



Geoscience ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (02): 335-349.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.069
• Sedimentology and Petroleum Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
DENG Yi1( ), GAO Chonglong2(
), GAO Chonglong2( ), WANG Jian3, LIU Ming3, MENG Yuanlin1, REN Ying2, LIU Ke1, WANG Ke4
), WANG Jian3, LIU Ming3, MENG Yuanlin1, REN Ying2, LIU Ke1, WANG Ke4
Received:2023-02-27
Revised:2023-06-29
Online:2024-04-10
Published:2024-05-22
CLC Number:
DENG Yi, GAO Chonglong, WANG Jian, LIU Ming, MENG Yuanlin, REN Ying, LIU Ke, WANG Ke. Deep Reservoir Characteristics and Control of Physical Properties of Qigu Formation in the Western Section of the Southern Margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 335-349.

Fig.1 Structural location (a), strata (b) and sedimentary facies of Jurassic Qigu Formation (c) in the western part of southern Junggar Basin ((c) modified after reference [9])
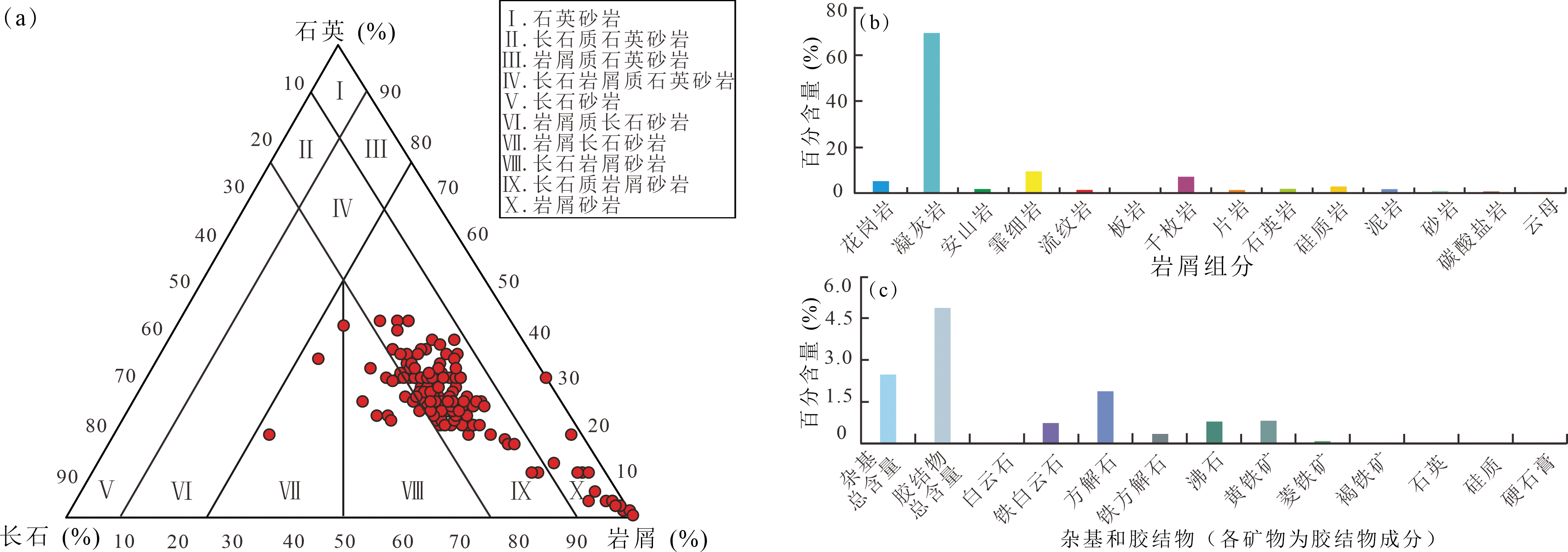
Fig.2 Triangular diagram of rock types (a), debris component content (b), matrix and cement component content distribution (c) of the Qigu Formation sandstone reservoir in the western section of southern Junggar Basin

Fig.4 Distribution diagram of the reservoir physical properties (a)(b), the correlation between porosity and permeability (c), pore diameter (d), roar diameter (e), and mercury injection curve (f) of Qigu Formation in the western section of southern Junggar Basin
| 类型 | 孔隙度(%) | 渗透率(10-3 μm2) | 沉积微相 | 评价 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 4.80~16.60 (11.01) | 0.14~461.00 (14.66) | 分流 河道 | 优质 储层 |
| Ⅱ | 4.60~13.60 (10.95) | 0.52~28.40 (13.40) | 河口坝 | 较好 储层 |
| Ⅲ | 4.50~21.71 (9.01) | 0.01~42.68 (2.63) | 席状砂 | 一般 储层 |
Table 1 Classification of reservoir evaluation of Qigu Formation in the western section of southern Junggar Basin
| 类型 | 孔隙度(%) | 渗透率(10-3 μm2) | 沉积微相 | 评价 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 4.80~16.60 (11.01) | 0.14~461.00 (14.66) | 分流 河道 | 优质 储层 |
| Ⅱ | 4.60~13.60 (10.95) | 0.52~28.40 (13.40) | 河口坝 | 较好 储层 |
| Ⅲ | 4.50~21.71 (9.01) | 0.01~42.68 (2.63) | 席状砂 | 一般 储层 |
| 成岩作用类型 | 强度 | 特点 | 物性控制 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 压实作用 | 中等 | 塑性岩屑压实变形和假杂基化,线接触为主 | 破坏储层物性 | |
| 胶 结 作 用 | 碳酸盐胶结 | 较弱 | 方解石为主,呈孔隙式和基底式出现 | 破坏储层物性 |
| 硅质胶结 | 弱 | 六方柱状自生石英微晶,I级石英次生加大 | 破坏储层物性 | |
| 黏土矿物 胶结 | 较弱 | 包壳状绿泥石;团块、散片或蠕虫状高岭石;丝缕状或弯曲片状伊利石;蜂窝状、似蜂窝状或不规则状伊/蒙混层 | 绿泥石包壳改善储层物性,其它 黏土矿物破坏储层物性 | |
| 其他胶结 | 弱 | 黄铁矿、石盐晶体和方沸石胶结 | 破坏储层物性 | |
| 溶蚀作用 | 较强 | 发育于易溶蚀颗粒边缘及内部,较为发育 | 改善储层物性 | |
Table 2 Types and characteristics of the reservoir diagenesis evolution
| 成岩作用类型 | 强度 | 特点 | 物性控制 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 压实作用 | 中等 | 塑性岩屑压实变形和假杂基化,线接触为主 | 破坏储层物性 | |
| 胶 结 作 用 | 碳酸盐胶结 | 较弱 | 方解石为主,呈孔隙式和基底式出现 | 破坏储层物性 |
| 硅质胶结 | 弱 | 六方柱状自生石英微晶,I级石英次生加大 | 破坏储层物性 | |
| 黏土矿物 胶结 | 较弱 | 包壳状绿泥石;团块、散片或蠕虫状高岭石;丝缕状或弯曲片状伊利石;蜂窝状、似蜂窝状或不规则状伊/蒙混层 | 绿泥石包壳改善储层物性,其它 黏土矿物破坏储层物性 | |
| 其他胶结 | 弱 | 黄铁矿、石盐晶体和方沸石胶结 | 破坏储层物性 | |
| 溶蚀作用 | 较强 | 发育于易溶蚀颗粒边缘及内部,较为发育 | 改善储层物性 | |
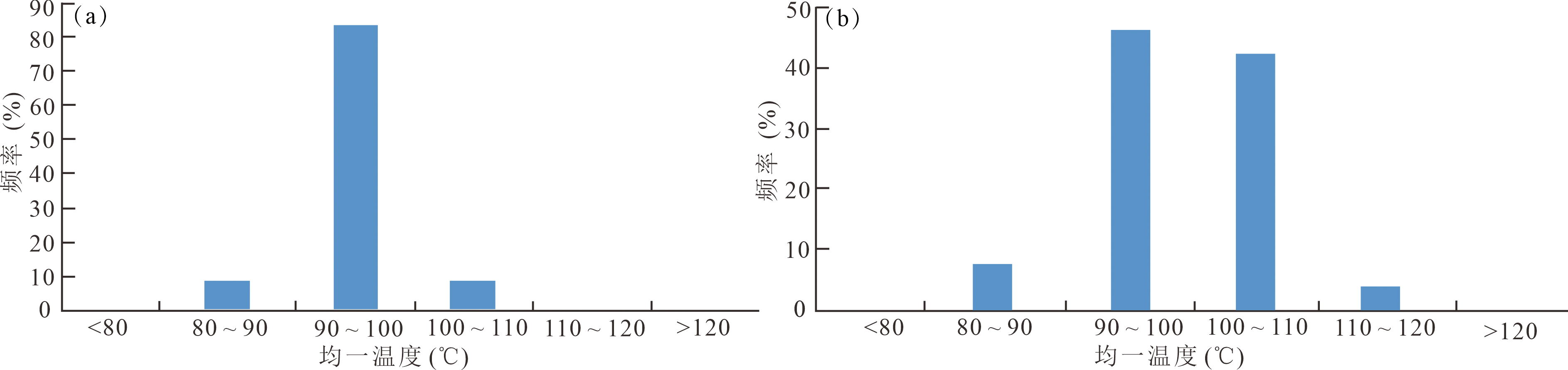
Fig.8 Distribution diagram of the homogeneous temperatures of the calcite cement fluid inclusions (a) and siliceous cement fluid inclusions (b) in Qigu Formation, the western section of southern Junggar Basin
| 井号 | 深度(m) | 宿主矿物 | 均一温度(℃) | 测点数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡001 | 4086.65 | 石英加大边 | 95.40~108.10 | 6 |
| 独山1 | 6414.46 | 石英加大边 | 95.50~106.40 | 9 |
| 高泉5 | 6063.53 | 石英加大边 | 88.00~112.00 | 10 |
| 高泉5 | 6061.02 | 石英加大边 | 85.00 | 1 |
| 高泉5 | 6061.02 | 方解石 | 89.00~103.00 | 13 |
Table 3 Homogeneous temperatures of the fluid inclusions of carbonate and siliceous cements in the Qigu Formation reservoir, the western section of southern Junggar Basin
| 井号 | 深度(m) | 宿主矿物 | 均一温度(℃) | 测点数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡001 | 4086.65 | 石英加大边 | 95.40~108.10 | 6 |
| 独山1 | 6414.46 | 石英加大边 | 95.50~106.40 | 9 |
| 高泉5 | 6063.53 | 石英加大边 | 88.00~112.00 | 10 |
| 高泉5 | 6061.02 | 石英加大边 | 85.00 | 1 |
| 高泉5 | 6061.02 | 方解石 | 89.00~103.00 | 13 |
| 井号 | 样品深度 (m) | 伊/蒙混层 (%) | 伊利石 (%) | 高岭石 (%) | 绿泥石 (%) | 伊/蒙混层中的 蒙皂石含量 (%) | 样品数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡001 | 4030.92~4127.24 | 3.00~81.00 (29.80) | 2.00~42.00 (13.10) | 0.00~22.00 (0.97) | 4.00~96.00 (56.10) | 20.00~70.00 (32.80) | 37 |
| 卡002 | 4030.92~4131.19 | 2.00~81.00 (30.70) | 2.00~42.00 (13.20) | 0.00~22.00 (1.80) | 4.00~96.00 (54.80) | 20.00~70.00 (33.00) | 38 |
| 卡003 | 4056.58~4145.56 | 4.00~38.00 (20.60) | 3.00~36.00 (18.70) | 0.00~56.00 (15.50) | 10.00~93.00 (45.00) | 15.00~30.00 (22.50) | 14 |
| 卡6 | 3957.79~3961.44 | 8.00~23.00 (11.00) | 3.00~11.00 (5.50) | — | 66.00~89.00 (83.50) | 20.00~30.00 (23.30) | 6 |
| 卡8 | 3929.37~4075.72 | 5.00~46.00 (19.60) | 8.00~22.00 (15.50) | 0.00~52.00 (20.30) | 13.00~76.00 (44.50) | 30.00~45.00 (34.50) | 12 |
| 四参1 | 3643.30~3702.32 | 15.00~33.00 (21.30) | 11.00~35.00 (24.30) | 27.00~59.00 (39.60) | 14.00~15.00 (14.60) | — | 3 |
| 西湖1 | 5997.00~6135.30 | 14.00~15.00 (14.50) | 7.00~53.00 (30.00) | 11.00~13.00 (12.00) | 19.00~68.00 (43.50) | 20.00 | 2 |
| 高101 | 6017.55~6019.75 | 20.00~29.00 (24.50) | 45.00~49.00 (47.00) | 5.00~14.00 (9.50) | 45.00~59.00 (52.00) | 15.00 | 2 |
| 总平均值 | 26.40 | 14.90 | 6.80 | 53.20 | 31.00 | ||
Table 4 Types and contents of the authigenic clay minerals in the reservoir of Qigu Formation in the western section of southern Junggar Basin
| 井号 | 样品深度 (m) | 伊/蒙混层 (%) | 伊利石 (%) | 高岭石 (%) | 绿泥石 (%) | 伊/蒙混层中的 蒙皂石含量 (%) | 样品数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 卡001 | 4030.92~4127.24 | 3.00~81.00 (29.80) | 2.00~42.00 (13.10) | 0.00~22.00 (0.97) | 4.00~96.00 (56.10) | 20.00~70.00 (32.80) | 37 |
| 卡002 | 4030.92~4131.19 | 2.00~81.00 (30.70) | 2.00~42.00 (13.20) | 0.00~22.00 (1.80) | 4.00~96.00 (54.80) | 20.00~70.00 (33.00) | 38 |
| 卡003 | 4056.58~4145.56 | 4.00~38.00 (20.60) | 3.00~36.00 (18.70) | 0.00~56.00 (15.50) | 10.00~93.00 (45.00) | 15.00~30.00 (22.50) | 14 |
| 卡6 | 3957.79~3961.44 | 8.00~23.00 (11.00) | 3.00~11.00 (5.50) | — | 66.00~89.00 (83.50) | 20.00~30.00 (23.30) | 6 |
| 卡8 | 3929.37~4075.72 | 5.00~46.00 (19.60) | 8.00~22.00 (15.50) | 0.00~52.00 (20.30) | 13.00~76.00 (44.50) | 30.00~45.00 (34.50) | 12 |
| 四参1 | 3643.30~3702.32 | 15.00~33.00 (21.30) | 11.00~35.00 (24.30) | 27.00~59.00 (39.60) | 14.00~15.00 (14.60) | — | 3 |
| 西湖1 | 5997.00~6135.30 | 14.00~15.00 (14.50) | 7.00~53.00 (30.00) | 11.00~13.00 (12.00) | 19.00~68.00 (43.50) | 20.00 | 2 |
| 高101 | 6017.55~6019.75 | 20.00~29.00 (24.50) | 45.00~49.00 (47.00) | 5.00~14.00 (9.50) | 45.00~59.00 (52.00) | 15.00 | 2 |
| 总平均值 | 26.40 | 14.90 | 6.80 | 53.20 | 31.00 | ||

Fig.9 Diagrams of the diagenetic sequence (a) and diagenetic-pore evolution model (b) of the Qigu Formation reservoir in the western section of the southern margin of Junggar Basin

Fig.10 Diagram of the relationship between the rock compositions, lithology, sorting coefficient, and physical properties of the Qigu Formation reservoir in the western section of southern Junggar Basin

Fig.11 Contribution of compaction and cementation to the pore loss (a) and vertical variation of the physical properties (b)(c) in Qigu Formation, the western section of southern margin of Junggar Basin
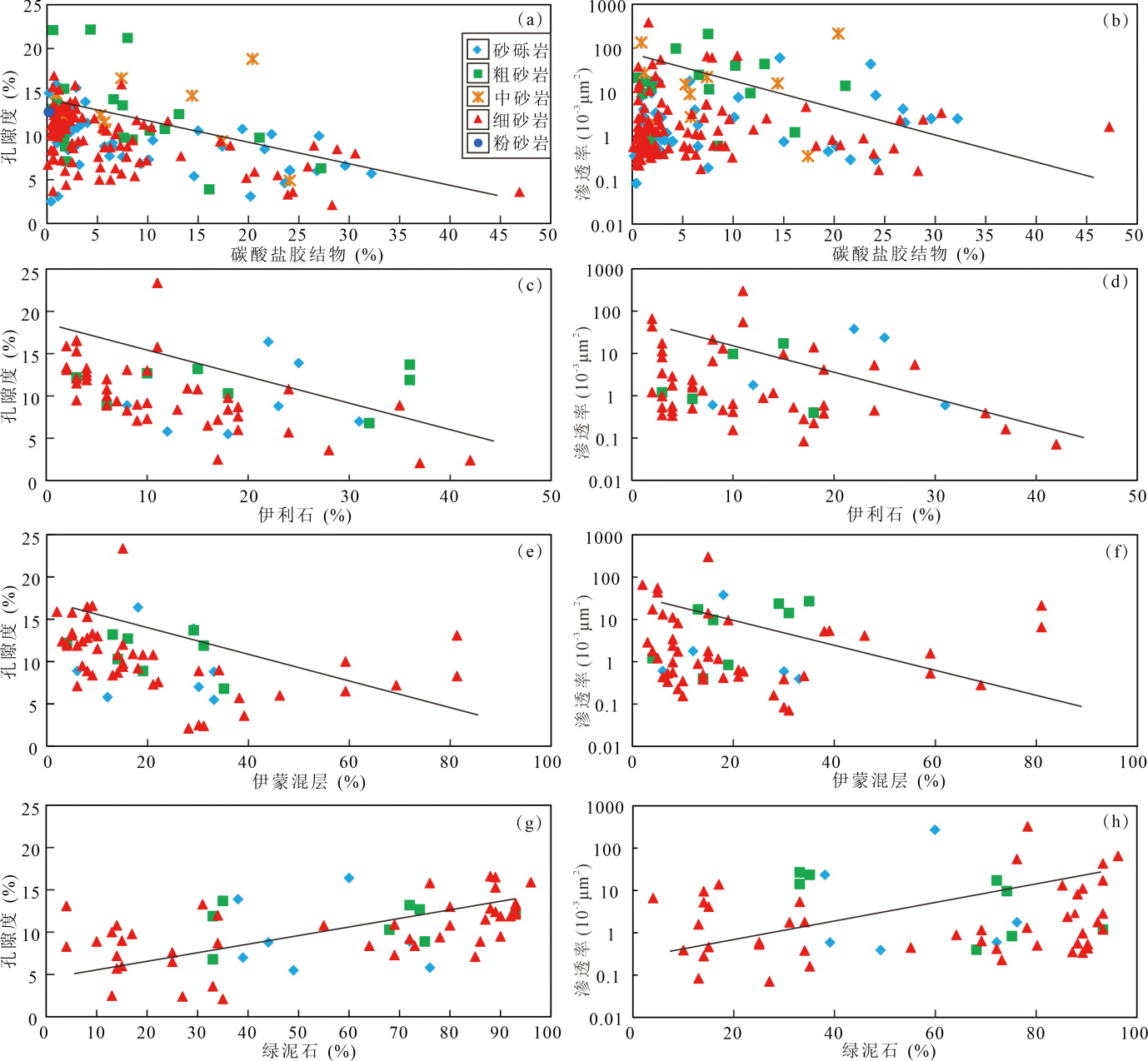
Fig.12 Diagrams of the relationship between carbonate cement, clay mineral content, and physical properties of the Qigu Formation reservoir in the western section of the southern margin of Junggar Basin
| [1] | 纪友亮, 周勇, 刘玉瑞, 等. 高邮凹陷古近系阜宁组一段沉积特征对储层成岩作用及物性的影响[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(7): 1299-1310. |
| [2] | 高崇龙, 纪友亮, 靳军, 等. 准噶尔盆地莫索湾地区清水河组深层优质储层特征及其物性控制因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(4): 990-1006. |
| [3] | 黄洁, 朱如凯, 侯读杰, 等. 深部碎屑岩储层次生孔隙发育机理研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2007, 26(6): 76-82. |
| [4] | 李会军, 吴泰然, 吴波, 等. 中国优质碎屑岩深层储层控制因素综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 2004, 23(4): 76-82. |
| [5] | 袁波, 汪新, 王心强, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘构造分层分带特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(10): 3946-3956. |
| [6] |
杜金虎, 支东明, 李建忠, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高探1井重大发现及下组合勘探前景展望[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(2): 205-215.
DOI |
| [7] | 范媛媛. 新疆准噶尔盆地南缘上侏罗统齐古组沉积相及沉积环境研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021. |
| [8] | 白斌. 准噶尔南缘构造沉积演化及其控制下的基本油气地质条件[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2008. |
| [9] | 王剑, 靳军, 高崇龙, 等. 准南西段侏罗系—白垩系物源特征及沉积背景[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(5): 1378-1392. |
| [10] | 孟颖, 靳军, 高崇龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘西段白垩系深层储层特征及物性保存机制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(2): 218-232. |
| [11] | 纪友亮. 油气储层地质学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2015. |
| [12] | 陈波, 王子天, 康莉, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛北地区三叠系百口泉组储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(1): 23-35. |
| [13] | 刘媛媛, 于炳松, 朱金富, 等. 辽河滩海西部凹陷古近系碎屑岩储层成岩作用及其对储层物性的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(4): 731-738. |
| [14] | 刘媛媛, 郭彦民, 邹丙方, 等. 辽河油田滩海西部古近系碎屑岩储层特征及主控因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(3): 569-574. |
| [15] | 季丽丹, 贾爱林, 何东博, 等. 川中广安地区上三叠统须六段储层特征及控制因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(6): 1100-1106. |
| [16] |
远光辉, 操应长, 葸克来, 等. 东营凹陷北带古近系碎屑岩储层长石溶蚀作用及其物性响应[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(5): 853-866.
DOI |
| [17] | 刘可, 高崇龙, 王剑, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘东段侏罗系头屯河组储层特征及物性控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(4): 579-592. |
| [18] | 操应长, 贾艳聪, 王艳忠, 等. 渤南洼陷北带沙四上亚段储层成岩流体演化[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1): 197-207. |
| [19] | CHIPERA S J, GOFF F, GOFF C J, et al. Zeolitization of intracaldera sediments and rhyolitic rocks in the 1.25 Ma lake of Valles caldera, New Mexico, USA[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2008, 178(2): 317-330. |
| [20] | 雷海艳, 樊顺, 鲜本忠, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系下乌尔禾组沸石成因及溶蚀机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(5): 102-112. |
| [21] | 王朝, 王冠民, 杨清宇, 等. 吴起—志丹地区延长组下组合浊沸石的纵向分布特征与成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2019, 49(5): 1247-1260. |
| [22] | 远光辉, 操应长, 贾珍臻, 等. 含油气盆地中深层碎屑岩储层异常高孔带研究进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(1): 28-42. |
| [23] | SURDAM R C, BOESE S W, CROSSEY L J. The chemistry of secondary porosity[J]. AAPG Memoir, 1984, 37(2): 127-149. |
| [24] | 王屿涛, 况军, 丁安娜. 准噶尔盆地天然气分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 1996, 7(1): 1-8. |
| [25] | 李二庭, 马万云, 李际, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系煤生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(5): 1313-1323. |
| [26] | 邱隆伟, 潘耀. 柯克亚凝析气田石英的溶解现象及其成因[J]. 矿物学报, 2005, 25(2): 183-190. |
| [27] | 田建锋, 刘池洋, 王桂成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组砂岩的碱性溶蚀作用[J]. 地球科学, 2011, 36(1): 103-110. |
| [28] | ALAA M M, SALEM S. MORAD LUIZ F. Diagenesis and reservoir-quality evolution of fluvial sandstones during progressive burial and uplift: Evidence from the Upper Jurassic boipeba member, reconcavo basin, northeastern Brazil[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84: 1015-1040. |
| [29] | 刘金库, 彭军, 刘建军, 等. 绿泥石环边胶结物对致密砂岩孔隙的保存机制: 以川中—川南过渡带包界地区须家河组储层为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(1): 53-58. |
| [30] | 谢武仁, 杨威, 赵杏媛, 等. 川中地区须家河组绿泥石对储集层物性的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6): 674-679. |
| [31] | 田建锋, 喻建, 张庆洲. 孔隙衬里绿泥石的成因及对储层性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(3): 741-748. |
| [32] | 吴家洋, 吕正祥, 卿元华, 等. 致密油储层中自生绿泥石成因及其对物性的影响: 以川中东北部沙溪庙组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(1): 76-85. |
| [33] | 远光辉, 操应长, 杨田, 等. 论碎屑岩储层成岩过程中有机酸的溶蚀增孔能力[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(5): 207-219. |
| [34] |
赵靖舟, 李军, 徐泽阳. 沉积盆地超压成因研究进展[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(9): 973-998.
DOI |
| [35] | 曲江秀, 查明. 准噶尔盆地异常压力类型及成因探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(4): 333-336. |
| [36] | CHILINGAR G V, SEREBRYAKOV V A, KATZ S A, et al. Methods of estimating and predicting abnormal rormation pressures[J]. Developments in Petroleum Science, 2002, 50:123-150. |
| [37] | 李宇志, 金杰华, 操应长, 等. 冀中坳陷霸县凹陷文安斜坡沙三段储层特征及有效储层控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 617-625. |
| [38] | 邱楠生. 中国西部地区沉积盆地热演化和成烃史分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(1): 6-8, 23. |
| [39] | 邱楠生, 杨海波, 王绪龙. 准噶尔盆地构造-热演化特征[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(4): 423-429. |
| [40] | 寿建峰, 张惠良, 沈扬, 等. 中国油气盆地砂岩储层的成岩压实机制分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(8): 2165-2170. |
| [41] | 高崇龙, 纪友亮, 高志勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部深层储层物性保存过程多因素耦合分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(3): 577-591. |
| [42] |
冯佳睿, 高志勇, 崔京钢, 等. 深层、超深层碎屑岩储层勘探现状与研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(7): 718-736.
DOI |
| [43] |
高崇龙, 王剑, 靳军, 等. 前陆冲断带深层储集层非均质性及油气差异聚集模式: 以准噶尔盆地南缘西段白垩系清水河组碎屑岩储集层为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(2): 322-332.
DOI |
| [1] | JIANG Daiqin, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao. Characteristics of Natural Fractures and Their Influence on Oil and Gas Enrichment and Preservation of the Jurassic Continental Shale in the Yuanba Area, Northeastern Sichuan Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 362-372. |
| [2] | CHANG Hailiang, DU Chunyan, ZHANG Hongwei, WANG Hongwei, ZHU Chaohui, CHEN Jingyi. Sandstone Reservoir Characteristics of the Upper Paleozoic Coal-bearing Strata in Luyi Sag, Southern North China Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 373-384. |
| [3] | LIU Yonglin, ZHAO Jiayu, LIU Yi, WU Mei, XIAO Huixian, LIU Dinghui, TIAN Xinglei. Differentiation Mechanism of Se Concentration in Soil Covering the Jurassic Strata in Chongqing: Case Studies from Jiangjin and Shizhu Regions [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(06): 1644-1654. |
| [4] | YANG Wenpeng, LI Chenglu, YANG Yuanjiang, FU Anzong, ZHENG Bo, ZHOU Tengfei, ZHAO Ruijun. Geochemistry, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting of the Middle Jurassic Taxi Plutons in Heilongjiang [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 390-403. |
| [5] | ZHANG Guobin, KONG Jingui, WU Zijie, FENG Yue, HE Yunlong, CHEN Xingkai. Geochronology and Petrogeochemical Characteristics of I-type Granites in Xinlitun Area, Northern Greater Hinggan Mountains and Their Geological Significance [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 404-418. |
| [6] | TANG Xianglu, JIANG Zhenxue, SHAO Zeyu, LONG Guohui, HE Shijie, LIU Xiaoxue, WANG Yuchao. Reservoir Characteristics and Dynamic Accumulation Process of the Quaternary Mudstone Biogas [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 682-694. |
| [7] | WANG Yuping, WU Wenbin, LIU Yongjun, LI Haiyang, WANG Xiaoliang, LI Chao. Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Geological Significance of Late Jurassic Intrusions at Xiuyan, Eastern Liaoning Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 955-967. |
| [8] | CUI Gaixia, WEI Qinlian, XIAO Ling, WANG Song, HU Rong, WANG Chonghuan. Reservoir Characteristics of Permian Lower He 8 Member in Longdong Area, Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 1088-1097. |
| [9] | SHEN Hua, LIU Zhen, SHI Yuanpeng, XU Zeyang, LI Yongjun, CHEN Shuguang, WANG Huilai, WANG Zhicheng, WANG Biao, LIU Chang. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Process and Exploration Potential in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 871-882. |
| [10] | GUO Na, LIU Cui, CUI Long, YAO Wei, LI Guoying, GAN Liming, HUANG Yong. Igneous Assemblage and Metallogenic Background of the Mawu Gold Deposit in the Min-Li Ore Belt of the Western Qinling Orogen [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1261-1276. |
| [11] | REN Yongjian, CHENG Shuo, ZHANG Mingming, CAO Guangyuan, YU Wang, ZHAO Han, LIANG Heng, WANG Fuqiang, QI Caiji. Geochemistry Characteristics and Tectonic Environment Analysis of Middle Jurassic A-type Granites in Zhangjiawan Area, Heilongjiang Province [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(05): 1067-1076. |
| [12] | YAO Zongquan, YU Xinghe, YUE Hongxing, , ZHOU Lihua, WANG Jin, GAO Yang. Reservoir Characteristics and Influence Factors of Gravel Sandstone:Case Study of Upper Triassic Karamay Formation in Hongshanzhui Area [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(06): 1188-1198. |
| [13] | WANG Di, TIAN Jijun, FENG Shuo, LU Xingyu. Petrography and Quality Characteristics of Lower-Middle Jurassic Coal Seam in the Southeastern Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(05): 975-984. |
| [14] | ZHAO Shengjin, GAO Lidong, YU Haiyang, PIAO Lili, LIU Zhihui, ZHOU Yingshuai, ZHANG Meng, ZHANG Yulong, YANG Haixing, ZHAO Wanli. Classification and Geological Significance of the Upper Jurassic Haritaolegai Formation Basalt in the Northern Da Hinggan Mountains [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(04): 718-726. |
| [15] | REN Yongjian, CHENG Shuo, ZHU Jingbin, WANG Bo, ZHANG Mingming, ZHANG Xu, YU Wang, HAN Yue. Genesis Study on Mafic Microgranular Enclave from Early Jurassic Granites in the Southern Zhangguangcai Mountains in Heilongjiang Province [J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(01): 33-45. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||