



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (02): 533-542.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.006
收稿日期:2021-10-20
修回日期:2022-03-01
出版日期:2022-04-10
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
郭华明
作者简介:郭华明,男,教授,博士生导师,1975年出生,水文地质学专业,从事水文地质学方面的教学与科研工作。Email: hmguo@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
CAO Yuanyuan( ), GUO Huaming(
), GUO Huaming( ), GAO Zhipeng
), GAO Zhipeng
Received:2021-10-20
Revised:2022-03-01
Online:2022-04-10
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
GUO Huaming
摘要:
季风性波动引起的降雨、径流和排泄过程会引发浅层地下水系统周期性氧化还原动态变化,从而对地下水系统中有害组分的迁移转化产生影响。为探讨氧化还原动态过程对沉积物中砷(As)和氟(F)释放的影响,本研究选择河北白洋淀地区沉积物样品,利用发酵罐作为反应器,建立氧化还原动态实验体系,并监测动态变化过程中实验体系各组分含量的变化。结果表明,碱性和还原环境均有利于地下水中As、F的富集。还原阶段较高的pH条件有利于溶液中F-的解吸,且体系中有机物降解会产生大量HC03-和C032-,与F-发生竞争吸附而有利于F-的富集。对于溶液中As的富集,一方面是由于还原条件下体系中的As以As(III)为主,受沉积物的吸附作用较弱,从而有利于As被释放到溶液中;另一方面是因为还原阶段较高的pH也会使反应体系中As和沉积物间的吸附作用被减弱,造成As的解吸附。由于实验所用沉积物砷含量较低,不同S042-浓度条件对氧化还原动态过程中As、F迁移的影响不明显。总之,氧化还原动态变化过程会强烈影响地下水系统中砷、氟的富集。
中图分类号:
曹元元, 郭华明, 高志鹏. 氧化还原动态变化对沉积物砷和氟释放的影响:以河北白洋淀平原为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(02): 533-542.
CAO Yuanyuan, GUO Huaming, GAO Zhipeng. Redox Dynamic Effect on Fluoride and Arsenic Released from Sediments in the Baiyangdian Plain, Hebei[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 533-542.
| 元素 | K | Fe | Ca | Ti | Ba | Mn | Sr | Zr | Rb | V | Zn | Cr | Co | Ta | Ni | Pb | Cu | Th | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量 | 21 749 | 12 496 | 4 633 | 1 199 | 440 | 245 | 229 | 112 | 67.3 | 64.9 | 25.1 | 18.8 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 12.5 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
表1 沉积物样品BDZK1-222不同元素含量(mg/kg)
Table 1 Background values of different elements in sediment sample BDZK1-222 (mg/kg)
| 元素 | K | Fe | Ca | Ti | Ba | Mn | Sr | Zr | Rb | V | Zn | Cr | Co | Ta | Ni | Pb | Cu | Th | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含量 | 21 749 | 12 496 | 4 633 | 1 199 | 440 | 245 | 229 | 112 | 67.3 | 64.9 | 25.1 | 18.8 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 12.5 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
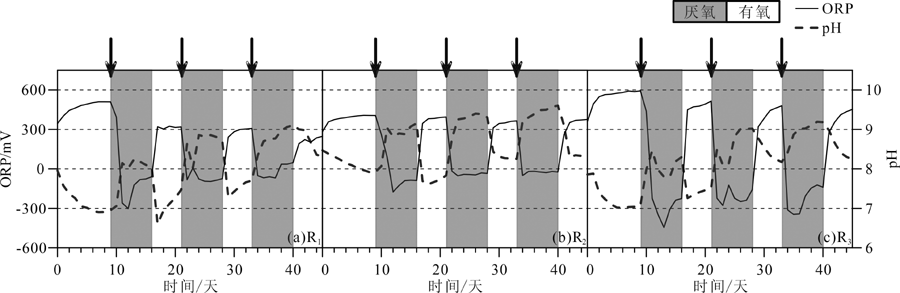
图3 反应器中ORP和pH随时间的变化(灰色和白色阴影区域分别表示还原和有氧阶段,乳酸钠添加点用箭头表示) (a) R1, 0.1 mM S O 4 2 -; (b) R2,1 mM S O 4 2 -; (c) R3, 5 mM S O 4 2 -。下文同
Fig.3 Temporal variations of ORP and pH in three experimental systems (grey and white shades denoting anoxic and oxic half-cycles, respectively; arrows showing the timing of sodium lactate addition)
| 反应器 | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.1 | 1 | 5 |
| F-质量浓度(最大值)/(mg/L) | 14.50 | 8.98 | 6.66 |
表2 反应器溶液中S O 4 2 -浓度与F-质量浓度对比
Table 2 Comparison of solution S O 4 2 - and F-concentrations in three experimental systems
| 反应器 | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.1 | 1 | 5 |
| F-质量浓度(最大值)/(mg/L) | 14.50 | 8.98 | 6.66 |
| [1] | 倪萍. 河套盆地含水层沉积物赋存态砷及对地下水砷富集的影响[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [2] | DUAN Y H, SCHAEFER M V, WANG Y X, et al. Experimental constraints on redox-induced arsenic release and retention from aquifer sediments in the central Yangtze River Basin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 649: 629-639. |
| [3] | FROHNE T, RINKLEBE J, DIAZ-BONE A R, et al. Controlled variation of redox conditions in a floodplain soil: Impact on metal mobilization and biomethylation of arsenic and antimony[J]. Geoderma, 2011, 160: 14-424. |
| [4] | AYENEW T. The distribution and hydrogeological controls of fluoride in the groundwater of central Ethiopian rift and adjacent highlands[J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 54(6): 1313-1324. |
| [5] | CHOWDHURY A, ADAK K M, MUKHERJEE A, et al. A critical review on geochemical and geological aspects of fluoride belts, fluorosis and natural materials and other sources for alternatives to fluoride exposure[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 574: 333-359. |
| [6] | Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality[M]. 4th ed. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2011. |
| [7] | PI K F, WANG Y X, XIE X J, et al. Hydrogeochemistry of co-occurring geogenic arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater at Datong Basin, northern China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 652-661. |
| [8] | LI J X, WANG Y X, XIE X J, et al. Cl/Br ratios and chlorine isotope evidences for groundwater salinization and its impact on groundwater arsenic, fluoride and iodine enrichment in the Datong basin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 544: 158-167. |
| [9] | WEN D G, ZHANG F C, ZHANG E Y, et al. Arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater of China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 135: 1-21. |
| [10] | GUO H M, WEN D G, LIU Z Y, et al. A review of high arsenic groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: Distribution, characteristics and geochemical processes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 41:196-217. |
| [11] | 郭华明, 倪萍, 贾永锋, 等. 原生高砷地下水的类型、化学特征及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4):1-12. |
| [12] | GUO H M, WANG Y X, SHPEIZER M G, et al. Natural occurrence of arsenic in shallow groundwater, Shanyin, Datong Basin, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, 2003, 38(11): 2565-2580. |
| [13] | GUO H M, YANG S Z, TANG X H, et al. Groundwater geochemistry and its implications for arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 339(1): 131-144. |
| [14] | ISLAM S F, GAULT G A, BOOTHMAN C, et al. Role of metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments[J]. Nature, 2004, 430: 0028-0836. |
| [15] | MCARTHUR J M, BANERJEE D M, HUDSON-EDWARDS K A, et al. Natural organic matter in sedimentary basins and its relation to arsenic in anoxic ground water: the example of West Bengal and its worldwide implications[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 19(8): 1255-1293. |
| [16] | GUO H M, ZHANG Y, XING L N, et al. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(11): 2187-2196. |
| [17] | VINSON S D, MCINTOSH C J, DWYER S G, et al. Arsenic and other oxyanion-forming trace elements in an alluvial basin aquifer: Evaluating sources and mobilization by isotopic tracers (Sr, B, S, O, H, Ra)[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(8): 1364-1376. |
| [18] | JONES W G, PICHLER T. Relationship between pyrite stability and arsenic mobility during aquifer storage and recovery in southwest central Florida[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(3): 723-730. |
| [19] | PILI E, TISSERAND D, BUREAU S. Origin, mobility, and temporal evolution of arsenic from a low-contamination catchment in alpine crystalline rocks[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 262(12): 887-895. |
| [20] | SHAH T M, DANISHWAR S. Potential fluoride contamination in the drinking water of Naranji area, northwest frontier province, Pakistan[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2003, 25(4): 475-481. |
| [21] | SU C L, WANG Y X, XIE X J, et al. An isotope hydrochemical approach to understand fluoride release into groundwaters of the Datong Basin, northern China[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2015, 17(4): 791-801. |
| [22] | MCNAB W W, SINGLETON J M, MORAN E J, et al. Ion exchange and trace element surface complexation reactions associated with applied recharge of low-TDS water in the San Joaquin Valley, California[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(1): 129-137. |
| [23] | KUMAR M, DAS N, GOSWAMI R, et al. Coupling fractionation and batch desorption to understand arsenic and fluoride co-contamination in the aquifer system[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 164: 657-667. |
| [24] | 万继涛, 郝奇琛, 巩贵仁, 等. 鲁西南地区高氟水分布规律与成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 448-453. |
| [25] | WANG Z, GUO H M, XING S P, et al. Hydrogeochemical and geothermal controls on the formation of high fluoride groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 598: 126372. |
| [26] | SCHAEFER V M, YING C S, BENNER G S, et al. Aquifer arsenic cycling induced by seasonal hydrologic changes within the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50: 3521-3529. |
| [27] | HUANG K, LIU Y Y, YANG C, et al. Identification of hydrobiogeochemical processes controlling seasonal variations in arsenic concentrations within a riverbank aquifer at Jianghan Plain, China[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54: 4294-4308. |
| [28] | FU H Y, ZHANG H, SUI Y, et al. Transformation of uranium species in soil during redox oscillations[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 208: 846-853. |
| [29] | THOMASARRIGO K L, MIKUTTA C, LOHMAYER R, et al. Sulfidization of organic freshwater flocs from a minerotrophic peatland: speciation changes of iron, sulfur, and arsenic[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(7): 3607-3616. |
| [30] | PARSONS T C, COUTURE R M, OMOREGIE O E, et al. The impact of oscillating redox conditions: arsenic immobilisation in contaminated calcareous floodplain soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2013, 178: 254-263. |
| [31] | COUTURE R M, CHARLET L, MARKELOVA E, et al. On-off mobilization of contaminants in soils during redox oscillations[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(5): 3015-3023. |
| [32] | 赵振宏. 河北平原深层高氟地下水水文地球化学特征[J]. 工程勘察, 1993(2): 28-31. |
| [33] | 林重阳. 漳卫河流域地下水的水化学特征和高氟地下水的形成[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [34] | PHAN V, BARDELLI F, PAPE L P, et al. Interplay of S and As in Mekong Delta sediments during redox oscillations[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 10(5): 1715-1729. |
| [35] | 高志鹏. 基于一维反应运移模型的河套平原地下水砷富集机理[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [36] | 陈毅. 白洋淀流域平原区地下水-孔隙水的水化学特征和水文地球化学过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. |
| [37] | 文丽青. 白洋淀水质污染分析及综合治理研究[J]. 河北环境科学, 2001, 9(3):46-48. |
| [38] | THOMPSON A, CHADWICK A O, RANCOURT G D, et al. Iron-oxide crystallinity increases during soil redox oscillations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(7): 1710-1727. |
| [39] | WANG Y H, PAPE L P, MORIN G, et al. Arsenic speciation in Mekong Delta sediments depends on their depositional environment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(6): 3431-3439. |
| [40] | GHORAI S, PANT K K. Equilibrium, kinetics and breakthrough studies for adsorption of fluoride on activated alumina[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2005, 42: 265-271. |
| [41] | 沈照理, 郭华明, 徐刚, 等. 地下水化学异常与地方病[J]. 自然杂志, 2010(2):83-89. |
| [42] | JACKS G, BHATTACHARYA P, CHAUDHARY V, et al. Controls on the genesis of some high-fluoride groundwaters in India[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(2): 221-228. |
| [43] | POLOMSKI J, FLUHLER H, BLASER P. Fluoride-induced mobilization and leaching of organic matter, iron, and aluminum[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1982, 11:452-456. |
| [44] | JESUßEK A, GRANDLE S, DAHMKE A. Impacts of subsurface heat storage on aquifer hydrogeochemistry[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 69(6): 1999-2012. |
| [45] | BONTE M, BREUKELEN M B, STUYFZAND J P. Temperature-induced impacts on groundwater quality and arsenic mobility in anoxic aquifer sediments used for both drinking water and shallow geothermal energy production[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(14): 5088-5100. |
| [46] | MOLINARI A, GUADAGNINI L, MARCACCIO M, et al. Arsenic release from deep natural solid matrices under experimentally controlled redox conditions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 444: 231-240. |
| [47] | SMEDLEY P L, KINNIBURGH D G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17: 517-568. |
| [48] | PHAN V, BERNIER-LATMANI R, TISSERAND D, et al. As release under the microbial sulfate reduction during redox oscillations in the Upper Mekong Delta aquifers, Vietnam: A mechanistic study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 663: 718-730. |
| [49] | PEDERSEN D H, POSTMA D, JAKOBSEN R. Release of arsenic associated with the reduction and transformation of iron oxides[J]. Science Direct, 2006, 70: 4116-4129. |
| [50] | GUO H M, ZHANG B, LI Y, et al. Hydrogeological and biogeochemical constrains of arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers from the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159: 876-883. |
| [51] | ANAWAR H M, KOMAKI K, AKAI J, et al. Diagenetic control on arsenic partitioning in sediments of the Meghna River delta, Bangladesh[J]. Environmental Geology, 2002, 41(7): 816-825. |
| [52] | MASSCHELEYN H P, DELAUNE D R, PATRICK H W. Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1991, 25(8): 1414-1419. |
| [53] | YAMAGUCHIA N, NAKAMURAB T, DONG D, et al. Arsenic release from flooded paddy soils is influenced by speciation, Eh, pH, and iron dissolution[J]. Chemosphere, 2011, 83: 925-932. |
| [54] | VAN GEEN A, BOSTICK B C, TRANG P T K, et al. Retardation of arsenic transport through a Pleistocene aquifer[J]. Nature, 2013, 501: 204-207. |
| [55] | QIAO W, GUO H M, HE C, et al. Molecular evidence of arsenic mobility linked to biodegradable organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54: 7280-7290. |
| [56] | 邢丽娜. 华北平原典型剖面上地下水化学特征和水文地球化学过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012. |
| [1] | 刘圣锋, 高柏, 易玲, 方正, 史天成, 丁燕. 海拉尔盆地水环境中砷和铀的分布特征及风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 933-942. |
| [2] | 张卓, 陈社明, 柳富田, 高志鹏, 牛笑童. 滨海平原区深层高氟地下水富集机理:以滦河三角洲为例[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(04): 925-932. |
| [3] | 刘一浩, 薛春纪, 赵云, 赵晓波, 褚海霞, 刘城先, 余亮, 王璐, 吴得海. 我国热液金矿中黄铁矿的载金性研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(01): 1-12. |
| [4] | 王文祥, 何锦, 张梦南, 安永会, 李文鹏, 吴玺, 龚磊, 王晓燕. 张掖盆地龙首山山前高氟地下水的形成[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 415-420. |
| [5] | 冯海波,董少刚,史晓珑,王克玲,刘白薇,李政葵,刘晓波. 内蒙古托克托县潜水与承压水中氟化物的空间分布特征及形成机理[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3): 672-679. |
| [6] | 荆继红,黄冠星,陈宗宇,孙继朝,刘凡,张英,王金翠. 氧化还原条件对土壤砷(Ⅴ)稳定化作用的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 370-376. |
| [7] | 王世雄,蒋峰芝,陈景. 铁盐絮凝法对阳宗海湖泊水体的除砷效果及底泥的稳定性考察[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 361-369. |
| [8] | 赵凯,郭华明,高存荣. 北方典型内陆盆地高砷地下水的水化学特征及处理技术[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 351-360. |
| [9] | 欧阳光明,谢作明,孙小燕,杨东,王焰新. 大同盆地浅层含水层沉积物中砷的生物可利用性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 260-264. |
| [10] | 周殷竹,郭华明,逯海. 高砷地下水中溶解性有机碳和无机碳稳定同位素特征[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(2): 252-259. |
| [11] | 万继涛, 郝奇琛, 巩贵仁, 苏晨, 崔亚莉,刘倩. 鲁西南地区高氟水分布规律与成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 448-453. |
| [12] | 李世君, 王新娟, 周俊, 汤新梅, 王兆萄. 北京大兴区第四系高氟地下水分布规律研究[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2): 407-414. |
| [13] | 柳青青, 杨忠芳, 周国华, 夏学齐, 侯青叶, 余涛, 翟大兴. 中国东部主要入海河流As元素分布、来源及影响因素分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(1): 114-124. |
| [14] | 王喜宽 朱锁刘东 夏学齐 包凤琴 赵锁志. 内蒙古河套地区多目标区域地球化学调查成果及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(6): 1064-1070. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||