothermal venting activities in the Early Cambrian, South China: Petrological, geochronological and stable isotopic constraints[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 258(3/4): 168-181. |
| [1] | MA Licheng, JIANG Wan, SHI Hui, HU Junjie, ZHANG Hao, CHEN Cheng, DONG Min, PENG Bo, FANG Xinxin. Relationship Between Cenozoic Superimposed Folds and Hydrocarbon Migration in the Gahainanshan Area, Eastern Qaidam Basin, China [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1209-1220. |
| [2] | TIAN Lanxi, ZHANG Guanjie, LEI Xin. Evaluation of Fault Sealing in the No.2 Fault Zone of the Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1235-1247. |
| [3] | JIANG Kunpeng, LIU Yalei, ZHOU Xingui, LIU Chengxin, CHENG Yan, DUAN Ye, BAI Zhongkai, ZHANG Yuanyin, MIAO Miaoqing. Fault Structural Characteristics of the Early Paleozoic in the Keping Fault-Uplift, Tarim Basin: A Case Study in the Southern Keping Area [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1248-1257. |
| [4] | DING Meng, FAN Tailiang, WU Jun, LI Yu, LI Chenchen, LÜ Kaidi. Sedimentary Microfacies in a High-precision Sequence Stratigraphic Framework of the Yijianfang Formation in the T738 Well Area of the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1270-1290. |
| [5] | LIU Xiaorui, LU Jungang, TAN Kaijun, LIAO Jianbo, LONG Liwen, CHEN Shijia, LI Yong, XIAO Zhenglu. Geochemical Characteristics and Oil Source Analysis of the Chang 7 and Chang 8 Members in the HQ Area, Southwestern Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1306-1324. |
| [6] | HE Xin, CHEN Shijia, HU Cong, ZHANG Haifeng, MOU Feisheng, LU Yifan, DAI Linfeng, FU Xiaoyan, HAN Meimei. Lithological Combination Model of the Continental Shale Series and Its Controls on Differential Crude Oil Enrichment: A Case Study of the Chang 7 Member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1325-1337. |
| [7] | LI Xiaodong, LI Zhijun, LI Xiwei, MA Xuefeng, LI Xiaoyan, CHEN Ketong, ZHANG Jichao, XU Mengting, ZHANG Ruixue, QIN Menghua, WANG Chengyun, LIU Jia, ZHANG Jianmiao, SHI Qianqian, LI Sumei. Genetic Mechanism of Low-Maturity Oil in the Qingyuan Tectonic Belt, Baoding Sag, Jizhong Depression [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1338-1353. |
| [8] | DENG Shuo, LI Sumei, CAO Jingtao, HUANG Taiming, LIU Jia, ZHANG Jianmiao, SHI Qianqian. High-Resolution Mass Spectrum Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Low Maturity Oil in the Liaohe Western Depression [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1354-1369. |
| [9] | LIU Xian, XI Binbin, CAO Tingting, JIANG Qigui, XU Jin, ZHU Jianhui. Phase Transformation Mechanisms and Controlling Factors of the Ultra-Deep Oil and Gas: Insights From Visual Thermal Simulation of Crude Oil [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1370-1382. |
| [10] | ZHANG Zhaohui, LIU Xianzheng, FENG Yan, LI Hongliang, LI Lei, YANG Cai, XIA Ning, LU Zhenquan, ZHANG Yunbo, LIU Guo, SUN Li, LIN Ziyang, LI Qing. Geological Indicators of Permafrost-associated Gas Hydrates in the Labudalin Basin, Northeastern Inner Mongolia [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1383-1399. |
| [11] | DONG Bo, CAO Daiyong, WEI Yingchun, WANG Anmin, LI Xin, ZHANG Yun. Advancements in Experimental Studies on the Tectonic Physical-chemical Mechanisms of Coal Metamorphism [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 892-909. |
| [12] | YU Huimin, SHEN Xiaoli, SU Huhu, JIA Wenchen, ZHANG Baolin, SU Jie. Application of Comprehensive Geophysical Exploration in the Lizichong Mining Area, Ailaoshan Tectonic Belt, Southwest Yunnan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 1054-1066. |
| [13] | SHEN Yuke, GUO Tao, HAN Fengbin, XIAO Changhao, YAN Shaohua, LI Kang, LIU Weimin. Alteration Fractural System and Orebody Locating in the Linglong Gold Field [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 1013-1025. |
| [14] | YANG Xianzhang, NENG Yuan, XU Zhenping, LI Kuayue, HUANG Shaoying, DUAN Yunjiang. Characteristics of the Hydrocarbon Accumulation Formed Through the Three Structural Cycles in Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 287-299. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zaizhen, ZENG Jianhui, ZHANG Benhua, WANG Zhiwei, LIU Jinhua, YU Shina, WU Qunhu, WANG Yanzhen. Neogene Volcanism and Its Petroleum Geological Significance in the Eastern Chengdao, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 312-321. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||