



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (01): 1-12.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.003
张招崇1,2( ), 王怀洪3, 谢秋红4, 沈立军3, 朱裕振3, 吕云鹤3, 金博文1
), 王怀洪3, 谢秋红4, 沈立军3, 朱裕振3, 吕云鹤3, 金博文1
收稿日期:2023-09-23
修回日期:2023-11-29
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-03-20
作者简介:张招崇,男,教授,博士生导师,1965年出生,地质学专业,主要从事岩浆岩岩石学与矿床学研究。Email: zczhang@cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
ZHANG Zhaochong1,2( ), WANG Huaihong3, XIE Qiuhong4, SHEN Lijun3, ZHU Yuzhen3, LÜ Yunhe3, JIN Bowen1
), WANG Huaihong3, XIE Qiuhong4, SHEN Lijun3, ZHU Yuzhen3, LÜ Yunhe3, JIN Bowen1
Received:2023-09-23
Revised:2023-11-29
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-03-20
摘要:
山东省西北部齐河—禹城地区矽卡岩型富铁矿找矿工作取得了重大突破,有望成为继莱芜、金岭和济南之后又一个重要的富铁矿基地。与传统的矽卡岩型铁矿产于岩体与碳酸盐岩接触带不同的是,齐河—禹城地区李屯铁矿的矿体产于石炭系—二叠系含煤地层内,富铁矿体与围岩呈截然的接触关系,并且矿体附近的围岩发生了强烈的角岩化。针对这一现象,本文提出上覆的煤系极低的热导率使得含矿热液能够保持高温状态,发生长距离迁移而就位于远接触带的石炭系—二叠系中。李屯铁矿的形成可能是高温的岩浆流体与低温的大气降水混合,导致温度和盐度下降发生快速沉淀的结果。另外,近矿岩体普遍发生强烈的钠长石化,导致了闪长质岩石“铁的丢失”,为出溶高浓度富铁流体以及富铁矿的形成奠定了重要的物质基础。幔源“高分异”的闪长岩以及浅侵位时岩浆流体的出溶,也是邯邢式铁矿形成的先决条件。
中图分类号:
张招崇, 王怀洪, 谢秋红, 沈立军, 朱裕振, 吕云鹤, 金博文. “禹城式”矽卡岩型富铁矿的形成机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 1-12.
ZHANG Zhaochong, WANG Huaihong, XIE Qiuhong, SHEN Lijun, ZHU Yuzhen, LÜ Yunhe, JIN Bowen. Genetic Mechanism of the “Yucheng-Type” High-Grade Skarn Iron Deposits[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(01): 1-12.

图2 齐河—禹城地区航空磁异常ΔT (nT)等值线平面图(a)和航空布格重力(10-5 m/s2)等值线平面图(b)[11] (a)图中:1.磁异常正等值线;2.磁异常零等值线; 3.磁异常负等值线; 4.磁异常值; 5.铁矿床位置; (b)图中:1.重力等值线;2.局部重力极大值;3.局部重力极小值;4.相对重力值;5.铁矿床位置
Fig.2 Maps of aero-magnetic ΔT contour (a) and aero-bouguer gravity contour (b) of the Qihe-Yucheng area [11]
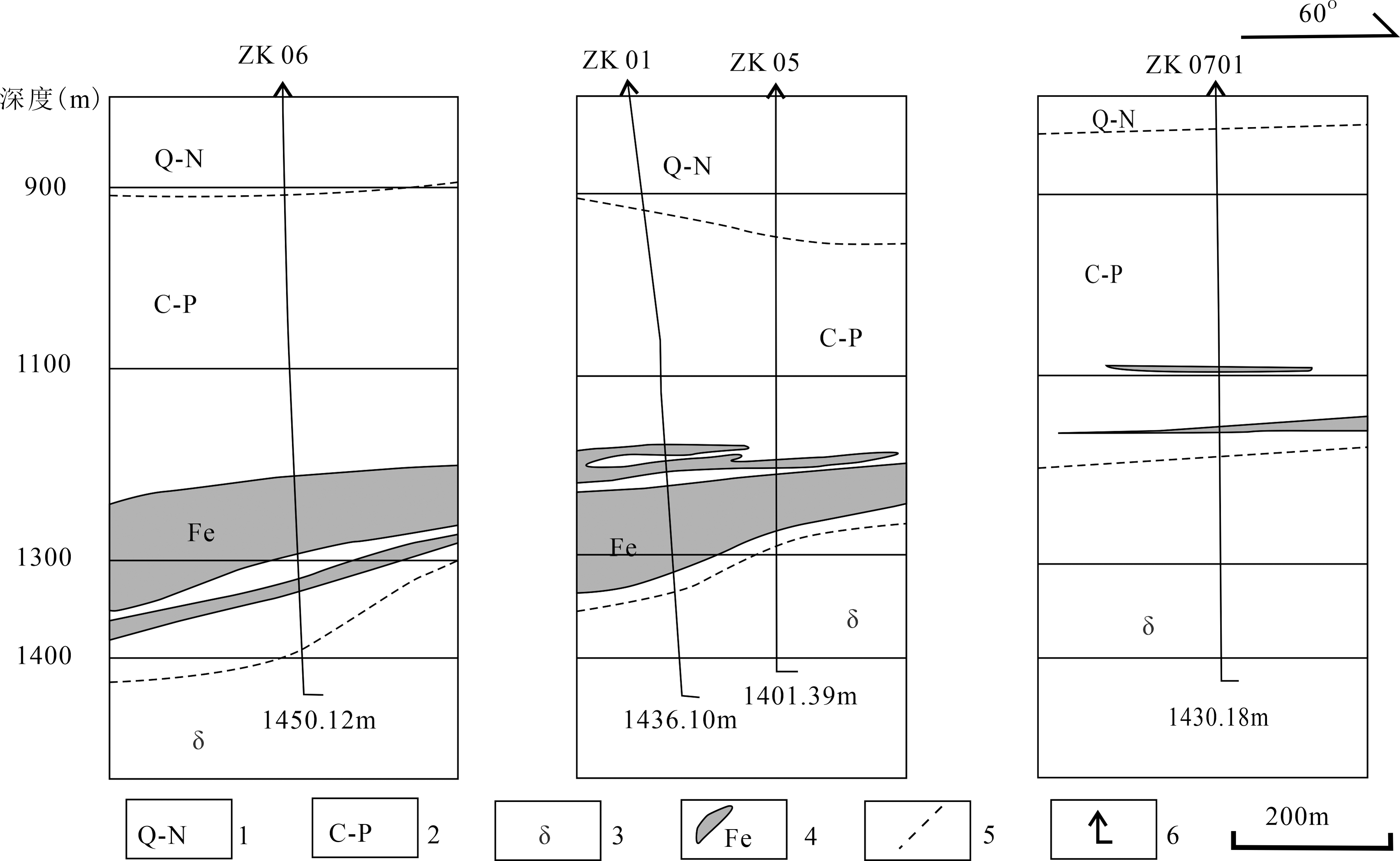
图4 李屯铁矿钻孔控制矿体剖面图简图[13] 1.第四系+新近系;2.石炭系—二叠系;3.闪长岩体;4.铁矿体;5.地质界线;6.钻孔编号及深度
Fig.4 Sketch cross section of the drillhole-controlled iron orebodies at the Litun iron deposit

图5 李屯铁矿体与围岩(角岩)有截然的接触界线和强烈的角岩化(ZK5)
Fig.5 Sharp contact boundary between iron orebody and country rock (horn) and strong horn metamorphismat the Litun iron deposit (ZK5)

图7 李屯近矿闪长岩强烈的钠长石化(a)和远离矿体大范围的不均一钠长石化(b)
Fig.7 Strong albite alteration of the diorite near iron orebody (a) and heterogeneous albite alteration of the diorite far from the iron orebody in a large scale

图8 大张地区 0 线勘探线剖面简图[11] 1.第四系;2.新近系;3.二叠系;4.石炭系;5.奥陶系;6.闪长岩体;7.铁矿体及编号;8.推断地质界线;9.钻孔位置;10.推测破碎带
Fig.8 Sketch cross geological section of No.0 exploration line at the Dazhang iron deposit
| 岩性 | 热导率(W/(m·K)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | |
| 煤 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.21 |
| 泥板岩、泥质页岩 | 0.25 | 3.01 | 1.22 |
| 粉砂岩 | 0.41 | 3.58 | 1.49 |
| 砂岩 | 0.38 | 5.17 | 1.66 |
| 砾岩、圆石砾岩 | 1.05 | 3.86 | 1.92 |
| 泥灰岩 | 0.50 | 3.91 | 1.92 |
| 片麻岩 | 0.94 | 4.86 | 2.02 |
| 正长花岗岩 | 1.30 | 2.97 | 2.05 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 1.64 | 2.48 | 2.11 |
| 石英斑岩 | 1.76 | 2.60 | 2.11 |
| 灰岩 | 0.92 | 4.40 | 2.40 |
| 花岗岩 | 1.34 | 3.69 | 2.40 |
| 片岩 | 1.03 | 4.93 | 2.46 |
| 大理岩 | 1.59 | 4.00 | 2.56 |
| 石英-碳酸盐岩 | 1.61 | 5.01 | 2.71 |
| 石英闪长岩 | 1.98 | 3.80 | 3.00 |
| 白云岩 | 1.63 | 6.50 | 3.24 |
| 角岩 | 2.12 | 6.10 | 3.39 |
| 石英岩 | 2.68 | 7.60 | 5.26 |
表1 不同岩性的热导率[19]
Table 1 Thermal conductivity of different rock types[19]
| 岩性 | 热导率(W/(m·K)) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | |
| 煤 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.21 |
| 泥板岩、泥质页岩 | 0.25 | 3.01 | 1.22 |
| 粉砂岩 | 0.41 | 3.58 | 1.49 |
| 砂岩 | 0.38 | 5.17 | 1.66 |
| 砾岩、圆石砾岩 | 1.05 | 3.86 | 1.92 |
| 泥灰岩 | 0.50 | 3.91 | 1.92 |
| 片麻岩 | 0.94 | 4.86 | 2.02 |
| 正长花岗岩 | 1.30 | 2.97 | 2.05 |
| 花岗闪长岩 | 1.64 | 2.48 | 2.11 |
| 石英斑岩 | 1.76 | 2.60 | 2.11 |
| 灰岩 | 0.92 | 4.40 | 2.40 |
| 花岗岩 | 1.34 | 3.69 | 2.40 |
| 片岩 | 1.03 | 4.93 | 2.46 |
| 大理岩 | 1.59 | 4.00 | 2.56 |
| 石英-碳酸盐岩 | 1.61 | 5.01 | 2.71 |
| 石英闪长岩 | 1.98 | 3.80 | 3.00 |
| 白云岩 | 1.63 | 6.50 | 3.24 |
| 角岩 | 2.12 | 6.10 | 3.39 |
| 石英岩 | 2.68 | 7.60 | 5.26 |
| [1] |
ZHANG Z C, HOU T, SANTOSH M, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China: An overview[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 57: 247-263.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 张招崇, 李厚民, 李建威, 等. 我国铁矿成矿背景与富铁矿成矿机制[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(6): 827-852. |
| [3] | 赵一鸣, 林文蔚, 毕承思. 中国矽卡岩矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012. |
| [4] | 王怀洪, 李洪奎, 周明磊. 山东省富铁矿构造环境和成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021. |
| [5] | 高继雷. 山东富铁矿地质[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2021. |
| [6] | 郝兴中, 杨毅恒, 刘伟. 山东潘店地区矽卡岩型铁矿地质特征及找矿意义[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(20): 51-58. |
| [7] | 王怀洪, 李秀章, 沈立军, 等. 山东齐河—禹城地区“禹城式”富铁矿地质特征与成矿模式[J]. 山东国土资源, 2021, 37(9): 26-35. |
| [8] | 郝兴中, 张华平, 王巧云, 等. 山东德州超深覆盖区矽卡岩型铁矿找矿标志[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(增): 139-140. |
| [9] | 朱裕振, 周明磊, 高志军, 等. 山东齐河—禹城地区矽卡岩型富铁矿的发现及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(5): 938-944. |
| [10] | 王怀洪, 周明磊, 朱裕振, 等. 黄河北煤田煤层下富铁矿深部找矿成果及重要意义[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2020, 32(12):8-12. |
| [11] | 郝兴中, 郭延明, 李英平, 等. 山东齐河—禹城矿集区矽卡岩型铁矿成矿规律[J]. 地质学刊, 2019, 43(4): 566-572. |
| [12] | 沈立军, 朱裕振, 王怀洪, 等. 山东齐河—禹城地区李屯富铁矿床地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(1): 84-98. |
| [13] | 李强, 田思清. 山东省齐河—禹城地区矽卡岩型铁矿磁铁矿元素地球化学特征及其对成矿作用的指示意义[J]. 山东国土资源, 2021, 37(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | EINAUDI M T, MEINERT L D, NEWBERRY R J. Skarn deposits[M]//Seventy-Fifth Anniversary Volume. Society of Economic Geologists, 1981:317-391. |
| [15] | MEINERT L D, DIPPLE G M, NICOLESCU S. World skarn deposits[M]//One Hundredth Anniversary Volume. Society of Economic Geologists, 2005:299-336. |
| [16] |
SCHOLTEN L, SCHMIDT C, LECUMBERRI-SANCHEZ P, et al. Solubility and speciation of iron in hydrothermal fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 252: 126-143.
DOI |
| [17] | 翟裕生. 长江中下游地区铁铜(金)成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992. |
| [18] | 陈儒庆, 袁奎荣. 岩石的热导率对岩石热变质的影响[J]. 桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1992, 12(3): 304-308. |
| [19] | 多尔特曼. 岩石和矿物的物理性质[M].蒋宏耀,译. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985. |
| [20] |
EUGSTER H P, CHOU I M. A model for the deposition of Cornwall-type magnetite deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1979, 74(4): 763-774.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
HEMLEY J J, CYGAN G L, FEIN J B, et al. Hydrothermal ore-forming processes in the light of studies in rock-buffered systems: I, Iron-copper-zinc-lead sulfide solubility relations[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87(1): 1-22.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HEMLEY J J, HUNT J P. Hydrothermal ore-forming processes in the light of studies in rock-buffered systems: II, Some general geologic applications[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87(1): 23-43.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 张兆年, 曹毅, 朱裕振, 等. 山东大张矽卡岩型铁矿床中铁的富集机制: 来自流体包裹体和氢、氧同位素的证据[J]. 矿床地质, 2022, 41(1): 91-105. |
| [24] |
HEDENQUIST J W, LOWENSTERN J B. The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Nature, 1994, 370: 519-527.
DOI |
| [25] |
NIIRANEN T, MÄNTTÄRI I, POUTIAINEN M, et al. Genesis of Palaeoproterozoic iron skarns in the Misi region, northern Finland[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2005, 40(2): 192-217.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHU B, ZHANG H F, ZHAO X M, et al. Iron isotope fractionation during skarn-type alteration: Implications for metal source in the Han-Xing iron skarn deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 74: 139-150.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
HAWKINS T, SMITH M P, HERRINGTON R J, et al. The geology and genesis of the iron skarns of the Turgai belt, northwestern Kazakhstan[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 85: 216-246.
DOI URL |
| [28] | LI H M, ZHANG Z J, LI L X, et al. Types and general characteristics of the BIF-related iron deposits in China[J]. Ore Geo-logy Reviews, 2014, 57: 264-287. |
| [29] | 李延河, 谢桂青, 段超, 等. 膏盐层在矽卡岩型铁矿成矿中的作用[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(9): 1324-1334. |
| [30] |
MAKHLUF A R, NEWTON R C, MANNING C E. Experimental investigation of phase relations in the system NaAlSi3O8-H2O at high temperatures and pressures: Liquidus relations, liquid-vapor mixing, and critical phenomena at deep crust-upper mantle conditions[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2020, 175(8): 76.
DOI |
| [31] |
SOWERBY J R, KEPPLER H. The effect of fluorine, boron and excess sodium on the critical curve in the albite-H2O system[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(1): 32-37.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LOUCKS R R, MAVROGENES J A. Gold solubility in supercritical hydrothermal brines measured in synthetic fluid inclusions[J]. Science, 1999, 284: 2159-2163.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 杜乐天, 王文广. 碱型地幔流体与富碱热液成矿[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(5): 599-610. |
| [34] |
SIMON A C, PETTKE T, CANDELA P A, et al. Magnetite solubility and iron transport in magmatic-hydrothermal environments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(23): 4905-4914.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 杜乐天. 碱交代作用地球化学原理[J]. 中国科学 (B辑), 1986, 16(1): 81-90. |
| [36] | 张招崇, 侯通, 李厚民, 等. 岩浆-热液系统中铁的富集机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(5): 1189-1204. |
| [37] |
WEBSTER J D. The exsolution of magmatic hydrosaline chloride liquids[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 210(1/2/3/4): 33-48.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 黄福生, 薛绥洲. 邯邢侵入体中幔源超镁铁质岩包体的发现及其矿物地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 1990, 6(4): 40-45, 97. |
| [39] | 许文良, 王冬艳, 王清海, 等. 鲁西中生代闪长岩中两类幔源捕虏体的岩石学和地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(4): 623-636. |
| [40] |
XIE Q H, ZHANG Z C, HOU T, et al. Petrogenesis of the Zhangmatun gabbro in the ji’nan complex, North China Craton: Implications for skarn-type iron mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 1197-1217.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
JIN Z L, ZHANG Z C, HOU T, et al. Genetic relationship of high-Mg dioritic pluton to iron mineralization: A case study from the Jinling skarn-type iron deposit in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 957-979.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
JIN Z L, ZHANG Z C, SANTOSH M, et al. Occurrence and chemical compositions of amphiboles in altered dioritic rocks of Laiwu skarn-type iron deposit in West Shandong area, China[J]. Resource Geology, 2018, 68(4): 425-445.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 侯婷婷, 姚玉增, 付建飞, 刘静, 张永利, 郭荣荣. 辽宁弓长岭富铁矿成矿过程元素迁移特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 56-67. |
| [2] | 张文艳, 朱裕振, 刘雪, 汝亮, 闫冰. 山东禹城李屯地区重磁异常特征与找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 68-76. |
| [3] | 蒙嘉琪, 王志猛, 贾三石, 付建飞, 张岩松. 基于地球物理技术圈定沉积变质型富铁矿体: 辽宁鞍山齐大山铁矿例析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 87-97. |
| [4] | 张保涛, 梅贞华, 李秀章, 姜晓平, 胡兆国, 王小玉, 赵晓博, 胡加斌, 柳森. 华北克拉通矽卡岩型富铁矿成矿关键控制因素:来自地层学的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 98-116. |
| [5] | 王晓彤, 刘军, 杨艳, 何军成. 新疆北部喇嘛苏铜矿床成矿时代与构造背景:来自石榴子石原位LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 645-661. |
| [6] | 邬秋敏, 陈翠华, 涂宗林, 张燕, 宋志娇, 赖翔. 西藏蒙亚啊铅锌矿床矽卡岩矿物特征及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 874-886. |
| [7] | 田浩浩 ,张寿庭 ,曹华文 ,韩江伟 ,唐利 ,裴秋明. 豫西栾川鱼库锌多金属矿床地质及S、Pb同位素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1051-1060. |
| [8] | 赵飞 ,尹京武 ,王梦亚 ,张振华 ,孙衍东 ,张飘 ,高宇威 ,汪林峰 ,宗志宏. 湖南黄沙坪矽卡岩矿物学特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1038-1050. |
| [9] | 王建荣,薛传东,黄河远,靳纪娟. 滇西保山核桃坪铅锌矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 721-730. |
| [10] | 曾小华,周宗桂. 青海省兴海县铜峪沟铜矿床成矿物质和流体来源的地球化学探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 348-358. |
| [11] | 耿新霞,左文喆,陈风河,蒋国豪,张志欣. 新疆准噶尔北缘索尔库都克铜钼矿氦—氩同位素组成及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(2): 331-338. |
| [12] | 郑硌, 顾雪祥, 曹华文, 李青. 湖南省七宝山钙矽卡岩-镁矽卡岩共生型多金属矿床地质地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1): 87-97. |
| [13] | 葛松胜 ,杜杨松,王树星,李大鹏,庞振山,沈立军,王开虎,晋晓明. 新疆西天山敦德铁矿区矽卡岩成因:矿物学和稀土元素地球化学约束[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1): 61-72. |
| [14] | 刘元晴,曾溅辉,周乐,翟圣佳. 惠民凹陷沙河街组地层水化学特征及其成因[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(5): 1110-1119. |
| [15] | 杨爽, 杜杨松, 曹毅, 张智宇, 刘绍锋. 安徽铜陵冬瓜山层控矽卡岩铜矿床形成过程——来自磁黄铁矿的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(1): 54-60. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||