



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (02): 719-728.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.193
曹兰柱1( ), 吴飘2,3, 侯读杰2(
), 吴飘2,3, 侯读杰2( ), 魏秀丽1, 郑荣华1
), 魏秀丽1, 郑荣华1
收稿日期:2021-04-05
修回日期:2021-07-20
出版日期:2022-04-10
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
侯读杰
作者简介:侯读杰,男,教授,1964年出生,石油地质学专业,主要从事油气地球化学与成藏研究。Email: houdj313@163.com。基金资助:
CAO Lanzhu1( ), WU Piao2,3, HOU Dujie2(
), WU Piao2,3, HOU Dujie2( ), WEI Xiuli1, ZHEN Ronghua1
), WEI Xiuli1, ZHEN Ronghua1
Received:2021-04-05
Revised:2021-07-20
Online:2022-04-10
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
HOU Dujie
摘要:
二连盆地已发现56个凹陷和21个凸起,每个凹陷按腾一段地层沉积中心的分割性可划分为2~3个洼槽。为开展洼槽地质分类及其与生烃潜力的相关性研究,通过对10个含油凹陷23个洼槽的地质和地球化学资料统计分析,发现各洼槽的古生界基底顶面(Tg)最大埋深、洼槽面积、阿尔善组及腾一段沉积期间的古水体盐度分别对阿尔善组和腾一段两套烃源岩的最大总厚度及成熟度、面积、有机质丰度及类型存在控制作用。据此提出按照基底埋深、深洼带面积和阿尔善组及腾一段的古水体盐度特征将洼槽划分为高熟型、成熟型和低熟型3大类14小类。结合洼槽生烃潜力评价,认为富生烃洼槽总体属于高熟大中型洼槽和成熟大中型咸水洼槽,咸水洼槽具有更优越的源储条件,更有利于致密油勘探。由于高熟咸水洼槽在马尼特坳陷和乌兰察布坳陷更发育,在勘探选区上应优先考虑这两个坳陷内的洼槽。
中图分类号:
曹兰柱, 吴飘, 侯读杰, 魏秀丽, 郑荣华. 二连盆地洼槽分类及其油气勘探意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 719-728.
CAO Lanzhu, WU Piao, HOU Dujie, WEI Xiuli, ZHEN Ronghua. Classification of Sub-sags in the Erlian Basin and Its Petroleum Prospecting Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 719-728.
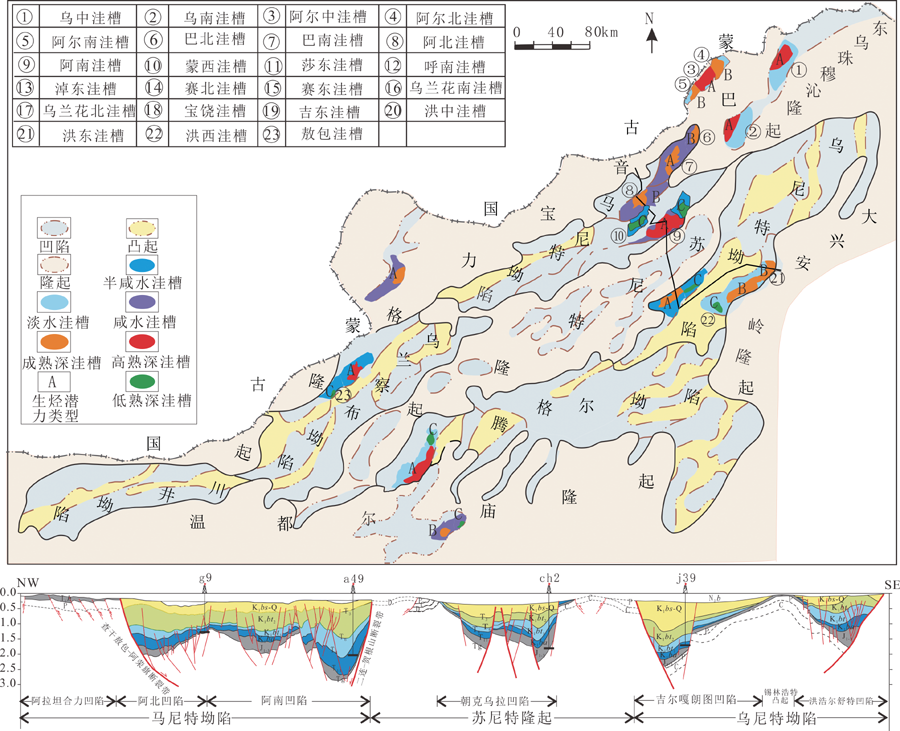
图1 二连盆地含油气凹陷洼槽分类、分布及NW-SE向构造剖面图
Fig.1 Sub-sag classification and distribution in petroliferous sags, and NW-SE-trending structural profile of the Erlian Basin
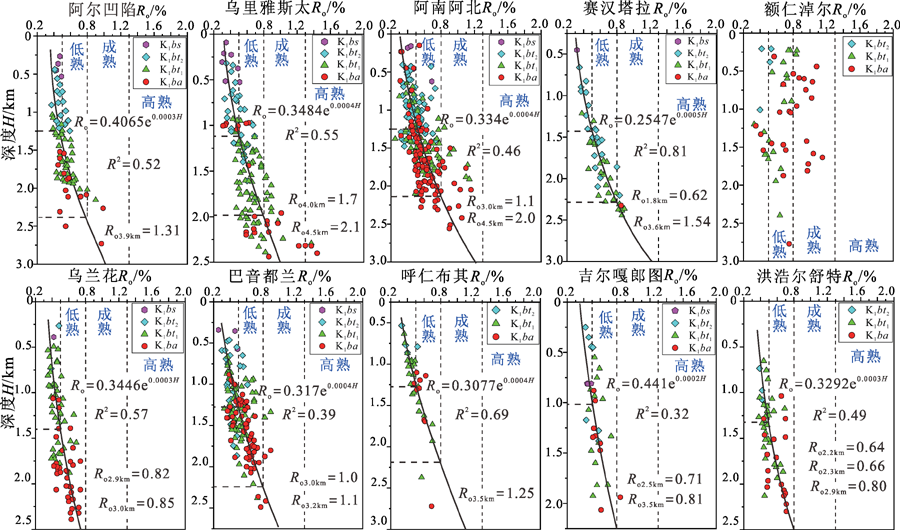
图3 二连盆地含油气凹陷下白垩统烃源岩Ro-深度关系图
Fig.3 Relationship between vitrinite reflectance and depth of the Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous source rocks in petroliferous sags of the Erlian Basin
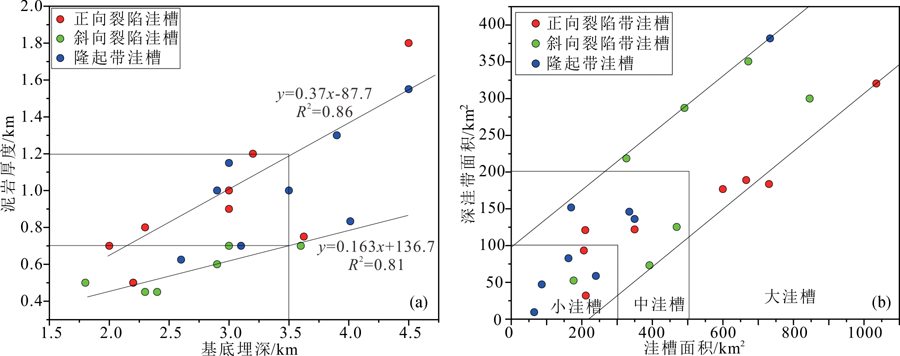
图4 二连盆地含油气凹陷洼槽古生界顶面(Tg)最大埋深与阿尔善组、腾一段烃源岩最大总厚度(a)、洼槽面积与深洼带面积(b)的相关性
Fig.4 Correlations between the maximum buried depth of the Paleozoic surface (Tg) and the maximum total thickness of source rock in the Aershan and Tenggeer (1st member) Formations (a), as well as area of sub-sags and deep sub-sags (b) in petroliferous sags of the Erlian Basin
| 洼槽名称 | 基底类型 | Pr/Ph 均值 | γ/C30H 均值 | 基底埋深 /m | 泥岩厚度 /m | 探明储量/ 104t | 最大生油强度/ (104t/km2) | 生油量/ 108t | 评价指数 Y | 评价 级别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 善南 | 正向裂陷 | 0.85 | 0.30 | 4 500 | 1 800 | 9 859 | 750 | 18.71 | 1.000 | A |
| 蒙西 | 正向裂陷 | 1.20 | 0.21 | 2 000 | 700 | 0 | / | 0.29 | / | C |
| 莎东 | 正向裂陷 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 2 300 | 800 | 0 | / | 0.93 | / | C |
| 阿北 | 正向裂陷 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 3 000 | 1 000 | 398 | 300 | 5.11 | 0.324 | B |
| 巴南 | 正向裂陷 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 3 200 | 1 200 | 2 249 | 500 | 10.49 | 0.603 | A |
| 巴北 | 正向裂陷 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 3 000 | 900 | 0 | 200 | 4.57 | 0.253 | B |
| 淖东 | 正向裂陷 | 0.53 | 0.20 | 3 625 | 750 | 1 970 | 320 | 7.31 | 0.405 | A |
| 敖包 | 正向裂陷 | 2 200 | 500 | 0 | / | 0.62 | / | C | ||
| 乌南 | 隆起 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 4 000 | 800 | 2 287 | 720 | 5.59 | 0.563 | A |
| 乌中 | 隆起 | 4 500 | 1 550 | 0 | 300 | 8.30 | 0.426 | A | ||
| 乌兰花南 | 隆起 | 0.78 | 0.20 | 3 000 | 1 150 | 162.7 | 350 | 5.82 | 0.373 | B |
| 乌兰花北 | 隆起 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 2 900 | 1 000 | 0 | 100 | 1.11 | 0.089 | C |
| 呼南 | 隆起 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 3 500 | 1 000 | 0 | 400 | 8.85 | 0.497 | A |
| 阿尔中 | 隆起 | 1.42 | 0.06 | 3 900 | 1 300 | 3 758 | 680 | 5.40 | 0.536 | A |
| 阿尔北 | 隆起 | 0.89 | 0.10 | 3 100 | 700 | 0 | 420 | 4.24 | 0.360 | B |
| 阿尔南 | 隆起 | 1.35 | 0.05 | 2 600 | 625 | 0 | 560 | 1.75 | 0.355 | B |
| 赛东 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.91 | 0.11 | 3 600 | 700 | 1 038.3 | 300 | 8.11 | 0.420 | A |
| 赛北 | 斜向裂陷 | 1.03 | 0.08 | 1 800 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 1.59 | 0.051 | C |
| 宝饶 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.80 | 0.13 | 3 000 | 700 | 2 755 | 450 | 6.55 | 0.450 | A |
| 吉东 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 2 400 | 450 | 0 | 30 | 1.30 | 0.058 | C |
| 洪中 | 斜向裂陷 | 1.08 | 0.10 | 2 900 | 600 | 200 | 240 | 6.81 | 0.346 | B |
| 洪西 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.71 | 0.11 | 2 200 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 1.50 | 0.048 | C |
| 洪东 | 斜向裂陷 | 1.14 | 0.13 | 2 300 | 450 | 2 026 | 160 | 4.13 | 0.218 | B |
表1 二连盆地含油气凹陷洼槽地质特征及生烃能力综合评价表
Table 1 Comprehensive evaluation of geological characteristics and hydrocarbon generation capacity of sub-sags in petroliferous sags of the Erlian Basin
| 洼槽名称 | 基底类型 | Pr/Ph 均值 | γ/C30H 均值 | 基底埋深 /m | 泥岩厚度 /m | 探明储量/ 104t | 最大生油强度/ (104t/km2) | 生油量/ 108t | 评价指数 Y | 评价 级别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 善南 | 正向裂陷 | 0.85 | 0.30 | 4 500 | 1 800 | 9 859 | 750 | 18.71 | 1.000 | A |
| 蒙西 | 正向裂陷 | 1.20 | 0.21 | 2 000 | 700 | 0 | / | 0.29 | / | C |
| 莎东 | 正向裂陷 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 2 300 | 800 | 0 | / | 0.93 | / | C |
| 阿北 | 正向裂陷 | 0.63 | 0.20 | 3 000 | 1 000 | 398 | 300 | 5.11 | 0.324 | B |
| 巴南 | 正向裂陷 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 3 200 | 1 200 | 2 249 | 500 | 10.49 | 0.603 | A |
| 巴北 | 正向裂陷 | 0.56 | 0.16 | 3 000 | 900 | 0 | 200 | 4.57 | 0.253 | B |
| 淖东 | 正向裂陷 | 0.53 | 0.20 | 3 625 | 750 | 1 970 | 320 | 7.31 | 0.405 | A |
| 敖包 | 正向裂陷 | 2 200 | 500 | 0 | / | 0.62 | / | C | ||
| 乌南 | 隆起 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 4 000 | 800 | 2 287 | 720 | 5.59 | 0.563 | A |
| 乌中 | 隆起 | 4 500 | 1 550 | 0 | 300 | 8.30 | 0.426 | A | ||
| 乌兰花南 | 隆起 | 0.78 | 0.20 | 3 000 | 1 150 | 162.7 | 350 | 5.82 | 0.373 | B |
| 乌兰花北 | 隆起 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 2 900 | 1 000 | 0 | 100 | 1.11 | 0.089 | C |
| 呼南 | 隆起 | 0.41 | 0.45 | 3 500 | 1 000 | 0 | 400 | 8.85 | 0.497 | A |
| 阿尔中 | 隆起 | 1.42 | 0.06 | 3 900 | 1 300 | 3 758 | 680 | 5.40 | 0.536 | A |
| 阿尔北 | 隆起 | 0.89 | 0.10 | 3 100 | 700 | 0 | 420 | 4.24 | 0.360 | B |
| 阿尔南 | 隆起 | 1.35 | 0.05 | 2 600 | 625 | 0 | 560 | 1.75 | 0.355 | B |
| 赛东 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.91 | 0.11 | 3 600 | 700 | 1 038.3 | 300 | 8.11 | 0.420 | A |
| 赛北 | 斜向裂陷 | 1.03 | 0.08 | 1 800 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 1.59 | 0.051 | C |
| 宝饶 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.80 | 0.13 | 3 000 | 700 | 2 755 | 450 | 6.55 | 0.450 | A |
| 吉东 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.83 | 0.13 | 2 400 | 450 | 0 | 30 | 1.30 | 0.058 | C |
| 洪中 | 斜向裂陷 | 1.08 | 0.10 | 2 900 | 600 | 200 | 240 | 6.81 | 0.346 | B |
| 洪西 | 斜向裂陷 | 0.71 | 0.11 | 2 200 | 500 | 0 | 0 | 1.50 | 0.048 | C |
| 洪东 | 斜向裂陷 | 1.14 | 0.13 | 2 300 | 450 | 2 026 | 160 | 4.13 | 0.218 | B |
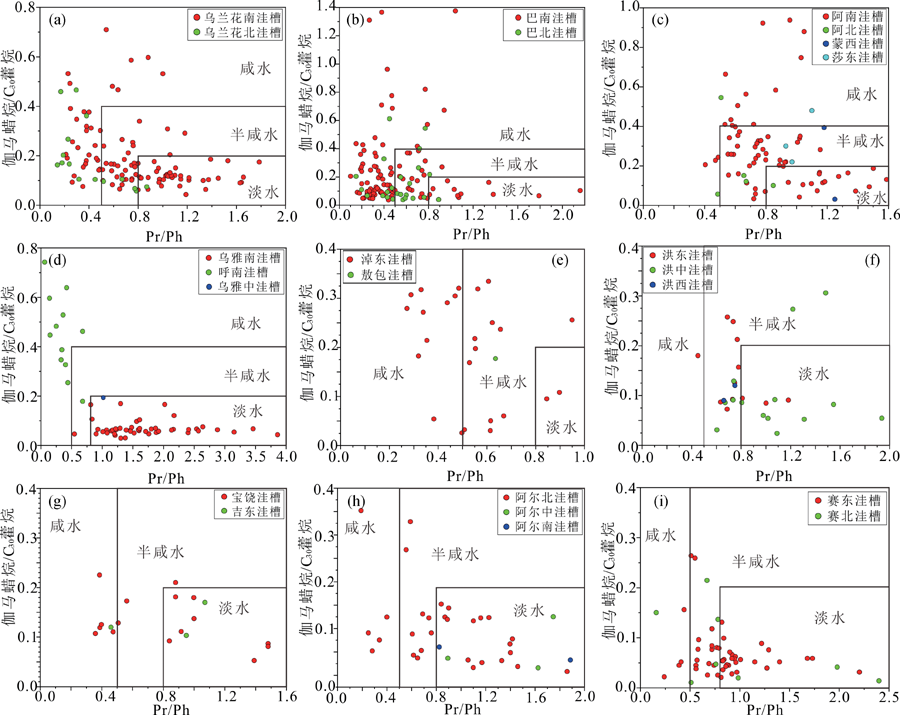
图5 二连盆地含油气洼槽阿尔善组及腾一段烃源岩抽提物的姥鲛烷/植烷与伽马蜡烷/C30藿烷指数散点图
Fig.5 Scatter plot between the index of the pristane/phytane and gammacerane/C30-hopane in the extract of source rock of the Aershan and Tenggeer (1st member) Formations in petroliferous sub-sags of the Erlian Basin
| 类型 | Ro/% | 埋深/m | 深洼面积/km2 | Pr/Ph | γ/C31H | 洼槽归类 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高熟型 | 大型半咸水洼槽 | 0.5~2.0 | >3 500 | >200 | 0.5~0.8 | 1.0~2.5 | 阿南 |
| 大型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 乌中、赛东 | ||||
| 中型半咸水洼槽 | 100~200 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 淖东 | |||
| 中型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 乌南、阿尔中 | ||||
| 成熟型 | 大型淡水洼槽 | 0.5~1.3 | 2 500~3 500 | >200 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 洪东、洪中 |
| 中型咸水洼槽 | 100~200 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 呼南、巴南、阿北 | |||
| 中型半咸水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 宝饶 | ||||
| 小型咸水洼槽 | <100 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 巴北、乌兰花南 | |||
| 小型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 阿尔北、阿尔南 | ||||
| 低熟型 | 大型淡水洼槽 | 0.4~0.8 | <2 500 | >200 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 赛北 |
| 中型淡水洼槽 | 100~200 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 吉东 | |||
| 小型咸水洼槽 | <100 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 乌兰花北 | |||
| 小型半咸水洼槽 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 敖包、莎东、蒙西 | ||||
| 小型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 洪西 | ||||
表2 二连盆地下白垩统含油气凹陷的洼槽综合分类表
Table 2 Integrated sub-sag classification of the Lower Cretaceous petroliferous sags in the Erlian Basin
| 类型 | Ro/% | 埋深/m | 深洼面积/km2 | Pr/Ph | γ/C31H | 洼槽归类 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高熟型 | 大型半咸水洼槽 | 0.5~2.0 | >3 500 | >200 | 0.5~0.8 | 1.0~2.5 | 阿南 |
| 大型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 乌中、赛东 | ||||
| 中型半咸水洼槽 | 100~200 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 淖东 | |||
| 中型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 乌南、阿尔中 | ||||
| 成熟型 | 大型淡水洼槽 | 0.5~1.3 | 2 500~3 500 | >200 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 洪东、洪中 |
| 中型咸水洼槽 | 100~200 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 呼南、巴南、阿北 | |||
| 中型半咸水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 宝饶 | ||||
| 小型咸水洼槽 | <100 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 巴北、乌兰花南 | |||
| 小型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 阿尔北、阿尔南 | ||||
| 低熟型 | 大型淡水洼槽 | 0.4~0.8 | <2 500 | >200 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 赛北 |
| 中型淡水洼槽 | 100~200 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 吉东 | |||
| 小型咸水洼槽 | <100 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 乌兰花北 | |||
| 小型半咸水洼槽 | <0.5 | >2.5 | 敖包、莎东、蒙西 | ||||
| 小型淡水洼槽 | >0.8 | <1.0 | 洪西 | ||||
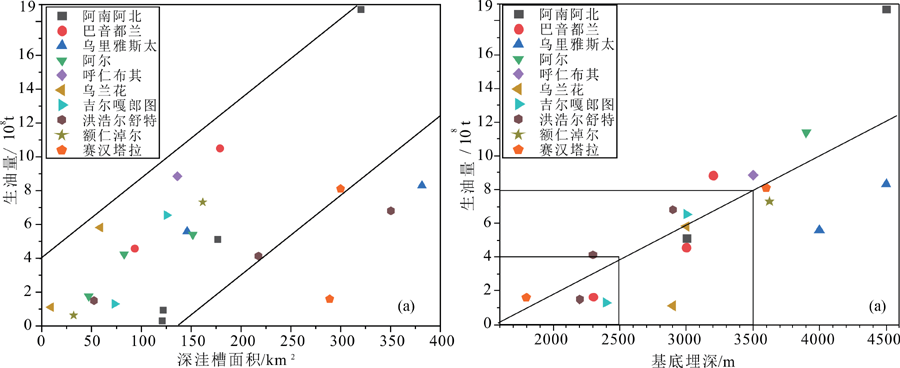
图6 二连盆地含油气凹陷洼槽深洼槽面积/基底埋深与生油量的相关关系
Fig.6 Correlations between oil generating quantity and area of deep sub-sags/maximum buried depth of the Paleozoic sub-sag surface in the petroliferous sags of the Erlian Basin
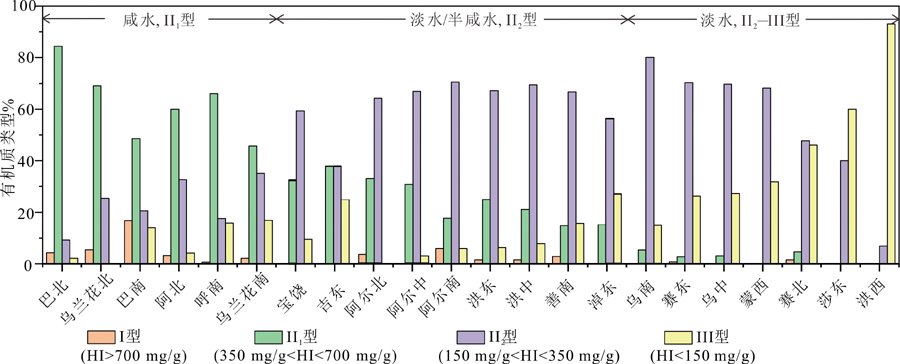
图7 二连盆地含油气洼槽阿尔善组及腾一段两套烃源岩的HI指数类型比例统计图
Fig.7 Statistics chart of hydrocarbon index types for source rock in the Aershan and Tenggeer (1st member) Formations of sub-sags in the petroliferous sags of the Erlian Basin
| [1] | 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 王权, 等. 陆相断陷盆地洼槽聚油理论及其应用--以渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷和二连盆地为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1):18-24. |
| [2] | 费宝生. 从二连盆地看东北亚地区裂谷盆地群油气勘探[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2002, 21(3):7-11. |
| [3] | 张文朝, 祝玉衡, 姜冬华, 等. 二连盆地“洼槽”控油规律与油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 1997, 18(4):25-31. |
| [4] | 祝玉衡, 张文朝. 二连盆地层序地层样式及油气意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1999, 26(4):49-53. |
| [5] | 谭洪, 陈庆, 费宝生. 二连盆地中生代裂谷型断陷油气勘探目标[J]. 勘探家, 1998, 3(4):26-31. |
| [6] | 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 王权, 等. 陆相断陷盆地洼槽聚油理论及其应用--以渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷和二连盆地为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1):18-24. |
| [7] | 刘池洋, 赵俊峰, 马艳萍, 等. 富烃凹陷特征及其形成研究现状与问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(1):75-88. |
| [8] | 易士威. 二连盆地凹陷结构与成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(2):8-12. |
| [9] | 赵贤正, 金凤鸣. 断陷斜坡油气藏形成分布与精细勘探[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. |
| [10] | 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 漆家福, 等. 二连盆地早白垩世复式断陷构造类型及其石油地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(7):1289-1298. |
| [11] | 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 王权, 等. 华北探区断陷洼槽区油气藏形成与分布[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2008, 13(2):1-8. |
| [12] | 王冰. 二连中生代盆地群构造地质特征与油气[J]. 石油实验地质, 1990, 12(1):8-20. |
| [13] | 杨涛, 徐树宝, 方杰. 二连裂谷系含油气系统特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1996, 23(6):16-19. |
| [14] | 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 张以明, 等. 二连盆地富油凹陷形成演化与油气富集[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2018. |
| [15] | 杜金虎, 易士威, 雷怀玉, 等. 二连盆地岩性地层油藏形成条件与油气分布规律[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2004(3):9-13+6. |
| [16] | 赵文智, 方杰. 不同类型断陷湖盆岩性-地层油气藏油气富集规律--以冀中坳陷和二连盆地岩性-地层油气藏对比为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(2):129-134. |
| [17] | 方杰, 侯凤香, 孙彤彤, 等. 二连裂谷系下白垩统烃源岩有机质热演化特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1998, 19(6):476-479. |
| [18] | 漆家福, 赵贤正, 李先平, 等. 二连盆地早白垩世断陷分布及其与基底构造的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3):118-128. |
| [19] | 王飞宇. 二连盆地烃源灶精细表征[R]. 任丘: 中国石油华北油田公司勘探开发研究院, 2019. |
| [20] | 曹兰柱. 富油凹陷油气富集规律与规模目标研究[R]. 任丘: 中国石油华北油田公司勘探开发研究院, 2019. |
| [21] | 侯读杰, 冯子辉. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011. |
| [22] | 叶爱娟, 朱扬明. 柴达木盆地第三系咸水湖相生油岩古沉积环境地球化学特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2006, 37(5):472-480. |
| [23] | HAO F, ZHOU X H, ZHU Y M, et al. Lacustrine source rock deposition in response to co-evolution of environments and organisms controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(4):323-339. |
| [24] | BECHTEL A, JIA J L, STROBL S, et al. Palaeoenvironmental conditions during deposition of the Upper Cretaceous oil shalesequences in the Songliao Basin (NE China): Implications from geochemical analysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2012, 46:76-95. |
| [25] | 李洪波, 张敏, 张春明, 等. 柴达木盆地西部南区第三系烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(4):519-523. |
| [26] | 钟剑鸣, 陈孔全, 沈均均, 等. 潜江凹陷毛场-马王庙地区新沟嘴组下段烃源岩地球化学特征[J]. 中国锰业, 2018, 36(2):56-61. |
| [27] | 宋一涛, 吴庆宇, 周文. 未熟低熟油的形成与成因机制[M]. 北京: 石油大学出版社, 2004. |
| [28] | 王会来, 高先志, 杨德相, 等. 二连盆地巴音都兰凹陷下白垩统湖相云质岩成因研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(3):560-567. |
| [29] | 王会来, 高先志, 杨德相, 等. 二连盆地下白垩统湖相云质岩分布及控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1):163-172. |
| [30] | 蒋有录, 苏圣民, 刘华, 等. 渤海湾盆地新生界沉积洼陷类型及与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(6):635-645. |
| [31] | 王权, 王建, 马学峰, 等. 华北探区第四次资源评价[R]. 任丘: 中国石油华北油田公司勘探开发研究院, 2016. |
| [32] | 杨德相, 蒋有录, 赵志刚, 等. 冀中坳陷洼槽地质特征及其与油气分布关系[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(5):990-1001. |
| [33] | 程顶胜, 刘松, 吴培红. 塔里木盆地石炭系生烃潜力的模糊数学综合评价[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(1):34-39. |
| [34] | 郭长春, 金强, 姚军. 用模糊数学方法评价烃源岩[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(4):50-53. |
| [35] | 魏巍, 朱筱敏, 朱世发, 等. 二连盆地阿南凹陷下白垩统腾格尔组湖相云质岩成因[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(2):258-272. |
| [36] | WEI W, ZHU X, HE M, et al. Original sediment composition of the Lower Cretaceous lacustrine tight-oil mudstone and influences on diagenesis and organic matter content, the Erennaoer Sag in Erlian Basin, NE China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 94:131-143. |
| [37] | 蓝宝锋, 杨克兵, 彭传利, 等. 二连盆地阿南凹陷致密油勘探潜力分析[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2014, 7(2):9-12. |
| [38] | 邢雅文, 冯赫青, 尹峥, 等. 二连盆地额仁淖尔凹陷云质岩致密油成藏特征与勘探潜力[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(4):159-168. |
| [39] | 曹青赟. 二连盆地下白垩统腾格尔组及阿尔善组致密油资源评价[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016. |
| [1] | 李志鹏, 余麒麟, 昝灵, 余文端, 张枝焕. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷阜二段不同岩性烃源岩的地球化学特征及生烃潜力对比[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1345-1357. |
| [2] | 张韩静, 李素梅, 高永进, 张林, 柯昌炜. 准噶尔盆地东南缘二叠系芦草沟组烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1538-1550. |
| [3] | 吕永华, 苗爱生, 王果, 李曙光, 高峥嵘. 二连盆地那仁地区铀成矿地质条件分析及找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 662-671. |
| [4] | 李杰豪, 侯读杰, 曹兰柱, 吴飘, 赵喆, 马潇潇. 二连盆地赛汉塔拉凹陷腾二段低熟油地球化学特征和油源对比[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 315-325. |
| [5] | 王元, 李贤庆, 王刚, 徐新德, 刘海钰. 莺琼盆地中新统海相羟源岩地球化学特征及生经潜力评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 500-510. |
| [6] | 王会来,高先志,杨德相,李浩,张志遥,王旭. 二连盆地下白垩统湖相云质岩分布及控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1): 163-172. |
| [7] | 屈晓艳,杨明慧,罗晓华,丁超,周多,龚婷,杨光. 二连盆地赛汉塔拉凹陷伸展构造特征及其控藏作用[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1023-1032. |
| [8] | 史晓颖 张传恒 蒋干清 刘娟 王议 刘典波. 华北地台中元古代碳酸盐岩中的微生物成因构造及其生烃潜力[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(5): 669-682. |
| [9] | 刘震,刘俊榜,高先志,辛海燕,肖伟,徐兆辉. 内蒙古二连盆地岩性油藏形成的相对早期性特征[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(3): 524-531. |
| [10] | 刘震,郝琦,赵贤正,张以明,易士威,杨德相. 内蒙古二连盆地岩性油气富集因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(4): 613-620. |
| [11] | 史淑玲,张海峰,张庆德,王玉生. 半地堑湖盆沉积体系的地球物理响应特征与勘探意义——以二连盆地乌里雅斯太断陷中次洼为例[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(Suppl): 101-104. |
| [12] | 何瑞武,姜在兴,郭增强,邱隆伟. 临南洼陷沙四上亚段烃源岩的生烃潜力研究[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(Suppl): 187-192. |
| [13] | 刘震,赵阳,肖伟,杜金虎,张以民,易士威,刘俊榜. 内蒙古二连盆地岩性油藏形成与分布的优势性特征[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(4): 570-578. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||