



Geoscience ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1193-1204.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.06.079
• Petroleum Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Ai1( ), ZHONG Dakang2,3(
), ZHONG Dakang2,3( ), LIU Zhongqun1, WANG Wei4, DU Hongquan4, ZHOU Zhiheng2,3, TANG Zicheng2,3
), LIU Zhongqun1, WANG Wei4, DU Hongquan4, ZHOU Zhiheng2,3, TANG Zicheng2,3
Received:2019-10-11
Revised:2019-12-25
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
Contact:
ZHONG Dakang
CLC Number:
WANG Ai, ZHONG Dakang, LIU Zhongqun, WANG Wei, DU Hongquan, ZHOU Zhiheng, TANG Zicheng. Diagenesis and Porosity Evolution of Calcareous Sandstone Reservoirs of Xu-3 Member in Western Yuanba of Northeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1193-1204.
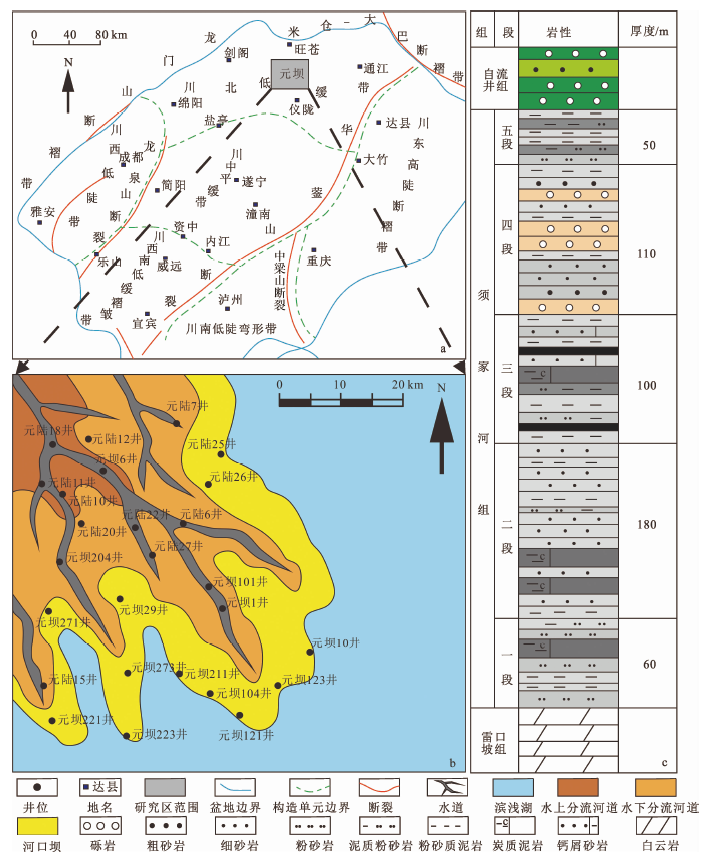
Fig.1 Sedimentary tectonic background and stratigraphic features of the study area (after Wang Wei, 2013; Du Hongquan, 2016; Li Jun, 2016; Tang Zicheng, 2019[4,7-6,27])
| 孔隙类型 | 残余粒间孔 | 晶间微孔隙 | 裂缝 | 溶蚀孔隙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均孔隙度/% | 0.04 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 总孔隙占比/% | 2.0 | 68.6 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
Table 1 Statistics of pore types and total pore ratios of the Xu-3 tight sandstones from western Yuanba
| 孔隙类型 | 残余粒间孔 | 晶间微孔隙 | 裂缝 | 溶蚀孔隙 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均孔隙度/% | 0.04 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 总孔隙占比/% | 2.0 | 68.6 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
| [1] | 邹才能, 陶士振, 侯连华, 等. 非常规油气地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 50-83. |
| [2] | 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012,39(2):129-136. |
| [3] | 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望——以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012,33(2):173-187. |
| [4] | 王威, 岳全玲. 四川盆地北部须家河组致密砂岩储层成因机制[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2012,35(1):13-17. |
| [5] | 张莉, 邹华耀, 郝芳, 等. 川东北元坝地区须家河组储层特征与超致密成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2017,91(9):2105-2118. |
| [6] | 李军, 胡东风, 邹华耀, 等. 四川盆地元坝—通南巴地区须家河组致密砂岩储层成岩—成藏耦合关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016,27(7):1164-1178. |
| [7] | 杜红权, 王威, 周霞, 等. 川东北元坝地区须三段钙屑砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016,37(4):565-571. |
| [8] | 王威. 高能河道砂体特征及勘探意义——以元坝地区须三段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013,35(6):657-661. |
| [9] | 肖开华, 李宏涛, 贾爽. 川东北元坝地区须三段钙屑砂岩储层特征及控气因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014,35(5):654-660. |
| [10] | 曾小英, 张小青, 钟玉梅. 川西坳陷中段须家河组四段钙屑砂岩气层的成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2007,25(6):84-90. |
| [11] | 黎静容, 李毓, 程洪亮, 等. 元坝地区须三段沉积特征[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,28(5):43-50. |
| [12] | 郝景宇. 川东北地区须家河组沉积与层序特征精细研究[D]. 武汉:长江大学, 2012. |
| [13] | 曾韬. 川东北元坝地区须三段沉积相及沉积演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014(4):468-475. |
| [14] | 张冲, 谢润成, 周文, 等. 川东北元坝地区须三段致密储集层裂缝特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2014,35(4):395-398. |
| [15] | 王杰, 秦建中, 刘文汇, 等. 川东北元坝地区中生代构造与动态热演化史——磷灰石、锆石(U-Th)/He定年分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012,34(1):19-24. |
| [16] | 黄进腊, 张哨楠, 刘成川, 等. 川东北元坝地区须家河组断层预测及发育特征[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2013,7(3):3-6. |
| [17] | 盘昌林. 四川盆地元坝地区上三叠统须家河组天然气成藏条件研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2011. |
| [18] | 秦华, 肖伟. 川东北元坝地区须家河组凝缩层的归属及成因[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2010,4(3):11-13. |
| [19] | 何志勇, 刘海涛, 肖伟, 等. 四川盆地元坝地区下侏罗统介壳灰岩储层分布预测[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(1):144-151. |
| [20] | TIAN Y, KOHN B P, ZHU C, et al. Post-orogenic evolution of the Mesozoic Micang Shan Foreland Basin system, central China[J]. Basin Research, 2012,24(1):70-90. |
| [21] | ENKELMANN E, RATSCHBACHER L, JONCKHEERE R, et al. Cenozoic exhumation and deformation of northeastern Tibet and the Qinling: Is Tibetan lower crustal flow diverging around the Sichuan Basin?[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006,118(5/6):651-671. |
| [22] |
YIN A, HARRISON T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000,28:211-280.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 黄仁春. 川东北元坝地区雷口坡组天然气来源与成藏分析[J]. 现代地质, 2014,28(2):412-418. |
| [24] | 张峰. 川东北地区上三叠统须家河组层序岩相古地理研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学, 2011. |
| [25] |
赵宗举, 朱琰, 李大成, 等. 中国南方构造形变对油气藏的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2002,23(1):19-25.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 陈龙博, 何登发, 王贝, 等. 川东北地区通南巴背斜中三叠世以来构造变形时间厘定及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017,41(3):433-445. |
| [27] | 唐自成, 钟大康, 王威, 等. 川东北元坝地区须家河组三段钙屑砂岩孔隙类型及地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019,40(5):1137-1147. |
| [28] |
TAN X, XIA Q, CHEN J, et al. Basin-scale sand deposition in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China: Sedimentary framework and conceptual model[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013,24(1):89-103.
DOI URL |
| [29] | BEARD D C, WEYL P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973,57(2):349-369. |
| [30] | HOUSEKNECHT D W. Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sandstones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987,71:633-642. |
| [31] |
LUNDEGARD P D. Sandstones porosity loss—a big picture view of the importance of compaction[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1992,62:250-260.
DOI URL |
| [32] | EHRENBERG S N. Measuring sandstone compaction from modal analyses of thin sections: how to do it and what the results mean[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1995,6:369-379. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||