



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (03): 694-705.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.064
杨鹏至1,2( ), 赵元1,2(
), 赵元1,2( ), 肖粤新1,2,3, 闵英姿1,2, 邓曌1,2, 郭军2, 韦晓堃1,2
), 肖粤新1,2,3, 闵英姿1,2, 邓曌1,2, 郭军2, 韦晓堃1,2
出版日期:2024-06-10
发布日期:2024-07-04
通讯作者:
赵元,男,工程师,1995年出生,主要从事地表关键带、土壤生态及碳循环、自然资源综合观测。Email: zhaoyuan1995@mail.cgs.gov.cn。
作者简介:杨鹏至,男,助理工程师,1996年出生,主要从事地表基质调查监测、自然资源综合观测。Email: 181292598@qq.com。
基金资助:
YANG Pengzhi1,2( ), ZHAO Yuan1,2(
), ZHAO Yuan1,2( ), XIAO Yuexin1,2,3, MIN Yingzi1,2, DENG Zhao1,2, GUO Jun2, WEI Xiaokun1,2
), XIAO Yuexin1,2,3, MIN Yingzi1,2, DENG Zhao1,2, GUO Jun2, WEI Xiaokun1,2
Online:2024-06-10
Published:2024-07-04
摘要:
为了评估国道交通对两侧土壤的影响,查明其重金属污染特征和来源,选取107国道岳阳县段作为研究区域。在该区域两侧各1 km范围内采集了246个表层土壤样品,并测定了Pb、As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn、Hg这8种重金属元素的含量。通过对比分析国道两侧土壤中重金属污染情况和元素含量差异,结合克里金空间插值法和PMF模型,进一步揭示这些重金属的潜在来源。结果表明:(1)107国道岳阳县段两侧土壤属强酸性土壤,重金属之间的差异反映了土地利用类型和人类活动对土壤重金属分布的显著影响。(2)单因子污染指数均值显示Cr、Ni、Zn、Cd无污染,Cu、As、Hg、Pb为轻度污染,内梅罗综合污染指数表明研究区土壤整体轻度污染。(3)空间插值分析显示,As、Cr、Cu、Ni在空间分布上高度重叠;Pb和Zn在空间上分布在农田耕地区域;Cd元素的空间分布异常区域主要为新开镇;Hg元素的空间分布特征显示林地为低值区域,说明了自然地质背景与土地利用类型对土壤重金属的复杂相互作用。(4)PMF源解析识别了4种污染源,分别为交通源、农业源、自然源、大气源,其中交通源和农业源合计占比80.3%,是影响107国道岳阳县段两侧土壤中重金属元素的主要因素,说明107国道两侧土壤受交通运输和人类活动影响较明显。综上所述,空间插值分析和PMF模型的结果相互之间验证效果较好,这一综合方法对重金属潜在来源的成分识别较为理想。
中图分类号:
杨鹏至, 赵元, 肖粤新, 闵英姿, 邓曌, 郭军, 韦晓堃. 基于空间插值与PMF模型的国道沿线土壤重金属源解析:以107国道岳阳段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(03): 694-705.
YANG Pengzhi, ZHAO Yuan, XIAO Yuexin, MIN Yingzi, DENG Zhao, GUO Jun, WEI Xiaokun. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Soils Along a National Highway Using Spatial Interpolation and PMF Model: A Case Study of the Yueyang Section of National Highway 107[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(03): 694-705.
| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Pb | 电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) | 2 |
| As | 原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) | 1 |
| Cd | 电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) | 0.03 |
| Cr | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 5 |
| Cu | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 1 |
| Ni | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 2 |
| Zn | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 4 |
| Hg | 原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) | 0.0005 |
表1 测试元素分析方法及检出限
Table 1 Analytical methods for testing metals and their detection limits
| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Pb | 电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) | 2 |
| As | 原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) | 1 |
| Cd | 电感耦合等离子质谱法(ICP-MS) | 0.03 |
| Cr | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 5 |
| Cu | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 1 |
| Ni | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 2 |
| Zn | 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | 4 |
| Hg | 原子荧光光谱法(HG-AFS) | 0.0005 |
| Pi | Pi≤1 | 1<Pi≤2 | 2<Pi≤3 | 3<Pi≤5 | Pi>5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 污染水平 | 无污染 | 轻度污染 | 中度污染 | 重度污染 | 极强污染 |
表2 土壤单因子污染程度分级
Table 2 Classification of soil pollution degree using single factor analysis
| Pi | Pi≤1 | 1<Pi≤2 | 2<Pi≤3 | 3<Pi≤5 | Pi>5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 污染水平 | 无污染 | 轻度污染 | 中度污染 | 重度污染 | 极强污染 |
| PN | PN ≤0.7 | 0.7<PN ≤1.0 | 1.0<PN ≤2.0 | 2.0<PN ≤3.0 | PN >3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 污染水平 | 安全 | 警戒线 | 轻污染 | 中污染 | 重污染 |
表3 内梅罗污染程度分级
Table 3 Classification of pollution degree using the Nemerow index
| PN | PN ≤0.7 | 0.7<PN ≤1.0 | 1.0<PN ≤2.0 | 2.0<PN ≤3.0 | PN >3.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 污染水平 | 安全 | 警戒线 | 轻污染 | 中污染 | 重污染 |
| 数值类型 | Pb (mg·kg-1) | As (mg·kg-1) | Cd (mg·kg-1) | Cr (mg·kg-1) | Cu (mg·kg-1) | Ni (mg·kg-1) | Zn (mg·kg-1) | Hg (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 171.00 | 74.60 | 5.25 | 237.00 | 179.00 | 111.00 | 509.00 | 0.32 | 5.99 |
| 最小值 | 21.40 | 3.26 | 0.04 | 25.70 | 12.10 | 9.94 | 36.70 | 0.03 | 4.10 |
| 国道两侧土壤平均值 | 36.53 | 13.39 | 0.30 | 77.96 | 27.20 | 24.69 | 77.93 | 0.11 | 4.85 |
| 未干扰地区土壤平均值 | 37.15 | 18.25 | 0.21 | 82.27 | 28.72 | 24.34 | 79.80 | 0.08 | 4.87 |
| 干扰地区土壤平均值 | 36.29 | 11.49 | 0.34 | 76.28 | 26.61 | 24.83 | 77.19 | 0.12 | 4.85 |
| 标准偏差 | 12.41 | 7.49 | 0.39 | 23.19 | 14.21 | 8.33 | 41.49 | 0.05 | - |
| 未干扰地变异系数 | 0.60 | 0.61 | 1.05 | 0.42 | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.91 | 0.45 | - |
| 干扰地变异系数 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 1.28 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.39 | - |
| 变异系数 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 1.29 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.53 | 0.44 | - |
| 洞庭湖背景值 | 31.69 | 12.35 | 0.31 | 88.20 | 26.01 | 27.50 | 86.10 | 0.10 | - |
表4 107国道岳阳段两侧重金属元素含量特征
Table 4 Characteristics of heavy metal element contents on both sides of the Yuegang section of national highway 107
| 数值类型 | Pb (mg·kg-1) | As (mg·kg-1) | Cd (mg·kg-1) | Cr (mg·kg-1) | Cu (mg·kg-1) | Ni (mg·kg-1) | Zn (mg·kg-1) | Hg (mg·kg-1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 | 171.00 | 74.60 | 5.25 | 237.00 | 179.00 | 111.00 | 509.00 | 0.32 | 5.99 |
| 最小值 | 21.40 | 3.26 | 0.04 | 25.70 | 12.10 | 9.94 | 36.70 | 0.03 | 4.10 |
| 国道两侧土壤平均值 | 36.53 | 13.39 | 0.30 | 77.96 | 27.20 | 24.69 | 77.93 | 0.11 | 4.85 |
| 未干扰地区土壤平均值 | 37.15 | 18.25 | 0.21 | 82.27 | 28.72 | 24.34 | 79.80 | 0.08 | 4.87 |
| 干扰地区土壤平均值 | 36.29 | 11.49 | 0.34 | 76.28 | 26.61 | 24.83 | 77.19 | 0.12 | 4.85 |
| 标准偏差 | 12.41 | 7.49 | 0.39 | 23.19 | 14.21 | 8.33 | 41.49 | 0.05 | - |
| 未干扰地变异系数 | 0.60 | 0.61 | 1.05 | 0.42 | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.91 | 0.45 | - |
| 干扰地变异系数 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 1.28 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.39 | - |
| 变异系数 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 1.29 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.53 | 0.44 | - |
| 洞庭湖背景值 | 31.69 | 12.35 | 0.31 | 88.20 | 26.01 | 27.50 | 86.10 | 0.10 | - |
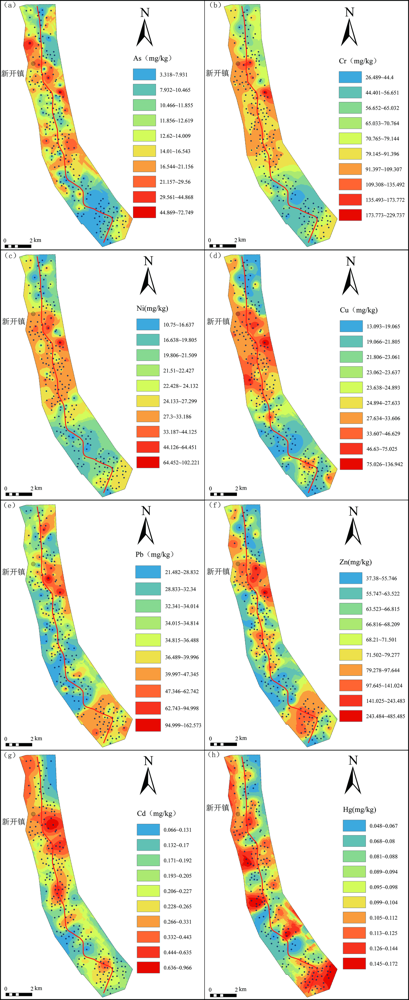
图2 107国道岳阳段两侧土壤重金属元素克里金空间插值空间分布图
Fig.2 Spatial distribution maps of heavy metal elements in the soil along both sides of the Yueyang Section of national highway 107 using Kriging spatial interpolation

图4 107国道岳阳段两侧重金属元素相关性图(*示p≤0.05,**示p≤0.01,***示p≤0.001)
Fig.4 Correlation diagram of heavy metal elements along the Yueyang Section of national highway 107 (*denoting p≤0.05, **denoting p≤0.01, ***denoting p≤0.001)
| [1] | AHMED F, FAKHRUDDIN A N M, TOUFICK IMAM M D, et al. Spatial distribution and source ide.pngication of heavy metal pollution in roadside surface soil: A study of Dhaka Aricha highway, Bangladesh[J]. Ecological Processes, 2016, 5(1): 16. |
| [2] | 周怡, 胡文友, 黄标, 等. 我国高速公路周边土壤重金属污染现状及研究进展[J]. 中国环境监测, 2020, 36(5): 112-120. |
| [3] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[R]. 2014. |
| [4] | 蔡雄飞, 段志斌, 王济, 等. 高速公路两侧农田土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2020, 47(1): 103-108. |
| [5] | 贺新星, 魏芳, 范健, 等. 宁连高速两侧土壤及小麦重金属污染特征研究[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2020, 32(5): 28-32. |
| [6] |
FENG J F, ZHAO J, BIAN X M, et al. Spatial distribution and controlling factors of heavy metals contents in paddy soil and crop grains of rice-wheat cropping system along highway in East China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2012, 34(5): 605-614.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | 冉德钦, 李轶然, 张林宏, 等. 公路路域农田土壤重金属污染分析研究[J]. 当代化工, 2022, 51(11): 2598-2601, 2609. |
| [8] | 翟云波, 戴青云, 蒋康, 等. 高速公路土壤重金属污染状况及健康风险评价[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(6): 149-156. |
| [9] | 周怡, 吴秋梅, 樊亚男, 等. 江苏省典型高速公路沿线土壤重金属分布特征及影响因素研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2023, 54(1): 161-170. |
| [10] | 黄蕾, 刘伟, 杜伟伟. 某市公路两侧土壤垂直剖面处重金属污染特征研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(21): 101-104. |
| [11] | SAEEDI M, HOSSEINZADEH M, JAMSHIDI A, et al. Assessment of heavy metals contamination and leaching characteristics in highway side soils, Iran[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 151(1): 231-241. |
| [12] | WANG G Y, ZHANG S R, XIAO L Y, et al. Heavy metals in soils from a typical industrial area in Sichuan, China: Spatial distribution, source ide.pngication, and ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(20): 16618-16630. |
| [13] | 张海琳, 张雨, 王顶, 等. 西南不同类型紫色土pH变化、重金属累积与潜在生态风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(4): 2440-2449. |
| [14] | 马搏研. 广州某造船厂土壤重金属污染时空分布特征与污染源分析[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2023. |
| [15] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 等. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 634-644. |
| [16] | 杜古尔·卫卫, 石海涛, 邢浩, 等. 新疆戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(3): 790-800. |
| [17] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 等. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(4): 1173-1182. |
| [18] | 肖凯琦, 徐宏根, 甘杰, 等. 湘西地区土壤重金属污染溯源分析及环境质量评价[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(3): 1760-1768. |
| [19] | 何溱, 李婷, 骆虹伶, 等. 地球化学元素高背景农作区土壤剖面重金属来源解析及污染评价[J]. 环境化学, 2023, 42(12): 4253-4263. |
| [20] | 卜兴兵, 俸强, 廖翀, 等. 基于主成分分析法的高速公路土壤重金属污染研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(4): 2241-2247. |
| [21] | 何本蜻, 王中伟, 张婷, 等. 贵黄公路沿线重金属分布特征、来源解析及风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(2): 164-171. |
| [22] | 程思茜. 基于PMF和PCA-APCS-MLR受体模型的地下水污染源定性识别和定量解析[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2021. |
| [23] | GAN R Y, LIU Y, LI H, et al. Natural sources, refined extraction, biosynthesis, metabolism, and bioactivities of dietary polymethoxyflavones (PMFs)[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness, 2024, 13(1): 27-49. |
| [24] | 赵庆令, 李清彩, 安茂国, 等. 基于PMF-PCA/APCS与PERI的菏泽油用牡丹种植区表层土壤重金属潜在来源识别及生态风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(9): 5253-5263. |
| [25] | 沈智杰, 李杰芹, 李彩霞, 等. 基于APCS-MLR和PMF模型的赤泥堆场周边耕地土壤重金属污染源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45(2): 1058-1068. |
| [26] | 段海静, 马嘉玉, 彭超月, 等. 基于APCS-MLR和PMF模型解析黄河下游文化公园土壤重金属污染特征及来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(8): 4406-4415. |
| [27] | 赵大双, 姜春露, 赵琦, 等. 基于PMF和PCA-APCS-MLR模型的煤矿区地下水多环芳烃分布特征及来源解析[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(5): 721-732. |
| [28] |
宁文婧, 谢先明, 严丽萍. 清远市清城区土壤中重金属的空间分布、来源解析和健康评价:基于PCA和PMF模型的对比[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4): 470-484.
DOI |
| [29] | 李娇, 吴劲, 蒋进元, 等. 近十年土壤污染物源解析研究综述[J]. 土壤通报, 2018, 49(1): 232-242. |
| [30] | MA J, SHEN Z J, WANG S L, et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in soils around a coal gangue heap with the APCS-MLR and PMF receptor models in Chongqing, southwest China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2023, 20(4): 1061-1073. |
| [31] | 徐克全, 金立新, 郑勇军, 等. 多种空间插值法在土地质量地球化学评价中对比分析: 以四川省叙永县麻城镇和摩尼镇为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2021, 43(5): 669-682. |
| [32] | 赵天瑞, 陈正瑞, 刘一鸣, 等. 基于GIS遥感数据分析的生活垃圾空间分布模型[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(2): 213-218. |
| [33] | 孔星杰, 王广昊, 孙彩丽, 等. 铅锌废渣场周边不同土地利用类型土壤重金属分布及植物富集特征[J/OL]. 生态学杂志. [2024-05-31]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230331.1035.010.html. |
| [34] | 贾晓琳. 区域土壤重金属污染的源汇空间分析和时空模拟研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020. |
| [35] |
宁银中. 基于Meta分析的农田土壤Pb、Zn污染现状[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(1): 179-185.
DOI |
| [36] | 孟龙, 黄涂海, 陈謇, 等. 镉污染农田土壤安全利用策略及其思考[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2019, 45(3): 263-271. |
| [37] | 赵万伏, 宋垠先, 管冬兴, 等. 典型黑色岩系分布区土壤重金属污染与生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7): 1332-1341. |
| [38] | 王钦. 煤燃烧过程中易挥发元素(Hg、As、Se)迁移规律研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2014. |
| [39] | 孙文. 土壤-植物系统中Cd、Hg迁移转化研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. |
| [40] |
YUAN X H, XUE N D, HAN Z G. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 101: 217-226.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | MA T T, ZHANG Y W, HU Q B, et al. Accumulation characteristics and pollution evaluation of soil heavy metals in different land use types: Study on the whole region of Tianjin[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(16): 10013. |
| [42] | ZHANG X Y, ZHONG T Y, LIU L, et al. Impact of soil heavy metal pollution on food safety in China[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0135182. |
| [43] | 安永龙, 殷秀兰, 李文娟, 等. 张家口市万全区某种植区土壤重金属污染评价与来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(6): 3544-3561. |
| [44] | 孟利, 左锐, 王金生, 等. 基于PCA-APCS-MLR的地下水污染源定量解析研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(10): 3773-3786. |
| [45] | 魏薇. 湘江涓水交汇处土壤重金属污染评价及来源解析[D]. 湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2022. |
| [46] | 俞诗颖. 区域土壤重金属污染源解析和污染风险情景模拟[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021. |
| [47] | 安礼航, 刘敏超, 张建强, 等. 土壤中砷的来源及迁移释放影响因素研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(2): 234-246. |
| [48] | HJORTENKRANS D S T, BERGBÄCK B G, HÄGGERUD A V. Metal emissions from brake linings and tires: Case studies of Stockholm, Sweden 1995/1998 and 2005[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(15): 5224-5230. |
| [49] | JOHANSSON C, NORMAN M, BURMAN L. Road traffic emission factors for heavy metals[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2009, 43(31): 4681-4688. |
| [50] | METRAK M, CHMIELEWSKA M, SUDNIK-WÓJCIKOWSKA B, et al. Does the function of railway infrastructure determine qualitative and quantitative composition of contaminants (PAHs, heavy metals) in soil and plant biomass?[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2015, 226(8): 253. |
| [51] | SUN J W, HU G R, YU R L, et al. Human health risk assessment and source analysis of metals in soils along the G324 Roadside, China, by Pb and Sr isotopic tracing[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 305: 293-304. |
| [52] | WANG M E, ZHANG H Z. Accumulation of heavy metals in roadside soil in urban area and the related impacting factors[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(6): 1064. |
| [53] | 冯春婷. 典型煤炭型城市重金属污染特征和健康风险评价[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2018. |
| [1] | 李楠, 曹明杰, 郝喆, 侯永莉, 陈红丹, 张颖. 基于不同土地利用方式的土壤重金属污染与潜在风险评价:以辽河流域(浑太水系)山水林田湖草沙一体化保护和修复工程为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1655-1664. |
| [2] | 杜古尔·卫卫, 石海涛, 邢浩, 娄雪聪, 胡宏利, 布龙巴特. 新疆戈壁荒漠区典型露天煤矿土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 790-800. |
| [3] | 刘同, 刘传朋, 康鹏宇, 赵秀芳, 邓俊, 王凯凯. 山东省沂南县东部土壤重金属地球化学特征及源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1173-1182. |
| [4] | 黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 李欢, 张沁瑞. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 634-644. |
| [5] | 臧传子, 温汉辉, 蔡立梅, 罗杰, 徐述邦, 梅敬娴. 广东省揭阳市土壤铅的空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1425-1432. |
| [6] | 唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 徐进力, 徐仁廷, 张富贵. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(05): 917-927. |
| [7] | 李朋飞, 刘超, 陶春军, 汪晶, 吴正. 再生铅工业园周边土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 663-671. |
| [8] | 王娟恒, 温汉辉, 蔡立梅, 罗杰, 王硕, 王秋爽, 穆桂珍, 蒋慧豪. 广东揭阳土壤镉含量的空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 88-96. |
| [9] | 刘海, 康博, 沈军辉. 基于反向地球化学模拟的地下水形成作用:以安徽省泗县为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 440-450. |
| [10] | 孙凯, 孙彬彬, 周国华, 贺灵, 曾道明, 吴超, 成晓梦. 福建龙海土壤重金属含量特征及影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1302-1310. |
| [11] | 汪名鹏. 江苏泗阳城区浅层地下水化学特征及其影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1329-1336. |
| [12] | 邱海军,曹明明,刘闻,郝俊卿,胡胜,高宇,刘琪. 区域滑坡空间分布的变维分形特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 443-448. |
| [13] | 钟聪, 杨忠芳, 夏学齐, 侯青叶, 姜伟. 青海省土壤有机碳储量估算及其源汇因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 896-909. |
| [14] | 傅倩倩, 王广才. 华北地区某工业场地土壤重金属分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4): 829-836. |
| [15] | 许光, 章巧秋, 姬丙艳, 张亚峰, 唐俊红. 青海民和—海石湾一带土壤重金属异常生态效应评价[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(5): 1007-1012. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||