



现代地质 ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (05): 979-989.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.007
任传真1,2( ), 褚润健1,2, 吴怀春1,2(
), 褚润健1,2, 吴怀春1,2( ), 房强1,2
), 房强1,2
收稿日期:2019-04-25
修回日期:2019-06-27
出版日期:2019-10-26
发布日期:2019-10-28
通讯作者:
吴怀春
作者简介:吴怀春, 男,教授,博士研究生导师,1977年出生,海洋地质学专业,主要从事旋回地层学和海洋地质学的教学和科研工作。Email: whcgeo@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
REN Chuanzhen1,2( ), CHU Runjian1,2, WU Huaichun1,2(
), CHU Runjian1,2, WU Huaichun1,2( ), FANG Qiang1,2
), FANG Qiang1,2
Received:2019-04-25
Revised:2019-06-27
Online:2019-10-26
Published:2019-10-28
Contact:
WU Huaichun
摘要:
显生宙沉积旋回会受到地球轨道参数偏心率、地轴斜率和岁差的周期性变化(米兰科维奇旋回)的控制,但目前对前寒武系的相关研究较为薄弱。天津蓟县剖面中元古界洪水庄组—铁岭组为一套潟湖-潮坪相沉积,主要呈砂岩—页岩互层的韵律性产出。为探索这种岩性韵律是否与轨道旋回有关,对其进行了高分辨率的岩性刻画,并以磁化率和伽马能谱数据作为古气候-古环境替代性指标,通过频谱分析等方法进行旋回地层学分析。结果表明各指标均记录了完整的米兰科维奇旋回。铁岭组一段下部由短偏心率、斜率和岁差控制的地层旋回厚度分别为1.2~1.5 m、0.4 m和0.17~0.19 m,其中0.1 m的半岁差周期也较明显;洪水庄组二段顶部由长偏心率、短偏心率、斜率和岁差控制的地层旋回厚度分别为1.1~1.8 m、0.34~0.54 m、0.14~0.16 m和0.08~0.09 m。以识别出的稳定长偏心率周期405 ka旋回对洪水庄组进行了天文年代校准,并估计出当时的短偏心率、斜率以及岁差周期分别为100 ka、22~24 ka和15 ka。在洪水庄组中记录的偏心率振幅变化周期为~2 Ma,比现今~2.4 Ma的周期略短。
中图分类号:
任传真, 褚润健, 吴怀春, 房强. 天津蓟县剖面前寒武系洪水庄组—铁岭组米兰科维奇旋回[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(05): 979-989.
REN Chuanzhen, CHU Runjian, WU Huaichun, FANG Qiang. Milankovitch Cycles of the Precambrian Hongshuizhuang-Tieling Formations at Jixian Section in Tianjin[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(05): 979-989.
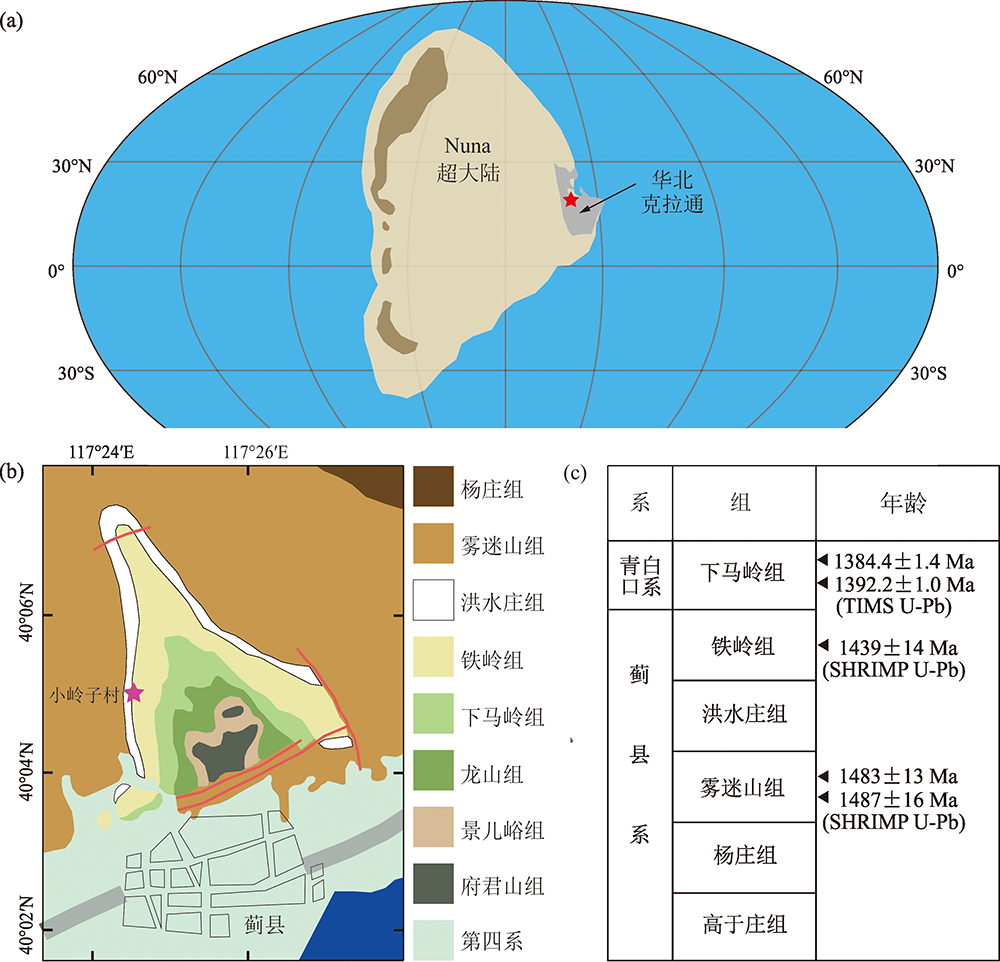
图1 研究区古地理位置及年代地层框架 (a)1.4 Ga全球古地理重建图(修改自Zhang等[19]),红五星代表蓟县剖面位置;(b)蓟县剖面岩性分布和数据采集点位置(修改自李怀坤等[24]);(c)雾迷山组、铁岭组和下马岭组地质年代(据李怀坤等[24]和Zhang等[4])
Fig.1 Paleogeography and chronological framework map of the study area
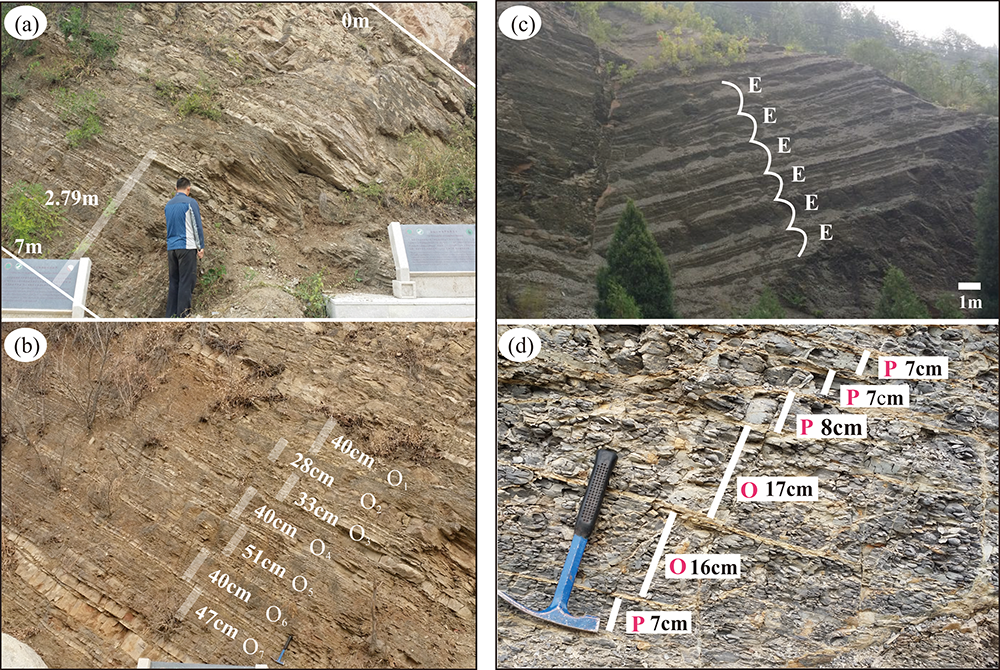

图2 铁岭组和洪水庄组受地球轨道力控制的岩性旋回 (a)铁岭组下部石英砂岩和粉砂质页岩呈现韵律层;(b)(a)图中2.79 m段对应的厘米级层束组解释为斜率(O)旋回;(c)洪水庄组二段墨绿色粉砂质伊利石页岩韵律层,1~2 m的旋回层解释为405 ka长偏心率(E)旋回;(d)洪水庄组二段厘米级旋回层解释为斜率(O)和岁差(P)旋回
Fig.2 Relationships between lithological cycles and Milankovitch-cycle-forced sedimentary bundling patterns in the Tieling-Hongshuizhuang formations
| GR | K | U | Th | MS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 0.96* | ||||
| U | 0.25* | 0.11 | |||
| Th | 0.84* | 0.78* | 0.01 | ||
| MS | 0.20* | 0.16* | 0.11 | 0.23* | |
| 岩性 | -0.20* | -0.21* | 0.06 | -0.22* | -0.10* |
表1 铁岭组古气候指标相关性矩阵
Table 1 Paleoclimatic proxy correlation matrix of Tieling Formation
| GR | K | U | Th | MS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 0.96* | ||||
| U | 0.25* | 0.11 | |||
| Th | 0.84* | 0.78* | 0.01 | ||
| MS | 0.20* | 0.16* | 0.11 | 0.23* | |
| 岩性 | -0.20* | -0.21* | 0.06 | -0.22* | -0.10* |
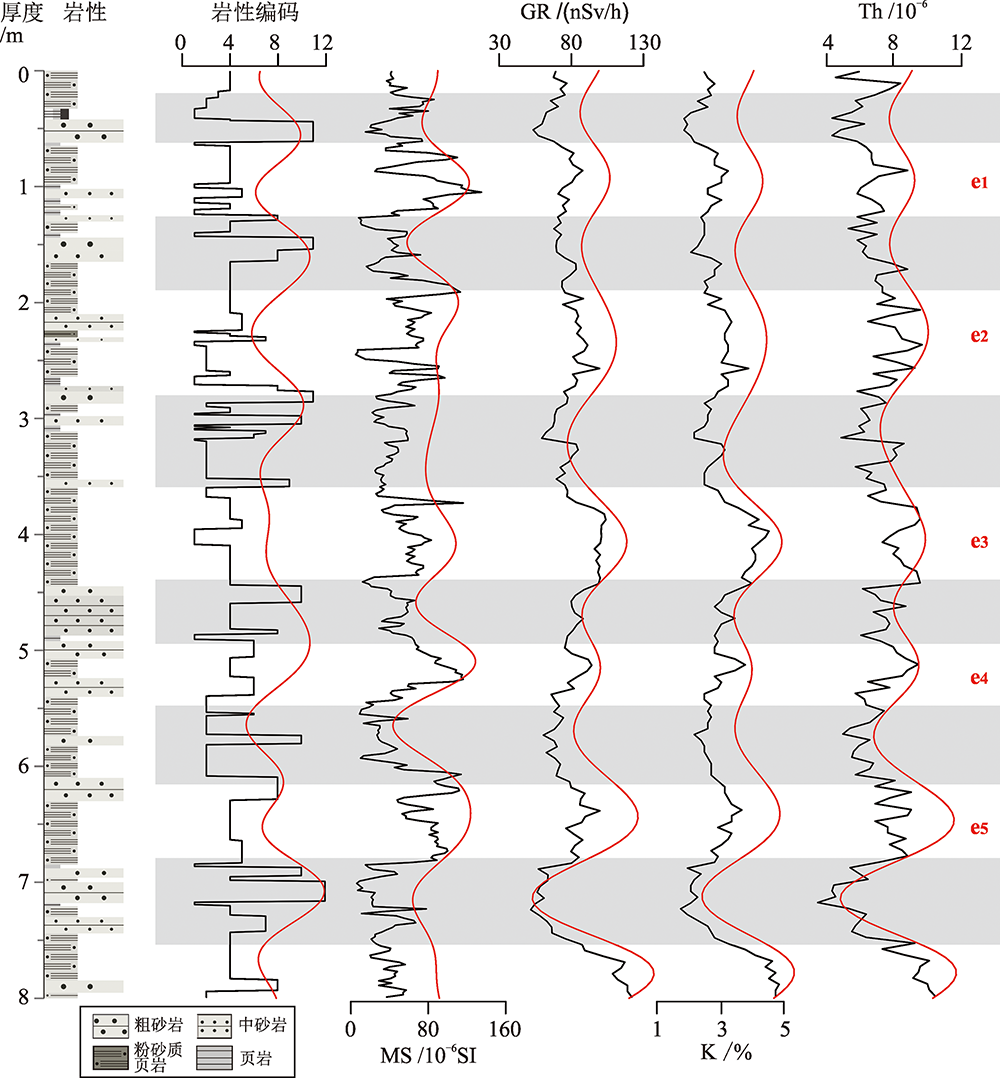
图3 铁岭组一段下部(0~8 m)旋回地层解释 岩性编码滤波中心频率为(0.762 5±0.452 0)旋回/m;MS滤波中心频率为(0.770 6±0.435 0)旋回/m;GR滤波中心频率为(0.658 3±0.354 0)旋回/m;K滤波中心频率为(0.658 4±0.324 0)旋回/m;Th滤波中心频率为(0.742 9±0.432 0)旋回/m;灰色阴影显示出各指标间相似的短偏心率(e)旋回信号
Fig.3 Cyclostratigraphy of the lower part (0~8 m)of Member 1 of the Tieling Formation

图4 铁岭组古气候替代性指标频谱分析(a)和理论地球轨道周期变化曲线(b)
Fig.4 Spectral analyses of the paleoclimate proxy data from the Tieling Formation (a) and predicted Earth orbital period changes since 2 000 Ma (b)
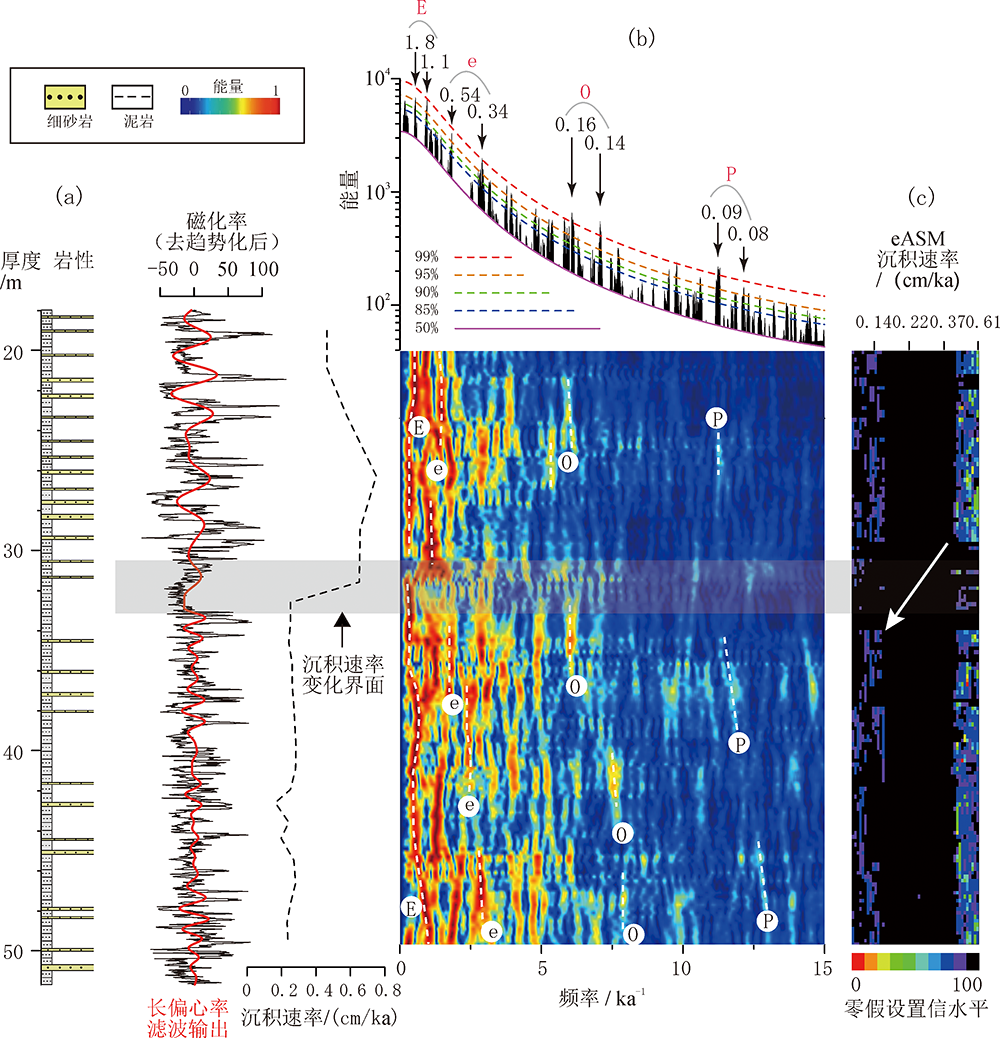
图5 洪水庄组二段顶部(18.0~51.7 m)磁化率(MS)序列旋回地层学分析 (a)去趋势化后磁化率(MS)序列(黑色)和长偏心率信号带通滤波结果(红色,地层18.0~32.0 m和32.0~51.7 m分别使用高斯带通滤波参数(0.55±0.1) m-1和(0.96±0.1) m-1);以405 ka长偏心率周期为基准,根据长偏心率信号滤波输出深度域周期估算出沉积速率变化曲线;(b)去趋势化后磁化率序列(白噪声>3 m)2π MTM频谱分析和滑动窗口(滑动窗口设为3 m,步长为0.2 m)频谱分析,E为长偏心率,e为短偏心率,O为斜率,P为岁差;(c)eASM分析得到的沉积速率变化,输入为去趋势化后的磁化率序列,滑动窗口设为3 m,步长为0.1 cm,每个窗口的序列添零为5 000;天文轨道频率设为1/405 ka-1、1/100 ka-1、1/25 ka-1、1/15 ka-1[43];10 000次蒙特卡洛模拟;每个窗口的ASM估计的沉积速率范围为0.10~0.61 cm/ka
Fig.5 Cyclostratigraphic analysis of the MS series from the 18-51.7 m interval of the upper part of Member 2 of Hongshuizhuang Formation after detrending

图6 405 ka长偏心率周期天文校准后洪水庄组时间域磁化率序列的频谱分析和偏心率、斜率调制信号与新生代天文解决方案(La2004)调制周期 (a)时间域磁化率序列2π MTM频谱分析和滑动窗口(窗口为600 ka)频谱分析,长偏心率滤波输出(用高斯方法利用(0.002 5±0.001 0)周期/ka作为滤波通带)和偏心率调制长周期信号(红色包络线),斜率滤波输出(用高斯方法利用(0.043±0.008)周期/ka作为滤波通带)和斜率调制长周期信号(红色包络线);(b)9 700~20 300 ka的La2004 ETP曲线滑动窗口分析(截取频率范围为0~0.03 周期/ka,窗口为600 ka,步长为10 ka),表现出斜率和偏心率调制长周期
Fig.6 Spectral analysis of the time domain MS series, which was calibrated by long eccentricity cycles in the Hongshuizhuang Formation to an artificial 405 ka eccentricity target curve, amplitude modulation of eccentricity and obliquity, and the modulation period of Cenozoic astronomical solution of La2004
| 长偏心率 | 短偏心率 | 斜率 | 岁差 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天文模型[ | 405 | 100 | 25 | 15 |
| 与岁差之比* | 27 | 6.7 | 1.7 | 1 |
| 下马岭组a/cm | 200 | 55~66 | 13~15 | 6~8 |
| 铁岭组a/cm | 120~150 | 40 | 17~19 | |
| 洪水庄组a/cm | 110~180 | 34~54 | 14~16 | 8~9 |
| 洪水庄组b/ka | 405 | 128 | 22~24 | 15 |
| 下马岭组b/ka | 405 | 131 |
表2 洪水庄组、铁岭组和下马岭组米兰科维奇旋回周期
Table 2 Period Milankovitch cycles of the Hongshuizhuang, Tieling and Xiamaling formations
| 长偏心率 | 短偏心率 | 斜率 | 岁差 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天文模型[ | 405 | 100 | 25 | 15 |
| 与岁差之比* | 27 | 6.7 | 1.7 | 1 |
| 下马岭组a/cm | 200 | 55~66 | 13~15 | 6~8 |
| 铁岭组a/cm | 120~150 | 40 | 17~19 | |
| 洪水庄组a/cm | 110~180 | 34~54 | 14~16 | 8~9 |
| 洪水庄组b/ka | 405 | 128 | 22~24 | 15 |
| 下马岭组b/ka | 405 | 131 |
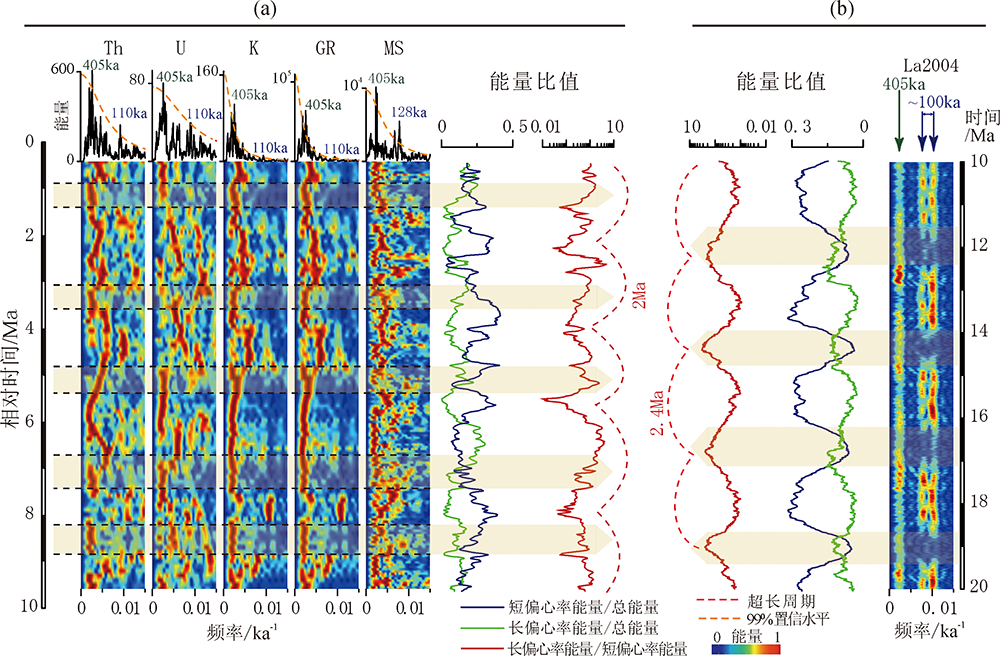
图7 14亿年前地质记录隐含的天文偏心率调制长周期与10~20 Ma的天文解决方案对比 (a)洪水庄组古气候替代性指标(Th、U、K、GR和MS)时间序列在频率范围0~0.015 ka-1内的2πMTM频谱分析和滑动窗口分析(窗口为600 ka,步长为100 ka),从磁化率(MS)序列提取的短偏心率和长偏心率带宽能量变化曲线,阴影表示~2 Ma的超长周期;(b)La2004 ETP[42]曲线在9 700~20 300 ka的滑动窗口分析结果(截取频率范围0~0.015 ka-1,窗口为600 ka,步长为10 ka),从La2004提取的短偏心率和长偏心率带宽能量变化曲线,磁化率和La2004 ETP[40]曲线的长偏心率能量、短偏心率能量和总能量截止频率范围分别为1/600~1/200 ka-1,1/150~1/50 ka-1和0~Nyquist频率;阴影表示~2.4 Ma的超长周期
Fig.7 Comparison between the long period of eccentricity modulation implied in geological records 1.4 Ga with the astronomical solution of 10-20 Ma (La2004)
| [1] |
HINNOV L A. Cyclostratigraphy and its revolutionizing applications in the Earth and planetary sciences[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2013,125(11/12):1703-1734.
DOI URL |
| [2] | HINNOV L A. Earth’s orbital parameters and cycle stratigraphy[M]/GRADSTEIN F M, OGG J G, SMITH A G. A Geologic Time Scale 2004. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004:55-62. |
| [3] |
WU H C, ZHANG S H, JIANG G Q, et al. The floating astronomical time scale for the terrestrial Late Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation from the Songliao Basin of Northeast China and its stratigraphic and paleoclimate implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009,278:308-323.
DOI URL |
| [4] | ZHANG S C, WANG X M, HAMARLUND E U, et al. Orbital forcing of climate 1.4 billion years ago[J]. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 2015,112(12):1406-1413. |
| [5] |
MEYERS S R, ALBERTO M. Proterozoic Milankovitch cycles and the history of the solar system[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018,115(25):6363-6368.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
吴怀春, 房强, 张世红, 等. 新生代米兰科维奇旋回与天文地质年代表[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016,36(5):1055-1074.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 黄春菊. 旋回地层学和天文年代学及其在中生代的研究现状[J]. 地学前缘, 2014,21(2):48-66. |
| [8] | 吴怀春, 钟阳阳, 房强, 等. 古生代旋回地层学与天文地质年代表[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017,36(5):750-770. |
| [9] |
GROTZINGER J P. Cyclicity and paleoenvironmental dynamics, Rocknest platform, northwest Canada[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1986,97(10):1208-1231.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HAINES P W. Storm-dominated mixed carbonate/siliciclastic shelf sequence displaying cycles of hummocky cross-stratification, Late Proterozoic Wonoka Formation, South Australia[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1988,58(2):237-254.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HOFMANN A, DIRKS P H G M, JELSMA H A. Shallowing-upward carbonate cycles in the Belingwe Greenstone Belt, Zimbabwe: A record of Archean sea-level oscillations[J]. Annales de Réadaptation et de Médecine Physique, 2004,50(9):721-723.
DOI URL |
| [12] | SHERMAN A G, NARBONNE G M, JAMES N P. Anatomy of a cyclically packaged Mesoproterozoic carbonate ramp in northern Canada[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2001,139(3/4):171-203. |
| [13] | 梅冥相, 白志达, 徐德斌, 等. 河北兴隆团山子组旋回层序特征及地层格架[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 1998,18(1):35-40. |
| [14] | 梅冥相, 周洪瑞, 杜本明, 等. 雾迷山旋回层的相序组构特征及其在长周期层序中的有序叠加形式——来自前寒武纪的米兰科维奇旋回证据[J]. 现代地质, 1999,13(2):226-227. |
| [15] | 梅冥相, 马永生, 郭庆银. 天津蓟县雾迷山旋回层基本模式及其马尔柯夫链分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001,7(3):288-299. |
| [16] | 周洪瑞, 梅冥相, 杜本明, 等. 天津蓟县雾迷山组高频旋回沉积特征[J]. 现代地质, 2006,20(2):209-215. |
| [17] | 郑斌嵩. 雾迷山旋回层:米级旋回的一个特例[J]. 现代地质, 2014,28(2):292-299. |
| [18] | 范文博. 前寒武纪旋回地层学研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科学, 2015,50(4):1293-1305. |
| [19] | ZHANG S H, LI Z X, EVANS D A D, et al. Pre-Rodinia supercontinent Nuna shaping up: A global synjournal with new paleomagnetic results from North China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012,353/354:145-155. |
| [20] | ZHAO G C, CAWOOD P A, WILDE S A, et al. Metamorphism of basement rocks in the Central Zone of the North China craton: implications for Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Precambrian Research, 2000,103:55-88. |
| [21] | 陆松年, 杨春亮, 李怀坤, 等. 华北古大陆与哥伦比亚超大陆[J]. 地学前缘, 2002,9(4):225-233. |
| [22] | 乔秀夫, 高林志, 张传恒. 中朝板块中、新元古界年代地层柱与构造环境新思考[J]. 地质通报, 2007,26(5):503-509. |
| [23] | 罗顺社, 吕奇奇, 李琳静, 等. 燕山地区宣龙坳陷洪水庄组和铁岭组沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012,28(2):10-16. |
| [24] | 李怀坤, 苏文博, 周红英, 等. 中—新元古界标准剖面蓟县系首获高精度年龄制约——蓟县剖面迷雾山组和铁岭组斑脱岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb同位素定年研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(10):2999-3012. |
| [25] | MA K, HU S Y, WANG T S, et al. Sedimentary environments and mechanisms of organic matter enrichment in the Mesoproterozoic Hongshuizhuang Formation of northern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017,475:176-187. |
| [26] | 孙淑芬. 天津蓟县洪水庄组微古植物群[J]. 前寒武纪研究进展, 2000,23(3):165-172. |
| [27] | 田树信. 天津市岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1996:37-39. |
| [28] | WU H C, ZHANG S H, JIANG G Q, et al. Astrochronology for the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota in northeastern China[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology, 2013,385:221-228. |
| [29] | WU H C, ZHANG S H, HINNOV L A, et al. Cyclostratigraphy and orbital tuning of the terrestrial Upper Santonian-Lower Danian in Songliao Basin, northeastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014,407:82-95. |
| [30] | FANG Q, WU H C, HINNOV L A, et al. A record of astronomically forced climate change in a Late Ordovician (Sandbian) deep marine sequence, Ordos Basin, North China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016,341:163-174. |
| [31] | KODAMA K P, HINNOV L A. Rock Magnetic Cyclostratigraphy, Wiley-Blackwell Fast-Track Monograph: New Analytical Methods in Earth and Environmental Science Series[M]. Chichester:John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2015:1-140. |
| [32] | SCHNYDER J, RUFFELL A, DECONINCK J F, et al. Conjunctive use of spectral gamma-ray logs and clay mineralogy in defining Late Jurassic-early Cretaceous palaeoclimate change (Dorset, UK)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology, 2006,229:303-320. |
| [33] | PAILLARD D, LABEYRIE L, YIOU P. Macintosh program performs time-series analysis[J]. Eos, Transactions of American Geophysical Union, 1996,77:379. |
| [34] | THOMSON D J. Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1982,70:1055-1096. |
| [35] | MEYERS S R. Seeing red in cyclic stratigraphy: spectral noise estimation for astrochronology[J]. Paleoceanography, 2012,27(3):PA3228. |
| [36] | HUSSON D. RedNoise_ConfidenceLevels[M/OL]. 2013-01-01. http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/45539-rednoise-confide ncelevels. |
| [37] | MEYERSN S R. Astrochron:an R package for astrochronology[M/OL]. 2014-01-01. https://cran.r-project.org/package=astrochron. |
| [38] | MEYERS S R, SAGEMAN B B. Quantification of deep-time orbital forcing by average spectral misfit[J]. American Journal of Science, 2007,307:773-792. |
| [39] |
MA C, MEYERS S R, SAGEMAN B B. Theory of chaotic orbital variations confirmed by Cretaceous geological evidence[J]. Nature, 2017,542:468-470.
URL PMID |
| [40] | HINNOV L A. New perspectives on orbitally forced stratigraphy[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000,28:419-475. |
| [41] | LI M S, HUANG C J, HINNOV L A, et al. Obliquity-forced climate during the Early Triassic hothouse in China[J]. Geology, 2016,44(8):623-626. |
| [42] | LASKAR J, ROBUTEL P, JOUTEL F, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2004,428:261-285. |
| [43] | BERGER A, LOUTRE M F. Astronomical forcing through geological time[M] //DE BOER P L,SMITH D G.Orbital Forcing and Cyclic Sequences. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1994,19:15-24. |
| [44] | BERGER A, LOUTRE M F, MÉLICE J L. Equatorial insolation: from precession harmonics to eccentricity frequencies[J]. Climate of the Past, 2006,2(2):131-136. |
| [45] |
LANTINK M L, DAVIES J H F L, MASON P R D, et al. Climate control on banded iron formations linked to orbital eccentricity[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2019,12:369-374.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 贾鹏,李伟,卢远征,樊茹,李鑫, 李明,曾乙洋,刘鑫. 四川盆地中南部地区洗象池群沉积旋回的碳氧同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1329-1338. |
| [2] | 汪新伟,沃玉进,张荣强. 扬子克拉通南华纪-早古生代的构造-沉积旋回[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(4): 525-533. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||