



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (05): 1270-1290.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.107
丁梦1,2( ), 樊太亮1,2(
), 樊太亮1,2( ), 吴俊1,2, 李煜3, 李晨晨4, 吕凯迪1
), 吴俊1,2, 李煜3, 李晨晨4, 吕凯迪1
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-11-13
通信作者:
樊太亮,男,教授,博士生导师,1961年出生,主要从事碳酸盐岩油气地质与层序地层学方面的教学与科研工作。Email: fantl@cugb.edu.cn。作者简介:丁梦,女,博士研究生,1987年出生,主要从事碳酸盐岩层序地层/沉积相研究。Email: 3006190005@cugb.edu.cn。
基金资助:
DING Meng1,2( ), FAN Tailiang1,2(
), FAN Tailiang1,2( ), WU Jun1,2, LI Yu3, LI Chenchen4, LÜ Kaidi1
), WU Jun1,2, LI Yu3, LI Chenchen4, LÜ Kaidi1
Published:2024-10-10
Online:2024-11-13
摘要:
塔河油田T738井区一间房组地质年代老、埋藏深度大,虽经历了复杂的构造与成岩改造,但仍具有良好的储集性能。目前该井区重点勘探开发主要集中在断裂带发育部位,以断溶体为主要钻探目标。然而,礁滩相勘探潜力巨大,但是对影响碳酸盐岩礁滩相储层发育沉积相认识的不足制约了勘探突破。本研究基于塔河油田T738井区重点井钻测井资料的分析和薄片鉴定工作,建立了T738井区一间房组高精度层序地层格架,总结了一间房组开阔台地内沉积微相常规测井相模式,对沉积微相类型和特征分别进行了划分和描述,分析了四级层序内部礁滩体厚度分布和沉积微相平面展布特征。结果显示,一间房组划分为1个三级层序(Sq1)和3个四级层序(Ssq1、Ssq2和Ssq3),在开阔台地相识别出高-中-低能滩、丘滩间、生物礁(丘)等几种沉积微相。其中,颗粒滩在常规测井判别值域分别对应AC为51~61 μs/m,DEN为2.5~2.6 g/cm3,CNL为1%~6 %,RD为80~3000 Ω·m。一间房组Ssq1层序礁滩体规模较小且孤立,仅分布在地势相对高部位,归因于其在三级层序内所处的海侵体系域低部位,水动力条件较弱。Ssq2、Ssq3层序礁滩体位于三级层序内高位体系域,其规模较大、连片性较好,厚度稳定,最大累计厚度达40 m。
中图分类号:
丁梦, 樊太亮, 吴俊, 李煜, 李晨晨, 吕凯迪. 塔里木盆地塔河油田T738井区一间房组高精度层序地层格架内沉积微相特征[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1270-1290.
DING Meng, FAN Tailiang, WU Jun, LI Yu, LI Chenchen, LÜ Kaidi. Sedimentary Microfacies in a High-precision Sequence Stratigraphic Framework of the Yijianfang Formation in the T738 Well Area of the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1270-1290.

图7 一间房组内部四级层序界面附近岩石学特征 (a)T738井,5963.80 m,亮晶砂屑灰岩,砂屑泥晶灰岩,弱冲刷侵蚀不整合面;(b)T738井,5963.85 m,亮晶砂屑灰岩,砂屑泥晶灰岩,弱冲刷侵蚀不整合面;(c)T738井,5964.00 m,亮晶砂屑灰岩,溶蚀晶洞充填Cal,可见示底构造;(d)AD6井,6088.00 m,泥晶灰岩,岩溶角砾岩;(e)T738井,5965.60 m,亮晶砂屑灰岩,世代胶结,第一期为纤柱状等厚环边,第二期为粒状方解石,可见油迹;(f)T738井,5966.70 m,亮晶砂屑灰岩,铸模孔被后期方解石充填。注:T738井薄片深度位置见图6
Fig.7 Petrological characteristics near the fourth-order sequence boundary in the Yijianfang Formation
| 系 | 统 | 组 | 层序底界面 | 四级层序 | 三级层序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 奥陶系 | 上统 | 恰尔巴克组 | |||
| 中统 | 一间房组 | SByj2 | Ssq3 | Sq1 | |
| SByj1 | Ssq2 | ||||
| Ssq1 |
表1 中下奥陶统一间房组层序地层划分方案
Table 1 Division scheme of sequence stratigraphy for the Yijianfang Formation of the Lower to Middle Ordovician
| 系 | 统 | 组 | 层序底界面 | 四级层序 | 三级层序 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 奥陶系 | 上统 | 恰尔巴克组 | |||
| 中统 | 一间房组 | SByj2 | Ssq3 | Sq1 | |
| SByj1 | Ssq2 | ||||
| Ssq1 |
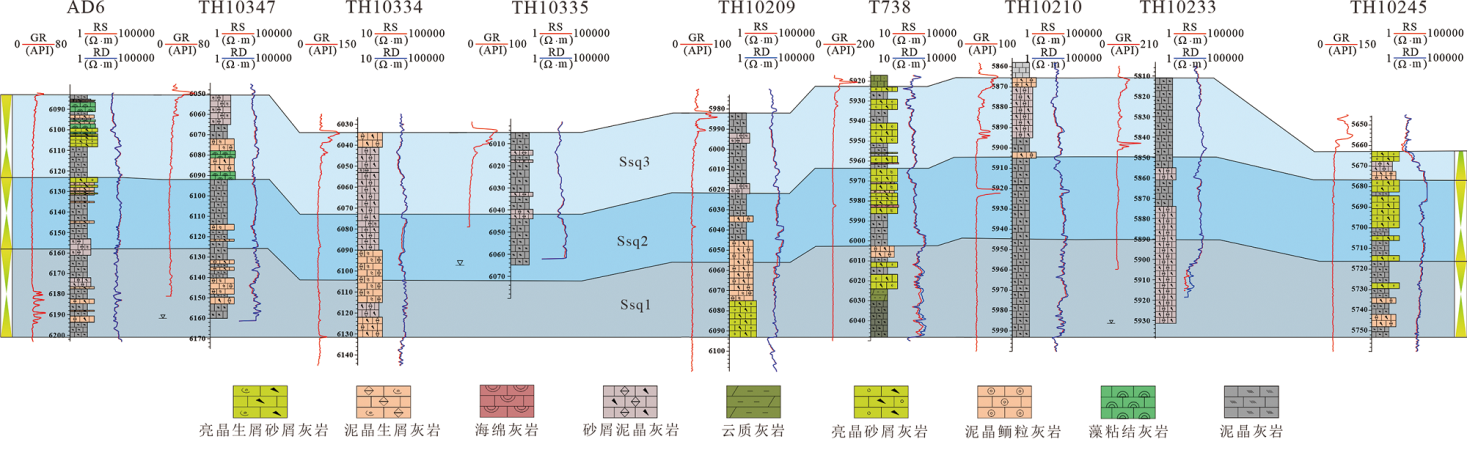
图8 AD6-TH10347-TH10334-TH10335-TH10209-T738-TH10210-TH10233-TH10245井层序对比剖面(剖面位置见图1(B)AA’)
Fig.8 Sequence correlation section of the wellAD6-TH10347-TH10334-TH10335-TH10209-T738-TH10210-TH10233-TH10245

图9 T738井区一间房组灰岩岩石学特征 (a)亮晶砂屑灰岩,T738井,5959.41 m;(b)亮晶鲕粒灰岩,T738井,5965.62 m;(c)亮晶生屑灰岩,T738井,5968.81 m;(d)泥晶砂屑灰岩,T728井,6119.14 m;(e)泥晶生屑灰岩,T728井,6000.5 m;(f)砂屑泥晶灰岩,AD6井,6103.81 m;(g)生屑泥晶灰岩,T728井,6001.30 m;(h)泥晶灰岩,T738井,6065.8 m
Fig.9 Petrological characteristics in the Yijianfang Formation of the T738 well area

图10 生物礁丘灰岩岩石学特征 (a)海绵灰岩,T750井,6090 m;(b)海绵灰岩,T709井,5948 m;(c)海绵灰岩,T738井,5972.12 m;(d)藻黏结灰岩,S91,5857.62 m
Fig.10 Petrological characteristics of reef-building organisms and organic boundstone
| 沉积相 | 亚相 | 岩心、薄片 识别微相 | 测井识别的 微相组合 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开阔台 地相 | 颗粒滩 | 砂屑滩、生屑 滩、鲕粒滩 | 高能滩、中能 滩、低能滩 |
| 丘滩间 | 丘滩间 | 丘滩间 | |
| 台内礁(丘) | 生物礁(丘) | / |
表2 塔河地区一间房组沉积相类型划分简表
Table 2 Classification scheme of sedimentary facies of the Yijianfang Formation in the Tahe area
| 沉积相 | 亚相 | 岩心、薄片 识别微相 | 测井识别的 微相组合 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开阔台 地相 | 颗粒滩 | 砂屑滩、生屑 滩、鲕粒滩 | 高能滩、中能 滩、低能滩 |
| 丘滩间 | 丘滩间 | 丘滩间 | |
| 台内礁(丘) | 生物礁(丘) | / |

图12 T704井优势沉积相典型薄片对应敏感测井曲线特征
Fig.12 Characteristics of sensitive logging curves corresponding to typical thin sections of dominant sedimentary facies in well T704

图13 关键井常规测井曲线交会图(AD6井、S91井、T704井、T737井和T738井) CNL.补偿中子;DEN.补偿密度;AC.声波时差;RD.深电阻率
Fig.13 Cross plot of conventional logging curves for key wells (AD6, S91, T704, T737, and T738)
| 测井曲线名称 | 值域范围 |
|---|---|
| AC(μs/m) | 51~61 |
| DEN(g/cm3) | 2.5~2.6 |
| CNL(%) | 1~6 |
| RD(Ω·m) | 80~3000 |
表3 常规测井曲线颗粒滩判别值域范围
Table 3 Range of discriminant values for particle shoals in conventional logging curves
| 测井曲线名称 | 值域范围 |
|---|---|
| AC(μs/m) | 51~61 |
| DEN(g/cm3) | 2.5~2.6 |
| CNL(%) | 1~6 |
| RD(Ω·m) | 80~3000 |

图14 S86-T705-T754-TH10244-TH10214-T738-TH12176-TH12179井沉积微相对比剖面(剖面位置见图1(B)BB’)
Fig.14 Microfacies correlation section of wells S86, T705, T754, TH10244, TH10214, T738, TH12176, and TH12179
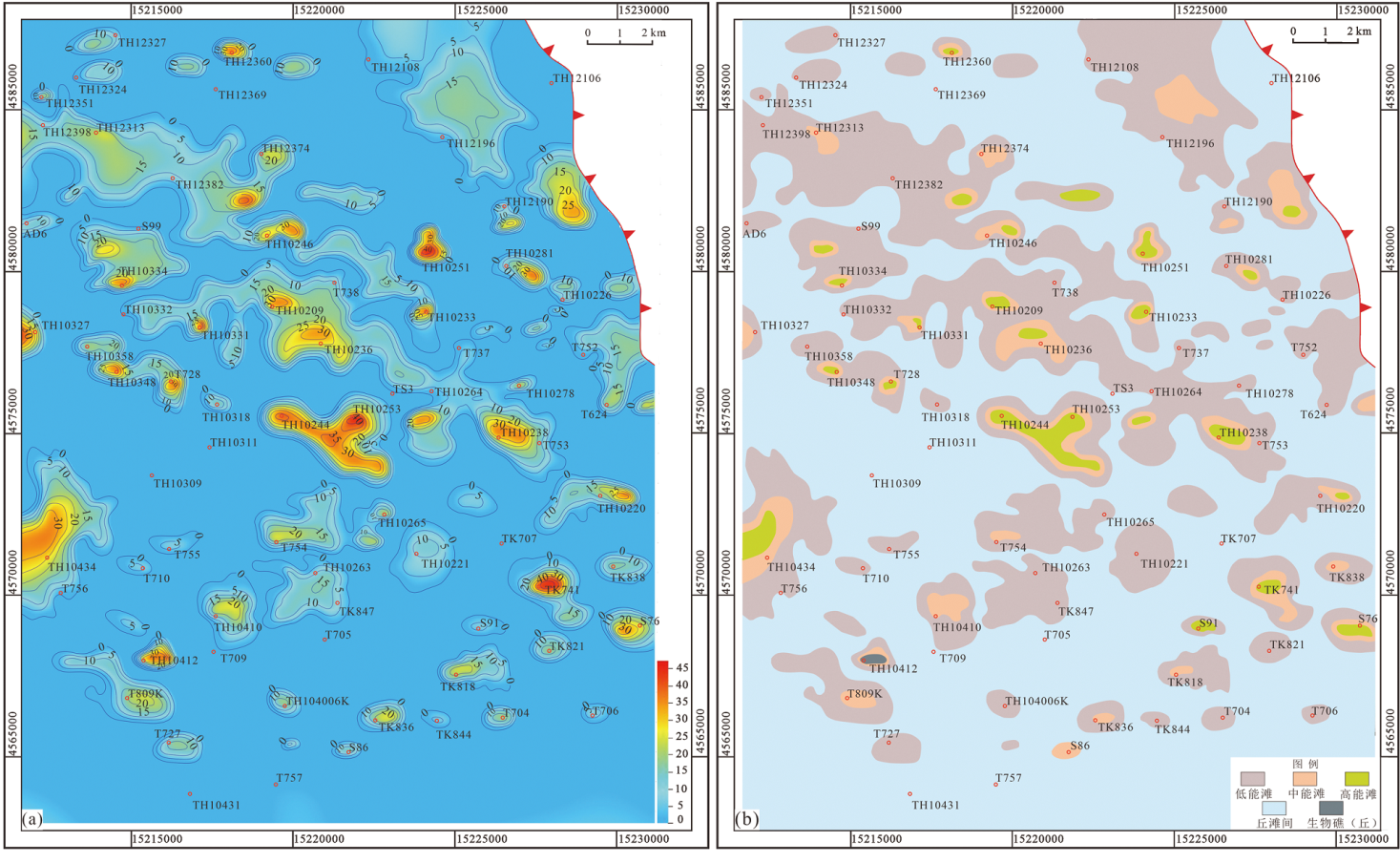
图15 一间房组Ssq1层序滩体等厚图(a)和层序沉积微相平面分布图(b)
Fig.15 Isopleth of shoals (a) and distribution of sedimentary microfacies (b) in the Ssql sequence of the Yijianfang Formation
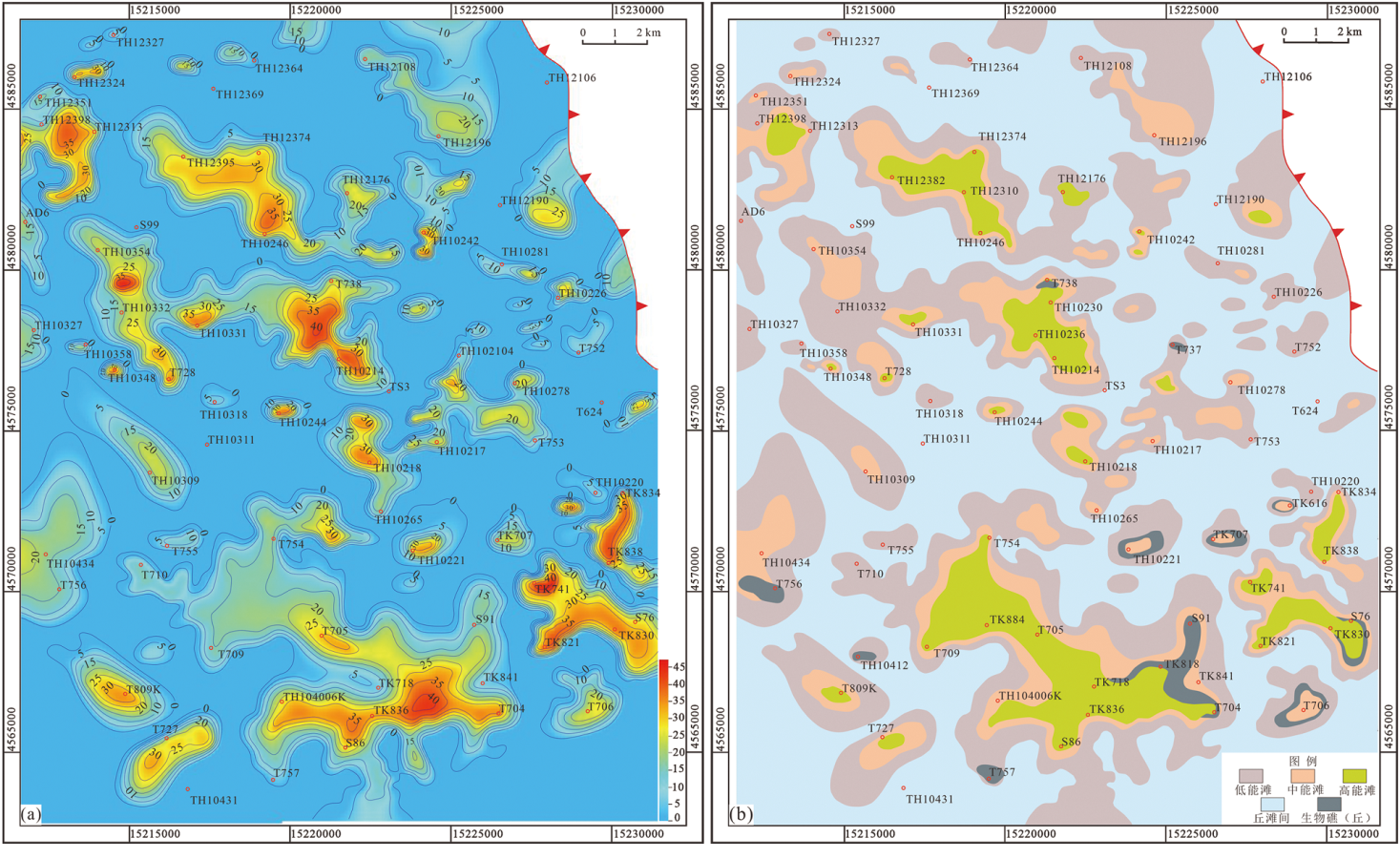
图16 一间房组Ssq2层序滩体等厚图(a)和层序沉积微相平面分布图(b)
Fig.16 Isopleth of shoals (a) and distribution of sedimentary microfacies (b) in the Ssq2 sequence of the Yijianfang Formation

图17 一间房组Ssq3层序滩体等厚图(a)和层序沉积微相平面分布图(b)
Fig.17 Isopleth of shoals (a) and distribution of sedimentary microfacies (b) in the Ssq3 sequence of the Yijianfang Formation
| [1] | 何治亮, 马永生, 朱东亚, 等. 深层-超深层碳酸盐岩储层理论技术进展与攻关方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(3): 533-546. |
| [2] | 庞雄奇, 林会喜, 郑定业, 等. 中国深层和超深层碳酸盐岩油气藏形成分布的基本特征与动力机制及发展方向[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(5): 673-695. |
| [3] | 康玉柱. 中国海相油气田勘探实例之四塔里木盆地塔河油田的发现与勘探[J]. 海相油气地质, 2005, 10(4): 31-38. |
| [4] | 康玉柱. 中国古生代海相油气田发现的回顾与启示[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(5): 570-575. |
| [5] | 何治亮, 金晓辉, 沃玉进, 等. 中国海相超深层碳酸盐岩油气成藏特点及勘探领域[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(1): 3-14. |
| [6] | FLÜGEL E, FLÜGEL C. Applied microfacies analysis: Provenance studies of Roman mosaic stones[J]. Facies, 1997, 37(1): 1-48. |
| [7] | REOLID M, GAILLARD C, LATHUILIÈRE B. Microfacies, microtaphonomic traits and foraminiferal assemblages from Upper Jurassic oolitic-coral limestones: Stratigraphic fluctuations in a shallowing-upward sequence (French Jura, Middle Oxfordian)[J]. Facies, 2007, 53(4): 553-574. |
| [8] | TIWARI R N, MISHRA D. Microfacies analysis of transgressive condensed sequence: A studyfrom the Oxfordian of Kachchh Basin, gujarat[J]. Journal of Geological Society of India (Online Archive from Vol 1 to Vol 78), 2007, 70(6): 923-932. |
| [9] | LANFRANCHI A, BERRA F, JADOUL F. Compositional changes in sigmoidal carbonateclinoforms (Late Tithonian, eastern Sardinia, Italy): Insights from quantitative microfacies analyses[J]. Sedimentology, 2011, 58(7): 2039-2060. |
| [10] | SALLER A H. Facies control on dolomitization and porosity in the Devonian Swan Hills Formation in the Rosevear area, west-central Alberta[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2001, 49(4): 458-471. |
| [11] | VANDEGINSTE V, SWENNEN R, REED M H, et al. Host rock dolomitization and secondary porosity development in the Upper Devonian Cairn Formation of theFairholme carbonate complex (South-west Alberta, Canadian Rockies): Diagenesis and geochemical modelling[J]. Sedimentology, 2009, 56(7): 2044-2060. |
| [12] | 宋倩, 马青, 刘莹, 等. 塔北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩颗粒滩沉积特征及分布规律[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(1): 46-54. |
| [13] |
邓小江, 李国蓉, 徐国强, 等. 塔河油田南部中奥陶统一间房组沉积相精细划分[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(1): 35-40.
DOI |
| [14] |
樊太亮, 高志前, 吴俊. 塔里木盆地深层碳酸盐岩建造-改造作用与多类型储层有序性分布[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4): 1-18.
DOI |
| [15] | 许志琴, 李思田, 张建新, 等. 塔里木地块与古亚洲/特提斯构造体系的对接[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 1-22. |
| [16] | 何碧竹, 焦存礼, 许志琴, 等. 阿尔金—西昆仑加里东中晚期构造作用在塔里木盆地塘古兹巴斯凹陷中的响应[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3435-3448. |
| [17] |
何碧竹, 焦存礼, 许志琴, 等. 塔里木盆地显生宙古隆起的分布及迁移[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3): 277-289.
DOI |
| [18] | 林畅松, 李思田, 刘景彦, 等. 塔里木盆地古生代重要演化阶段的古构造格局与古地理演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 210-218. |
| [19] | 何登发, 孙方原, 何金有, 等. 温宿北—野云沟断裂的构造几何学与运动学特征及塔北隆起的成因机制[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(4): 917-934. |
| [20] | 张云鹏, 任建业, 阳怀忠, 等. 塔里木盆地轮南低凸起构造特征及演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(3): 440-447, 460. |
| [21] | 严威, 王兴志, 丁勇, 等. 塔河南部奥陶系海西早期岩溶的发现[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33(3): 53-60. |
| [22] | TIAN F, JIN Q, LU X B, et al. Multi-layered Ordovicianpaleokarst reservoir detection and spatial delineation: A case study in the Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, Western China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 69: 53-73. |
| [23] | 吴俊. 碳酸盐岩盖层特征及封盖性能控制因素[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [24] | 郁文谊. 塔里木盆地塔河地区奥陶系鹰山组层序地层与沉积相研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [25] | 谷雨. 塔河油田主区中奥陶统一间房组沉积微相特征与展布[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020. |
| [26] | 高泽. 塔河油田四、六区鹰山组暗河岩溶储层发育特征及控制因素[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021. |
| [27] | 贾承造. 中国塔里木盆地构造特征与油气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997. |
| [28] | CHEN C M, LU H F, JIA D, et al. Closing history of the southern Tianshan oceanic basin,Western China: An oblique collisional orogeny[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 302(1/2): 23-40. |
| [29] | 王邱春. 塔里木盆地上寒武统—中下奥陶统关键界面识别与表征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016. |
| [30] | SCHLAGER W. Drowning unconformities on carbonate platforms[M]//CREVELLO P D, WILSON J L, SARG J F, et al, eds. Controls on Carbonate Platforms and Basin Development. USA: SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology), 1989: 15-25. |
| [31] | 张玉. 塔河一间房组储层酸蚀导流能力与产能模型研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2015. |
| [32] | 赵永强. 塔里木盆地顺北—顺南地区鹰山组四级层序地层划分及地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 49(4): 454-467. |
| [33] | DUNHAM R J. Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional textures[J]. 1962,1:108-121. |
| [34] | 曾允孚, 夏文杰. 沉积岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986. |
| [35] | 冯增昭. 沉积岩石学-下册: 第二版[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1993: 1-326. |
| [36] | Carbonate platform facies models[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69: 1-21. |
| [37] | WILSON J L. Carbonate Facies in Geologic History[M]. New York, NY: Springer New York, 1975. |
| [38] | 余秋均. 多井测井资料的标准化处理方法: 以M油田为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2020, 34(6): 118-122. |
| [39] | 高春云, 周立发, 路萍. 测井曲线标准化研究进展综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(5): 1777-1783. |
| [1] | 陈格格, 高志前, 焦存礼, 胡宗全, 袁钰轩, 卫端, 翟昕箐, 畅哲. 塔里木盆地北部下寒武统肖尔布拉克组海进-海退转换背景下的微生物礁滩发育模式[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(05): 1169-1181. |
| [2] | 武重阳, 于炳松, 王红军, 阮壮, 程传捷, 郭同翠, 张良杰, 程木伟. 阿姆河右岸B区中部卡洛夫-牛津阶高精度层序地层划分及层序发育模式[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 924-937. |
| [3] | 谭聪, 于炳松, 阮壮, 郝士龙, 李琨, 罗忠, 刘润达. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组高分辨率层序地层研究[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(02): 290-301. |
| [4] | 左璠璠,林畅松,高达,赵建华,夏世强,李虹. 塔中地区西北部良里塔格组沉积特征及其演化规律[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(5): 1008-1016. |
| [5] | 陈贤良,纪友亮,樊太亮,王宏语,郝悦娟,聂文彬,闫宁. 松辽盆地七棵树油田沙河子组层序地层格架与油气的关系[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 968-977. |
| [6] | 徐少华,徐国强,杨俊华,李小刚,胡琏,蔡长娥,郭伟. 南海北部白云凹陷深水区SQ13.8深水扇砂体识别与分布研究:以SF-5为例[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(2): 366-372. |
| [7] | 李儒峰, 柳广弟, 马国富, 高岗, 方晶, 刘玉娥. 武威盆地石炭系层序地层学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(6): 1048-1056. |
| [8] | 张海, 甘凤伟, 魏宁. 贵州东南区埃迪卡拉系层序地层格架[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(2): 221-227. |
| [9] | 王居峰, 郭彦如, 张延玲, 刘昊伟, 马德波. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组层序地层格架与沉积相构成现代地质[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(5): 803-808. |
| [10] | 刘震,谭卓,蔡东升,刘明全,付东阳. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组岩性圈闭形成条件[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 239-246. |
| [11] | 傅强,李益. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长8—长7油层组高分辨率层序地层格架及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(4): 579-584. |
| [12] | 梅冥相 张丛 张海 孟晓庆 陈永红. 上扬子区下寒武统的层序地层格架及其形成的古地理背景[J]. 现代地质, 2006, 20(2): 195-208. |
| [13] | 梅冥相,马永生,邓军,张海,孟晓庆,陈永红. 上扬子区下古生界层序地层格架的初步研究[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(4): 551-562. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||