



现代地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (05): 1089-1099.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.043
收稿日期:2023-02-10
修回日期:2023-04-11
出版日期:2023-10-10
发布日期:2023-11-14
作者简介:孙自明,男,博士,高级工程师,1964年出生,矿产普查与勘探专业,主要从事油气勘探研究工作。Email:sunzm.syky@sinopec.com。
基金资助:
SUN Ziming( ), BIAN Changrong, LIU Guangxiang
), BIAN Changrong, LIU Guangxiang
Received:2023-02-10
Revised:2023-04-11
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-11-14
摘要:
近年来峨眉山大火成岩省及其地幔柱成因研究取得了重要进展,但关于地幔柱在四川盆地的作用范围和二叠纪成盆动力学机制等方面存在认识分歧。基于大量文献调研并结合近期研究,采用深部地幔活动控制表层系统演变的研究思路,系统梳理峨眉山大火成岩省及其深部地质特征。地幔柱是诱发峨眉山玄武岩大规模喷发并形成大火成岩省的主导因素,但地幔柱仅对四川盆地部分地区具有直接影响,具体表现为地幔柱上涌引起地壳隆升并导致中二叠统茅口组顶部出现地层差异剥蚀和对盆地中南部二叠纪沉积的控制作用,而盆地中北部中晚二叠世—早三叠世拉张槽群和“凹凸相间”沉积-构造格局的形成则主要受控于南秦岭洋岩石圈板块的拉张。
中图分类号:
孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 刘光祥. 峨眉山地幔柱主要研究进展及四川盆地二叠纪成盆动力学机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1089-1099.
SUN Ziming, BIAN Changrong, LIU Guangxiang. Advances on the Understanding in the Emeishan Mantle Plume and Dynamic Mechanism of the Permian Sichuan Basin Formation[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1089-1099.

图1 峨眉山大火成岩省与四川盆地分布(据文献[20????-25]修编)
Fig.1 Distribution of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province (ELIP) and the Sichuan Basin (modified after references [20????-25])
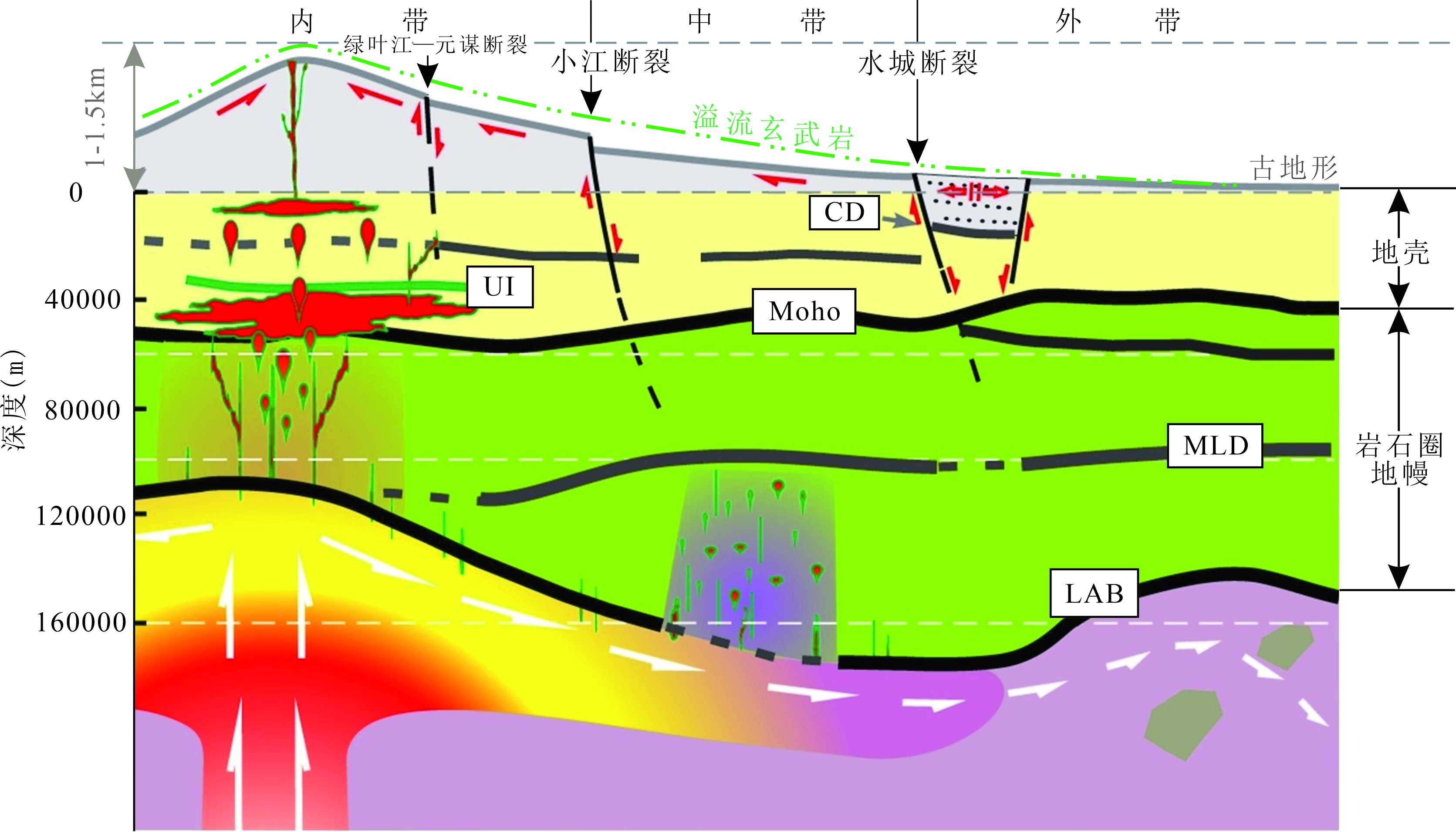
图2 峨眉山大火成岩省岩石圈内部主要界面和地质解释(据文献[7]修改) UI.下地壳底侵层顶界面; CD.康拉德不连续面; CB.结晶基底顶界面; Moho.莫霍面; MLD.岩石圈地幔内部间断面; LAB.岩石圈底界; 岩石圈内部主要界面形态均来自接收函数偏移成像结果,古地形由重力均衡估算得到
Fig.2 Seismic intra-lithospheric discontinuities and geological interpretation of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province(modified after reference [7])
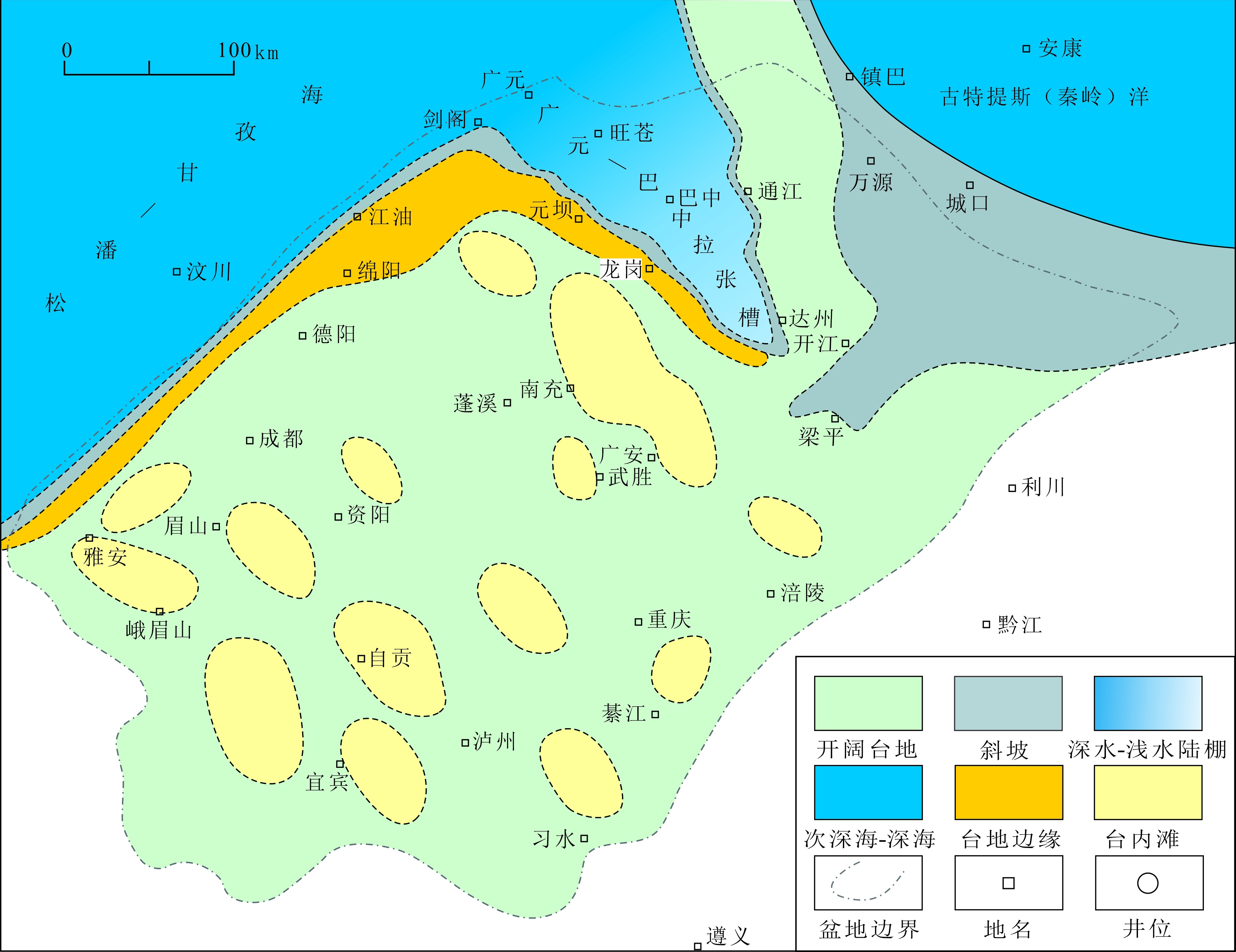
图3 四川盆地中二叠世茅口组沉积晚期沉积-构造格局及相带展布(据文献[53?-55]修编)
Fig.3 Distribution of the sedimentary-tectonic framework and sedimentary facies at the Late Maokou period of the Middle Permian in/around the Sichuan Basin (modified after references [53?-55])

图4 四川盆地及邻区晚二叠世长兴期沉积-构造格局及相带展布(据文献[58-59,62]修编)
Fig.4 Distribution of the sedimentary-tectonic framework and sedimentary facies at Late Permian Changxing period in/around the Sichuan Basin (modified after references [58-59,62])
| [1] |
WIGNALL P B. Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 53(1/2): 1-33.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WIGNALL P. The link between large igneous province eruptions and mass extinctions[J]. Elements, 2005, 1(5): 293-297.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WIGNALL P B, SUN Y D, BOND D P G, et al. Volcanism, mass extinction, and carbon isotope fluctuations in the Middle Permian of China[J]. Science, 2009, 324: 1179-1182.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | 王德滋, 周金城. 大火成岩省研究新进展[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(1): 1-8. |
| [5] | 徐义刚, 何斌, 罗震宇, 等. 我国大火成岩省和地幔柱研究进展与展望[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(1): 25-39. |
| [6] | 徐义刚, 钟孙霖. 峨眉山大火成岩省: 地幔柱活动的证据及其熔融条件[J]. 地球化学, 2001, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [7] | 徐义刚, 钟玉婷, 位荀, 等. 二叠纪地幔柱与地表系统演变[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017, 36(3): 359-373, 358. |
| [8] | 徐义刚. 地幔柱构造、大火成岩省及其地质效应[J]. 地学前缘, 2002, 9(4): 341-353. |
| [9] | 张招崇, MAHONEY John J, 王福生, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省西部苦橄岩及其共生玄武岩的地球化学: 地幔柱头部熔融的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6): 1538-1552. |
| [10] | 张招崇. 关于峨眉山大火成岩省一些重要问题的讨论[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3): 634-646. |
| [11] | 何冰辉, 刘瀚, 李雷. 峨眉山大火成岩省与二叠纪生物灭绝事件[J]. 四川地质学报, 2016, 36(4): 553-557. |
| [12] | 胡瑞忠, 陶琰, 钟宏, 等. 地幔柱成矿系统: 以峨眉山地幔柱为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(1): 42-54. |
| [13] | 赖旭龙, 孙亚东, 江海水. 峨眉山大火成岩省火山活动与中、晚二叠世之交生物大灭绝[J]. 中国科学基金, 2009, 23(6): 353-356. |
| [14] | 宋谢炎, 张成江, 胡瑞忠, 等. 峨眉火成岩省岩浆矿床成矿作用与地幔柱动力学过程的耦合关系[J]. 矿物岩石, 2005, 25(4): 35-44. |
| [15] | 汤庆艳, 张铭杰, 余明, 等. 晚二叠世峨眉山地幔柱岩浆成矿作用[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(5): 680-692. |
| [16] | 王登红. 地幔柱的概念、分类、演化与大规模成矿: 对中国西南部的探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(3): 67-72. |
| [17] | 夏茂龙, 文龙, 李亚, 等. 四川盆地简阳地区二叠系火山喷发旋回、环境与模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(9): 11-22. |
| [18] | 朱江, 张招崇. 大火成岩省与二叠纪两次生物灭绝关系研究进展[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(1): 137-148. |
| [19] | 朱江, 张招崇, 侯通, 等. 贵州盘县峨眉山玄武岩系顶部凝灰岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄: 对峨眉山大火成岩省与生物大规模灭绝关系的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(9): 2743-2751. |
| [20] |
HE L J. Emeishan mantle plume and its potential impact on the Sichuan Basin: Insights from numerical modeling[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2022, 323: 106841.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 陈辉, 邓江红, 刘树根, 等. 川西YS-1井玄武岩特征及与峨眉山玄武岩对比[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(3): 299-315. |
| [22] | 何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省的形成机制及空间展布: 来自沉积地层学的新证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(2): 194-202. |
| [23] | 刘冉, 李亚, 赵立可, 等. 四川华蓥偏岩子晚二叠世玄武岩地球化学特征及其与峨眉山大火成岩省的成因关系[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2022, 41(1): 1-17. |
| [24] | 朱传庆, 田云涛, 徐明, 等. 峨眉山超级地幔柱对四川盆地烃源岩热演化的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(1): 119-127. |
| [25] | 朱江. 峨眉山大火成岩省地幔柱动力学及其环境效应研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. |
| [26] |
XU Y G. Mantle plume, large igneous provinces and lithospheric evolution[J]. Episodes, 2007, 30(1): 5.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
COFFIN M F, ELDHOLM O. Large igneous provinces: Crustal structure, dimensions, and external consequences[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1994, 32(1): 1-36.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
BRYAN S E, ERNST R E. Revised definition of large igneous provinces (LIPs)[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2008, 86(1/2/3/4): 175-202.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ERNST R E, BUCHAN K L, CAMPBELL I H. Frontiers in large igneous Province research[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(3/4): 271-297.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LI H B, ZHANG Z C, SANTOSH M, et al. Late Permian basalts in the Yanghe area, eastern Sichuan Province, SW China: Implications for the geodynamics of the Emeishan flood basalt Province and Permian global mass extinction[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 134: 293-308.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
XIAO L, XU Y G, CHUNG S L, et al. Chemostratigraphic correlation of Upper Permian lavas from Yunnan Province, China: Extent of the Emeishan large igneous Province[J]. International Geology Review, 2003, 45(8): 753-766.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 孙浩伟, 范存辉, 张云峰, 等. 川东地区二叠系火山岩储层特征[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2022, 36(2): 34-40. |
| [33] | 何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 等. 峨眉山地幔柱上升的沉积响应及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2006, 52(1): 30-37. |
| [34] | 梁宇馨, 李红, 张冬冬, 等. 四川盆地华蓥山峨眉玄武岩地球化学特征及其成因分析[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(1): 288-302. |
| [35] |
FENG Q Q, QIU N S, FU X D, et al. Maturity evolution of Permian source rocks in the Sichuan Basin, southwestern China: The role of the Emeishan mantle plume[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 229: 105180.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
CAMPBELL I H, GRIFFITHS R W. Implications of mantle plume structure for the evolution of flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1990, 99(1/2): 79-93.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
RICHARDS M A, DUNCAN R A, COURTILLOT V E. Flood basalts and hot-spot tracks: Plume heads and tails[J]. Science, 1989, 246: 103-107.
PMID |
| [38] |
WHITE R, MCKENZIE D. Magmatism at rift zones: The generation of volcanic continental marginsand flood basalts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1989, 94: 7685-7729.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 李宏博, 朱江. 峨眉山玄武岩与茅口组灰岩的接触关系: 对峨眉山地幔柱动力学模型的指示意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(4): 571-579. |
| [40] | 张廷山, 陈晓慧, 刘治成, 等. 峨眉地幔柱构造对四川盆地栖霞期沉积格局的影响[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(8): 1251-1264. |
| [41] |
SUN Y D, LAI X L, WIGNALL P B, et al. Dating the onset and nature of the Middle Permian Emeishan large igneous province eruptions in SW China using conodont biostratigraphy and its bearing on mantle plume uplift models[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2): 20-33.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
UKSTINS PEATE I, BRYAN S E. Re-evaluating plume-induced uplift in the Emeishan large igneous Province[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(9): 625-629.
DOI |
| [43] | 李宏博, 张招崇, 吕林素, 等. 栖霞组和茅口组等厚图: 对峨眉山地幔柱成因模式的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(10): 2963-2974. |
| [44] | 李宏博, 张招崇, 吕林素. 峨眉山大火成岩省基性墙群几何学研究及对地幔柱中心的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(10): 3143-3152. |
| [45] | 宋谢炎, 侯增谦, 曹志敏, 等. 峨眉大火成岩省的岩石地球化学特征及时限[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(4): 498-506. |
| [46] |
SHELLNUTT J G, ZHOU M F, YAN D P, et al. Longevity of the Permian Emeishan mantle plume (SW China): 1 Ma, 8 Ma or 18 Ma?[J]. Geological Magazine, 2008, 145(3): 373-388.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
SHELLNUTT J G, DENYSZYN S W, MUNDIL R. Precise age determination of mafic and felsic intrusive rocks from the Permian Emeishan large igneous province (SW China)[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(1): 118-126.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
YANG J H, CAWOOD P A, DU Y S, et al. Early Wuchiapingian cooling linked to Emeishan basaltic weathering?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 492: 102-111.
DOI URL |
| [49] | 宋谢炎, 王玉兰, 曹志敏, 等. 峨眉山玄武岩、峨眉地裂运动与幔热柱[J]. 地质地球化学, 1998, 26(1): 47-52. |
| [50] | 徐涛, 张忠杰, 刘宝峰, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省地壳速度结构与古地幔柱活动遗迹: 来自丽江—清镇宽角地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2015, 45(5): 561-576. |
| [51] |
CHEN Y, XU Y G, XU T, et al. Magmatic underplating and crustal growth in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China, revealed by a passive seismic experiment[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432: 103-114.
DOI URL |
| [52] | 李大军, 陈辉, 陈洪德, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组储层形成与古构造演化关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5): 756-763. |
| [53] |
张玺华, 陈聪, 黄婕, 等. 四川盆地中二叠世广元—巴中拉张槽的发现及其油气地质意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(4): 466-475.
DOI |
| [54] | 周进高, 姚根顺, 杨光, 等. 四川盆地栖霞组—茅口组岩相古地理与天然气有利勘探区带[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(4): 8-15. |
| [55] |
王兴志, 李博, 杨西燕, 等. 四川盆地北部中二叠世晚期“广元—旺苍”海槽特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 562-574.
DOI |
| [56] | 胡朝伟, 胡广, 张玺华, 等. 川西北地区茅口组上部黑色岩系的层位、沉积环境及生烃潜力评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(2): 202-214. |
| [57] |
HE B, XU Y G, CHUNG S L, et al. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 213(3/4): 391-405.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 刘树根, 孙玮, 李智武, 等. 四川叠合盆地海相碳酸盐岩油气分布特征及其构造主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(5): 1-18. |
| [59] |
李秋芬, 苗顺德, 王铜山, 等. 四川盆地晚二叠世克拉通内裂陷作用背景下的盐亭—潼南海槽沉积充填特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 67-76.
DOI |
| [60] | 王一刚, 文应初, 洪海涛, 等. 四川盆地及邻区上二叠统—下三叠统海槽的深水沉积特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(5): 702-714. |
| [61] | 马永生, 牟传龙, 谭钦银, 等. 关于开江—梁平海槽的认识[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(3): 326-331. |
| [62] | 李洪奎. 四川盆地地质结构及叠合特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020. |
| [63] | 张奇, 屠志慧, 饶雷, 等. 四川川中地区晚二叠世蓬溪—武胜台凹对台内生物礁滩分布的控制作用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2010, 33(4): 1-4, 7, 91. |
| [64] | 罗志立, 孙玮, 韩建辉, 等. 峨眉地幔柱对中上扬子区二叠纪成藏条件影响的探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(6): 144-154. |
| [65] | 罗志立. 峨眉地裂运动和四川盆地天然气勘探实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2009, 30(4): 419-424. |
| [66] | 姚军辉, 罗志立, 孙玮, 等. 峨眉地幔柱与广旺—开江—梁平等拗拉槽形成关系[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2011, 32(1): 97-101. |
| [67] | 黄仁春. 四川盆地二叠纪—三叠纪开江—梁平陆棚形成演化与礁滩发育[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 41(4): 452-457. |
| [68] | 文龙, 张奇, 杨雨, 等. 四川盆地长兴组—飞仙关组礁、滩分布的控制因素及有利勘探区带[J]. 天然气工业, 2012, 32(1): 39-44, 120. |
| [69] | 邹才能, 徐春春, 汪泽成, 等. 四川盆地台缘带礁滩大气区地质特征与形成条件[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(6): 641-651. |
| [70] | 杨巍, 张廷山, 魏国齐, 等. 城口—鄂西海槽西侧晚二叠世碳酸盐台地边缘发育新认识[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(1): 79-93. |
| [71] | 郑斌嵩. 晚二叠世—早三叠世鄂西海槽沉积演化及其大地构造意义——兼论华南PTB斑脱岩的来源[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019. |
| [72] | 谭秀成, 罗冰, 江兴福, 等. 四川盆地基底断裂对长兴组生物礁的控制作用研究[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(2): 277-284. |
| [73] |
SONG X Y, ZHOU M F, CAO Z M, et al. Late Permian rifting of the South China Craton caused by the Emeishan mantle plume?[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2004, 161(5): 773-781.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 胡力文, 邹华耀, 杨伟强, 黎霆, 邓成昆, 程忠贞, 诸丹诚, 陈星岳. 川北寒武系碳酸盐岩压溶作用的影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1221-1231. |
| [2] | 李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 刘若冰, 蔡益栋, 李刚, 周秦, 肖贤明. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1293-1305. |
| [3] | 孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 张荣强, 孙炜, 武重阳, 林娟华. 四川盆地东南部震旦系灯影组四段台缘带天然气勘探前景[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 979-987. |
| [4] | 张宏辉, 吴亮, 李鸿, 余杨忠, 袁永盛, 张沥元, 李仕忠, 赵见波, 潘江涛, 詹华思, 石海涛, 陈贵仁. 滇东北乌蒙山地区峨眉地幔柱活动与火山-沉积盆地的响应关系[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 225-243. |
| [5] | 张宏辉, 袁永盛, 余杨忠, 李鸿, 张沥元, 李致伟, 郭太堂, 潘江涛, 詹华思, 石海涛. 扬子板块西缘中生代—新生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自峨眉山玄武岩的锆石U-Pb同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1155-1177. |
| [6] | 孙晓东, 陈海云, 于光宁. 内蒙古海拉斯图乌拉A型花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1218-1230. |
| [7] | 潘力, 何青林, 梁生贤, 陈先洁, 陈文, 谢光华, 黎洋, 夏青, 马乾. 基于正演模拟的火山岩重磁响应特征研究:以川西地区二叠系为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(05): 1471-1479. |
| [8] | 孙自明, 张荣强, 孙炜, 郝运轻, 卞昌蓉. 四川盆地东部海相下组合油气勘探领域与有利勘探方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 798-806. |
| [9] | 贾鹏, 黄福喜, 林世国, 宋涛, 高阳, 吕维宁, 汪少勇, 刘策, 范晶晶, 欧阳靖琳. 四川盆地及其邻区中上寒武统洗象池群沉积相与沉积模式特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(03): 807-818. |
| [10] | 鞠鹏程, 王训练, 王振涛, 刘喜方, 仲佳爱, 张在明. 渝北温泉镇地区三叠系“绿豆岩”特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(03): 431-449. |
| [11] | 郭硕, 何鹏, 刘洋, 滕飞, 胡晓佳, 王文龙, 杨泽黎. 内蒙古别鲁乌图铜多金属矿床锆石U-Pb年龄和S、Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 40-50. |
| [12] | 肖莎, 高志前. 广西东兰-凤山地区石炭纪-二叠纪碳酸盐岩洞穴发育特点及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1208-1219. |
| [13] | 曾严, 余心起, 刘秀, 胡军, 刘孟言, 汪子莘. 皖赣交界地区历口群岩石组成及其对造山后超大陆裂解的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 535-550. |
| [14] | 刘庆山, 魏玉帅, 张宝森, 潘婉莹. 古新世特提斯喜马拉雅南亚带石英砂岩成因及其构造意义:以藏南岗巴地区古新统基堵拉组为例[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 561-573. |
| [15] | 王子轶, 高志前, 石文睿, 王兴志, 赵红燕. 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组笔石与页岩气关系探讨[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 379-388. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||