



现代地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (01): 212-220.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.170
收稿日期:2021-10-11
修回日期:2021-12-05
出版日期:2022-02-10
发布日期:2022-03-08
通讯作者:
魏士平
作者简介:魏士平,男,博士,副教授,1969年出生,微生物学专业,主要从事地质微生物方面的研究。Email: weishiping@cugb.edu.cn。基金资助:
CHEN Huijia( ), ZHANG Huiqing, FENG Ying, WEI Shiping(
), ZHANG Huiqing, FENG Ying, WEI Shiping( )
)
Received:2021-10-11
Revised:2021-12-05
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2022-03-08
Contact:
WEI Shiping
摘要:
产脲酶细菌普遍存在于自然界,其对碳酸钙的矿化作用被广泛用于工程地质和环境等各项工程领域;本研究旨在从北戴河新河河口海洋沉积物中分离产脲酶细菌,探讨其诱导形成碳酸钙的特征,为地质与工程领域的应用提供良好的材料。从海洋沉积物样品中共分离出33株细菌,经筛选,其中有10株细菌具有产脲酶活性,16S rRNA基因序列分析表明:其中有3株细菌属于苍白杆菌属(Ochrobactrum sp.),而其他7株细菌属于赖氨酸芽孢杆菌属(Lysinibacillus sp.)。对其中两株有代表性的菌株人苍白杆菌(O. anthropic)CP57和赖氨酸芽孢杆菌(L. fusiformis) CP66诱导形成碳酸钙沉淀进行了实验,X射线晶体衍射(XRD)分析表明:CP57菌株诱导形成的沉淀由方解石组成,而CP66菌株诱导形成的沉淀则包含了方解石和球霰石两种晶相;扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察显示:CP57形成的沉淀呈不规则形,而CP66形成的沉淀包含了不规则形和球形两种形态;进一步用透射电子显微镜(TEM)和选区电子衍射(SAED)对两种不同形态的碳酸钙沉淀进行了矿物相的分析,结果显示:不规则形碳酸钙沉淀为方解石,球形碳酸钙沉淀为球霰石;采用傅立叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)对细菌所形成的碳酸钙进行了表征,结果显示:CP57形成的沉淀分别在波数1 422 cm-1、875 cm-1和711 cm-1处出现明显吸收峰,和方解石的FTIR图谱特征吻合;而CP66除出现以上方解石的吸收峰外,还在1 081 cm-1和743 cm-1处出现明显对应球霰石的特征吸收峰。研究结果为进一步揭示不同细菌诱导碳酸钙形成不同的形貌和晶相奠定了基础。
中图分类号:
陈慧佳, 张慧卿, 冯莹, 魏士平. 海洋产脲酶细菌的筛选及诱导形成碳酸钙矿物的特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 212-220.
CHEN Huijia, ZHANG Huiqing, FENG Ying, WEI Shiping. Screening of Marine Urease-producing Bacteria and Characterization of Their Produced Calcium Carbonate Minerals[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(01): 212-220.
| 菌株 | 属种 | 基因号 | 相似性/% | 产脲酶活性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP49 | Ochrobactrum anthropi | KY770534 | 98.21 | ++ |
| CP50 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | KU159195 | 98.67 | ++ |
| CP51 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | KU159195 | 98.52 | ++ |
| CP56 | Ochrobactrum anthropi | MN176368 | 99.50 | +++ |
| CP57 | Ochrobactrum anthropi | KY770534 | 98.09 | +++ |
| CP66 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | MN543803 | 98.91 | ++++ |
| CP76 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | MW876146 | 99.37 | + |
| CP77 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | KF208480 | 99.67 | ++ |
| CP78 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus | KU904281 | 99.77 | + |
| CP79 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus | KJ183074 | 98.95 | + |
表1 产脲酶细菌的16S rRNA基因序列比对结果
Table 1 Comparison of the 16S rRNA gene sequences of the urease-producing bacteria
| 菌株 | 属种 | 基因号 | 相似性/% | 产脲酶活性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP49 | Ochrobactrum anthropi | KY770534 | 98.21 | ++ |
| CP50 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | KU159195 | 98.67 | ++ |
| CP51 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | KU159195 | 98.52 | ++ |
| CP56 | Ochrobactrum anthropi | MN176368 | 99.50 | +++ |
| CP57 | Ochrobactrum anthropi | KY770534 | 98.09 | +++ |
| CP66 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | MN543803 | 98.91 | ++++ |
| CP76 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | MW876146 | 99.37 | + |
| CP77 | Lysinibacillus fusiformis | KF208480 | 99.67 | ++ |
| CP78 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus | KU904281 | 99.77 | + |
| CP79 | Lysinibacillus sphaericus | KJ183074 | 98.95 | + |

图3 O. anthropi CP57和L. fusiformis CP66所形成碳酸钙沉淀的SEM图((a)—(c)CP57;(d)—(f)CP66)
Fig.3 SEM images of calcium carbonate precipitates formed by O. anthropi CP57 and L. fusiformis CP66((a)—(c)CP57;(d)—(f)CP66)
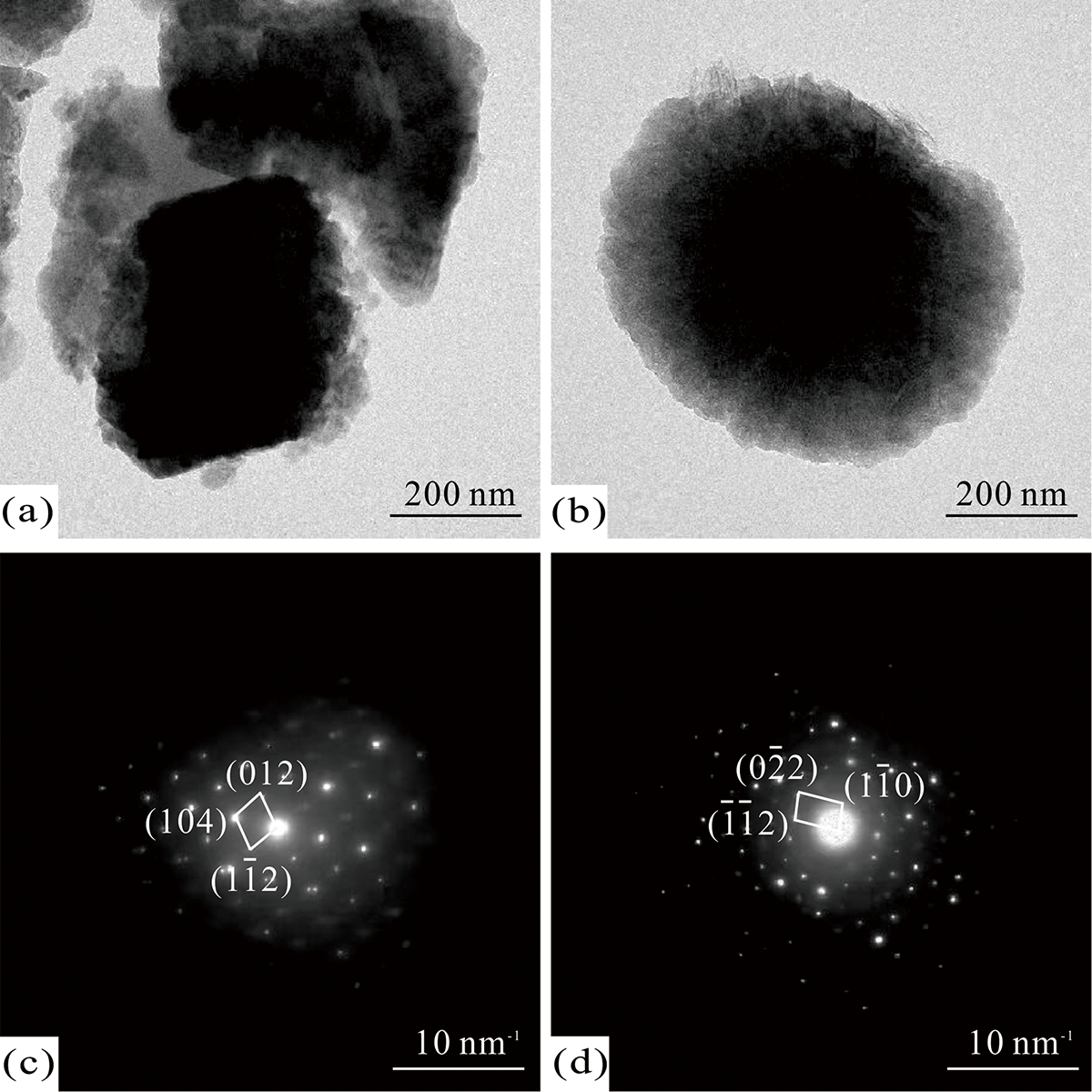
图4 O. anthropi CP57 (a)(c)和L. fusiformis CP66 (b)(d)所形成碳酸钙沉淀物的TEM (a)(b)及SAED (c)(d)图
Fig.4 TEM (a)(b) and SAED (c)(d) images of calcium carbonate precipitates formed by O. anthropi CP57 (a)(c) and L. fusiformis CP66 (b)(d)

图5 O. anthropic CP57和L. fusiformis CP66所形成的碳酸钙沉淀的FTIR图谱
Fig.5 FTIR spectra of calcium carbonate precipitations formed by O. anthropic CP57 and L. fusiformis CP66
| [1] |
PHILLIPS A J, GERLACH R, LAUCHNOR E, et al. Engineered applications of ureolytic biomineralization: A review[J]. Biofouling, 2013, 29(6): 715-733.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ANBU P, KANG C H, SHIN Y J, et al. Formations of calcium carbonate minerals by bacteria and its multiple applications[J]. Springer Plus, 2016, 5(1): 250.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GÖRGEN S, BENZERARA K, SKOURI-PANET F, et al. The diversity of molecular mechanisms of carbonate biomineralization by bacteria[J]. Discover Materials, 2021, 1(1): 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 王红梅, 吴晓萍, 邱轩, 等. 微生物成因的碳酸盐矿物研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2013, 40(1): 180-189. |
| [5] | 周根陶, 李涵, 黄亚蓉, 等. 微生物矿化碳酸盐矿物的微观机制研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2018, 38(增刊): 87-88. |
| [6] |
MITCHELL A C, DIDERIKSEN K, SPANGLER L H, et al. Microbially enhanced carbon capture and storage by mineral-trapping and solubility-trapping[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(13): 5270-5276.
DOI URL |
| [7] | DHAMI N K, REDDY M S, MUKHERJEE A. Biomineralization of calcium carbonates and their engineered applications: A review[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2013, 4: 314. |
| [8] | 钱春香, 王欣, 於孝牛. 微生物水泥研究与应用进展[J]. 材料工程, 2015, 43(8): 92-103. |
| [9] | 王茂林, 吴世军, 杨永强, 等. 微生物诱导碳酸盐沉淀及其在固定重金属领域的应用进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(2): 206-214. |
| [10] | CASTRO-ALONSO M J, MONTAÑEZ-HERNANDEZ L E, SAÑCHEZ-MUNOZ M A, et al. Microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation (MICP) and its potential in bioconcrete: microbiological and molecular concepts[J]. Frontiers in Ma-terials, 2019, 6: 126. |
| [11] | 李驰, 史冠宇, 武慧敏, 等. 基于脲酶诱导碳酸钙沉积的微生物矿化技术在分散性土改良中应用的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(2): 333-342. |
| [12] |
PRINCE PRAKASH JEBA KUMAR J, RAJAN BABN B, NANDHAGOPAL G, et al. In vitro synthesis of bio-brick using locally isolated marine ureolytic bacteria, a comparison with natural calcareous rock[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2019, 138:97-105.
DOI URL |
| [13] | MOBLEY H L, HAUSINGER R P. Microbial ureases: Significance, regulation, and molecular characterization[J]. Micro-biological Reviews, 1989, 53(1): 85-108. |
| [14] |
HAMMES F, BOON N, DE VILLIERS J, et al. Strain-specific ureolytic microbial calcium carbonate precipitation[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(8): 4901-4909.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 季斌, 陈威, 樊杰, 等. 产脲酶微生物诱导钙沉淀及其工程应用研究进展[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(1): 191-198. |
| [16] |
SARAYU K, IYER N R, MURTHY A R. Exploration on the biotechnological aspect of the ureolytic bacteria for the production of the cementitious materials-A review[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 172(5): 2308-2323.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HARKES M P, VAN PAASSEN L A, BOOSTER J L, et al. Fi-xation and distribution of bacterial activity in sand to induce carbonate precipitation for ground reinforcement[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2009, 36(2): 112-117.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
KIM H K, PARK S J, HAN J I, et al. Microbially mediated calcium carbonate precipitation on normal and lightweight concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 38: 1073-1082.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LAUCHNOR E G, SCHULTZ L N, BUGNI S, et al. Bacterially induced calcium carbonate precipitation and strontium coprecipitation in a porous media flow system[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(3): 1557-1564.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SEIFAN M, SARMAH A K, EBRAHIMINEZHAD A, et al. Bio-reinforced self-healing concrete using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2018, 102(5): 2167-2178.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ACHAL V, MUKHERJEE A, REDDY M S. Microbial concrete: Way to enhance the durability of building structures[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2011, 23(6): 730-734.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHU J, STABNIKOV V, IVANOV V. Microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation on surface or in the bulk of soil[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2012, 29(6): 544-549.
DOI URL |
| [23] | LV J J, MA F, LI F C, et al. Vaterite induced by Lysinibacillus sp.GW-2 strain and its stability[J]. Structural Biology, 2017, 200(2): 97-105. |
| [24] |
ZHUANG D, YAN H X, TUCKERD M E, et al. Calcite precipitation induced by Bacillus cereus MRR2 cultured at different Ca2+ concentrations: further insights into biotic and abiotic calcite[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 500: 64-87.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HAN Z, WANG J, ZHAO H, et al. Mechanism of biomineralization induced by Bacillus subtilis J2 and characteristics of the biominerals[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(4): 218.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SHIRAKAWA M A, CINCOTTO M A, ATENCIO D, et al. Effect of culture medium on biocalcification by Pseudomonas putida, Lysinibacillus sphaericus and Bacillus subtilis[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2011, 42(2): 499-507.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
BRAISSANT O, CAILLEAU G, DUPRAZ C, et al. Bacterially induced mineralization of calcium carbonate in terrestrial environments: The role of exopolysaccharides and amnio acids[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(3): 485-490.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
WEI S P, CUI H P, JIANG Z L, et al. Biomineralization processes of calcite induced by bacteria isolated from marine sediments[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 2015, 46(2): 455-464.
DOI URL |
| [29] | SENSOY T, BOZBEYOGLU N N, DOGAN N M, et al. Characterization of calcium carbonate produced by ureolytic bacteria (Sporocarcina pasteurii ATCC 6453 and Bacillus aerius U2) and effect of environmental conditions on production of calcium carbonate[M]// 15th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology. Rhodes: University of the Aegean, 2017:1. |
| [30] |
GHOSH T, BHADURI S, MONTEMAGNO C, et al. Sporosarcina pasteurii can form nanoscale calcium carbonate crystals on cell surface[J/OL]. PLOS One, 2019, 14. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210339.
DOI |
| [31] |
SONDI I, SAILOPEK-SONDI B. Influence of the primary structure of enzymes on the formation of CaCO3 polymorphs: a comparison of plant (Canavalia ensiformis) and bacterial (Bacillus pasteurii) ureases[J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21(19): 8876-8882.
DOI URL |
| [32] | ERCOLE C, CACCHIO P, BOTTA A L, et al. Bacterially induced mineralization of calcium carbonate: the role of exopolysaccharides and capsular polysaccharides[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2007, 13(1): 42-50. |
| [33] |
KAWAGUCHI T, DECHO A W. A laboratory investigation of cyanobacterial extracellular polymeric secretions (EPS) in influencing CaCO3 polymorphism[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2002, 240(1): 230-235.
DOI URL |
| [34] | SEIFAN M, SAMANI A K, BERENJIAN A. New insights into the role of pH and aeration in the bacterial production of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechno-logy, 2017, 101(8): 3131-3142. |
| [35] | 郭策, 刘贝贝, 孙明雪, 等. 北戴河海洋沉积物中L-半胱氨酸脱硫细菌的多样性及其特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(7): 1582-1589. |
| [36] |
PEI Y Y, AN Q D, XIAO Z Y, et al. Biomass-based carbon beads with a tailored hierarchical structure and surface chemistry for efficient batch and column uptake of methylene blue[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2018, 44(4): 2867-2887.
DOI URL |
| [37] | SARAYA M E S I, ROKBAA H H A L. Preparation of vaterite calcium carbonate in the form of spherical nano-size particles with the aid of polycarboxylate superplasticizer as a capping agent[J]. American Journal of Nanomaterials, 2016, 4(2): 44-51. |
| [38] |
VAGENAS N V, GATSOULI A, KONTOYANNIS C G. Quantitative analysis of synthetic calcium carbonate polymorphs using FT-IR spectroscopy[J]. Talanta, 2003, 59(4): 831-836.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
HAN Y, SUNB, YAN H X, et al. Biomineralization of carbonate minerals induced by the moderate halophile Staphylococcus warneri YXY2[J]. Crystals, 2020, 10(2): 58.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
LINGA RAJU C, NARASIMHULU K V, GOPAL N O, et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance, optical and infrared spectral studies on the marine mussel Arca burnesi shells[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2002, 608(2): 201-211.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
BOQUET E, BORONAT A, RAMOS-CORMENZANA A. Production of calcite (calcium carbonate) crystals by soil bacteria is a general phenomenon[J]. Nature, 1973, 246: 527-529.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
DOUGLAS S, BEVERIDGE T J. Mineral formation by bacteria in natural microbial communities[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1998, 26(2): 79-88.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
RIVADENEYRA M A, DELGADO G, RAMOS-CORMENZANA A, et al. Biomineralization of carbonates by Halomonas eurihalina in solid and liquid media with different salinities: crystal formation sequence[J]. Research Microbiology, 1998, 149(4): 277-287.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
PECKMAN J, PAUL J, THIEL V. Bacterially mediated formation of diagenetic aragonite and native sulfur in Zechstein carbonates (Upper Permian, Central Germany)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1999, 126(1): 205-222.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZAMARREÑO D V, INKPEN R, MAY E. Carbonate crystals precipitated by freshwater bacteria and their use as a limestone consolidant[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(18): 5981-5990.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
LÜ X, HE Q F, WANG Z J, et al. Calcium carbonate precipitation mediated by bacterial carbonic anhydrase in a karst cave: Crystal morphology and stable isotopic fractionation[J/OL]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 530. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119331.
DOI |
| [47] |
SEIFAN M, BERENJIAN A. Microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation: a widespread phenomenon in the biological world[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 103(12): 4693-4708.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
RODRIGUEZ-NAVARRO C, JIMENEZ-LOPEZ C, RODRIGUEZ-NAVARRO A, et al. Bacterially mediated mineralization of vaterite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(5): 1197-1213.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
TOURNEYJ, NGWENYA B T. Bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) mediate CaCO3 morphology and polymorphism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 262(3): 138-146.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
RODRIGUEZ-NAVARRO C, RODRIGUEZ-GALLEGO M, BEN CHEKROUN K, et al. Conservation of ornamental stone by Myxococcus xanthus-induced carbonate biomineralization[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2003, 69(4): 2182-2193.
DOI URL |
| [51] | LI Q, ZHANG B J, GE Q Y, et al. Calcium carbonate precipitation induced by calcifying bacteria in culture experiments: Influence of the medium on morphology and mineralogy[J]. International Biodeterioration Biodegration, 2018, 134: 83-92. |
| [52] |
ACHAL V, PAN X L, ZHANG D Y. Bioremediation of strontium (Sr) contaminated aquifer quartz sand based on carbonate precipitation induced by Sr resistant Halomonas sp.[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 89(6): 764-768.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
LI W, LIU L P, CHEN W S, et al. Calcium carbonate precipitation and crystal morphology induced by microbial carbonic anhydrase and other biological factors[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2010, 45(6): 1017-1021.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
DEMUYNCK W, DE BELIE N, VERSTRAETE W. Microbial carbonate precipitation in construction materials: A review[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(2): 118-136.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李林积, 李堂积, 王丹. 西秦岭大水金矿床方解石Sm-Nd等时线年龄及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(03): 469-475. |
| [2] | 曹正端, 杨瑞东, 高军波, 陈军, 张伟, 沈明联, 张旭, 李纪. 贵州紫云方解石矿床地球化学特征及成因研究[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(04): 757-767. |
| [3] | 李飞 ,李少龙 ,曾溅辉 ,刘井旺 ,刘佳,葛黛薇 ,王阳 ,穆永晶. 霸县凹陷牛驼镇凸起潜山内幕古流体和现今流体特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1115-1123. |
| [4] | 张文浩,史晓颖, 汤冬杰,蒋干清. 华北地台西缘早—中寒武世之交的核形石: 微组构与生物矿化机制研究[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(1): 1-15. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||