



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (04): 947-958.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.090
出版日期:2024-08-10
发布日期:2024-10-16
通信作者:
和文言,男,副教授,1986年出生,主要从事岩浆作用与成矿、区域成矿规律研究。Email: wyhe@cugb.edu.cn。作者简介:陈浩宇,男,硕士研究生,1998年出生,主要从事矿物学、岩石学、矿床学的研究工作。Email: hygg_chen@126.com。
基金资助:
CHEN Haoyu1,2,3( ), HE Wenyan1,2,3(
), HE Wenyan1,2,3( )
)
Published:2024-08-10
Online:2024-10-16
摘要:
斑岩型矿床是全球铜、金、银、钼等战略性矿产的重要来源,其主要分布于汇聚板块边缘。已有研究揭示大型斑岩矿床一般起源于板片俯冲产生的岩浆作用,俯冲板块脱水诱发地幔楔部分熔融形成初始弧岩浆,在经历过一系列复杂的演化后,最终上升至近地表(3~5 km)成矿。而岩浆硫化物能强烈络合亲铜元素,对岩浆演化过程金属的富集起着重要作用,研究硫化物中亲铜元素富集与活化过程是揭示斑岩矿床成矿机理的重要一环。本文对近年来斑岩矿床中岩浆硫化物的研究成果进行系统总结,梳理硫化物饱和的控制因素与分异过程,对比分析岩浆硫化物饱和过程对斑岩矿床金属富集的控制。岩浆硫化物饱和受温度、压力、氧逸度等多种因素共同控制,其中氧逸度变化是导致硫化物饱和的关键;硫化物饱和将促使金属Cu、Au、PGE等高效浓聚,PGE元素和Au对硫化物饱和异常敏感,少量硫化物饱和会导致大量PGE和Au聚集。岩浆硫化物饱和过程对斑岩成矿潜力影响存在争议,一些研究认为硫化物饱和是斑岩成矿的关键步骤,因为饱和的硫化物将促使金属Cu、Au高效浓聚,当新的岩浆注入或岩浆氧逸度或硫逸度变化时,硫化物将被再次溶解使成矿金属重新在硅酸盐熔体中富集;一些研究则认为岩浆演化过程中硫化物饱和不妨碍斑岩成矿,因为早期少量硫化物饱和沉淀并不会降低剩余岩浆中成矿元素丰度,不影响成矿潜力。厚地壳中硫化物饱和一般发生在早期,薄地壳中硫化物在晚期饱和。
中图分类号:
陈浩宇, 和文言. 岩浆演化过程中硫化物饱和对斑岩型Cu-Au矿床形成的控制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(04): 947-958.
CHEN Haoyu, HE Wenyan. Control of Sulfide Saturation on the Formation of Porphyry Cu-Au Deposits During Magmatic Evolution[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 947-958.

图2 硫化物分馏过程中亲硫元素配分示意图(据文献[19]修改) ISS.中间硫化物固溶; MSS.单硫化物固溶体
Fig.2 Schematic diagrams of the allocation of sulfurophilic elements in the process of sulfide fractionation (modified after reference [19])
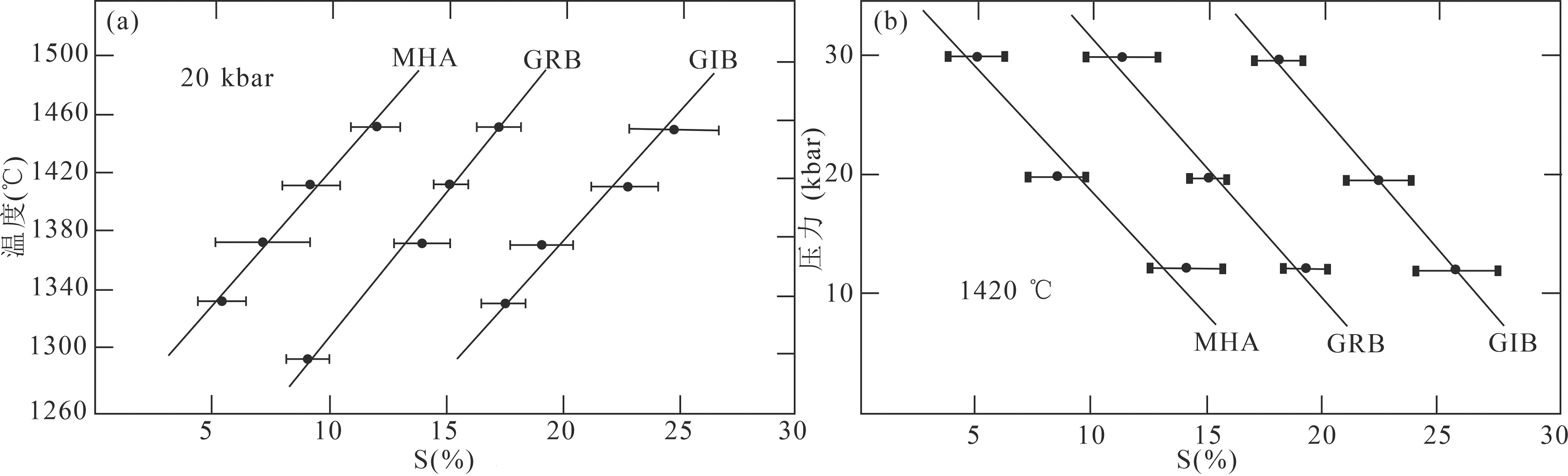
图3 硫化物饱和度与温度、压力关系示意图(据文献[20]修改,1kbar=100 MPa) MHA.Mt.Hood安山岩;GRB.Grandeur Ronde玄武岩;GIB.Goose Island玄武岩
Fig.3 Diagrams of the relationship between sulfide saturation and temperature and pressure(after modified reference[20])

图4 地壳深部岩浆房内含碳变质沉积岩同化混染示意图(据文献[65]修改)
Fig.4 Schematic diagram of assimilation and mixing of carbon-metasedimentary rocks in the deep crustal magmachamber(modified after reference [65])
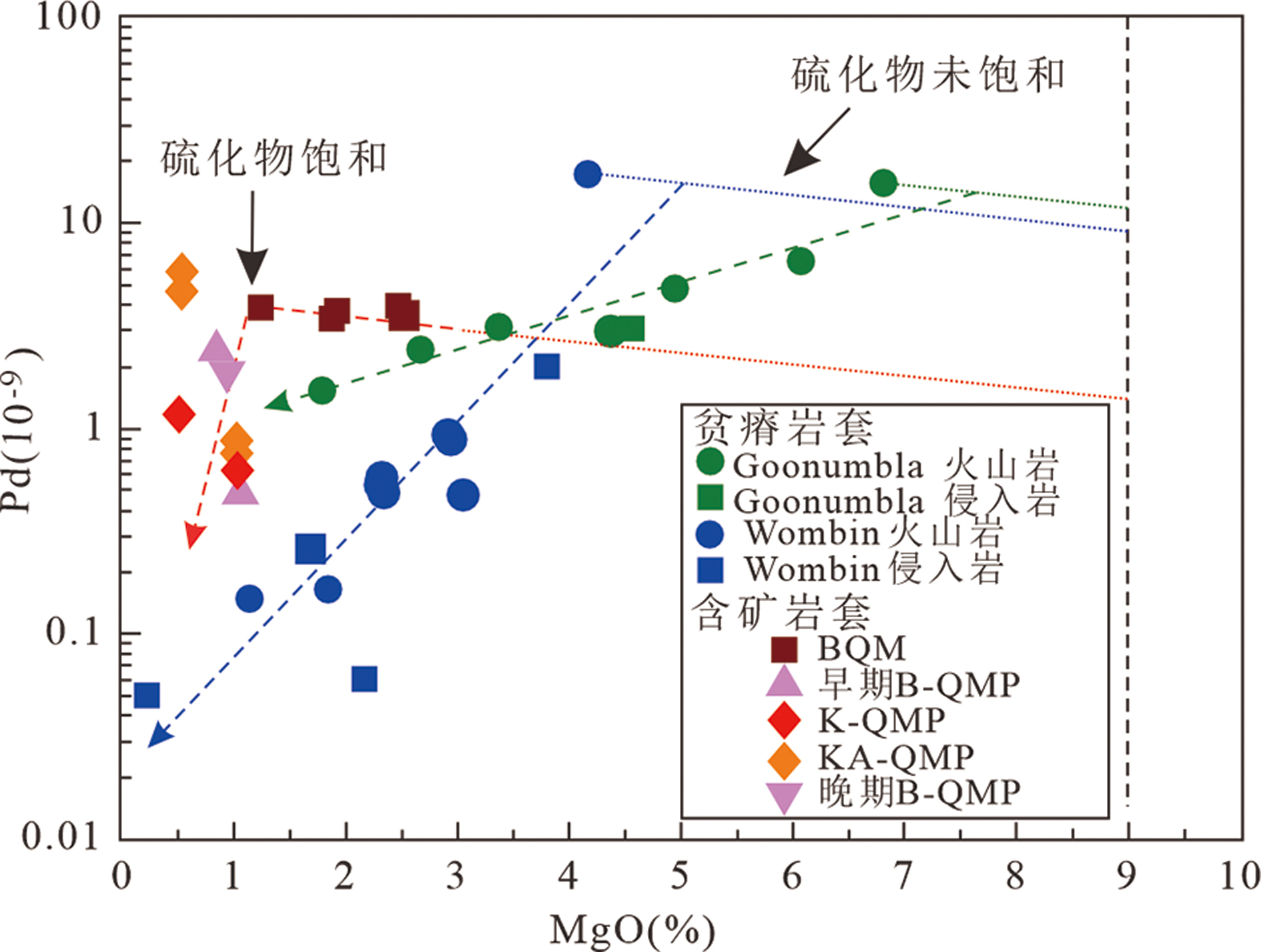
图5 Northparkes矿区贫矿火山岩与侵入岩、伴生矿侵入岩中Pd与MgO对比图(据文献[66]) BQM.弱矿化黑云母-石英二长岩;B-QMP.黑云母石英二长斑岩;K-QMP.同矿化钾长石型石英二长斑岩;KA-QMP.晚期矿化奥辉岩-黑云母-钾长石石英二长斑岩
Fig.5 Comparison of Pd against MgO for barren volcanic and intrusive rocks, and the ore-associated intrusions (after reference[66])
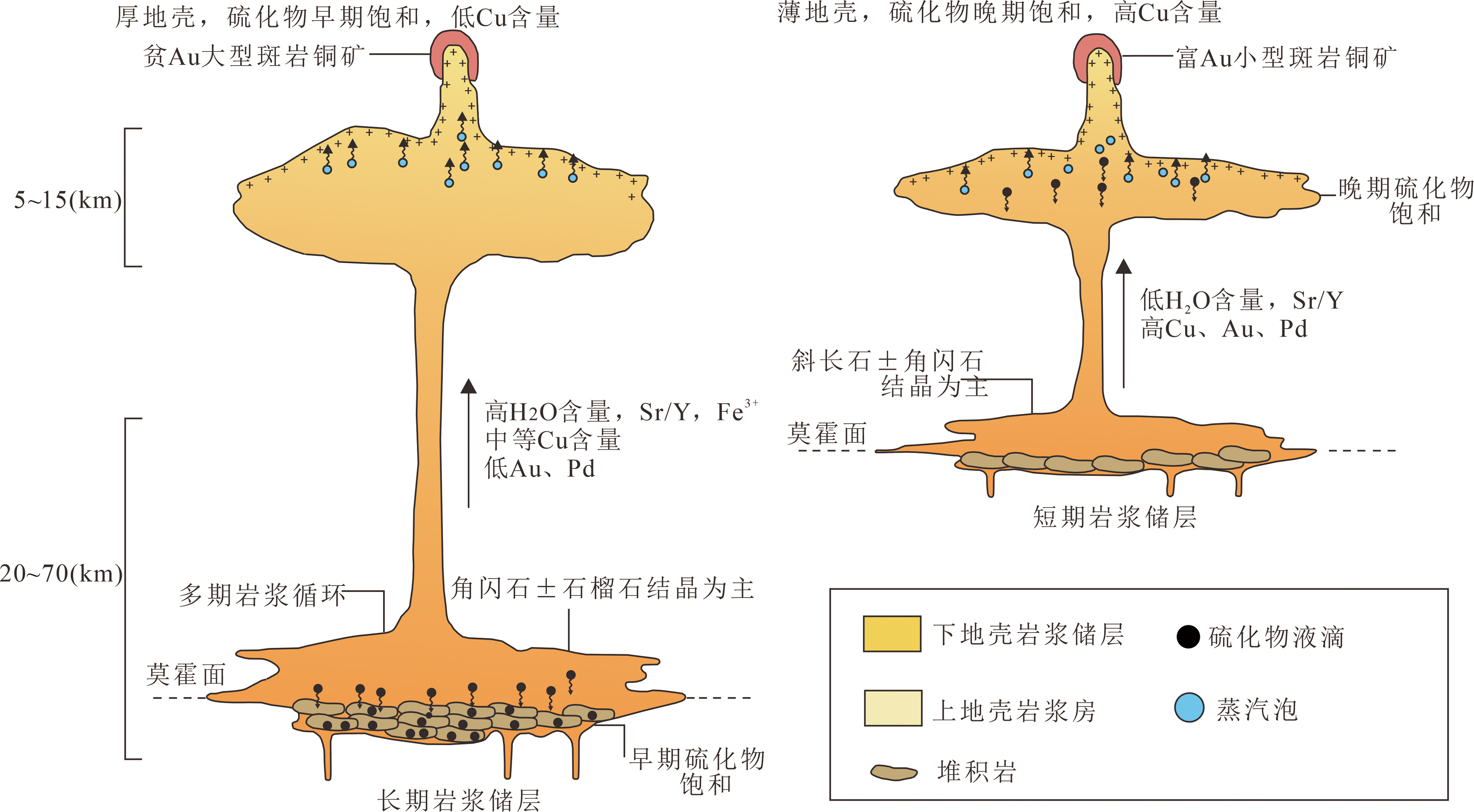
图6 厚弧与薄弧岩浆分异过程中硫化物饱和差异(据文献[67]修改)
Fig.6 Sulfide saturation difference during magmatic differentiation between thick arc and thin arc(modified after reference[67])
| [1] | WILKINSON J J. Triggers for the formation of porphyry ore deposits in magmatic arcs[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6: 917-925. |
| [2] | RICHARDS J P. Magmatic to hydrothermal metal fluxes in convergent and collided margins[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 40(1): 1-26. |
| [3] | SILLITOE R H. Porphyry copper systems[J]. Economic Geo-logy, 2010, 105(1): 3-41. |
| [4] | DU J G, AUDÉTAT A. Early sulfide saturation is not detrimental to porphyry Cu-Au Formation[J]. Geology, 2020, 48(5): 519-524. |
| [5] |
侯增谦, 杨志明, 王瑞, 等. 再论中国大陆斑岩Cu-Mo-Au矿床成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(2): 20-44.
DOI |
| [6] | KAMENETSKY V S, KAMENETSKY M B. Magmatic fluids immiscible with silicate melts: Examples from inclusions in phenocrysts and glasses, and implications for magma evolution and metal transport[J]. Geofluids, 2010, 10(1/2): 293-311. |
| [7] | BLANCHARD I, ABEYKOON S, FROST D J, et al. Sulfur content at sulfide saturation of peridotitic melt at upper mantle conditions[J]. American Mineralogist, 2021, 106(11): 1835-1843. |
| [8] | GEORGATOU A, CHIARADIA M, REZEAU H, et al. Magmatic sulphides in Quaternary Ecuadorian arc magmas[J]. Lithos, 2018, 296: 580-599. |
| [9] | GEORGATOU A A, CHIARADIA M. Magmatic sulfides in high-potassium calc-alkaline to shoshonitic and alkaline rocks[J]. Solid Earth, 2020, 11(1): 1-21. |
| [10] | NALDRETT A J. Magmatic Sulfide Deposits: Geology, Geoche-mistry and Exploration[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2004. |
| [11] | SAVELYEV D P, KAMENETSKY V S, DANYUSHEVSKY L V, et al. Immiscible sulfide melts in primitive oceanic magmas: Evidence and implications from picrite lavas (Eastern Kamchatka, Russia)[J]. American Mineralogist, 2018, 103(6): 886-898. |
| [12] | DANYUSHEVSKY L V, MCNEILL A W, SOBOLEV A V. Experimental and petrological studies of melt inclusions in phenocrysts from mantle-derived magmas: An overview of techniques, advantages and complications[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 183(1/2/3/4): 5-24. |
| [13] | SOBOLEV A V. Origin of Siberian Meimechites in relation to the general problem of ultramafic magma[D]. Moscow: Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry Moscow, 1983. |
| [14] | SOBOLEV A V, DANYUSHEVSKY L V. Petrology and geochemistry of boninites from the north termination of the Tonga trench: Constraints on the generation conditions of primary high-Ca boninite magmas[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1994, 35(5): 1183-1211. |
| [15] | DISTLER V V. Platinum mineralization of the Noril’sk deposits[M]// LightfootPC, NALDRETTAJ. Proceedings of Sudbury-Noril’sk Symposium. Ont Geol Surv Spec 5:243-260, 1994. |
| [16] | NALDRETT A J, ASIF M, GORBACHEV N S, et al. The Composition of the Ni-Cu Ores of the Oktyabr’sky Deposit,Noril’sk Region[M]//LIGHTFOOT PC, NALDRETT A J. Proceedings of Sudbury Noril'sk symposium, Ontario: Ontario Geological Survey, 1994: 357-373. |
| [17] | 宋谢炎, 肖家飞, 朱丹, 等. 岩浆通道系统与岩浆硫化物成矿研究新进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1): 153-163. |
| [18] | HOLWELL B D A, MCDONALD I. A review of the behaviour of platinum group elements within natural magmatic sulfide ore systems[J]. Platinum Metals Review, 2010, 54(1): 26-36. |
| [19] | DURAN C J, BARNES S J, MANSUR E T, et al. Magnetite chemistry by LA-ICP-MS records sulfide fractional crystallization in massive nickel-copper-platinum group element ores from the norilsk-talnakh mining district (Siberia, Russia): Implications for trace element partitioning into magnetite[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(6): 1245-1266. |
| [20] | WENDLANDT R F. Sulfide saturation of basalt and andesite melts at high pressures and temperatures[J]. American Minera-logist, 1982, 67, 877-885. |
| [21] | MAVROGENES J A, ST C O’NEILL H. The relative effects of pressure, temperature and oxygen fugacity on the solubility of sulfide in mafic magmas[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(7/8): 1173-1180. |
| [22] | PATTEN C, BARNES S J, MATHEZ E A. Textural variations in morb sulfide droplets due to differences in crystallization history[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2012, 50(3): 675-692. |
| [23] | KELLEY K A, COTTRELL E. The influence of magmatic differentiation on the oxidation state of Fe in a basaltic arc magma[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 329: 109-121. |
| [24] | BROUNCE M N, KELLEY K A, COTTRELL E. Variations in Fe3+/∑Fe of Mariana arc basalts and mantle wedge $f_{O_{2}}$[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2014, 55(12): 2513-2536. |
| [25] | BROUNCE M, KELLEY K A, COTTRELL E, et al. Temporal evolution of mantle wedge oxygen fugacity during subduction initiation[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(9): 775-778. |
| [26] | JUGO P J, LUTH R W, RICHARDS J P. Experimental data on the speciation of sulfur as a function of oxygen fugacity in basaltic melts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(2): 497-503. |
| [27] | WALLACE P J, CARMICHAEL I S E. S speciation in submarine basaltic glasses as determined by measurements of S Kα X-ray wavelength shifts[J]. American Mineralogist, 1994, 79(1-2): 161-167. |
| [28] | CARROLL M, RUTHERFORD M. Sulfur speciation in hydrous experimental glasses of varying oxidation state-Results from measured wavelength shifts of sulfur X-rays[J]. American Mineralogist, 1988, 73: 845-849. |
| [29] | JUGO P J. Sulfur content at sulfide saturation in oxidized magmas[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(5): 415-418. |
| [30] | FINCHAM C J B, RICHARDSON F D. The behaviour of sulphur in silicate and aluminate melts[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London(Series A,Mathematical and Physical Sciences), 1954, 223: 40-62. |
| [31] | WYKES J L, ST C O’NEILL H, MAVROGENES J A. The effect of FeO on the sulfur content at sulfide saturation (SCSS)and the selenium content at selenide saturation of silicate melts[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2015, 56(7): 1407-1424. |
| [32] | HAUGHTON D R, ROEDER P L, SKINNER B J. Solubility of sulfur in mafic magmas[J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69(4): 451-467. |
| [33] | ST C O’NEILL H, MAVROGENES J A. The sulfide capacity and the sulfur content at sulfide saturation of silicate melts at 1400℃ and 1 bar[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2002, 43(6): 1049-1087. |
| [34] | PETFORD N, CRUDEN A R, MCCAFFREY K J, et al. Granite magma formation, transport and emplacement in the Earth’s crust[J]. Nature, 2000, 408: 669-673. |
| [35] | SCHOENE B, SCHALTEGGER U, BRACK P, et al. Rates of magma differentiation and emplacement in a ballooning pluton recorded by U-Pb TIMS-TEA, Adamello batholith, Italy[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 355: 162-173. |
| [36] | GLAZNER A F, BARTLEY J M, COLEMAN D S, et al. Are plutons assembled over millions of years by amalgamation from small magma chambers?[J]. GSA Today, 2004, 14(4): 4. |
| [37] | HOLZHEID A, GROVE T L. Sulfur saturation limits in silicate melts and their implications for core formation scenarios for terrestrial planets[J]. American Mineralogist, 2002, 87(2/3): 227-237. |
| [38] |
HALTER W E, PETTKE T, HEINRICH C A. The origin of Cu/Au ratios in porphyry-type ore deposits[J]. Science, 2002, 296: 1844-1846.
PMID |
| [39] | NALDRETT A J, VON GRUENEWALDT G. Association of platinum-group elements with chromitite in layered intrusions and ophiolite complexes[J]. Economic Geology, 1989, 84(1): 180-187. |
| [40] | IRVINE T N. Origin of chromitite layers in the Muskox intrusion and other stratiform intrusions: A new interpretation[J]. Geology, 1977, 5(5): 273. |
| [41] | LIGHTFOOT P C, HAWKESWORTH C J. Flood basalts and magmatic Ni, Cu, and PGE sulphide mineralization: Comparative geochemistry of the Noril’sk (Siberian traps)and West Greenland sequences[M]// Large Igneous Provinces:Continental, Oceanic, and Planetary Flood Volcanism. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2013: 357-380. |
| [42] | RIPLEY E M, LI C S. Sulfide saturation in mafic magmas: Is external sulfur required for magmatic Ni-Cu-(PGE)ore genesis?[J]. Economic Geology, 2013, 108(1): 45-58. |
| [43] | WALLACE P J. Volatiles in subduction zone magmas: Concentrations and fluxes based on melt inclusion and volcanic gas data[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2005, 140(1/2/3): 217-240. |
| [44] | DE HOOG J C M, MASON P R D, VAN BERGEN M J. Sulfur and chalcophile elements in subduction zones: Constraints from a laser ablation ICP-MS study of melt inclusions from Galunggung Volcano, Indonesia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(18): 3147-3164. |
| [45] | WALLACE P J, EDMONDS M. The sulfur budget in magmas: Evidence from melt inclusions, submarine glasses, and volcanic gas emissions[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2011, 73(1): 215-246. |
| [46] | EVANS K A. The redox budget of subduction zones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 113(1/2): 11-32. |
| [47] | EVANS K A, ELBURG M A, KAMENETSKY V S. Oxidation state of subarc mantle[J]. Geology, 2012, 40(9): 783-786. |
| [48] |
KELLEY K A, COTTRELL E. Water and the oxidation state of subduction zone magmas[J]. Science, 2009, 325: 605-607.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | MÉTRICH N, BONNIN-MOSBAH M, SUSINI J, et al. Presence of sulfite (SIV)in arc magmas: Implications for volcanic sulfur emissions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(11): 33-1. |
| [50] | PARK J W, CAMPBELL I H, MALAVIARACHCHI S P K, et al. Chalcophile element fertility and the formation of porphyry Cu±Au deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2019, 54(5): 657-670. |
| [51] | RICHARDS J P. Postsubduction porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposits: Products of remelting of subduction-modified lithosphere[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(3): 247-250. |
| [52] | MUNGALL J E, BRENAN J M. Partitioning of platinum-group elements and Au between sulfide liquid and basalt and the origins of mantle-crust fractionation of the chalcophile elements[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 125: 265-289. |
| [53] | MAIER W D. Platinum-group element (PGE)deposits and occurrences: Mineralization styles, genetic concepts, and exploration criteria[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 41(3): 165-191. |
| [54] | LI Y, AUDÉTAT A. Partitioning of V, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Mo, Ag, Sn, Sb, W, Au, Pb, and Bi between sulfide phases and hydrous basanite melt at upper mantle conditions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 355: 327-340. |
| [55] | LAURENZ V, FONSECA R O C, BALLHAUS C, et al. The solubility of palladium and ruthenium in picritic melts: 2.The effect of sulfur[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 108: 172-183. |
| [56] | HAO H D, CAMPBELL I H, RICHARDS J P, et al. Platinum-group element geochemistry of the escondida igneous suites, northern Chile: Implications for ore formation[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2019, 60(3): 487-514. |
| [57] | BARNES S J, COUTURE J F, SAWYER E W, et al. Nickel-copper occurrences in the Belleterre-Angliers Belt of the Pontiac Subprovince and the use of Cu-Pd ratios in interpreting platinum-group element distributions[J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88(6): 1402-1418. |
| [58] | BARNES S J, RIPLEY E M. Highly siderophile and strongly chalcophile elements in magmatic ore deposits[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2015, 81(1): 725-774. |
| [59] | JUGO P J, CANDELA P A, PICCOLI P M. Magmatic sulfides and Au: Cu ratios in porphyry deposits: An experimental study of copper and gold partitioning at 850℃, 100 MPa in a haplogranitic melt-pyrrhotite-intermediate solid solution-gold metal assemblage, at gas saturation[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 573-589. |
| [60] | PARK J W, CAMPBELL I H, KIM J, et al. The role of late sulfide saturation in the formation of a Cu-and Au-rich magma: Insights from the platinum group element geochemistry of Niuatahi-motutahi lavas, Tonga rear arc[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2015, 56(1): 59-81. |
| [61] | JENNER F E. Cumulate causes for the low contents of sulfide-loving elements in the continental crust[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2017, 10(7): 524-529. |
| [62] | AGUE J J, BRIMHALL G H. Granites of the batholiths of California: Products of local assimilation and regional-scale crustal contamination[J]. Geology, 1987, 15(1): 63. |
| [63] | TOMKINS A G, REBRYNA K C, WEINBERG R F, et al. Magmatic sulfide formation by reduction of oxidized arc basalt[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2012, 53(8): 1537-1567. |
| [64] | COCKER H A, VALENTE D L, PARK J W, et al. Using platinum group elements to identify sulfide saturation in a porphyry Cu system: The El Abra porphyry Cu deposit, northern Chile[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2015, 56(12): 2491-2514. |
| [65] | TASSARA S, AGUE J J. A role for crustal assimilation in the formation of copper-rich reservoirs at the base of continental arcs[J]. Economic Geology, 2022, 117(7): 1481-1496. |
| [66] | HAO H D, CAMPBELL I H, PARK J W, et al. Platinum-group element geochemistry used to determine Cu and Au fertility in the Northparkes igneous suites, New South Wales, Australia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2017, 216: 372-392. |
| [67] | PARK J W, CAMPBELL I H, CHIARADIA M, et al. Crustal magmatic controls on the formation of porphyry copper deposits[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2021, 2: 542-557. |
| [68] | CHEN H Y, WU C. Metallogenesis and major challenges of porphyry copper systems above subduction zones[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2020, 63(7): 899-918. |
| [69] | GASCHNIG R M, RUDNICK R L, MCDONOUGH W F, et al. Compositional evolution of the upper continental crust through time, as constrained by ancient glacial diamictites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 186: 316-343. |
| [70] | CHEN K, RUDNICK R L, WANG Z C, et al. How mafic was the Archean upper continental crust? Insights from Cu and Ag in ancient glacial diamictites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 278: 16-29. |
| [71] | CHIARADIA M. Copper enrichment in arc magmas controlled by overriding plate thickness[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7: 43-46. |
| [72] | 王瑞, 朱弟成, 王青, 等. 特提斯造山带斑岩成矿作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000, 30: 38. |
| [73] | ALONSO-PEREZ R, MÜNTENER O, ULMER P. Igneous garnet and amphibole fractionation in the roots of island arcs: Experimental constraints on andesitic liquids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2009, 157(4): 541-558. |
| [74] | LEE C T A, TANG M. How to make porphyry copper deposits[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 529: 115868. |
| [75] | LEE C T A, LEE T C, WU C T. Modeling the compositional evolution of recharging, evacuating, and fractionating (REFC)magma chambers: Implications for differentiation of arc magmas[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 143: 8-22. |
| [76] | CHEN K, TANG M, LEE C T A, et al. Sulfide-bearing cumulates in deep continental arcs: The missing copper reservoir[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 531: 115971. |
| [77] | TANG M, ERDMAN M, ELDRIDGE G, et al. The redox “filter” beneath magmatic orogens and the formation of continental crust[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(5): eaar4444. |
| [78] | AHMAD I, RICHARDS J P, PEARSON D G, et al. Fractionation of Sulfide Phases Controls the Chalcophile Metal Budget of Arc Magmas: Evidence from the Chilas Complex, Kohistan Arc, Pakistan[J]. 2021. |
| [79] | LOWCZAK J N, CAMPBELL I H, COCKER H, et al. Platinum-group element geochemistry of the Forest Reef Volcanics, southeastern Australia: Implications for porphyry Au-Cu minerali-sation[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 220:385-406. |
| [80] | AUDÉTAT A, PETTKE T. Evolution of a porphyry-Cu mineralized magma system at santa rita, new Mexico (USA)[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47(10): 2021-2046. |
| [81] | HEINRICH C A, CONNOLLY J A D. Physical transport of magmatic sulfides promotes copper enrichment in hydrothermal ore fluids[J]. Geology, 2022, 50(10): 1101-1105. |
| [82] |
杨立强, 杨伟, 张良, 等. 热液成矿系统构造控矿理论[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(1): 239-266.
DOI |
| [1] | 张靓, 陈奇, 高添, 李雯, 钱金龙, 刘俐君, 王长明. 三江特提斯马厂箐斑岩铜钼矿床成矿时间尺度探讨:来自石英中Ti-Al扩散年代学的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1509-1523. |
| [2] | 郝金华, 陈建平, 董庆吉, 田永革, 李玉龙, 陈冬. 青海省纳日贡玛斑岩钼铜矿床成矿花岗斑岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(1): 45-53. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||