



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (05): 1321-1335.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.005
金霄1,2,3( ), 冯艳芳1,2, 罗晓玲1,2, 温心禹4, 张所文5, 张枝焕3
), 冯艳芳1,2, 罗晓玲1,2, 温心禹4, 张所文5, 张枝焕3
收稿日期:2022-05-28
修回日期:2023-02-27
出版日期:2023-10-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
作者简介:金 霄,男,博士,1990年出生,石油地质专业,主要从事油气地球化学研究及标准化工作。Email:jinx622109@foxmail.com。
基金资助:
JIN Xiao1,2,3( ), FENG Yanfang1,2, LUO Xiaoling1,2, WEN Xinyu4, ZHANG Suowen5, ZHANG Zhihuan3
), FENG Yanfang1,2, LUO Xiaoling1,2, WEN Xinyu4, ZHANG Suowen5, ZHANG Zhihuan3
Received:2022-05-28
Revised:2023-02-27
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-11-14
摘要:
为了探究准噶尔盆地南缘环博格达山中二叠统富有机质泥页岩的生烃潜力,对该地区不同构造单元的烃源岩进行生烃动力学研究,并讨论不同研究结果的物理化学意义以及影响活化能分布的化学反应机理。研究结果显示,受控于加热温度,含水体系恒温裂解模拟结果侧重于揭示干酪根生油的过程,而Rock-Eval开放体系的结果反映烃源岩产生所有烃类的过程。位于博格达山东北麓的中二叠统黑色泥页岩生烃活化能主峰约为55 kcal/mol,在北麓泉子街地区的活化能主峰约为60 kcal/mol,在西部的井井子沟地区和南部柴窝堡凹陷的活化能主峰约分布在65~70 kcal/mol之间。I型有机质表现出的高热解活化能可能与高峰度的链烷烃组分相关,因为链烷烃环化所需要的活化能高于其他脱氢反应。环博格达山地区,逆冲断层下盘的深部地层存在一定规模的油气聚集。
中图分类号:
金霄, 冯艳芳, 罗晓玲, 温心禹, 张所文, 张枝焕. 准噶尔盆地南缘环博格达山中二叠统黑色泥页岩生烃动力学研究:对周边探区油气勘探启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1321-1335.
JIN Xiao, FENG Yanfang, LUO Xiaoling, WEN Xinyu, ZHANG Suowen, ZHANG Zhihuan. Kinetic and Hydrocarbon Generation of Middle Permian Black Shale Around the Bogda Mountain, Southern Junggar Basin: Implications for Petroleum Exploration[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1321-1335.

图1 准噶尔盆地南缘环博格达山钻井与野外剖面分布情况(a)和中二叠统沉积相发育情况(b)
Fig.1 Map showing distribution of drilling and field profiles around the Bogda Mountain in southern Junggar Basin (a) and Middle Permian sedimentary facies around the Bogda Mountain (b)

图2 环博格达山地区二叠系地层岩性分布特征(a)和富有机质页岩的野外照片(b)
Fig.2 Permian stratigraphic and lithologic columns around the Bogda Mountain (a) and field photograph of organic-rich shale (b)
| 样品编号 | 井号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC(%) | S1+S2(mg/g) | Ro(%) | HI(mg/g) | TS(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1-100 | 奇1 | P2p | 灰质油泥岩 | 7.48 | 69.11 | 0.80 | 905.0 | |
| Q1-123 | 奇1 | P2p | 深灰色泥岩 | 5.90 | 37.67 | 0.78 | 623.0 | |
| D-17 | 西锅底坑 | P2l | 黑色页岩 | 3.59 | 22.37 | 0.76 | 616.6 | 0.020 |
| J-6 | 井井子沟 | P2p | 黑色页岩 | 4.26 | 8.70 | 202.2 | 0.027 | |
| J-11 | 井井子沟 | P2p | 黑色页岩 | 31.99 | 194.43 | 0.62 | 605.5 | 0.044 |
| J-16 | 井井子沟 | P2p | 黑色页岩 | 4.85 | 15.41 | 316.9 | 0.035 | |
| Q-2 | 泉子街 | P2p | 黑色泥岩 | 5.60 | 17.51 | 291.9 | 0.051 | |
| Q-6 | 泉子街 | P2p | 黑色泥岩 | 10.04 | 65.90 | 0.59 | 643.1 | 0.041 |
| Q-10 | 泉子街 | P2p | 黑色泥岩 | 21.35 | 195.31 | 911.6 | 0.059 |
表1 生烃动力学与生烃模拟实验样品地球化学信息
Table 1 Geochemical information of samples for the hydrocarbon generation kinetics experiment
| 样品编号 | 井号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC(%) | S1+S2(mg/g) | Ro(%) | HI(mg/g) | TS(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1-100 | 奇1 | P2p | 灰质油泥岩 | 7.48 | 69.11 | 0.80 | 905.0 | |
| Q1-123 | 奇1 | P2p | 深灰色泥岩 | 5.90 | 37.67 | 0.78 | 623.0 | |
| D-17 | 西锅底坑 | P2l | 黑色页岩 | 3.59 | 22.37 | 0.76 | 616.6 | 0.020 |
| J-6 | 井井子沟 | P2p | 黑色页岩 | 4.26 | 8.70 | 202.2 | 0.027 | |
| J-11 | 井井子沟 | P2p | 黑色页岩 | 31.99 | 194.43 | 0.62 | 605.5 | 0.044 |
| J-16 | 井井子沟 | P2p | 黑色页岩 | 4.85 | 15.41 | 316.9 | 0.035 | |
| Q-2 | 泉子街 | P2p | 黑色泥岩 | 5.60 | 17.51 | 291.9 | 0.051 | |
| Q-6 | 泉子街 | P2p | 黑色泥岩 | 10.04 | 65.90 | 0.59 | 643.1 | 0.041 |
| Q-10 | 泉子街 | P2p | 黑色泥岩 | 21.35 | 195.31 | 911.6 | 0.059 |
| 时长(d) | 温度(℃) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 330 | 360 | 370 | |
| 1 | 13.75 | 66.28 | ||
| 2 | 0.83 | 7.78 | 46.07 | |
| 3 | 23.01 | 99.99 | ||
| 5 | 23.74 | 72.66 | ||
| 7 | 44.20 | 63.33 | 79.19 | |
| 9 | 4.59 | 99.68 | ||
表2 J-11样品各实验条件下的转化率(%)
Table 2 Transformation ratio of J-11 sample under high P-T(%)
| 时长(d) | 温度(℃) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 330 | 360 | 370 | |
| 1 | 13.75 | 66.28 | ||
| 2 | 0.83 | 7.78 | 46.07 | |
| 3 | 23.01 | 99.99 | ||
| 5 | 23.74 | 72.66 | ||
| 7 | 44.20 | 63.33 | 79.19 | |
| 9 | 4.59 | 99.68 | ||
| 样品编号 | Q1-100 | Q1-123 | D-17 | J-6 | J-11 | J-16 | Q-2 | Q-6 | Q-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 井位/露头 | 奇1井 | 奇1井 | 西锅底坑 | 井井子沟 | 井井子沟 | 井井子沟 | 泉子街 | 泉子街 | 泉子街 |
| HI(mg/g) | 905 | 623 | 616 | 202 | 606 | 317 | 292 | 643 | 911 |
| A(s-1) | 9.00×1015 | 2.80×1015 | 2.35×1019 | 7.58×1020 | 2.32×1020 | 7.72×1018 | 4.18×1017 | 7.74×1018 | 3.62×1016 |
| 38(0.05) | 37(0.07) | 46(0.02) | 51(0.03) | 49(0.36) | 45(0.61) | 42(0.20) | 45(0.02) | 40(0.09) | |
| 40(0.05) | 38(0.27) | 47(0.02) | 52(0.01) | 51(0.35) | 46(0.10) | 43(0.13) | 46(0.10) | 41(0.13) | |
| 41(0.09) | 39(0.41) | 48(0.03) | 53(0.04) | 52(0.20) | 47(0.83) | 44(0.56) | 47(0.12) | 42(0.21) | |
| 42(0.05) | 40(0.37) | 49(0.08) | 54(0.01) | 53(0.35) | 48(0.25) | 45(0.42) | 48(0.21) | 43(0.21) | |
| 43(0.14) | 41(0.38) | 50(0.06) | 55(0.04) | 54(0.25) | 49(0.66) | 46(0.63) | 49(0.20) | 44(0.18) | |
| 44(0.06) | 42(0.42) | 51(0.12) | 56(0.05) | 55(0.46) | 51(0.82) | 47(0.57) | 50(0.22) | 45(0.40) | |
| 45(0.23) | 43(0.38) | 52(0.08) | 57(0.04) | 56(0.26) | 52(0.19) | 48(0.57) | 51(0.25) | 46(0.16) | |
| 46(0.07) | 44(0.45) | 53(0.16) | 58(0.06) | 57(0.58) | 53(0.47) | 49(0.60) | 52(0.21) | 47(0.62) | |
| 47(0.21) | 45(0.38) | 54(0.14) | 59(0.11) | 58(0.30) | 54(0.51) | 50(0.58) | 53(0.27) | 48(0.02) | |
| 48(0.28) | 46(0.28) | 55(0.25) | 60(0.06) | 59(0.88) | 55(0.65) | 51(0.69) | 54(0.27) | 49(1.18) | |
| 50(0.18) | 47(0.67) | 56(0.32) | 61(0.20) | 60(0.16) | 56(0.42) | 52(0.56) | 55(0.23) | 51(0.97) | |
| 51(1.30) | 51(0.37) | 57(0.37) | 62(0.11) | 61(1.58) | 57(1.08) | 53(1.16) | 56(0.43) | 52(1.43) | |
| 55(85.49) | 53(73.38) | 58(0.74) | 63(0.40) | 63(2.44) | 58(0.37) | 54(0.55) | 57(0.35) | 54(1.32) | |
| 57(5.05) | 54(14.16) | 59(0.64) | 64(0.14) | 64(2.18) | 59(1.59) | 55(2.02) | 58(0.66) | 55(10.29) | |
| 58(2.29) | 56(3.43) | 60(1.51) | 65(1.18) | 66(7.01) | 60(0.95) | 56(0.98) | 59(0.22) | 56(8.42) | |
| 60(1.33) | 57(0.26) | 61(2.13) | 66(0.40) | 67(4.47) | 61(3.28) | 57(2.62) | 60(2.12) | 57(15.42) | |
| 62(0.72) | 58(0.78) | 62(2.06) | 67(1.57) | 68(13.06) | 62(1.05) | 58(2.42) | 61(0.35) | 58(27.47) | |
| Ea(kcal/mol) | 63(0.73) | 59(0.81) | 63(6.81) | 68(0.81) | 69(2.22) | 63(6.82) | 59(9.74) | 62(5.33) | 59(12.43) |
| 67(1.68) | 61(0.81) | 64(9.04) | 69(5.03) | 70(20.00) | 64(22.24) | 60(25.86) | 63(15.19) | 61(5.17) | |
| 62(0.46) | 65(22.90) | 70(27.98) | 72(18.21) | 65(25.06) | 61(22.51) | 64(31.21) | 62(1.40) | ||
| 65(0.67) | 66(21.32) | 71(24.50) | 73(0.07) | 66(10.95) | 62(8.48) | 65(17.50) | 63(0.78) | ||
| 66(0.66) | 67(14.16) | 72(16.79) | 74(5.30) | 67(6.77) | 63(4.57) | 66(8.55) | 64(2.85) | ||
| 69(0.13) | 68(6.18) | 73(6.50) | 75(1.27) | 68(2.38) | 64(2.03) | 67(3.41) | 65(0.22) | ||
| 69(3.12) | 74(4.12) | 76(2.18) | 69(2.11) | 65(1.90) | 68(2.67) | 66(2.76) | |||
| 70(1.72) | 75(1.86) | 77(3.04) | 70(1.40) | 66(1.33) | 69(1.55) | 69(3.75) | |||
| 71(1.38) | 76(1.62) | 78(0.27) | 71(0.96) | 67(0.95) | 70(1.45) | 70(0.38) | |||
| 72(0.77) | 77(1.14) | 79(2.98) | 72(1.14) | 68(1.28) | 71(1.08) | 73(1.63) | |||
| 73(0.86) | 78(0.97) | 80(0.25) | 73(0.35) | 69(0.25) | 72(0.95) | ||||
| 74(0.41) | 79(0.78) | 81(3.07) | 74(0.90) | 70(1.43) | 73(0.75) | ||||
| 75(0.65) | 80(0.39) | 84(4.14) | 75(0.41) | 72(0.78) | 74(0.96) | ||||
| 76(0.11) | 81(0.82) | 88(2.13) | 77(1.21) | 73(0.89) | 75(0.25) | ||||
| 77(0.68) | 83(0.85) | 83(3.45) | 78(2.74) | 76(1.19) | |||||
| 78(0.19) | 84(0.07) | 79(1.73) | |||||||
| 80(0.51) | 86(0.81) | ||||||||
| 81(0.28) | 90(0.50) | ||||||||
| 84(0.17) |
表3 Rock-Eval实验求算研究区中二叠统烃源岩生烃动力学参数
Table 3 Kinetic results of Middle Permian source rocks for hydrocarbon generation by Rock-Eval analysis in the study area
| 样品编号 | Q1-100 | Q1-123 | D-17 | J-6 | J-11 | J-16 | Q-2 | Q-6 | Q-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 井位/露头 | 奇1井 | 奇1井 | 西锅底坑 | 井井子沟 | 井井子沟 | 井井子沟 | 泉子街 | 泉子街 | 泉子街 |
| HI(mg/g) | 905 | 623 | 616 | 202 | 606 | 317 | 292 | 643 | 911 |
| A(s-1) | 9.00×1015 | 2.80×1015 | 2.35×1019 | 7.58×1020 | 2.32×1020 | 7.72×1018 | 4.18×1017 | 7.74×1018 | 3.62×1016 |
| 38(0.05) | 37(0.07) | 46(0.02) | 51(0.03) | 49(0.36) | 45(0.61) | 42(0.20) | 45(0.02) | 40(0.09) | |
| 40(0.05) | 38(0.27) | 47(0.02) | 52(0.01) | 51(0.35) | 46(0.10) | 43(0.13) | 46(0.10) | 41(0.13) | |
| 41(0.09) | 39(0.41) | 48(0.03) | 53(0.04) | 52(0.20) | 47(0.83) | 44(0.56) | 47(0.12) | 42(0.21) | |
| 42(0.05) | 40(0.37) | 49(0.08) | 54(0.01) | 53(0.35) | 48(0.25) | 45(0.42) | 48(0.21) | 43(0.21) | |
| 43(0.14) | 41(0.38) | 50(0.06) | 55(0.04) | 54(0.25) | 49(0.66) | 46(0.63) | 49(0.20) | 44(0.18) | |
| 44(0.06) | 42(0.42) | 51(0.12) | 56(0.05) | 55(0.46) | 51(0.82) | 47(0.57) | 50(0.22) | 45(0.40) | |
| 45(0.23) | 43(0.38) | 52(0.08) | 57(0.04) | 56(0.26) | 52(0.19) | 48(0.57) | 51(0.25) | 46(0.16) | |
| 46(0.07) | 44(0.45) | 53(0.16) | 58(0.06) | 57(0.58) | 53(0.47) | 49(0.60) | 52(0.21) | 47(0.62) | |
| 47(0.21) | 45(0.38) | 54(0.14) | 59(0.11) | 58(0.30) | 54(0.51) | 50(0.58) | 53(0.27) | 48(0.02) | |
| 48(0.28) | 46(0.28) | 55(0.25) | 60(0.06) | 59(0.88) | 55(0.65) | 51(0.69) | 54(0.27) | 49(1.18) | |
| 50(0.18) | 47(0.67) | 56(0.32) | 61(0.20) | 60(0.16) | 56(0.42) | 52(0.56) | 55(0.23) | 51(0.97) | |
| 51(1.30) | 51(0.37) | 57(0.37) | 62(0.11) | 61(1.58) | 57(1.08) | 53(1.16) | 56(0.43) | 52(1.43) | |
| 55(85.49) | 53(73.38) | 58(0.74) | 63(0.40) | 63(2.44) | 58(0.37) | 54(0.55) | 57(0.35) | 54(1.32) | |
| 57(5.05) | 54(14.16) | 59(0.64) | 64(0.14) | 64(2.18) | 59(1.59) | 55(2.02) | 58(0.66) | 55(10.29) | |
| 58(2.29) | 56(3.43) | 60(1.51) | 65(1.18) | 66(7.01) | 60(0.95) | 56(0.98) | 59(0.22) | 56(8.42) | |
| 60(1.33) | 57(0.26) | 61(2.13) | 66(0.40) | 67(4.47) | 61(3.28) | 57(2.62) | 60(2.12) | 57(15.42) | |
| 62(0.72) | 58(0.78) | 62(2.06) | 67(1.57) | 68(13.06) | 62(1.05) | 58(2.42) | 61(0.35) | 58(27.47) | |
| Ea(kcal/mol) | 63(0.73) | 59(0.81) | 63(6.81) | 68(0.81) | 69(2.22) | 63(6.82) | 59(9.74) | 62(5.33) | 59(12.43) |
| 67(1.68) | 61(0.81) | 64(9.04) | 69(5.03) | 70(20.00) | 64(22.24) | 60(25.86) | 63(15.19) | 61(5.17) | |
| 62(0.46) | 65(22.90) | 70(27.98) | 72(18.21) | 65(25.06) | 61(22.51) | 64(31.21) | 62(1.40) | ||
| 65(0.67) | 66(21.32) | 71(24.50) | 73(0.07) | 66(10.95) | 62(8.48) | 65(17.50) | 63(0.78) | ||
| 66(0.66) | 67(14.16) | 72(16.79) | 74(5.30) | 67(6.77) | 63(4.57) | 66(8.55) | 64(2.85) | ||
| 69(0.13) | 68(6.18) | 73(6.50) | 75(1.27) | 68(2.38) | 64(2.03) | 67(3.41) | 65(0.22) | ||
| 69(3.12) | 74(4.12) | 76(2.18) | 69(2.11) | 65(1.90) | 68(2.67) | 66(2.76) | |||
| 70(1.72) | 75(1.86) | 77(3.04) | 70(1.40) | 66(1.33) | 69(1.55) | 69(3.75) | |||
| 71(1.38) | 76(1.62) | 78(0.27) | 71(0.96) | 67(0.95) | 70(1.45) | 70(0.38) | |||
| 72(0.77) | 77(1.14) | 79(2.98) | 72(1.14) | 68(1.28) | 71(1.08) | 73(1.63) | |||
| 73(0.86) | 78(0.97) | 80(0.25) | 73(0.35) | 69(0.25) | 72(0.95) | ||||
| 74(0.41) | 79(0.78) | 81(3.07) | 74(0.90) | 70(1.43) | 73(0.75) | ||||
| 75(0.65) | 80(0.39) | 84(4.14) | 75(0.41) | 72(0.78) | 74(0.96) | ||||
| 76(0.11) | 81(0.82) | 88(2.13) | 77(1.21) | 73(0.89) | 75(0.25) | ||||
| 77(0.68) | 83(0.85) | 83(3.45) | 78(2.74) | 76(1.19) | |||||
| 78(0.19) | 84(0.07) | 79(1.73) | |||||||
| 80(0.51) | 86(0.81) | ||||||||
| 81(0.28) | 90(0.50) | ||||||||
| 84(0.17) |

图6 量子化学计算模拟有机质脱氢反应及其活化自由能垒 (a)乙烷脱氢产生带双键的乙烯;(b)正己烷脱氢产生环己烷;(c)环己烷脱氢产生带双键的环己烯;(d)两分子二苯并噻吩通过芳基—芳基键合产生二聚体
Fig.6 Simulation of dehydrogenations and their activation free energy barriers of organic matter via quantum chemical calculation (a) dehydrogenation of ethane to form C=C double bonds; (b) cyclization of n-hexane to form cyclohexane; (c) dehydrogenatioin of cyclohexane to form cyclohexene; (d) aryl-aryl coupling by use of dibenzothiophene
| 芴 | 菲 | 芘 | 蒄 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 芴 | 122.26 | |||
| 菲 | 114.70 | 115.96 | ||
| 芘 | 122.22 | 123.60 | 122.51 | |
| 蒄 | 118.00 | 119.35 | 119.16 | 122.13 |
表4 常见芳烃相互发生芳基—芳基键合所需的活化能(kcal/mol)
Table 4 Apparent activation energy for aryl-aryl coupling between different aromatic hydrocarbons(kcal/mol)
| 芴 | 菲 | 芘 | 蒄 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 芴 | 122.26 | |||
| 菲 | 114.70 | 115.96 | ||
| 芘 | 122.22 | 123.60 | 122.51 | |
| 蒄 | 118.00 | 119.35 | 119.16 | 122.13 |
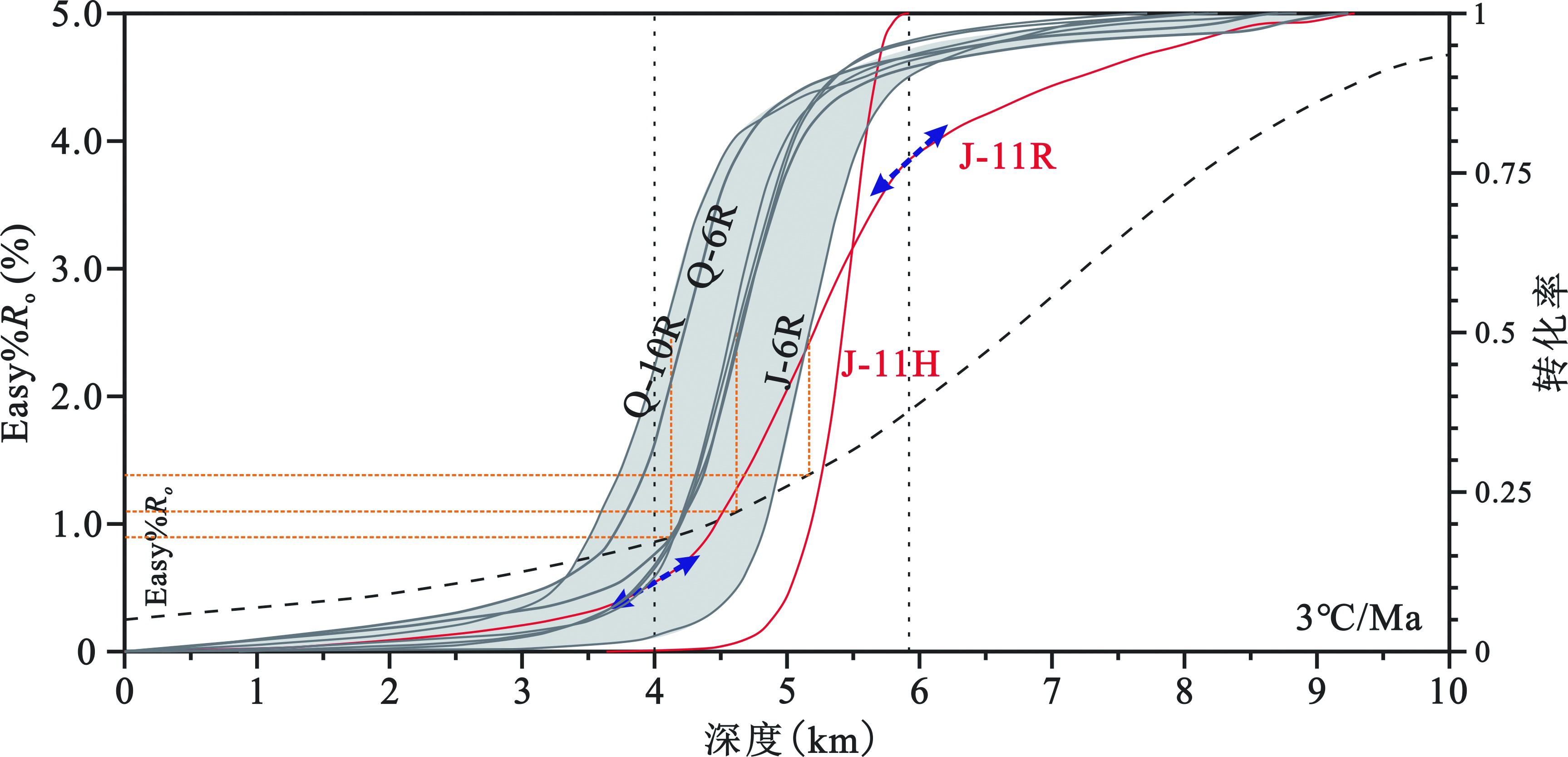
图7 研究区各烃源岩在虚拟盆地中的生烃门限对比(灰色实线及区间代表Rock-Eval求算的动力学曲线,红色实线代表两种方法求算的J-11黑色页岩动力学曲线。黑色虚线为Easy%Ro值)
Fig.7 Diagram showing the comparison of hydrocarbon generation threshold of source rocks under heating rate of virtual basin (solid gray line and the shadow denote the dynamic curve calculated by Rock-Eval method; solid red line denotes the dynamic curve of J-11 black shale calculated by the two methods; black dotted line denotes the Easy%Ro value)

图8 博格达山东北缘和西部不同构造单元的埋藏史与生烃史恢复 (a)博格达山东北麓和西部地震剖面地理位置示意图,灰色地层各自代表平地泉组(P2p)和芦草沟组(P2l);(b)奇1井埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果;(c)虚拟井1的埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果;(d)虚拟井2的埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果
Fig.8 Burial history and hydrocarbon generation history recovery of different tectonic units in the northeastern and western margin of Bogda Mountain

图9 博格达山南部柴窝堡凹陷不同构造单元的埋藏史与生烃史恢复 (a)柴窝堡凹陷构造区块划分以及地层剖面分布图,灰色地层代表红雁池组(P2h)和芦草沟组(P2l);(b)达1井的埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果;(c)虚拟井3的埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果;(d)虚拟井4的埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果;e:虚拟井5的埋藏史与生烃史恢复结果
Fig.9 Burial history and hydrocarbon generation history recovery of different tectonic units in the Chaiwobu subsag, southern Bogda Mountain
| [1] | 张希良, 黄晓丹, 张达, 等. 碳中和目标下的能源经济转型路径与政策研究[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38(1): 35-66. |
| [2] |
ZOU C N, DONG D Z, WANG Y M, et al. Shale gas in China: Characteristics, challenges and prospects (II)[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(2): 182-196.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZOU C N, DONG D Z, WANG Y M, et al. Shale gas in China: Characteristics, challenges and prospects (I)[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(6): 753-767.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GHANIZADEH A, CLARKSON C R, AQUINO S, et al. Petrophysical and geomechanical characteristics of Canadian tight oil and liquid-rich gas reservoirs: I.Pore network and permeability characterization[J]. Fuel, 2015, 153: 664-681.
DOI URL |
| [5] | ZOU C N. Unconventional Petroleum Geology[M]. Burlington, Mass: Elsevier, 2013. |
| [6] |
ZOU C N, ZHU R K, CHEN Z Q, et al. Organic-matter-rich shales of China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 189: 51-78.
DOI |
| [7] |
LUO Q Y, GONG L, QU Y S, et al. The tight oil potential of the Lucaogou Formation from the southern Junggar Basin, China[J]. Fuel, 2018, 234: 858-871.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 齐雪峰, 吴晓智, 唐勇, 等. 新疆博格达山北麓二叠系油页岩成矿特征及资源潜力[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(4): 1271-1285. |
| [9] | 张传恒, 刘典波, 张传林, 等. 新疆博格达山初始隆升时间的地层学标定[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(1): 294-302. |
| [10] | MAIER C G, ZIMMERLEY S R. Chemical dynamics of the transformation of organic matter to bitumen in oil-shale[J]. Utah Univ Res Invest Bull, 1924, 14,62-81. |
| [11] | TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1978. |
| [12] |
AHMAD THANA’ANI N A, MUSTAPHA K A, IDRIS M. Source rock pyrolysis and bulk kinetic modelling of Miocene sedimentary sequences in southeastern Sabah, Malaysia: The variability of thermal maturity to oil-gas producing kerogen[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109513.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SINGH D P, HAZRA B, WOOD D A, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and kinetics: A case study of Permian shales, India[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 222: 104960.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIANG H R, XU G S, XU F H, et al. Oil generation of lacustrine Type II shale: A case study of the Shahejie Formation, Laizhou Bay Sag, Bohai Bay Basin (China)[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107839.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LIAO L L, WANG Y P, CHEN C S, et al. Kinetic study of marine and lacustrine shale grains using Rock-Eval pyrolysis: Implications to hydrocarbon generation, retention and expulsion[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 89: 164-173.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
MONTHIOUX M, LANDAIS P, MONIN J C. Comparison between natural and artificial maturation series of humic coals from the Mahakam delta, Indonesia[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1985, 8(4): 275-292.
DOI URL |
| [17] | LEWAN M D, WILLIAMS J A. Evaluation of petroleum generation from resinites by hydrous pyrolysis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71: 207-214. |
| [18] | BEHAR F, VANDENBROUCKE M. Experimental determination of the rate constants of the n-C25 thermal cracking at 120, 400, and 800 bar: Implications for high-pressure/high-temperature prospects[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1996, 10(6): 605-612. |
| [19] |
DARTIGUELONGUE C, BEHAR F, BUDZINSKI H, et al. Thermal stability of dibenzothiophene in closed system pyrolysis: Experimental study and kinetic modelling[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37: 98-116.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LEWAN M D, RUBLE T E. Comparison of petroleum generation kinetics by isothermal hydrous and nonisothermal open-system pyrolysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(12): 1457-1475.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
JIANG Z L, DU H L, LI Y J, et al. Simulation of gas generation from the Paleogene Enping formation in the Baiyun sag in the deepwater area of the Pearl River mouth basin, the South China Sea[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29(2): 577-586.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
RAGAB S M, NICOLAJ M, NADIAH O L, et al. Phase kinetics for assessing the compositional evolution of petroleum generated from the early to Late Miocene source rock, Belait Formation, Brunei-Muara district, Brunei Darussalam[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 206: 108965.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KUMAR S, OJHA K. Reaction kinetic, maturity, burial and thermal histories modelling of Cambay shale source rocks, Cambay Basin, Western India[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 202: 108543.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIANG B L, LI E T, GAO X W, et al. Petroleum generation kinetics for Permian lacustrine source rocks in the Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 98: 1-17.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 顾连兴, 胡受奚, 于春水, 等. 论博格达俯冲撕裂型裂谷的形成与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(4): 585-597. |
| [26] | 顾连兴, 胡受奚, 于春水, 等. 博格达陆内碰撞造山带挤压-拉张构造转折期的侵入活动[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(2): 187-198. |
| [27] | 郑瑞辉. 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷油源条件及油气成藏研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019. |
| [28] | 郭威, 周鼎武, 欧阳征建, 等. 博格达山南缘达坂城东沟乡二叠纪岩浆岩及其形成地质环境[J]. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 37(1): 103-108. |
| [29] | 郭威, 周鼎武, 欧阳征建, 等. 博格达二叠纪区域伸展背景下的滑塌堆积特征[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 41(4): 658-662, 675. |
| [30] |
CAI Y F, ZHANG H, FENG Z, et al. A Germaropteris-dominated flora from the upper Permian of the Dalongkou section, Xinjiang, Northwest China, and its paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2019, 266: 61-71.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
METCALFE I, FOSTER C B, AFONIN S A, et al. Stratigraphy, biostratigraphy and C-isotopes of the permian-triassic non-marine sequence at dalongkou and lucaogou, Xinjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(6): 503-520.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 李丕龙, 冯建辉, 陆永潮. 准噶尔盆地构造沉积与成藏[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010. |
| [33] |
FOSTER C B, AFONIN S A. Syndesmorion gen.nov.— a coenobial alga of Chlorococcalean affinity from the continental Permian-Triassic deposits of Dalongkou section, Xinjiang Province, China[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2006, 138(1): 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 李婧婧. 博格达山北麓二叠系芦草沟组油页岩地球化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009. |
| [35] |
ZHAO Y, TRUHLAR D G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions,excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06 functionals and 12 other functionals[J]. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts, 2008, 119(5): 525.
DOI URL |
| [36] | MARENICH A V, CRAMER C J, TRUHLAR D G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 2009, 113(18): 6378-6396. |
| [37] |
QIU N S, ZHA M, WANG X L, et al. Tectono-thermal evolution of the Junggar Basin, NW China: Constraints from Ro and apatite fission track modelling[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2005, 11(4): 361-372.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
PETERS K E, BURNHAM A K, WALTERS C C, et al. Guidelines for kinetic input to petroleum system models from open-system pyrolysis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 979-986.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 张多多. 新疆博格达山北缘大龙口逆冲带构造恢复研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2016. |
| [40] |
SHI Y Q, JI H C, YU J W, et al. Provenance and sedimentary evolution from the Middle Permian to Early Triassic around the Bogda Mountain, NW China: A tectonic inversion responding to the consolidation of Pangea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 114: 104169.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
TANG W H, ZHANG Z C, LI J F, et al. Late Paleozoic to Jurassic tectonic evolution of the Bogda area (northwest China): Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 626: 144-156.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 李红. 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷油气地质条件综合研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2006. |
| [43] | 魏国财. 塔北塔中地区志留系剥蚀厚度恢复及古构造分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. |
| [1] | 张韩静, 李素梅, 高永进, 张林, 柯昌炜. 准噶尔盆地东南缘二叠系芦草沟组烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(06): 1538-1550. |
| [2] | 倪斌, 汤良杰, 郭颖, 余腾孝, 岳勇. 塔里木盆地玉北地区埋藏史及热史分析[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 357-366. |
| [3] | 曲江秀, 艾热提·吾甫尔, 查明, 陈洪, 丁修建, 高长海, 苏阳, 廉欢, 赖仁. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密油形成条件与分布规律[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(01): 119-128. |
| [4] | 张亚奇 ,马世忠 ,高阳 ,李映艳 ,张景 ,王黎 , 孙雨 ,许方哲 ,张宇鹏 ,. 咸化湖相高分辨率层序地层特征与致密油储层分布规律:以吉木萨尔凹陷A区芦草沟组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1096-1104. |
| [5] | 刘洋,何坤,李贤庆,徐红卫,张吉振,扈松林,王刚,樊志伟. 湖相烃源岩生烃动力学及排油效率—以松辽盆地青山口组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3): 627-634. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||