



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (05): 1311-1322.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.077
许可可1,2( ), 杨振京1(
), 杨振京1( ), 宁凯1, 韩强强3, 毕志伟1, 赵楠楠4
), 宁凯1, 韩强强3, 毕志伟1, 赵楠楠4
收稿日期:2021-04-20
修回日期:2021-06-03
出版日期:2021-10-10
发布日期:2021-11-04
通讯作者:
杨振京
作者简介:杨振京,男,博士,研究员,1966年出生,古生物学与地层学专业,主要从事孢粉及相关地层研究。Email: yangzhenjing1966@163.com。基金资助:
XU Keke1,2( ), YANG Zhenjing1(
), YANG Zhenjing1( ), NING Kai1, HAN Qiangqiang3, BI Zhiwei1, ZHAO Nannan4
), NING Kai1, HAN Qiangqiang3, BI Zhiwei1, ZHAO Nannan4
Received:2021-04-20
Revised:2021-06-03
Online:2021-10-10
Published:2021-11-04
Contact:
YANG Zhenjing
摘要:
银川盆地位于东亚季风与西风带的交界带,地层沉积物记录着气候环境的演变信息。通过对银川盆地LS01钻孔沉积物进行光释光定年、粒度分析以及端元分析重建了该地区MIS6—MIS5时期的气候演变序列。结果表明,端元分析得到4个有具体环境指示意义的端元Em1—Em4:Em1代表了水动力较弱的弱流水或湖沼相沉积;Em2代表了水动力较强的河流沉积;Em3和Em4可指代区域构造抬升事件。气候演变分为6个阶段:150~137 ka(MIS6),银川盆地气候冷干,出现两次构造抬升事件;137~110 ka(MIS5),气候整体较为暖湿,期间有3次暖事件a1(137~129 ka)、a2(124~120 ka)和a3(118~111 ka);110~107 ka(MIS5),气候转向冷干;107~102 ka(MIS5),气候由冷转暖,出现冷事件b1(106~104 ka),整体偏暖湿;102~87 ka(MIS5),气候较冷干;87~75 ka(MIS5),出现冷事件b2(87~84 ka),但整体偏暖湿。该区域MIS6—MIS5阶段气候变化主要受夏季太阳辐射和岁差驱动。
中图分类号:
许可可, 杨振京, 宁凯, 韩强强, 毕志伟, 赵楠楠. 基于端元法的银川盆地MIS6—MIS5气候变化探究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1311-1322.
XU Keke, YANG Zhenjing, NING Kai, HAN Qiangqiang, BI Zhiwei, ZHAO Nannan. MIS6-MIS5 Climate Change of Yinchuan Basin Based on End-member Method[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1311-1322.
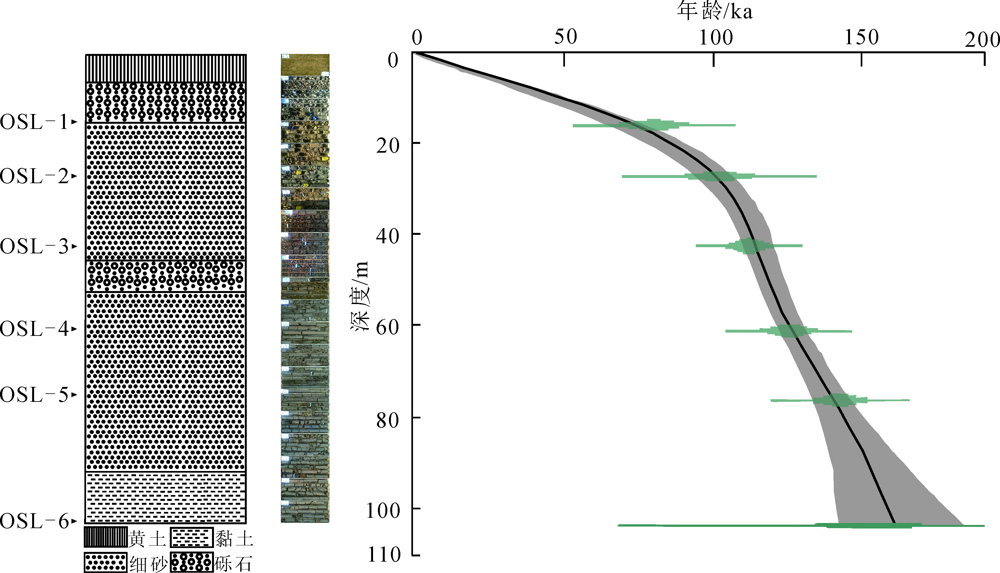
图2 LS01钻孔剖面岩性及年龄深度关系(图中线条为线性内插结果,虚影为置信区间)
Fig.2 Lithology and age-depth relationship of borehole LS01(the line showing the result of linear interpolation, and the virtual shadow showing the confidence interval)
| 样号 | α系数 | 深度/m | U/10-6 | Th/10-6 | K/% | 含水率/% | 剂量率/(Gy/ka) | 等效剂量/Gy | 年龄/ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL-1 | 0.04±0.02 | 15.3 | 2.71 | 14.38 | 2.17 | 25±5 | 3.78±0.21 | 300.64±11.84 | 79.58±5.42 |
| OSL-2 | 0.04±0.02 | 26.5 | 1.95 | 11.24 | 1.84 | 29±5 | 2.91±0.16 | 296.12±11.32 | 101.72±6.67 |
| OSL-3 | 0.04±0.02 | 41.7 | 1.90 | 11.33 | 1.72 | 28±5 | 2.35±0.07 | 262.22±2.11 | 111.58±3.49 |
| OSL-4 | 0.04±0.02 | 60.2 | 2.55 | 10.00 | 1.75 | 20±5 | 2.61±0.09 | 325.65±1.61 | 124.91±4.17 |
| OSL-5 | 0.04±0.02 | 75.4 | 1.83 | 7.71 | 1.74 | 29±5 | 2.12±0.07 | 301.41±1.32 | 142.17±4.60 |
| OSL-6 | 0.04±0.02 | 102.8 | 2.17 | 4.92 | 2.13 | 20±5 | 2.93±0.15 | 445.38±43.82 | 151.85±16.81 |
表1 LS01孔光释光测年结果及参数
Table 1 OSL ages and dating parameters of borehole LS01
| 样号 | α系数 | 深度/m | U/10-6 | Th/10-6 | K/% | 含水率/% | 剂量率/(Gy/ka) | 等效剂量/Gy | 年龄/ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OSL-1 | 0.04±0.02 | 15.3 | 2.71 | 14.38 | 2.17 | 25±5 | 3.78±0.21 | 300.64±11.84 | 79.58±5.42 |
| OSL-2 | 0.04±0.02 | 26.5 | 1.95 | 11.24 | 1.84 | 29±5 | 2.91±0.16 | 296.12±11.32 | 101.72±6.67 |
| OSL-3 | 0.04±0.02 | 41.7 | 1.90 | 11.33 | 1.72 | 28±5 | 2.35±0.07 | 262.22±2.11 | 111.58±3.49 |
| OSL-4 | 0.04±0.02 | 60.2 | 2.55 | 10.00 | 1.75 | 20±5 | 2.61±0.09 | 325.65±1.61 | 124.91±4.17 |
| OSL-5 | 0.04±0.02 | 75.4 | 1.83 | 7.71 | 1.74 | 29±5 | 2.12±0.07 | 301.41±1.32 | 142.17±4.60 |
| OSL-6 | 0.04±0.02 | 102.8 | 2.17 | 4.92 | 2.13 | 20±5 | 2.93±0.15 | 445.38±43.82 | 151.85±16.81 |
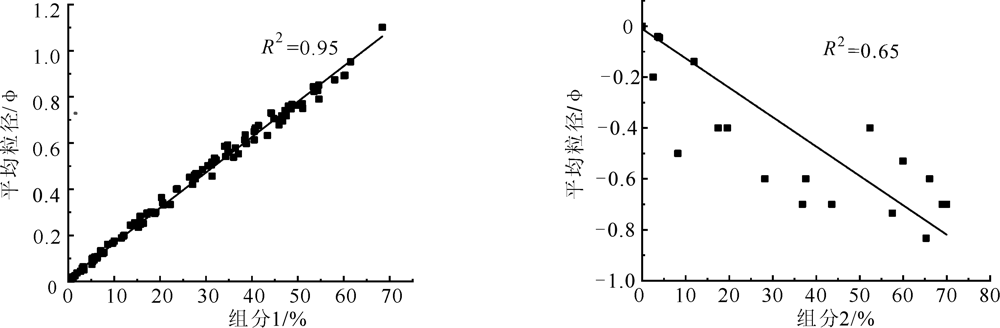
图7 粒级145~273 μm(组分1)和1 240~1 596 μm(组分2)含量与各自平均粒径相关性分析
Fig.7 Correlation analysis of 145-273 μm and 1 240-1 596 μm fractions with the mean of each grain size
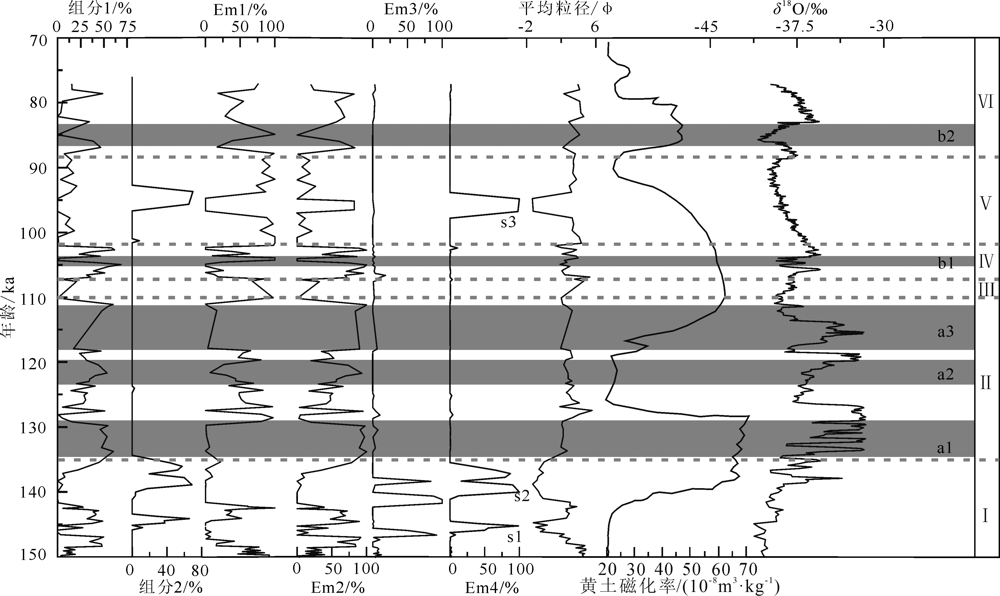
图8 LS01钻孔剖面敏感粒级、端元组分和平均粒径与黄土磁化率、δ18O的对比 s1—s3.构造抬升事件;a1—a3.暖事件;b1—b3.冷事件;Ⅰ—Ⅵ.划分的气候阶段。下文同
Fig.8 Comparison of sensitive grain size, end-members and average grain size of borehole LS01 with loess magnetic susceptibility and δ18O values
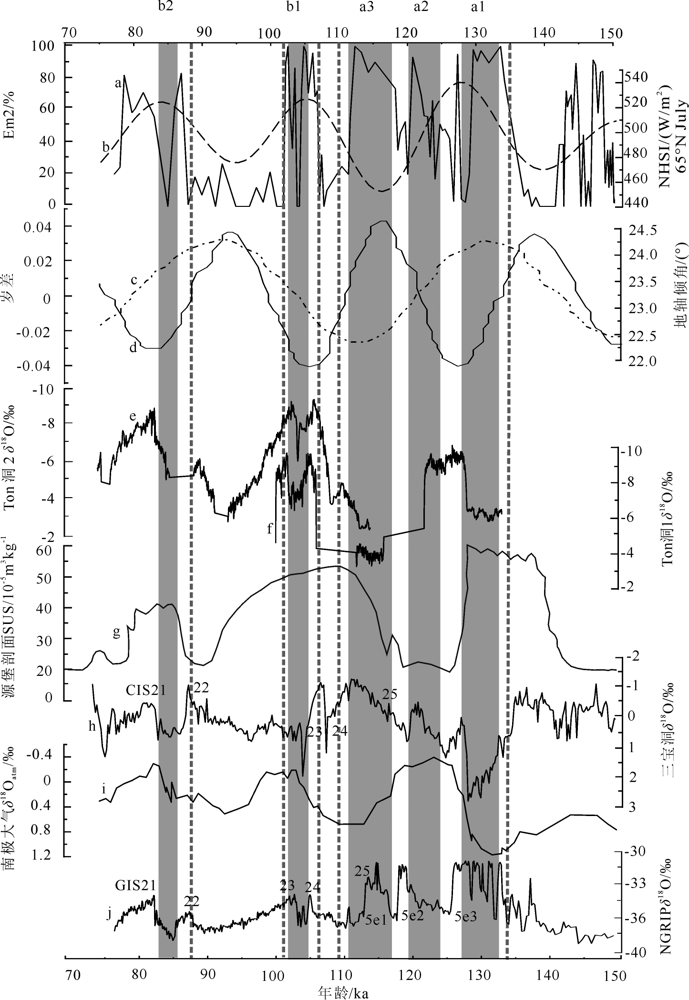
图9 Em2曲线和其他气候记录对比 a.Em2曲线;b.NHSI,北半球夏季太阳辐射[46];c.岁差[49];d.地轴倾角[49];e.中亚乌兹别克斯坦Ton洞2石笋记录[45];f.中亚乌兹别克斯坦Ton洞1石笋记录[45];g.中国源堡黄土剖面[35];h.神农架三宝洞石笋记录[43];i.NGRIP δ18O,格陵兰冰心氧同位素记录,南极大气氧同位素记录[47];j.格陵兰冰心氧同位素记录[36]
Fig.9 Comparison of Em2 curve and other climatic records
| [1] | 赵红梅, 刘林敬, 赵华, 等. 滹沱河古河道剖面粒度参数特征及沉积环境[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):485-492. |
| [2] | 殷志强, 秦小光, 吴金水, 等. 湖泊沉积物粒度多组分特征及其成因机制研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(2):161-169. |
| [3] | 孙东怀, 安芷生, 苏瑞侠, 等. 古环境中沉积物粒度组分分离的数学方法及其应用[J]. 自然科学进展, 2001, 11(3):47-54. |
| [4] | MCMANUS J. Grain size determination and interpretation[M]// TRUCKER M. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford: Backwell, 1988:63-85. |
| [5] | 陈洪云, 孙有斌. 黄土高原风尘沉积的物质来源研究:回顾与展望[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(5):892-900. |
| [6] | 周建超, 吴敬禄, 曾海鳌. 新疆乌伦古湖沉积物粒度特征揭示的环境信息[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6):1158-1165. |
| [7] |
SUN D H, BLOEMENDALC J, READ D K, et al. Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments, and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(3):263-277.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 陈国成, 郑洪波, 李建如, 等. 南海西部陆源沉积粒度组成的控制动力及其反映的东亚季风演化[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(23):2768-2776. |
| [9] | 商圣潭, 钟巍, 魏志强, 等. 南岭东部定南大湖沉积物粒度敏感组分及末次冰消期环境记录[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(2):310-318. |
| [10] |
孔霄, 来风兵, 陈蜀江, 等. 别里库姆沙漠胡杨回涡沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(3):657-664.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.057.
DOI |
| [11] | 何继山, 梁杏, 李静, 等. 天津滨海平原区深孔沉积物环境敏感粒度提取及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2015, 40(7):1215-1225. |
| [12] |
WELTJE G J. End-member modeling of compositional data: Numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem[J]. Mathematical Geology, 1997, 29(4):503-549.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 张威, 成然, 马瑞丰, 等. 辽南地区金州西团瓢湖沼相沉积物粒度化学特征及环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3):195-207. |
| [14] | 王兆夺, 黄春长, 周亚利, 等. 关中东部全新世黄土—古土壤序列粒度组分变化特征及古气候意义[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(3):293-304. |
| [15] | 程良清, 宋友桂, 李越, 等. 粒度端元模型在新疆黄土粉尘来源与古气候研究中的初步应用[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(6):1148-1156. |
| [16] | 牟雪松, 马俊, 王永达, 等. 粒度分布的端元建模分析及检验:以“吉兰泰—河套”盆地西部DK-12钻孔晚第四纪沉积物为例[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(3):489-500. |
| [17] | 童国榜. 银川盆地第四纪地层学研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 1998, 22(1):42-51. |
| [18] | 杨振京, 郑宏瑞, 童国榜, 等. 银川盆地中更新世以来的孢粉植物群古气候旋回探讨[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 2001, 31(3):213-216. |
| [19] | 刘平贵, 范淑贤, 李雪菊. 银川盆地第四纪地球化学元素特征及沉积环境[J]. 地质力学学报, 2000, 6(4):43-50,94. |
| [20] | 孙爱芝, 韩晓丽, 强杨, 等. 海原剖面12.5~7.2 kaBP期间化学元素与粒度组成的古环境意义[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2011, 25(7):146-149. |
| [21] | 林畅松. 贺兰拗拉槽盆地充填演化分析[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995:1-143. |
| [22] |
周特先. 宁夏构造地貌格局及其形成与发展[J]. 地理学报, 1985, 40(3):215-224.
DOI |
| [23] | 熊毅, 席承藩. 华北平原第四纪沉积物的性质及其演变[J]. 科学通报, 1958, 1(6):61-69. |
| [24] | 吴正. 风沙地貌与治沙工程学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003:1-448. |
| [25] |
PATERSON G, HESLOP D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16:4494-4506.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
BLAAUW M. Methods and code for “classical” age-modeling of radiocarbon sequences[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2010, 5(5):512-518.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 鹿化煜, 安芷生. 黄土高原黄土粒度组成的古气候意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 1998, 28(3):87-92. |
| [28] | 肖尚斌, 李安春. 东海内陆架泥区沉积物的环境敏感粒度组分[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, 23(1):122-129. |
| [29] | 葛本伟, 刘安娜. 天山北麓黄土沉积的光释光年代学及环境敏感粒度组分研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(2):110-116. |
| [30] |
DIETZE E, MAUSSION F, AHLBORN M, et al. Sediment transport processes across the Tibetan Plateau inferred from robust grain-size end members in lake sediments[J]. Climate of the Past, 2014, 10(1):91-106.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LI Z J, SUN D H, CHEN F H, et al. Chronology and paleoen-vironmental records of a drill core in the central Tengger Desert of China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 85(1):85-98.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 成都地质学院陕北队. 沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978:1-147. |
| [33] | 邢成起, 尹功明, 丁国瑜, 等. 黄河黑山峡阶地的砾石Ca膜厚度与粗碎屑沉积地貌面形成年代的测定[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(3):167-172. |
| [34] | 蒋复初, 傅建利, 王书兵, 等. 关于黄河贯通三门峡的时代[J]. 地质力学学报, 2005, 11(4):293-301. |
| [35] | 曹继秀, 张宇田. 塬堡黄土剖面15万年以来磁化率气候记录及黄土磁化率时空特征[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 33(1):124-132. |
| [36] |
ANDERSEN K K, AZUMA N, BARNOLA J M, et al. High-resolution record of Northern Hemisphere climate extending into the last interglacial period[J]. Nature, 2004, 431:147-151.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 杨星辰, 叶培盛, 蔡茂堂, 等. 150ka以来内蒙古河套古大湖沉积物粒度记录的湖泊水位变化[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(6):1043-1050. |
| [38] | 王兆荣, 胡秀章, 周德昌, 等. 北京周口店石笋稳定同位素古气候探讨[J]. 科技通报, 1997, 13(4):21-25. |
| [39] | 温仰磊. 天山北麓黄土记录的末次间冰期以来气候变化初探[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2015:1-49. |
| [40] | 杜恕环, 赵欣楠, 李保生, 等. 萨拉乌苏河流域MGS5层段CaCO3记录的末次间冰期东亚季风与沙漠环境演化[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(11):1187-1193. |
| [41] | 刘宇飞, 李保生, 杨艺, 等. 末次间冰期我国半干旱盆地Rb、Sr的迁移聚集规律与环境演变——以萨拉乌苏河流域米浪沟湾剖面研究结果为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(3):341-344. |
| [42] | 赵希涛, 朱大岗, 严富华, 等. 西藏纳木错末次间冰期以来的气候变迁与湖面变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2003, 23(1):41-52. |
| [43] |
WANG Y J, HAI C, EDWARDS R L, et al. Millennial-and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224,000 years[J]. Nature, 2008, 451:1090-1093.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 管清玉, 潘保田, 高红山, 等. 高分辨率黄土剖面记录的末次间冰期东亚季风的不稳定性特征[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2007, 37(1):86-93. |
| [45] |
CHENG H, SPTL C, BREITENBACH S F M, et al. Climate variations of Central Asia on orbital to millennial timescales[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:36975.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
BERGER A, LOUTRELOUTRE M F. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1991, 10(4):297-317.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
PETIT J R, JOUZEL J, RAYNAUD D, et al. Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420,000 years from the Vostok Ice Core[J]. Nature, 1999, 399:429-436.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 李新周, 刘晓东. 最近15万年来东亚古气候变化对日射响应的瞬变模拟[J]. 地球环境学报, 2012, 3(2):801-809. |
| [49] |
BERGER A. Long-term variations of caloric insolation resulting from the Earth’s orbital elements[J]. Quaternary Research, 1978, 9(2):139-167.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘晓鸿. 克什克腾世界地质公园晚第四纪黄土沉积特征及其古气候意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 821-833. |
| [2] | 安国英, 郭兆成, 叶佩. 云南大理地区1989—2019年期间气候变化及对洱海水质的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 406-417. |
| [3] | 王雪木, 瞿洪宝, 熊元凯, 吕琳, 胡克. 海南昌化江入海口底表沉积物粒度特征及输运趋势[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 88-95. |
| [4] | 王香莲, 黄庭, 肖河, 吴代赦, 张小龙, 程胜高, 毛绪美. 东北哈尼泥炭沉积物磁化率特征及古气候意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1323-1331. |
| [5] | 罗松英, 全晓文, 陈碧珊, 邱锦坤, 梁家新, 邓子艺. 湛江湾红树林湿地沉积柱粒度特征及沉积动力分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 647-656. |
| [6] | 孔霄, 来风兵, 陈蜀江, 朱选. 别里库姆沙漠胡杨回涡沙丘表层沉积物粒度特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 657-664. |
| [7] | 赵建鹏, 崔利凯, 陈惠, 李宁, 王自亮, 马瑶, 杜贵超. 基于CT扫描数字岩心的岩石微观结构定量表征方法[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(06): 1205-1213. |
| [8] | 路晶芳, 张克信, 宋博文, 徐亚东, 张楗钰, 黄威, 张道来. 柴达木盆地大红沟地区始新世—上新世孢粉记录及气候变化[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(04): 732-744. |
| [9] | 郑德顺, 杨东亮, 杨文涛, 李雨. 豫西鲁山地区寒武系辛集组沉积环境及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 604-614. |
| [10] | 陈碧珊, 陈诗敏, 何炽鹏. 雷州半岛红树林湿地表层沉积物粒度分布特征[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(01): 198-205. |
| [11] | 陈松, 陈剑, 乔春生, 马俊学, 刘超. 图解法与矩值法在金沙江上游雪隆囊古滑坡堰塞湖溃坝堆积物粒度分析中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1278-1283. |
| [12] | 马俊学, 陈剑, 崔之久, 刘超, 陈松. 堰塞湖溃坝堆积物的粒度特征分析:以岷江上游叠溪古滑坡堰塞湖为例[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(06): 1261-1268. |
| [13] | 赵红梅,刘林敬,赵华,毕志伟,王利康,宋磊,王成敏,杨劲松. 滹沱河古河道剖面粒度参数特征及沉积环境[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2): 485-492. |
| [14] | 王建勇,张绪教,何泽新,赵秋晨,何祥丽,盛余应. 黄土高原北缘中部末次冰期冰楔假型的发现及意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(4): 816-824. |
| [15] | 杨慧君,王永,迟振卿,姚培毅,董进,田明中,刘瑾. 河北白洋淀老河头剖面25.5 ka BP以来气候环境变化的沉积记录[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 291-298. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||