



Geoscience ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (06): 1557-1570.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2024.019
• Energy Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Tingting1,2( ), DU Li1,2, TAN Xin3, LIU Junrong4, LUO Lu1,2, ZHANG Hui1,2, LI Hao1,2
), DU Li1,2, TAN Xin3, LIU Junrong4, LUO Lu1,2, ZHANG Hui1,2, LI Hao1,2
Online:2024-12-10
Published:2024-12-09
CLC Number:
HE Tingting, DU Li, TAN Xin, LIU Junrong, LUO Lu, ZHANG Hui, LI Hao. Genetic Model and Development Potential of the Guantao Formation Sandstone Geothermal System in the Zhongmu Sag, Kaifeng Depression[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(06): 1557-1570.
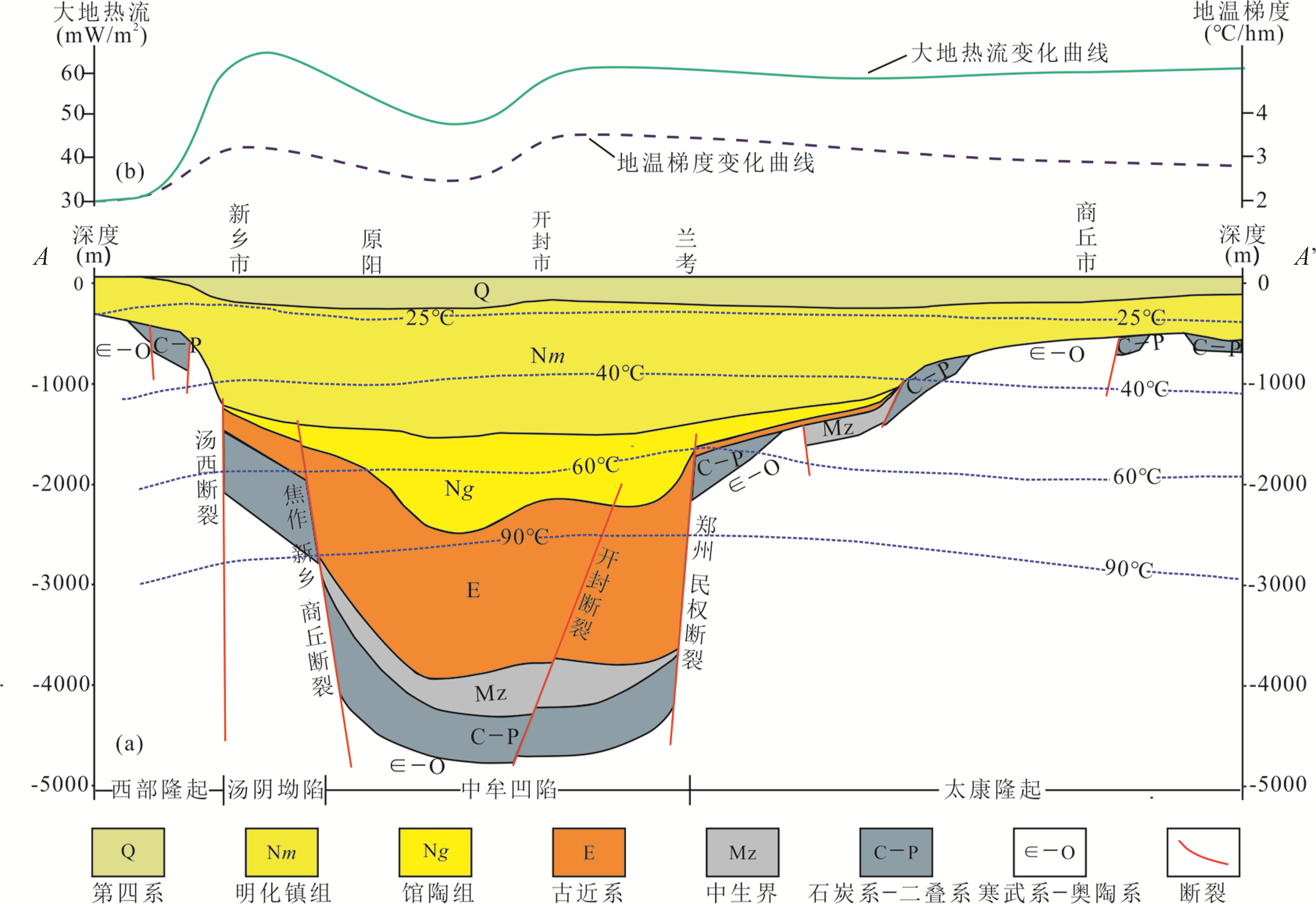
Fig.2 Profile of the geothermal reservoir and temperature distribution (a), and profile of heat flow and geothermal gradient distribution in the Zhongmu Sag (b)
| 构造 单元 | 地区 | 位置 | 井名 | 取水层段(m) | 馆陶组底面 埋深垂深(m) | 温度范围/ 井口水温(℃) | 地温梯度及均值 (℃/hm) | 资料 来源 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太康 隆起 | 郑州 | 市区 | 410~1071.6 | 800~900 | 20~45 | 2.03~3.79(2.89) | 河南省地 热资源现 状调查评 价与区划 | ||
| 通许 | 县城 | 370.3~1171.1 | 1100~1200 | 29~55 | 3.04~3.74(3.5) | ||||
| 汤阴 凹陷 | 新乡 | 市区 | 421.5~1215 | 1000~1100 | 25~73 | 2.22~4.82(3.15) | |||
| 京华园 | 926.5 | 42 | 2.93 | 2.93 | |||||
| 东濮 凹陷 | 长垣 | 县城北 | 2400 | 2100~2200 | 93 | 3.26 | 3.26 | ||
| 封丘 | 曹岗 | 2100 | 2000~2100 | 88 | 3.49 | 3.49 | |||
| 中牟 凹陷 | 开封 | 市区 | DJ2 | 1716~2150 | 2150 | 82 | 3.46 | 3.43 | 中石化实钻地热井 数据 |
| DJ4 | 1819.13~2289.06 | 2135 | 85 | 3.4 | |||||
| 兰考 | 市区 | ZY1 | 1381.82~1890.22 | 1909.39 | 74 | 3.6 | 3.27 | ||
| LW1 | 1552.12~2137.45 | 1905.16 | 71 | 3.03 | |||||
| DR4 | 1602.61~1927.15 | 1903.36 | 71 | 3.16 | |||||
| 新乡 | 平原新区 | XX1 | 1378.49~1753 | 1753 | 53 | 2.4 | 2.4 | ||
Table 1 Testing data geothermal boreholes in the Zhongmu Sag and its adjacent areas
| 构造 单元 | 地区 | 位置 | 井名 | 取水层段(m) | 馆陶组底面 埋深垂深(m) | 温度范围/ 井口水温(℃) | 地温梯度及均值 (℃/hm) | 资料 来源 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 太康 隆起 | 郑州 | 市区 | 410~1071.6 | 800~900 | 20~45 | 2.03~3.79(2.89) | 河南省地 热资源现 状调查评 价与区划 | ||
| 通许 | 县城 | 370.3~1171.1 | 1100~1200 | 29~55 | 3.04~3.74(3.5) | ||||
| 汤阴 凹陷 | 新乡 | 市区 | 421.5~1215 | 1000~1100 | 25~73 | 2.22~4.82(3.15) | |||
| 京华园 | 926.5 | 42 | 2.93 | 2.93 | |||||
| 东濮 凹陷 | 长垣 | 县城北 | 2400 | 2100~2200 | 93 | 3.26 | 3.26 | ||
| 封丘 | 曹岗 | 2100 | 2000~2100 | 88 | 3.49 | 3.49 | |||
| 中牟 凹陷 | 开封 | 市区 | DJ2 | 1716~2150 | 2150 | 82 | 3.46 | 3.43 | 中石化实钻地热井 数据 |
| DJ4 | 1819.13~2289.06 | 2135 | 85 | 3.4 | |||||
| 兰考 | 市区 | ZY1 | 1381.82~1890.22 | 1909.39 | 74 | 3.6 | 3.27 | ||
| LW1 | 1552.12~2137.45 | 1905.16 | 71 | 3.03 | |||||
| DR4 | 1602.61~1927.15 | 1903.36 | 71 | 3.16 | |||||
| 新乡 | 平原新区 | XX1 | 1378.49~1753 | 1753 | 53 | 2.4 | 2.4 | ||
| 井名 | 井深(m) | pH值 | 溶解性总固体 (mg·L-1) | 水化学 类型 | 离子含量(mg·L-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | Ca2+ | Cl- | |||||||
| DJ2 | 2170 | 6.57 | 2.71×104 | Cl-Na | 6295.57 | 1877.61 | 14535.83 | 361.34 | 105.91 |
| DJ4 | 2310 | 6.56 | 2.53×104 | Cl-Na | 6178.76 | 1745.58 | 13102.75 | 346.49 | 105.04 |
| DR4 | 1980 | 6.90 | 1.41×104 | Cl-Na | 4172.40 | 573.76 | 7340.40 | 598.28 | 152.92 |
| LW1 | 2200 | 6.73 | 1.43×104 | Cl-Na | 4248.75 | 586.42 | 8001.65 | 661.96 | 152.73 |
| ZY1 | 1946 | 7.56 | 1.90×104 | Cl-Na | 5361.38 | 914.47 | 9859.78 | 907.22 | 129.20 |
| FHC2 | 2150 | 7.80 | 1.61×104 | Cl-Na | 5115.00 | 871.54 | 9070.95 | 609.98 | 133.63 |
| XX1 | 1782 | 7.96 | 0.89×103 | HCO3-Na | 329.00 | 10.17 | 132.94 | 119.93 | 580.01 |
Table 2 Hydrochemical data of the Zhongmu Sag
| 井名 | 井深(m) | pH值 | 溶解性总固体 (mg·L-1) | 水化学 类型 | 离子含量(mg·L-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | Ca2+ | Cl- | |||||||
| DJ2 | 2170 | 6.57 | 2.71×104 | Cl-Na | 6295.57 | 1877.61 | 14535.83 | 361.34 | 105.91 |
| DJ4 | 2310 | 6.56 | 2.53×104 | Cl-Na | 6178.76 | 1745.58 | 13102.75 | 346.49 | 105.04 |
| DR4 | 1980 | 6.90 | 1.41×104 | Cl-Na | 4172.40 | 573.76 | 7340.40 | 598.28 | 152.92 |
| LW1 | 2200 | 6.73 | 1.43×104 | Cl-Na | 4248.75 | 586.42 | 8001.65 | 661.96 | 152.73 |
| ZY1 | 1946 | 7.56 | 1.90×104 | Cl-Na | 5361.38 | 914.47 | 9859.78 | 907.22 | 129.20 |
| FHC2 | 2150 | 7.80 | 1.61×104 | Cl-Na | 5115.00 | 871.54 | 9070.95 | 609.98 | 133.63 |
| XX1 | 1782 | 7.96 | 0.89×103 | HCO3-Na | 329.00 | 10.17 | 132.94 | 119.93 | 580.01 |

Fig.4 Temperature and depth variation curves of the geothermal well in the Zhongmu Sag (red dotted line representsing temperature after reaching steady state)
| 井名 | 地热水δD (‰) | 地热水δ18O (‰) | 取样点海拔 (m) | 补给区海拔 (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJ4 | -69.81 | -7.8 | 70 | 557 |
| LW1 | -72.30 | -7.8 | 70 | 668 |
| DR4 | -73.08 | -7.8 | 72.5 | 705 |
| TXGS | -68.80 | -8.615 | 80 | 522 |
Table 3 Elevation calculation for the geothermal water supply area in the Zhongmu Sag
| 井名 | 地热水δD (‰) | 地热水δ18O (‰) | 取样点海拔 (m) | 补给区海拔 (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJ4 | -69.81 | -7.8 | 70 | 557 |
| LW1 | -72.30 | -7.8 | 70 | 668 |
| DR4 | -73.08 | -7.8 | 72.5 | 705 |
| TXGS | -68.80 | -8.615 | 80 | 522 |
| 层位 | 热储 层段 | 平均有效 厚度(m) | 平均孔隙 度(%) | 平均温度 (℃) | 地热资源量 (108GJ) | 地热资源量折合 标准煤(104t) | 可采地热资源 量(108GJ) | 可采地热资源量 折合标准煤(104t) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馆陶组 | Ng1 | 32.9 | 20.7 | 50.2 | 147.86 | 5046.44 | 36.97 | 1261.61 | ||||||
| Ng2 | 48.2 | 22.3 | 54.9 | 250.24 | 8540.52 | 62.56 | 2135.13 | |||||||
| Ng3 | 56.6 | 21.4 | 60.1 | 329.19 | 11235.17 | 82.30 | 2808.79 | |||||||
| Ng4 | 40.7 | 20.5 | 64.8 | 263.61 | 8997.07 | 65.90 | 2249.27 | |||||||
| Ng5 | 173.3 | 23.4 | 70.2 | 1254.51 | 42815.97 | 313.63 | 10703.99 | |||||||
| 合计 | 351.7 | 2245.41 | 76635.16 | 561.35 | 19158.79 | |||||||||
Table 4 Evaluation parameters and calculation results of the geothermal resources in the Guantao Formation
| 层位 | 热储 层段 | 平均有效 厚度(m) | 平均孔隙 度(%) | 平均温度 (℃) | 地热资源量 (108GJ) | 地热资源量折合 标准煤(104t) | 可采地热资源 量(108GJ) | 可采地热资源量 折合标准煤(104t) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馆陶组 | Ng1 | 32.9 | 20.7 | 50.2 | 147.86 | 5046.44 | 36.97 | 1261.61 | ||||||
| Ng2 | 48.2 | 22.3 | 54.9 | 250.24 | 8540.52 | 62.56 | 2135.13 | |||||||
| Ng3 | 56.6 | 21.4 | 60.1 | 329.19 | 11235.17 | 82.30 | 2808.79 | |||||||
| Ng4 | 40.7 | 20.5 | 64.8 | 263.61 | 8997.07 | 65.90 | 2249.27 | |||||||
| Ng5 | 173.3 | 23.4 | 70.2 | 1254.51 | 42815.97 | 313.63 | 10703.99 | |||||||
| 合计 | 351.7 | 2245.41 | 76635.16 | 561.35 | 19158.79 | |||||||||
| [1] | HELGESON H C. Geologic and thermodynamic characteristics of the Salton Sea geothermal system[J]. American Journal of Science, 1968, 266(3): 129-166. |
| [2] | RYBACH L, MUFFLER L J P. Geothermal System:Principles and Analysis of Typical Geothermal Systems[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1985. |
| [3] | 汪集暘. 地热学及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 1-6. |
| [4] |
何治亮, 冯建赟, 张英, 等, 试论中国地热单元分级分类评价体系[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3):168-179.
DOI |
| [5] |
张英, 冯建赟, 何治亮, 等. 地热系统类型划分与主控因素分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3): 190-198.
DOI |
| [6] | 汪新伟, 王婷灏, 张瑄, 等. 太原盆地西温庄地热田的成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3):1042-1056. |
| [7] |
王迪, 汪新伟, 毛翔, 等. 河北武城凸起地热田地热地质特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(3): 269-280.
DOI |
| [8] | 曹瑛倬, 鲍志东, 鲁锴, 等. 冀中坳陷雄县地热田主控因素及成因模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(4): 863-872. |
| [9] | 黄旭, 沈传波, 杜利, 等. 沧县隆起中段献县凸起和阜城凹陷岩溶型地热资源特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(4): 997-1008. |
| [10] | 高楠安, 汪新伟, 梁海军, 等. 冀中坳陷束鹿凹陷地热系统成因模式[J]. 高校地质学报, 2022, 28(6): 920-932. |
| [11] | 汪新伟, 王婷灏, 李海泉, 等. 太原盆地岩溶地热系统的形成演化及其地热资源潜力[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(3): 716-731. |
| [12] | 赵明坤, 孙亚军, 段忠丰, 等. 河南漯河市明化镇组温热水地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 507-514. |
| [13] | 王心义, 聂新良, 赵卫东. 开封凹陷区地温场特征及成因机制探析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2001, 29(5): 4-7. |
| [14] | 张心勇, 马传明. 开封凹陷区地温场特征分析[J]. 工程勘察, 2009, 37(10): 44-49. |
| [15] | 王现国, 张慧, 张娟娟. 开封凹陷区地热水水化学特征及同位素分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2012, 19(6):88-92. |
| [16] | 沈俊超, 刘朝武, 张灵, 等. 河南中牟凹陷地热地质背景与深层地热水开发[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 33(5): 598-603. |
| [17] | 齐玉峰. 河南省开封凹陷区地热田地热资源分析[J]. 西南科技大学学报, 2009, 24(3): 75-78. |
| [18] | 高景宏, 佟铁钢, 强建科, 等. 开封凹陷区地热资源大地电磁测深研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(4): 440-443. |
| [19] | 徐汉林, 赵宗举, 杨以宁, 等. 南华北盆地构造格局及构造样式[J]. 地球学报, 2003, 24(1): 27-33. |
| [20] | 河南省地质调查院. 河南省地热资源现状调查评价与区划[R]. 郑州: 河南省地质调查院, 2015. |
| [21] | MAJOROWICZ J, CHAN J, CROWELL J, et al. The first deep heat flow determination in crystalline basement rocks beneath the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2014, 197(2): 731-747. |
| [22] | 柳鉴容, 宋献方, 袁国富, 等. 中国东部季风区大气降δ18O的特征及水汽来源[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54(22): 3521-3531. |
| [23] | 霍冬雪, 周训, 刘海生, 等. 云南祥云县王家庄碱性温泉水化学特征与成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(3): 680-690. |
| [24] | 杨峰田, 石宇佳, 李文庆. 基于水文地球化学特征的辽宁丹东地区地热水成因模式研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2): 474-483. |
| [25] | 姜哲, 周训, 陈柄桦, 等. 四川康定市二道桥地区地下热水稳定同位素特征及热储温度计算[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(4): 1183-1192. |
| [26] | 何争光, 刘池洋, 赵俊峰, 等. 华北克拉通南部地区现今地温场特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 2009, 55(3): 428-434. |
| [27] | 左银辉, 邱楠生, 邓已寻, 等. 查干凹陷大地热流[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(9):3038-3050. |
| [28] |
姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(8): 2892-2910.
DOI |
| [29] | 毛小平. 地热田高地温异常成因机理及温度分布特征[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(2): 216-224. |
| [30] | 孟甲, 秦鹏, 史启朋, 等. 断陷盆地碳酸盐岩热储勘查及研究: 以鱼台凹陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4):38-45. |
| [31] | 田禹. 鲁东地热区氢氧同位素特征及地热水补给来源[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(6): 182-185. |
| [32] | 钱会, 马致远. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005: 124-133. |
| [33] | 张鹏, 王良书, 刘绍文, 等. 南华北盆地群地温场研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(2): 604-608. |
| [1] | WU Chenbingjie, LUO Lu, GAO Nan’an, WANG Xinwei, CUI Zixian. Study on Characteristics of Neogene Sandstone Geothermal Reservoir in Xi’an Sag,Guanzhong Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(06): 1571-1584. |
| [2] | WEI Chonghui, ZHENG Yuan, SUN Wenyan, WANG Min, LIU Gang, ZHANG Zhiguang. Evaluation of Geotourism Resources in Longyan UNESCO Global Geopark and Its Development Strategy [J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(04): 1192-1204. |
| [3] | LIU Chen, LI Jianghai, WANG Zhichen. Dynamic Model Analysis of Formation and Evolution of the South China Sea [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(02): 259-269. |
| [4] | ZHAO Mingkun, SUN Yajun, DUAN Zhongfeng, SHEN Quanwei, LU Guijing. Geochemical Signature and Genesis of Geothermal Water in Minghuazhen Formation, Luohe, Henan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 507-514. |
| [5] | YANG Fengtian, SHI Yujia, LI Wenqing. Genesis Model of Geothermal Water in Dandong Area of Liaoning Province Based on Hydrogeochemical Characteristics [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 474-483. |
| [6] | ZHANG Luming, YANG Dong, ZHOU Yong, LIU Peng. Genetic Model, Outbreak Features and Prevention of Post-seismic Deep-cut Trough-type Debris Flow: An Example from Yazhagou of Jiuzhaigou, Sichuan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 744-752. |
| [7] | LU Li, CHEN Yudao, DAI Junge, WANG Zhe, ZOU Shengzhang, FAN Lianjie, LIN Yongsheng, ZHOU Changsong. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Zhuhe Hot Springs in Zhaojue, Sichuan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 703-710. |
| [8] | LEI Han, HUANG Wenhui, SUN Qilong, CHE Qingsong. Dedolomitization Origin and Model for the Ordovician Majiagou Formation (5th Member) in the Southern Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 378-387. |
| [9] | XU Jiahong, KANG Zhihong, LAN Xixi. Karst Reservoir Type, Cave Structure and Genetic Model of Ordovician Tahe Reservoirs: Case Study of Fracture-cavity Unit T615 in Tahe Oilfield 7 Block [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1181-1192. |
| [10] | MA Jiayi, XIE Shuyun, ZHANG Mohai, JIAO Cunli, HAN Jun, BAO Zhengyu, WU Tie, ZHANG Hai. Geochemical Features and Genesis of Dolomite in Sinian Dengying Formation of Zigui Area, Hubei Province [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(01): 74-87. |
| [11] | WANG Dapeng, YIN Jinyin, TIAN Naxin, GUO Jinrui, ZHAO Lihua, TIAN Kun. Division and Resource Evaluation of Hydrocarbon Plays in the Senegal Basin, West Africa [J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(06): 1201-1213. |
| [12] | . Division of Hydrocarbon Plays and Resources Evaluation in the North Ustyurt Basin, Central Asia [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(1): 192-199. |
| [13] | LI Gong-ke, WANG Wei-xing, YANG Feng-tian, LI Hong, SHEN Jian, DONG Lu-yang. Genesis Model of the Tangquan Geothermal Field in Hebei Province [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(1): 220-228. |
| [14] | LONG Hua-shan,WANG Xu-long,XIANG Cai-fu,LEI De-wen,GUO Ji-gang,ABU. Evaluation on Jurassic Hydrocarbon Source Rock Developed in Southern Margin of Junggar Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(5): 1070-1080. |
| [15] | YAN Wei-Feng, LI Jian-Zhong, WANG Li-Wu, ZHANG Qiang-Chun1, Yang-Tao1, Ma-Yan,. Prediction of the Deep Natural Gas Potential of Changling Fault Depression,Songliao Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(5): 902-907. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||