



Geoscience ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (02): 356-369.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.02.14
• Petroleum Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Minglei( ), ZHU Dancheng, LI Tao, LI Haiping, LI Ting, ZOU Huayao(
), ZHU Dancheng, LI Tao, LI Haiping, LI Ting, ZOU Huayao( )
)
Received:2019-07-20
Revised:2019-10-15
Online:2020-05-25
Published:2020-05-25
Contact:
ZOU Huayao
CLC Number:
YANG Minglei, ZHU Dancheng, LI Tao, LI Haiping, LI Ting, ZOU Huayao. Control of Eogenetic Karst Reservoir by Shoals in Middle Permian Maokou Formation, Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(02): 356-369.
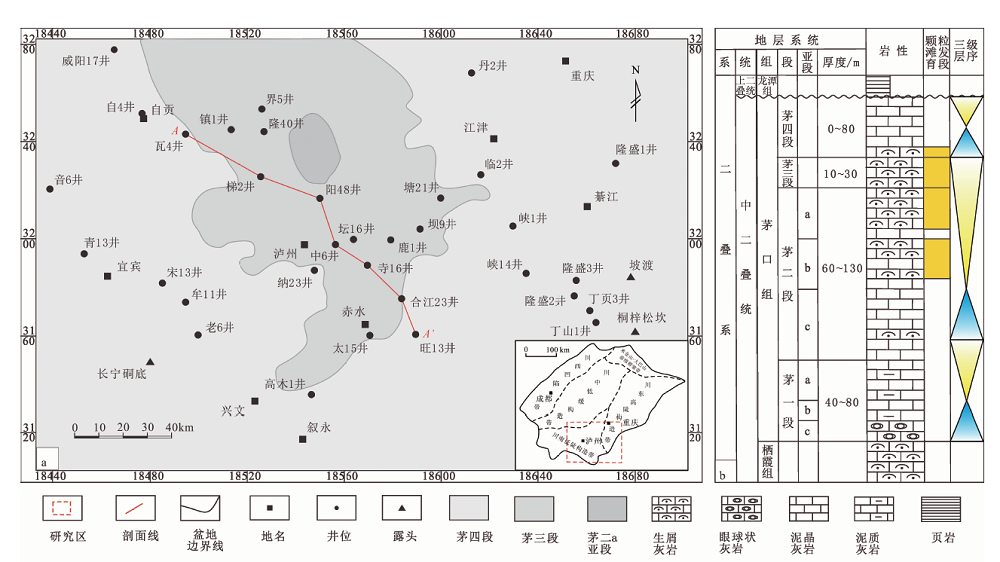
Fig.1 Paleogeologic map of Maokou Formation in the end Middle Permian in southern Sichuan Basin (a) and synthetical stratigraphic log of Maokou Formation in the study area (b)
| 岩石类型 | 代码 | 岩性描述 | 沉积环境解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 泥质生屑 泥晶灰岩 | M-b | 生屑以腕足类和有孔虫为主,少见藻类和介形虫等,生屑含量10%~20%,粒径介于0.1~1.5 mm之间,分选磨圆一般( | 化石组合为腕足类有孔虫组合,显示较深水低能的碳酸盐台地环境[ |
| 含泥质生屑 泥晶灰岩 | W-mb | 眼球状灰岩的眼皮部分,生屑以腕足类和有孔虫为主,生屑破碎呈定向分布,疑似与上升流作用有关[ | 化石组合为腕足类有孔虫组合,显示较深水低能的碳酸盐台地环境[ |
| 生屑泥晶 灰岩 | W-b | 生屑主要是藻类、腕足类和有孔虫,少见海百合、双壳类和腹足类等,生屑含量30%~50%,粒径介于0.1~2 mm之间,分选磨圆均较差( | 浅海潮下中等-低能环境 |
| 泥晶生屑 灰岩 | P-b | 生屑以有孔虫和藻类为主,可见海百合、腕足类和单体珊瑚等,生屑含量60%~80%,粒径介于0.1~2 mm之间,分选一般,磨圆较差,生物种类丰富,保存较完整( | 清澈浅水、轻微动荡的潮下中-高能环境 |
| 泥晶 灰岩 | P-p | 生物以为主,其次可见有孔虫、藻类、腕足类和海百合等,生屑含量大于60%,生屑粒径介于1~2 mm之间,生屑分选磨圆均较差( | 水体较浅的潮下中-高能沉积环境 |
| 泥晶藻灰 岩 | P-a | 绿藻以粗枝藻和松藻为主,红藻以二叠钙藻为主;有孔虫、腕足类和海百合以碎片的形式充填于藻屑之间,生屑含量大于80%,生屑粒径介于0.5~2.5 mm之间,生屑分选磨圆均较差( | 米齐藻和二叠钙藻的共存是开阔台地的一种标志[ |
| 亮晶生屑 灰岩 | G-b | 生屑以有孔虫、藻类和海百合为主,其次是珊瑚和腹足类等,生物种类丰富,亮晶胶结,生屑含量60%~80%,粒径介于0.5~1.5 mm之间( | 浪基面之上波浪作用较强的高能环境 |
| 亮晶藻屑 灰岩 | G-a | 红藻以翁格达藻为主,其次可见有孔虫、海百合骨板和藻砂屑等充填其间,亮晶胶结,生屑含量大于80%,生屑粒径介于0.2~1.5 mm之间,颗粒分选磨圆均较差( | 化石组合为有孔虫藻类组合,显示浅水高能开阔台地环境[ |
Table 1 Rock types and sedimentary environment interpretation of Maokou Formation in the study area
| 岩石类型 | 代码 | 岩性描述 | 沉积环境解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 泥质生屑 泥晶灰岩 | M-b | 生屑以腕足类和有孔虫为主,少见藻类和介形虫等,生屑含量10%~20%,粒径介于0.1~1.5 mm之间,分选磨圆一般( | 化石组合为腕足类有孔虫组合,显示较深水低能的碳酸盐台地环境[ |
| 含泥质生屑 泥晶灰岩 | W-mb | 眼球状灰岩的眼皮部分,生屑以腕足类和有孔虫为主,生屑破碎呈定向分布,疑似与上升流作用有关[ | 化石组合为腕足类有孔虫组合,显示较深水低能的碳酸盐台地环境[ |
| 生屑泥晶 灰岩 | W-b | 生屑主要是藻类、腕足类和有孔虫,少见海百合、双壳类和腹足类等,生屑含量30%~50%,粒径介于0.1~2 mm之间,分选磨圆均较差( | 浅海潮下中等-低能环境 |
| 泥晶生屑 灰岩 | P-b | 生屑以有孔虫和藻类为主,可见海百合、腕足类和单体珊瑚等,生屑含量60%~80%,粒径介于0.1~2 mm之间,分选一般,磨圆较差,生物种类丰富,保存较完整( | 清澈浅水、轻微动荡的潮下中-高能环境 |
| 泥晶 灰岩 | P-p | 生物以为主,其次可见有孔虫、藻类、腕足类和海百合等,生屑含量大于60%,生屑粒径介于1~2 mm之间,生屑分选磨圆均较差( | 水体较浅的潮下中-高能沉积环境 |
| 泥晶藻灰 岩 | P-a | 绿藻以粗枝藻和松藻为主,红藻以二叠钙藻为主;有孔虫、腕足类和海百合以碎片的形式充填于藻屑之间,生屑含量大于80%,生屑粒径介于0.5~2.5 mm之间,生屑分选磨圆均较差( | 米齐藻和二叠钙藻的共存是开阔台地的一种标志[ |
| 亮晶生屑 灰岩 | G-b | 生屑以有孔虫、藻类和海百合为主,其次是珊瑚和腹足类等,生物种类丰富,亮晶胶结,生屑含量60%~80%,粒径介于0.5~1.5 mm之间( | 浪基面之上波浪作用较强的高能环境 |
| 亮晶藻屑 灰岩 | G-a | 红藻以翁格达藻为主,其次可见有孔虫、海百合骨板和藻砂屑等充填其间,亮晶胶结,生屑含量大于80%,生屑粒径介于0.2~1.5 mm之间,颗粒分选磨圆均较差( | 化石组合为有孔虫藻类组合,显示浅水高能开阔台地环境[ |
| 井名 | 产量 | 层位 | 井漏井涌 | 钻具放空/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合4 | 累计3.26亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 | 0.17 |
| 付5 | 累计15.92亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 | 0.3 |
| 自2 | 累计48.5亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 | 4.45 |
| 界5 | 23万方/天 | 茅二段 | 有 | 0.2 |
| 工13 | 65.5万方/天 | 茅一段 | 有 | 0.15 |
| 螺观1 | 38.89万方/天 | 茅二段 | 有 | |
| 孔21 | 10.16万方/天 | 茅四段 | 有 | |
| 白18 | 22万方/天 | 茅二段 | 有 | 1.14 |
| 老6 | 累计12.4亿方 | 茅三段 | 有 | 0.14 |
| 宋1 | 累计11.1亿方 | 茅四段 | 有 | 1.67 |
| 阳7 | 累计20.5亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 |
Table 2 Cave drilling anomalies in high-yield well of Maokou Formation in the study area
| 井名 | 产量 | 层位 | 井漏井涌 | 钻具放空/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 合4 | 累计3.26亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 | 0.17 |
| 付5 | 累计15.92亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 | 0.3 |
| 自2 | 累计48.5亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 | 4.45 |
| 界5 | 23万方/天 | 茅二段 | 有 | 0.2 |
| 工13 | 65.5万方/天 | 茅一段 | 有 | 0.15 |
| 螺观1 | 38.89万方/天 | 茅二段 | 有 | |
| 孔21 | 10.16万方/天 | 茅四段 | 有 | |
| 白18 | 22万方/天 | 茅二段 | 有 | 1.14 |
| 老6 | 累计12.4亿方 | 茅三段 | 有 | 0.14 |
| 宋1 | 累计11.1亿方 | 茅四段 | 有 | 1.67 |
| 阳7 | 累计20.5亿方 | 茅二段 | 有 |

Fig.9 Isoline map of thickness of high-energy shoal (a) and low-energy shoal (b) in P2m2b, southern Sichuan Basin;Isoline map of thickness of high-energy shoal (c) and low-energy shoal (d) in P2m2a
| [1] | JAMES N P, CHOQUETTE P W. Paleokarst[M]. New York: Springer, 1988: 1-98. |
| [2] | 任美锷, 刘振中. 岩溶学概论[M]. 北京: 商务印书馆, 1983: 1-90. |
| [3] |
ZHONG Y, TAN X, ZHAO L, et al. Identification of facies-controlled eogenetic karstification in the Upper Cretaceous of the Halfaya oilfield and its impact on reservoir capacity[J]. Geological Journal, 2019,54(1):450-465.
DOI URL |
| [4] | WANG B, AL-AASM I S . Karst-controlled diagenesis and reservoir development: Example from the Ordovician main-reservoir carbonate rocks on the eastern margin of the Ordos basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002,86(9):1639-1658. |
| [5] |
XIAO D, TAN X, ZHANG D, et al. Discovery of syngenetic and eogenetic karsts in the Middle Ordovician gypsum-bearing dolomites of the eastern Ordos Basin (central China) and their heterogeneous impact on reservoir quality[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019,99:190-207.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
XIAO D, TAN X, XI A, et al. An inland facies-controlled eogenetic karst of the carbonate reservoir in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation, southern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016,72:218-233.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
谭秀成, 肖笛, 陈景山, 等. 早成岩期喀斯特化研究新进展及意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2015,17(4):441-456.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 淡永, 梁彬, 曹建文, 等. 碳酸盐岩早成岩岩溶作用及油气地质意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015,34(2):126-135. |
| [9] | LACE M J, MYLROIE J E. Coastal Karst Landforms[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2013: 7-60. |
| [10] | 陈红汉, 吴悠, 朱红涛, 等. 塔中地区北坡中—下奥陶统早成岩岩溶作用及储层形成模式[J]. 石油学报, 2016,37(10):1231-1246. |
| [11] | 刘嘉庆, 李忠, 韩银学, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中上奥陶统碳酸盐台地高频层序控制的早期成岩作用及其对储层分布的影响[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(12):3629-3640. |
| [12] |
张恒, 蔡忠贤, 漆立新, 等. 塔中地区西北部鹰山组成岩早期岩溶作用类型及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016,37(3):291-303.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 拜文华, 吕锡敏, 李小军, 等. 古岩溶盆地岩溶作用模式及古地貌精细刻画——以鄂尔多斯盆地东部奥陶系风化壳为例[J]. 现代地质, 2002,16(3):292-298. |
| [14] | 卢朝进, 刘震, 田海芹, 等. 受多级海平面控制的早成岩期岩溶发育模式——以鄂西渝东-湘鄂西地区石龙洞组为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018,47(5):1055-1067. |
| [15] | 黄士鹏, 江青春, 冯庆付, 等. 川南地区中二叠统茅口组岩溶储集层类型与分布规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019,46(2):281-289. |
| [16] |
肖笛, 谭秀成, 郗爱华, 等. 四川盆地南部中二叠统茅口组碳酸盐岩岩溶特征:古大陆环境下层控型早成岩期岩溶实例[J]. 古地理学报, 2015,17(4):457-476.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
肖笛, 谭秀成, 山述娇, 等. 四川盆地南部中二叠统茅口组二段沉积微相研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2015,33(6):1182-1191.
DOI URL |
| [18] | 黎荣, 胡明毅, 杨威, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统沉积相模式及有利储集体分布[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019,40(2):369-379. |
| [19] | 胡明毅, 胡忠贵, 魏国齐, 等. 四川盆地茅口组层序岩相古地理特征及储集层预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012,39(1):45-55. |
| [20] |
姜自然, 陆正元, 吕宗刚, 等. 四川盆地东吴期泸州古隆起与茅口组碳酸盐岩缝洞储层分布[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014,36(4):411-415.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 厚刚福, 周进高, 谷明峰, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统栖霞组、茅口组岩相古地理及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2017,22(1):25-31. |
| [22] | 冯增昭. 碳酸盐岩分类[J]. 石油学报, 1982(1):11-18. |
| [23] | FLÜGEL E. Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks[M]. New York: Springer Verlag, 2004: 1-200. |
| [24] | 冯增昭, 杨玉卿, 金振奎, 等. 中国南方二叠纪岩相古地理[M]. 东营: 石油大学出版社, 1997: 7-53. |
| [25] | 罗进雄, 何幼斌. 中—上扬子地区二叠系眼球状石灰岩特征及成因研究[J]. 地质论评, 2010,56(5):629-637. |
| [26] | 汪泽成, 江青春, 黄士鹏, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组天然气大面积成藏的地质条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2018,38(1):30-38. |
| [27] | 张学丰, 蔡忠贤, 胡文瑄, 等. 应用Adobe Photoshop定量分析岩石结构[J]. 沉积学报, 2009(4):667-673. |
| [28] | 黄思静. 碳酸盐岩的成岩作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010: 7-90. |
| [29] | 张学丰, 石开波, 刘波, 等. 保持性成岩作用与深部碳酸盐岩储层孔隙的保存[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014,33(2):80-85. |
| [30] |
BENNETT R H, FISCHER K M, LI H, et al. In situ porosity and permeability of selected carbonate sediment: Great Bahama bank Part 2: Microfabric[J]. Marine Geotechnology, 1990,9(1):29-47.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 金民东, 曾伟, 谭秀成, 等. 四川磨溪—高石梯地区龙王庙组滩控岩溶型储集层特征及控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014,41(6):650-660. |
| [32] | 王英华. 碳酸盐岩成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 沉积学报, 1992(3):85-95. |
| [33] |
MELZER S E, BUDD D A. Retention of high permeability during shallow burial (300 to 500 m) of carbonate grainstones[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2008,78(8):548-561.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MALIVA R G, MISSIMER T M, CLAYTON E A, et al. Diagenesis and porosity preservation in Eocene microporous limestones, South Florida, USA[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2009,217(1/4):85-94.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
唐雪松, 谭秀成, 刘宏, 等. 四川盆地东部中二叠统茅口组白云岩及云质硅岩储层特征与发育规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016,37(5):731-743.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 许化政, 王传刚, 刘春燕. 海相碳酸盐岩成岩作用与排烃特征[J]. 海相油气地质, 2010,15(1):51-54. |
| [37] |
TIAN X, SHI Z, YIN G, et al. Carbonate diagenetic products and processes from various diagenetic environments in Permian paleokarst reservoirs: a case study of the limestone strata of Maokou formation in Sichuan Basin, South China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2017,32(2):215-230.
DOI URL |
| [38] | FRITZ R D, WILSON J L, YUREWICZ D A. Paleokarst Related Hydrocarbon Reservoirs[M]. New Orleans: SEPM, 1993: 1-70. |
| [39] | 廖小漫, 张本健, 徐后伟, 等. 川西地区中二叠统储集层成岩作用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2012,33(3):312-315. |
| [40] | 陈宗清. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组天然气勘探[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2007(5):1-11. |
| [41] |
EHRENBERG S N, NADEAU P H. Sandstone vs. carbonate petroleum reservoirs: A global perspective on porosity-depth and porosity-permeability relationships[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005,89(4):435-445.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
EHRENBERG S N, NADEAU P H, STEEN Ø. Petroleum reservoir porosity versus depth: Influence of geological age[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009,93(10):1281-1296.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 张健, 周刚, 张光荣, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统天然气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2018,38(1):10-20. |
| [44] | MYLROIE J E, CAREW J L. Karst development on carbonate islands[J]. AAPG Memoir, 1995,63:55-76. |
| [45] |
HUSINEC A, JELASKA V. Relative sea-level changes recorded on an isolated carbonate platform: Tithonian to Cenomanian Succession, Southern Croatia[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2006,76(10):1120-1136.
DOI URL |
| [46] | 樊太亮, 于炳松, 高志前. 塔里木盆地碳酸盐岩层序地层特征及其控油作用[J]. 现代地质, 2007,21(1):57-65. |
| [47] | 周进高, 郝毅, 邓红婴, 等. 四川盆地中西部栖霞组—茅口组孔洞型白云岩储层成因与分布[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019,24(4):67-78. |
| [48] | 桑琴, 黄静, 程超, 等. 蜀南地区茅口组古岩溶地貌与缝洞系统发育关系研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012,31(2):212-219. |
| [49] | 江青春, 胡素云, 汪泽成, 等. 四川盆地茅口组风化壳岩溶古地貌及勘探选区[J]. 石油学报, 2012,33(6):949-960. |
| [50] |
李大军, 陈辉, 陈洪德, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统茅口组储层形成与古构造演化关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016,37(5):756-763.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 李振宏, 王欣, 杨遂正, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系岩溶储层控制因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2006,30(2):299-306. |
| [1] | CHEN Huaxing, KANG Zhihong, KANG Zhijiang. Stratified Structure and Formation Mechanism of Paleokarst Cave in Carbonate Reservoir of Tahe Oilfield [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 695-708. |
| [2] | ZHANG Honghui, WU Liang, LI Hong, YU Yangzhong, YUAN Yongsheng, ZHANG Liyuan, LI Shizhong, ZHAO Jianbo, PAN Jiangtao, ZHAN Huasi, SHI Haitao, CHEN Guiren. Relation Between the Emeishan Mantle Plume Activity and Wumengshan Volcanic-Sedimentary Basin in Northeastern Yunnan [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(01): 225-243. |
| [3] | HUANG Xu, SHEN Chuanbo, DU Li, WEI Guangren, LUO Lu, TANG Guo. Geothermal Geological Characteristics of the Xianxian High and Fucheng Sag in the Middle Cangxian Uplift, Bohai Bay Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 997-1008. |
| [4] | LI Ting, ZHU Dancheng, LI Haiping, YANG Minglei, LI Tao, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao. Genetic Mechanism of Dolomite in Middle Permian Maokou Formation:Case Study of Central and Eastern Sichuan Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(02): 345-355. |
| [5] | JIA Peng,LI Wei,LU Yuanzheng, FAN Ru,LI Xin, LI Ming,ZENG Yiyang,LIU Xin. Carbon and Oxygen Isotopic Compositions and Their Evolution Records of the Xixiangchi Group in Sedimentary Sequences of Centralsouthern Sichuan Basin and Their Geological Implications [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(6): 1329-1338. |
| [6] | TANG Pan1,WU Shi-qiang2,YU Bing-song1,QIAN Yi-xiong3,PENG Shou-tao2. Genesis Characteristics and Research Means of Paleokarst Collapse [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(3): 675-683. |
| [7] | KANG Zhi-hong,RONG Yi-min,WEI Li-ling,LI Xue,CHEN Yi,CHEN Lin. Approach to Karst Reservoir Types and Classification of Ordovician Carbonate in Tahe Oilfield [J]. Geoscience, 2014, 28(5): 986-994. |
| [8] | ZHAO Pei, LI Xian-qing, SUN Jie, LAI Shou-ning, FU Tong-yang, SU Gui-ping. Study on Mineral Composition and Brittleness Characteristics of Shale Gas Reservoirs from the Lower Paleozoic in the Southern Sichuan Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2014, 28(2): 396-403. |
| [9] | GAO Da, LIN Chang-song, HUANG Li-li, ZUO Fan-fan, LI Hao, GENG Xiao-jie. Paleokarst Characteristics and Their Significances on Reservoir Potential for the Yingshan Formation, Xiker Outcrop Area, Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2014, 28(1): 156-162. |
| [10] | FAN Tai-liang, YU Bing-song, GAO Zhi-qian. Characteristics of Carbonate Sequence Stratigraphy and Its Control on Oil-gas in Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(1): 57-65. |
| [11] | LI Zhen-hong, WANG Xin , YANG Sui-zheng,ZHENG Cong-bin. Analysis of Control Factors of Ordovician Karst Reservoir in Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2006, 20(2): 299-306. |
| [12] | ZHANG Li-li,ZHANG Ning,XIA Wen-chen. THE "MAOKOU" FORMATION CONODONTS FROM MAOERSHAN SECTION IN ENSHI,THE WEST OF HUBEI PROVINCE [J]. Geoscience, 2004, 18(3): 297-304. |
| [13] | MEI Ming-xiang,LI Hao,DENG Jun,WANG Xin-wen,ZHENG Kuan-bing. PRELIMINARY OBSERVATION AND STUDY ON THE OLD OIL POOL OF DOLOMITIC-TYPE FOR THE PERMIAN MAOKOU FORMATION IN WUDANG OF GUIYANG [J]. Geoscience, 2004, 18(3): 353-359. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||