



Geoscience ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (06): 1157-1169.
• OPetrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YAO Zheng( ), ZHANG Yafeng, YANG Tao, YI Pengfei, ZHENG Shuxin
), ZHANG Yafeng, YANG Tao, YI Pengfei, ZHENG Shuxin
Received:2016-12-12
Revised:2017-05-04
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-12-25
CLC Number:
YAO Zheng, ZHANG Yafeng, YANG Tao, YI Pengfei, ZHENG Shuxin. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Petrogeochemistry of Huangniupu Plutons in Western Section of the North Qinling Mountains and Their Geological Significance[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(06): 1157-1169.
| 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值及误差 | 同位素年龄及误差/Ma | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb* | 232Th | 238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 208Pb/232Th | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 208Pb/232Th | |||||||||||||||||
| 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | ||||||||||||
| 01 | 24.4 | 210 | 287 | 0.73 | 0.055 53 | 0.000 88 | 0.547 38 | 0.007 18 | 0.071 46 | 0.000 43 | 0.023 67 | 0.000 18 | 434 | 35 | 443 | 5 | 445 | 3 | 473 | 3 | |||||||
| 02 | 20.2 | 173 | 236 | 0.73 | 0.059 18 | 0.000 88 | 0.585 31 | 0.006 95 | 0.071 70 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 60 | 0.000 17 | 574 | 32 | 468 | 4 | 446 | 3 | 471 | 3 | |||||||
| 03 | 25.1 | 251 | 294 | 0.86 | 0.053 05 | 0.000 91 | 0.517 96 | 0.007 49 | 0.070 78 | 0.000 44 | 0.021 49 | 0.000 17 | 331 | 38 | 424 | 5 | 441 | 3 | 430 | 3 | |||||||
| 04 | 25.8 | 278 | 277 | 1.01 | 0.056 40 | 0.000 80 | 0.569 91 | 0.006 26 | 0.073 25 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 44 | 0.000 14 | 468 | 31 | 458 | 4 | 456 | 3 | 468 | 3 | |||||||
| 05 | 20.9 | 184 | 251 | 0.73 | 0.056 07 | 0.000 92 | 0.545 39 | 0.007 41 | 0.070 51 | 0.000 43 | 0.022 01 | 0.000 17 | 455 | 36 | 442 | 5 | 439 | 3 | 440 | 3 | |||||||
| 06 | 24.1 | 202 | 289 | 0.70 | 0.056 56 | 0.000 83 | 0.553 84 | 0.006 40 | 0.070 99 | 0.000 41 | 0.022 57 | 0.000 16 | 474 | 32 | 448 | 4 | 442 | 2 | 451 | 3 | |||||||
| 07 | 16.6 | 147 | 197 | 0.75 | 0.056 44 | 0.001 03 | 0.550 95 | 0.008 70 | 0.070 77 | 0.000 45 | 0.022 29 | 0.000 19 | 469 | 40 | 446 | 6 | 441 | 3 | 446 | 4 | |||||||
| 08 | 18.7 | 158 | 214 | 0.74 | 0.056 12 | 0.000 86 | 0.566 08 | 0.006 97 | 0.073 13 | 0.000 43 | 0.023 67 | 0.000 17 | 457 | 33 | 456 | 5 | 455 | 3 | 473 | 3 | |||||||
| 09 | 31.6 | 322 | 342 | 0.94 | 0.056 28 | 0.000 78 | 0.568 54 | 0.006 06 | 0.073 24 | 0.000 41 | 0.023 72 | 0.000 14 | 463 | 31 | 457 | 4 | 456 | 2 | 474 | 3 | |||||||
| 10 | 27.4 | 262 | 309 | 0.85 | 0.056 04 | 0.000 80 | 0.557 13 | 0.006 14 | 0.072 08 | 0.000 41 | 0.023 18 | 0.000 15 | 454 | 31 | 450 | 4 | 449 | 2 | 463 | 3 | |||||||
| 11 | 25.8 | 242 | 292 | 0.83 | 0.055 70 | 0.000 79 | 0.552 06 | 0.006 10 | 0.071 86 | 0.000 41 | 0.023 29 | 0.000 15 | 440 | 31 | 446 | 4 | 447 | 2 | 465 | 3 | |||||||
| 12 | 11.8 | 71 | 145 | 0.49 | 0.055 71 | 0.001 25 | 0.553 41 | 0.011 19 | 0.072 02 | 0.000 51 | 0.024 68 | 0.000 30 | 441 | 49 | 447 | 7 | 448 | 3 | 493 | 6 | |||||||
| 13 | 26.7 | 221 | 306 | 0.72 | 0.056 52 | 0.000 89 | 0.567 09 | 0.007 30 | 0.072 76 | 0.000 43 | 0.023 61 | 0.000 17 | 472 | 35 | 456 | 5 | 453 | 3 | 472 | 3 | |||||||
| 14 | 22.2 | 235 | 240 | 0.98 | 0.055 95 | 0.000 86 | 0.558 53 | 0.006 92 | 0.072 39 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 01 | 0.000 15 | 450 | 34 | 451 | 5 | 451 | 3 | 460 | 3 | |||||||
| 15 | 19.8 | 153 | 223 | 0.69 | 0.067 84 | 0.001 04 | 0.678 30 | 0.008 32 | 0.072 51 | 0.000 43 | 0.026 16 | 0.000 19 | 864 | 32 | 526 | 5 | 451 | 3 | 522 | 4 | |||||||
| 16 | 28.7 | 303 | 304 | 1.00 | 0.057 35 | 0.001 03 | 0.572 86 | 0.008 72 | 0.072 44 | 0.000 45 | 0.023 90 | 0.000 18 | 505 | 39 | 460 | 6 | 451 | 3 | 478 | 4 | |||||||
| 17 | 22.9 | 229 | 249 | 0.92 | 0.056 12 | 0.000 85 | 0.561 16 | 0.006 81 | 0.072 52 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 66 | 0.000 16 | 457 | 33 | 452 | 4 | 451 | 3 | 473 | 3 | |||||||
| 18 | 14.5 | 112 | 166 | 0.67 | 0.062 52 | 0.001 04 | 0.618 76 | 0.008 55 | 0.071 78 | 0.000 44 | 0.025 27 | 0.000 20 | 692 | 35 | 489 | 5 | 447 | 3 | 504 | 4 | |||||||
| 19 | 26.2 | 255 | 290 | 0.88 | 0.057 19 | 0.000 93 | 0.571 03 | 0.007 57 | 0.072 43 | 0.000 43 | 0.022 54 | 0.000 16 | 498 | 35 | 459 | 5 | 451 | 3 | 450 | 3 | |||||||
| 20 | 50.3 | 636 | 508 | 1.25 | 0.056 67 | 0.000 74 | 0.564 69 | 0.005 35 | 0.072 28 | 0.000 39 | 0.022 53 | 0.000 12 | 478 | 29 | 455 | 3 | 450 | 2 | 450 | 2 | |||||||
| 21 | 44.8 | 397 | 504 | 0.79 | 0.056 37 | 0.000 84 | 0.556 70 | 0.006 56 | 0.071 64 | 0.000 41 | 0.024 16 | 0.000 16 | 466 | 33 | 449 | 4 | 446 | 2 | 483 | 3 | |||||||
| 22 | 27.5 | 254 | 302 | 0.84 | 0.056 58 | 0.000 81 | 0.563 16 | 0.006 17 | 0.072 21 | 0.000 40 | 0.024 19 | 0.000 15 | 475 | 32 | 454 | 4 | 450 | 2 | 483 | 3 | |||||||
| 23 | 24.8 | 216 | 280 | 0.77 | 0.056 50 | 0.000 88 | 0.563 51 | 0.006 99 | 0.072 36 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 05 | 0.000 16 | 472 | 34 | 454 | 5 | 450 | 3 | 461 | 3 | |||||||
| 24 | 25.2 | 239 | 277 | 0.86 | 0.056 40 | 0.000 88 | 0.567 17 | 0.007 08 | 0.072 97 | 0.000 42 | 0.022 65 | 0.000 16 | 467 | 34 | 456 | 5 | 454 | 3 | 453 | 3 | |||||||
| 25 | 18.5 | 147 | 209 | 0.70 | 0.056 78 | 0.001 14 | 0.569 92 | 0.010 02 | 0.072 84 | 0.000 48 | 0.024 50 | 0.000 23 | 482 | 44 | 458 | 6 | 453 | 3 | 489 | 5 | |||||||
Table 1 Results of U-Pb isotopic dating of zircons in Huangniupu plutons
| 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值及误差 | 同位素年龄及误差/Ma | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb* | 232Th | 238U | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 208Pb/232Th | 207Pb/206Pb | 207Pb/235U | 206Pb/238U | 208Pb/232Th | |||||||||||||||||
| 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | 比值 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | 年龄 | 1σ | ||||||||||||
| 01 | 24.4 | 210 | 287 | 0.73 | 0.055 53 | 0.000 88 | 0.547 38 | 0.007 18 | 0.071 46 | 0.000 43 | 0.023 67 | 0.000 18 | 434 | 35 | 443 | 5 | 445 | 3 | 473 | 3 | |||||||
| 02 | 20.2 | 173 | 236 | 0.73 | 0.059 18 | 0.000 88 | 0.585 31 | 0.006 95 | 0.071 70 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 60 | 0.000 17 | 574 | 32 | 468 | 4 | 446 | 3 | 471 | 3 | |||||||
| 03 | 25.1 | 251 | 294 | 0.86 | 0.053 05 | 0.000 91 | 0.517 96 | 0.007 49 | 0.070 78 | 0.000 44 | 0.021 49 | 0.000 17 | 331 | 38 | 424 | 5 | 441 | 3 | 430 | 3 | |||||||
| 04 | 25.8 | 278 | 277 | 1.01 | 0.056 40 | 0.000 80 | 0.569 91 | 0.006 26 | 0.073 25 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 44 | 0.000 14 | 468 | 31 | 458 | 4 | 456 | 3 | 468 | 3 | |||||||
| 05 | 20.9 | 184 | 251 | 0.73 | 0.056 07 | 0.000 92 | 0.545 39 | 0.007 41 | 0.070 51 | 0.000 43 | 0.022 01 | 0.000 17 | 455 | 36 | 442 | 5 | 439 | 3 | 440 | 3 | |||||||
| 06 | 24.1 | 202 | 289 | 0.70 | 0.056 56 | 0.000 83 | 0.553 84 | 0.006 40 | 0.070 99 | 0.000 41 | 0.022 57 | 0.000 16 | 474 | 32 | 448 | 4 | 442 | 2 | 451 | 3 | |||||||
| 07 | 16.6 | 147 | 197 | 0.75 | 0.056 44 | 0.001 03 | 0.550 95 | 0.008 70 | 0.070 77 | 0.000 45 | 0.022 29 | 0.000 19 | 469 | 40 | 446 | 6 | 441 | 3 | 446 | 4 | |||||||
| 08 | 18.7 | 158 | 214 | 0.74 | 0.056 12 | 0.000 86 | 0.566 08 | 0.006 97 | 0.073 13 | 0.000 43 | 0.023 67 | 0.000 17 | 457 | 33 | 456 | 5 | 455 | 3 | 473 | 3 | |||||||
| 09 | 31.6 | 322 | 342 | 0.94 | 0.056 28 | 0.000 78 | 0.568 54 | 0.006 06 | 0.073 24 | 0.000 41 | 0.023 72 | 0.000 14 | 463 | 31 | 457 | 4 | 456 | 2 | 474 | 3 | |||||||
| 10 | 27.4 | 262 | 309 | 0.85 | 0.056 04 | 0.000 80 | 0.557 13 | 0.006 14 | 0.072 08 | 0.000 41 | 0.023 18 | 0.000 15 | 454 | 31 | 450 | 4 | 449 | 2 | 463 | 3 | |||||||
| 11 | 25.8 | 242 | 292 | 0.83 | 0.055 70 | 0.000 79 | 0.552 06 | 0.006 10 | 0.071 86 | 0.000 41 | 0.023 29 | 0.000 15 | 440 | 31 | 446 | 4 | 447 | 2 | 465 | 3 | |||||||
| 12 | 11.8 | 71 | 145 | 0.49 | 0.055 71 | 0.001 25 | 0.553 41 | 0.011 19 | 0.072 02 | 0.000 51 | 0.024 68 | 0.000 30 | 441 | 49 | 447 | 7 | 448 | 3 | 493 | 6 | |||||||
| 13 | 26.7 | 221 | 306 | 0.72 | 0.056 52 | 0.000 89 | 0.567 09 | 0.007 30 | 0.072 76 | 0.000 43 | 0.023 61 | 0.000 17 | 472 | 35 | 456 | 5 | 453 | 3 | 472 | 3 | |||||||
| 14 | 22.2 | 235 | 240 | 0.98 | 0.055 95 | 0.000 86 | 0.558 53 | 0.006 92 | 0.072 39 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 01 | 0.000 15 | 450 | 34 | 451 | 5 | 451 | 3 | 460 | 3 | |||||||
| 15 | 19.8 | 153 | 223 | 0.69 | 0.067 84 | 0.001 04 | 0.678 30 | 0.008 32 | 0.072 51 | 0.000 43 | 0.026 16 | 0.000 19 | 864 | 32 | 526 | 5 | 451 | 3 | 522 | 4 | |||||||
| 16 | 28.7 | 303 | 304 | 1.00 | 0.057 35 | 0.001 03 | 0.572 86 | 0.008 72 | 0.072 44 | 0.000 45 | 0.023 90 | 0.000 18 | 505 | 39 | 460 | 6 | 451 | 3 | 478 | 4 | |||||||
| 17 | 22.9 | 229 | 249 | 0.92 | 0.056 12 | 0.000 85 | 0.561 16 | 0.006 81 | 0.072 52 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 66 | 0.000 16 | 457 | 33 | 452 | 4 | 451 | 3 | 473 | 3 | |||||||
| 18 | 14.5 | 112 | 166 | 0.67 | 0.062 52 | 0.001 04 | 0.618 76 | 0.008 55 | 0.071 78 | 0.000 44 | 0.025 27 | 0.000 20 | 692 | 35 | 489 | 5 | 447 | 3 | 504 | 4 | |||||||
| 19 | 26.2 | 255 | 290 | 0.88 | 0.057 19 | 0.000 93 | 0.571 03 | 0.007 57 | 0.072 43 | 0.000 43 | 0.022 54 | 0.000 16 | 498 | 35 | 459 | 5 | 451 | 3 | 450 | 3 | |||||||
| 20 | 50.3 | 636 | 508 | 1.25 | 0.056 67 | 0.000 74 | 0.564 69 | 0.005 35 | 0.072 28 | 0.000 39 | 0.022 53 | 0.000 12 | 478 | 29 | 455 | 3 | 450 | 2 | 450 | 2 | |||||||
| 21 | 44.8 | 397 | 504 | 0.79 | 0.056 37 | 0.000 84 | 0.556 70 | 0.006 56 | 0.071 64 | 0.000 41 | 0.024 16 | 0.000 16 | 466 | 33 | 449 | 4 | 446 | 2 | 483 | 3 | |||||||
| 22 | 27.5 | 254 | 302 | 0.84 | 0.056 58 | 0.000 81 | 0.563 16 | 0.006 17 | 0.072 21 | 0.000 40 | 0.024 19 | 0.000 15 | 475 | 32 | 454 | 4 | 450 | 2 | 483 | 3 | |||||||
| 23 | 24.8 | 216 | 280 | 0.77 | 0.056 50 | 0.000 88 | 0.563 51 | 0.006 99 | 0.072 36 | 0.000 42 | 0.023 05 | 0.000 16 | 472 | 34 | 454 | 5 | 450 | 3 | 461 | 3 | |||||||
| 24 | 25.2 | 239 | 277 | 0.86 | 0.056 40 | 0.000 88 | 0.567 17 | 0.007 08 | 0.072 97 | 0.000 42 | 0.022 65 | 0.000 16 | 467 | 34 | 456 | 5 | 454 | 3 | 453 | 3 | |||||||
| 25 | 18.5 | 147 | 209 | 0.70 | 0.056 78 | 0.001 14 | 0.569 92 | 0.010 02 | 0.072 84 | 0.000 48 | 0.024 50 | 0.000 23 | 482 | 44 | 458 | 6 | 453 | 3 | 489 | 5 | |||||||
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNP01 | 62.03 | 0.73 | 15.60 | 1.91 | 3.69 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 4.72 | 3.65 | 3.00 |
| HNP02 | 62.27 | 0.68 | 16.21 | 2.19 | 3.42 | 0.10 | 3.11 | 5.28 | 3.32 | 2.98 |
| HNP03 | 60.49 | 0.78 | 15.99 | 2.28 | 4.10 | 0.11 | 3.54 | 5.24 | 3.31 | 3.17 |
| HNP04 | 62.89 | 0.66 | 15.72 | 1.85 | 3.49 | 0.10 | 2.97 | 4.77 | 3.25 | 3.39 |
| HNP05 | 63.09 | 0.61 | 15.41 | 2.07 | 3.19 | 0.10 | 2.88 | 4.70 | 3.48 | 3.83 |
| HNP06 | 62.16 | 0.70 | 16.03 | 2.21 | 3.38 | 0.11 | 3.09 | 5.04 | 3.42 | 2.95 |
| HNP07 | 58.41 | 0.83 | 15.66 | 2.32 | 4.71 | 0.13 | 4.09 | 6.54 | 3.67 | 3.09 |
| 样品号 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | σ | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd |
| HNP01 | 0.25 | 2.15 | 2.32 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 52.57 | 43.10 | 81.70 | 9.37 | 37.30 |
| HNP02 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 2.06 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 50.68 | 38.50 | 66.70 | 7.49 | 28.60 |
| HNP03 | 0.32 | 1.37 | 2.40 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 50.68 | 37.60 | 69.00 | 8.12 | 32.00 |
| HNP04 | 0.27 | 1.25 | 2.22 | 1.04 | 0.89 | 50.68 | 41.00 | 79.50 | 8.97 | 34.10 |
| HNP05 | 0.24 | 0.96 | 2.66 | 1.10 | 0.84 | 50.43 | 34.90 | 64.80 | 7.51 | 28.70 |
| HNP06 | 0.27 | 1.37 | 2.12 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 50.68 | 41.90 | 71.30 | 8.11 | 30.00 |
| HNP07 | 0.35 | 0.96 | 2.97 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 51.73 | 40.50 | 79.00 | 9.46 | 36.60 |
| 样品号 | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| HNP01 | 7.52 | 1.85 | 5.85 | 0.78 | 3.77 | 0.84 | 2.27 | 0.34 | 2.26 | 0.31 |
| HNP02 | 5.62 | 1.64 | 4.73 | 0.61 | 3.40 | 0.60 | 1.81 | 0.25 | 1.61 | 0.28 |
| HNP03 | 6.58 | 1.82 | 5.34 | 0.67 | 3.80 | 0.68 | 2.06 | 0.29 | 1.93 | 0.29 |
| HNP04 | 6.90 | 1.74 | 5.45 | 0.78 | 3.95 | 0.72 | 2.28 | 0.32 | 2.09 | 0.34 |
| HNP05 | 5.65 | 1.58 | 4.78 | 0.59 | 3.44 | 0.63 | 1.88 | 0.27 | 1.92 | 0.29 |
| HNP06 | 5.88 | 1.60 | 5.18 | 0.60 | 3.22 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.26 |
| HNP07 | 7.71 | 1.93 | 6.38 | 0.79 | 4.39 | 0.88 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 2.39 | 0.35 |
| 样品号 | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Y | Cu | Pb |
| HNP01 | 197.26 | 180.84 | 16.42 | 11.01 | 12.89 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 24.20 | 54.60 | 25.60 |
| HNP02 | 161.84 | 148.55 | 13.29 | 11.18 | 16.16 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 19.80 | 43.60 | 29.00 |
| HNP03 | 170.18 | 155.12 | 15.06 | 10.30 | 13.16 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 21.80 | 45.80 | 25.30 |
| HNP04 | 188.14 | 172.21 | 15.93 | 10.81 | 13.26 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 23.90 | 54.40 | 144.50 |
| HNP05 | 156.94 | 143.14 | 13.80 | 10.37 | 12.28 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 20.20 | 32.90 | 28.10 |
| HNP06 | 172.54 | 158.79 | 13.75 | 11.55 | 15.56 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 20.20 | 44.40 | 27.50 |
| HNP07 | 193.03 | 175.20 | 17.83 | 9.83 | 11.45 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 26.20 | 33.30 | 26.30 |
| 样品号 | Zn | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Ga | Sc | Sr | Ba | Rb |
| HNP01 | 58.40 | 18.54 | 31.50 | 88.70 | 147.70 | 18.30 | 14.50 | 597.80 | 967.10 | 124.80 |
| HNP02 | 56.30 | 17.60 | 24.80 | 57.00 | 120.40 | 19.30 | 12.90 | 663.30 | 906.10 | 150.60 |
| HNP03 | 67.60 | 20.70 | 31.00 | 70.20 | 142.10 | 19.60 | 15.80 | 742.60 | 833.20 | 157.40 |
| HNP04 | 64.40 | 17.70 | 25.30 | 63.50 | 128.50 | 18.50 | 14.50 | 579.90 | 802.00 | 142.20 |
| HNP05 | 55.00 | 15.80 | 20.90 | 73.70 | 115.00 | 17.50 | 12.50 | 555.00 | 779.00 | 147.00 |
| HNP06 | 57.60 | 20.40 | 25.90 | 68.30 | 112.60 | 18.10 | 15.50 | 575.90 | 837.10 | 143.60 |
| HNP07 | 68.50 | 25.70 | 30.60 | 70.80 | 165.20 | 19.60 | 18.80 | 633.60 | 691.70 | 121.70 |
| 样品号 | Cs | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | P | Ti | K |
| HNP01 | 5.88 | 19.40 | 1.31 | 120.20 | 1.31 | 3.73 | 18.20 | 1 236.00 | 3 912.30 | 23 806.25 |
| HNP02 | 7.22 | 10.10 | 1.04 | 167.90 | 1.00 | 5.88 | 14.56 | 1 408.40 | 3 425.60 | 23 806.25 |
| HNP03 | 4.01 | 10.80 | 1.00 | 199.50 | 1.01 | 4.05 | 17.40 | 1 602.30 | 4 007.70 | 25 268.75 |
| HNP04 | 4.48 | 11.90 | 1.23 | 174.60 | 1.27 | 4.03 | 20.00 | 1 403.90 | 3 396.70 | 27 056.25 |
| HNP05 | 4.76 | 11.00 | 1.06 | 164.00 | 1.06 | 3.97 | 16.90 | 1 306.00 | 3 073.00 | 30 712.50 |
| HNP06 | 4.38 | 9.37 | 1.06 | 169.80 | 1.03 | 4.54 | 18.60 | 1 215.50 | 3 045.00 | 23 562.50 |
| HNP07 | 4.99 | 12.00 | 1.19 | 130.70 | 1.16 | 4.51 | 11.70 | 1 812.90 | 4 182.60 | 24 700.00 |
Table 2 Results of major elements (%), trace elements (10-6 ) and REEs (10-6 ) of Huangniupu plutons
| 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNP01 | 62.03 | 0.73 | 15.60 | 1.91 | 3.69 | 0.11 | 3.36 | 4.72 | 3.65 | 3.00 |
| HNP02 | 62.27 | 0.68 | 16.21 | 2.19 | 3.42 | 0.10 | 3.11 | 5.28 | 3.32 | 2.98 |
| HNP03 | 60.49 | 0.78 | 15.99 | 2.28 | 4.10 | 0.11 | 3.54 | 5.24 | 3.31 | 3.17 |
| HNP04 | 62.89 | 0.66 | 15.72 | 1.85 | 3.49 | 0.10 | 2.97 | 4.77 | 3.25 | 3.39 |
| HNP05 | 63.09 | 0.61 | 15.41 | 2.07 | 3.19 | 0.10 | 2.88 | 4.70 | 3.48 | 3.83 |
| HNP06 | 62.16 | 0.70 | 16.03 | 2.21 | 3.38 | 0.11 | 3.09 | 5.04 | 3.42 | 2.95 |
| HNP07 | 58.41 | 0.83 | 15.66 | 2.32 | 4.71 | 0.13 | 4.09 | 6.54 | 3.67 | 3.09 |
| 样品号 | P2O5 | 烧失量 | σ | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | Mg# | La | Ce | Pr | Nd |
| HNP01 | 0.25 | 2.15 | 2.32 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 52.57 | 43.10 | 81.70 | 9.37 | 37.30 |
| HNP02 | 0.28 | 0.98 | 2.06 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 50.68 | 38.50 | 66.70 | 7.49 | 28.60 |
| HNP03 | 0.32 | 1.37 | 2.40 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 50.68 | 37.60 | 69.00 | 8.12 | 32.00 |
| HNP04 | 0.27 | 1.25 | 2.22 | 1.04 | 0.89 | 50.68 | 41.00 | 79.50 | 8.97 | 34.10 |
| HNP05 | 0.24 | 0.96 | 2.66 | 1.10 | 0.84 | 50.43 | 34.90 | 64.80 | 7.51 | 28.70 |
| HNP06 | 0.27 | 1.37 | 2.12 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 50.68 | 41.90 | 71.30 | 8.11 | 30.00 |
| HNP07 | 0.35 | 0.96 | 2.97 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 51.73 | 40.50 | 79.00 | 9.46 | 36.60 |
| 样品号 | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| HNP01 | 7.52 | 1.85 | 5.85 | 0.78 | 3.77 | 0.84 | 2.27 | 0.34 | 2.26 | 0.31 |
| HNP02 | 5.62 | 1.64 | 4.73 | 0.61 | 3.40 | 0.60 | 1.81 | 0.25 | 1.61 | 0.28 |
| HNP03 | 6.58 | 1.82 | 5.34 | 0.67 | 3.80 | 0.68 | 2.06 | 0.29 | 1.93 | 0.29 |
| HNP04 | 6.90 | 1.74 | 5.45 | 0.78 | 3.95 | 0.72 | 2.28 | 0.32 | 2.09 | 0.34 |
| HNP05 | 5.65 | 1.58 | 4.78 | 0.59 | 3.44 | 0.63 | 1.88 | 0.27 | 1.92 | 0.29 |
| HNP06 | 5.88 | 1.60 | 5.18 | 0.60 | 3.22 | 0.60 | 1.80 | 0.27 | 1.82 | 0.26 |
| HNP07 | 7.71 | 1.93 | 6.38 | 0.79 | 4.39 | 0.88 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 2.39 | 0.35 |
| 样品号 | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Y | Cu | Pb |
| HNP01 | 197.26 | 180.84 | 16.42 | 11.01 | 12.89 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 24.20 | 54.60 | 25.60 |
| HNP02 | 161.84 | 148.55 | 13.29 | 11.18 | 16.16 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 19.80 | 43.60 | 29.00 |
| HNP03 | 170.18 | 155.12 | 15.06 | 10.30 | 13.16 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 21.80 | 45.80 | 25.30 |
| HNP04 | 188.14 | 172.21 | 15.93 | 10.81 | 13.26 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 23.90 | 54.40 | 144.50 |
| HNP05 | 156.94 | 143.14 | 13.80 | 10.37 | 12.28 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 20.20 | 32.90 | 28.10 |
| HNP06 | 172.54 | 158.79 | 13.75 | 11.55 | 15.56 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 20.20 | 44.40 | 27.50 |
| HNP07 | 193.03 | 175.20 | 17.83 | 9.83 | 11.45 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 26.20 | 33.30 | 26.30 |
| 样品号 | Zn | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Ga | Sc | Sr | Ba | Rb |
| HNP01 | 58.40 | 18.54 | 31.50 | 88.70 | 147.70 | 18.30 | 14.50 | 597.80 | 967.10 | 124.80 |
| HNP02 | 56.30 | 17.60 | 24.80 | 57.00 | 120.40 | 19.30 | 12.90 | 663.30 | 906.10 | 150.60 |
| HNP03 | 67.60 | 20.70 | 31.00 | 70.20 | 142.10 | 19.60 | 15.80 | 742.60 | 833.20 | 157.40 |
| HNP04 | 64.40 | 17.70 | 25.30 | 63.50 | 128.50 | 18.50 | 14.50 | 579.90 | 802.00 | 142.20 |
| HNP05 | 55.00 | 15.80 | 20.90 | 73.70 | 115.00 | 17.50 | 12.50 | 555.00 | 779.00 | 147.00 |
| HNP06 | 57.60 | 20.40 | 25.90 | 68.30 | 112.60 | 18.10 | 15.50 | 575.90 | 837.10 | 143.60 |
| HNP07 | 68.50 | 25.70 | 30.60 | 70.80 | 165.20 | 19.60 | 18.80 | 633.60 | 691.70 | 121.70 |
| 样品号 | Cs | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | P | Ti | K |
| HNP01 | 5.88 | 19.40 | 1.31 | 120.20 | 1.31 | 3.73 | 18.20 | 1 236.00 | 3 912.30 | 23 806.25 |
| HNP02 | 7.22 | 10.10 | 1.04 | 167.90 | 1.00 | 5.88 | 14.56 | 1 408.40 | 3 425.60 | 23 806.25 |
| HNP03 | 4.01 | 10.80 | 1.00 | 199.50 | 1.01 | 4.05 | 17.40 | 1 602.30 | 4 007.70 | 25 268.75 |
| HNP04 | 4.48 | 11.90 | 1.23 | 174.60 | 1.27 | 4.03 | 20.00 | 1 403.90 | 3 396.70 | 27 056.25 |
| HNP05 | 4.76 | 11.00 | 1.06 | 164.00 | 1.06 | 3.97 | 16.90 | 1 306.00 | 3 073.00 | 30 712.50 |
| HNP06 | 4.38 | 9.37 | 1.06 | 169.80 | 1.03 | 4.54 | 18.60 | 1 215.50 | 3 045.00 | 23 562.50 |
| HNP07 | 4.99 | 12.00 | 1.19 | 130.70 | 1.16 | 4.51 | 11.70 | 1 812.90 | 4 182.60 | 24 700.00 |
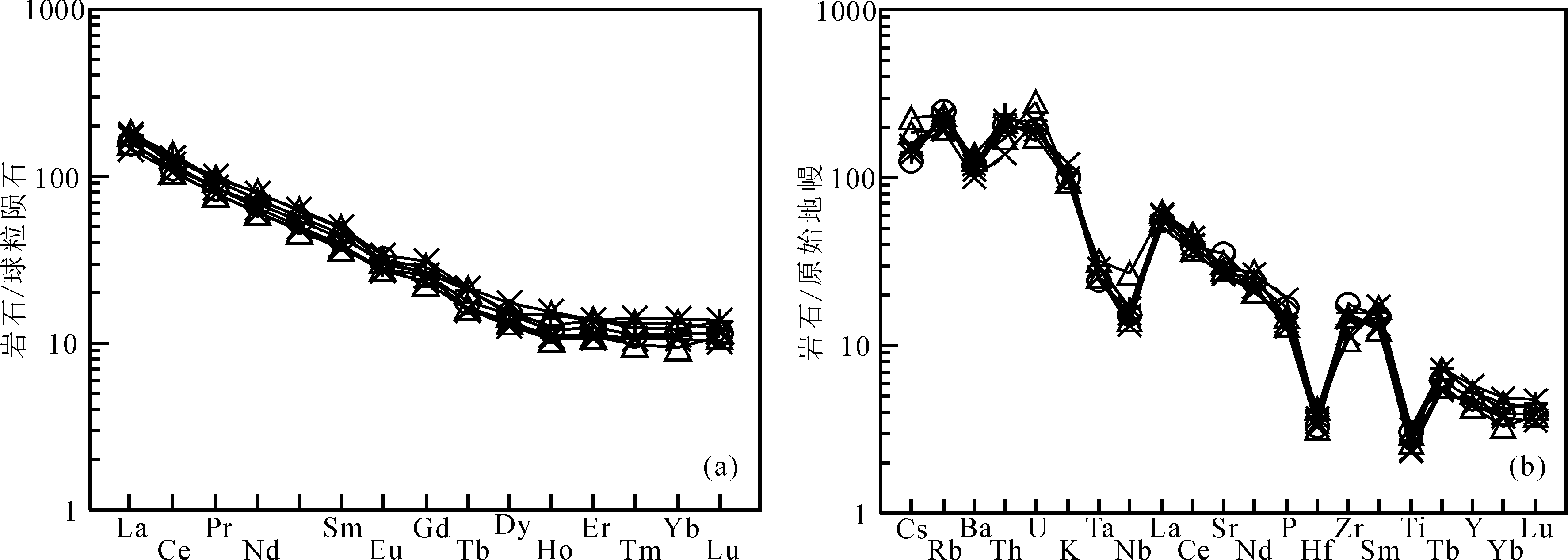
Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spider diagram (b) for Huangniupu plutons (normalization values after SUN et al.[38])
| [1] |
MATTAUER M, MATTE P, MALAVIEILLE J, et al. Tectonics of the Qinling belt: build-up and evolution of eastern Asia[J]. Nature, 1985, 317: 496-500.
DOI |
| [2] | 许志琴, 卢一伦, 汤耀庆, 等. 东秦岭复合山链的形成:变形、 演化及板块动力学[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1986: 1-193. |
| [3] | 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 1-855. |
| [4] | 裴先治, 张维吉, 王涛, 等. 北秦岭造山带的地质特征及其构造演化[J]. 西北地质, 1995, 16(4): 8-12. |
| [5] | 张本仁, 欧阳建平, 韩吟文, 等. 北秦岭古汇聚带壳幔再循环[J]. 地球科学, 1996, 21(5): 469-475. |
| [6] | 张国伟, 张宗清, 董云鹏. 秦岭造山带主要构造岩石地层单元的构造性质及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(2): 101-114. |
| [7] | 张国伟, 董云鹏, 姚安平. 秦岭造山带基本组成与结构及其构造演化[J]. 陕西地质, 1997, 15(2): 1-14. |
| [8] | 王宗起, 闫全人, 闫臻, 等. 秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(11): 1527-1546. |
| [9] | 王平安, 陈毓川. 秦岭造山带构造-成矿旋回与演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 1997, 3(1): 10-20. |
| [10] | 张旗, 张宗清, 孙勇, 等. 陕西商县—丹凤地区丹凤群变质玄武岩的微量元素和同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(1): 43-54. |
| [11] | 张成立, 周鼎武, 韩松. 陕西商州地区丹凤变质火山岩的地球化学特征[J]. 地质科学, 1994, 29(4): 384 -392. |
| [12] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 中央造山带早古生代地体格架与高压/超高压变质带的形成[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(12): 1793-1806. |
| [13] | 王涛, 王晓霞, 田伟, 等. 北秦岭古生代花岗岩组合、岩浆时空演变及其对造山作用的启示[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2009, 39(7): 949-971. |
| [14] | 李源, 杨经绥, 裴先治, 等. 秦岭造山带早古生代蛇绿岩的多阶段演化: 从岛弧到弧间盆地[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(6): 1896-1914. |
| [15] | 王晓霞, 王涛, 张成立. 秦岭造山带花岗质岩浆作用与造山带演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2015, 45(8): 1109-1125. |
| [16] | 骆庭川, 张宏飞, 张本仁. 北秦岭丹凤—西峡地区古岛弧花岗岩类成分极性及原因探讨[J]. 地球科学, 1993, 18(1): 67-72. |
| [17] | 刘丙祥, 聂虎, 齐玥, 等. 豫西南地区北秦岭地体新元古代花岗岩类岩石成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(7): 2437-2455. |
| [18] | 王洪亮, 肖绍文, 徐学义, 等. 北秦岭西段吕梁期构造岩浆事件的年代学及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(10): 1728-1738. |
| [19] | 张成立, 刘良, 王涛, 等. 北秦岭早古生代大陆碰撞过程中的花岗岩浆作用[J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(23): 2323-2329. |
| [20] | 王晓霞, 王涛, 齐秋菊, 等. 秦岭晚中生代花岗岩时空分布、成因演变及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(6): 1573-1593. |
| [21] | 王洪亮, 何世平, 陈隽璐, 等. 北秦岭西段红花铺俯冲型侵入体LA-ICP-MS定年及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(4): 536-544. |
| [22] | 王洪亮, 何世平, 陈隽璐, 等. 北秦岭西段胡店片麻状二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(1): 17-25. |
| [23] | 陈隽璐, 王宗起, 徐学义, 等. 北秦岭两河口岩体的地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(5): 1043-1054. |
| [24] | 陈隽璐, 徐学义, 王洪亮, 等. 北秦岭西段唐藏石英闪长岩岩体的形成时代及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(1): 45-52. |
| [25] | 陈隽璐, 徐学义, 王洪亮, 等. 北秦岭西段早古生代埃达克岩地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(4): 475-484. |
| [26] | 王洪亮, 徐学义, 陈隽璐, 等. 北秦岭西段岩湾加里东期碰撞型侵入体形成时代及地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3): 353-364. |
| [27] | 董增产, 王洪亮, 郭彩莲, 等. 北秦岭西段奥陶纪红花铺岩体岩石地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 109-117. |
| [28] | 吕星球, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 北秦岭太白花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(1): 37-52. |
| [29] | 宫相宽, 陈丹玲, 朱小辉, 等. 北秦岭西段三叠纪超镁铁岩-正长岩体的确定及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(1): 177-192. |
| [30] | 严阵. 陕西省花岗岩[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 1985: 1-321. |
| [31] | 张亚峰, 蔺新望, 郭岐明, 等. 阿尔泰南缘可可托海地区阿拉尔花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学特征及其源区意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(2): 339-354. |
| [32] |
ANDERSON T. Correction of common Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 袁洪林, 吴福元, 高山, 等. 东北地区新生代侵入体的锆石激光探针U-Pb年龄测定与稀土元素成分分析[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(14): 1511-1520. |
| [34] |
RUBATTO D. Zircon trace element geochemistry:Partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 184(1/2): 123-138.
DOI URL |
| [35] | 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. |
| [36] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81.
DOI URL |
| [38] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]// SUNDERSA D, NORRYM J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society Special Publication, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. |
| [39] | 张本仁. 大陆造山带地球化学研究:岩石构造环境地球化学判别的改进[J]. 西北地质, 2001, 34(3): 1-15. |
| [40] | 张招崇, 周刚, 闫升好, 等. 阿尔泰山南缘晚古生代火山岩的地质地球化学特征及其对构造演化的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(3): 344-358. |
| [41] | 路凤香, 桑隆康. 岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 72-73. |
| [42] |
COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 535-551.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等. 福建北东沿海高分异I型花岗岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(11): 2468-2484. |
| [45] | 王永文, 颜丹平, 刘红旭, 等. 西天山伊犁地块北缘桦木沟高分异 I 型花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(3): 529-541. |
| [46] | 王德滋, 刘昌实. 桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(1): 44-54. |
| [47] | 段丰浩, 李永军, 王冉, 等. 西准噶尔都伦河东岩体镁铁质微粒包体的发现及成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(2): 10-16. |
| [48] | 王梁, 王根厚, 雷时斌, 等. 岩浆混合成因暗色微粒包体的识别标志[J]. 高校地质学报, 2013, 19(增刊): 199-200. |
| [49] | 黄岗, 牛广智, 王新录, 等. 新疆东准噶尔早志留世弧岩浆岩:来自姜格尔库都克石英二长闪长岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6): 1219-1233. |
| [50] |
STERN R J, KOHUT E, BLOOMER S H, et al. Subduction factory processes beneath the Guguan cross-chain, Mariana Arc: No role for sediments, are serpentinites important?[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 151(2): 202-221.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
TURNER S, HAWKESWORTH C, ROGERS N, et al. U-Th isotope disequilibria and ocean island basalt generation in the Azores[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 139(1/4): 145-164.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
PLANK T, LANGMUIR C H. The chemical composition of subducting sediments and its consequence for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 145(3/4): 325-394.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
ALTHER R, HOLL A, HEGNER E, et al. High-potassium, calc-alkaline I-type plutonsism in the European Variscides: Northern Vosges(France) and northern Schwarzwald (Germany)[J]. Lithos, 2000, 50(1/3): 51-73.
DOI URL |
| [54] | DAVIDSON J P. Deciphering mantle and crustal signatures in subduction zone magmatism[J]. Geophysical Monograph Series, 1996, 96(3): 251-262. |
| [55] |
DEFANT M J, DRUMMOND M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665.
DOI |
| [56] | PEARCE J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[J]. Andesites, 1982, 8: 525-548. |
| [57] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4): 956-983.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 陈隽璐, 徐学义, 王宗起, 等. 西秦岭太白地区岩湾-鹦鸽咀蛇绿混杂岩的地质特征及形成时代[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(4): 500-509. |
| [59] | 裴先治, 丁仨平, 李佐臣, 等. 西秦岭北缘早古生代天水-武山构造带及其构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(11): 1547-1564. |
| [60] | 杨钊, 董云鹏, 柳小明, 等. 西秦岭关子镇蛇绿岩锆石LA-ICP-MS定年研究[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(11):1321-1325. |
| [61] | 陈隽璐. 北秦岭造山带西端早古生代火山岩成因环境与造山作用过程[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2008: 54-136. |
| [62] | 闫全人, 王宗起, 陈隽璐, 等. 北秦岭斜峪关群和草滩沟群火山岩成因的地球化学和同位素约束、SHRIMP年代及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(4): 487-500. |
| [63] | 裴先治, 丁仨平, 张国伟, 等. 西秦岭天水地区百花基性岩浆杂岩的LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 中国科学(D 辑), 2007, 37(增刊): 224-234. |
| [64] |
YAN Q R, CHEN J L, WANG Z Q, et al. Zircon U-Pb and geochemical analysis forleucorcratic intrusive rocks in pillow lavas in the Danfeng Group, north Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Science in China, 2008, 51(2): 249-262.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||