



Geoscience ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (05): 911-929.
• Research on the Main Geohazards and Engineering Geological Problems Along the SichuanTibet Railway • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Langping1( ), LAN Hengxing1,2(
), LAN Hengxing1,2( ), GUO Changbao3,4, ZHANG Yongshuang3,4, LI Quanwen1,5, WU Yuming1
), GUO Changbao3,4, ZHANG Yongshuang3,4, LI Quanwen1,5, WU Yuming1
Received:2016-10-12
Revised:2017-05-10
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-11-06
CLC Number:
LI Langping, LAN Hengxing, GUO Changbao, ZHANG Yongshuang, LI Quanwen, WU Yuming. Geohazard Susceptibility Assessment Along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and Its Adjacent Area Using an Improved Frequency Ratio Method[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(05): 911-929.

Fig.16 ROC curves of the geohazard susceptibilities by combining different influencing factors along Sichuan-Tibet Railway and its adjacent areas assessed using the improved frequency ratio method

Fig.19 ROC curves of the geohazard susceptibilities along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and its adjacent area assessed using the conventional and improved frequency ratio methods
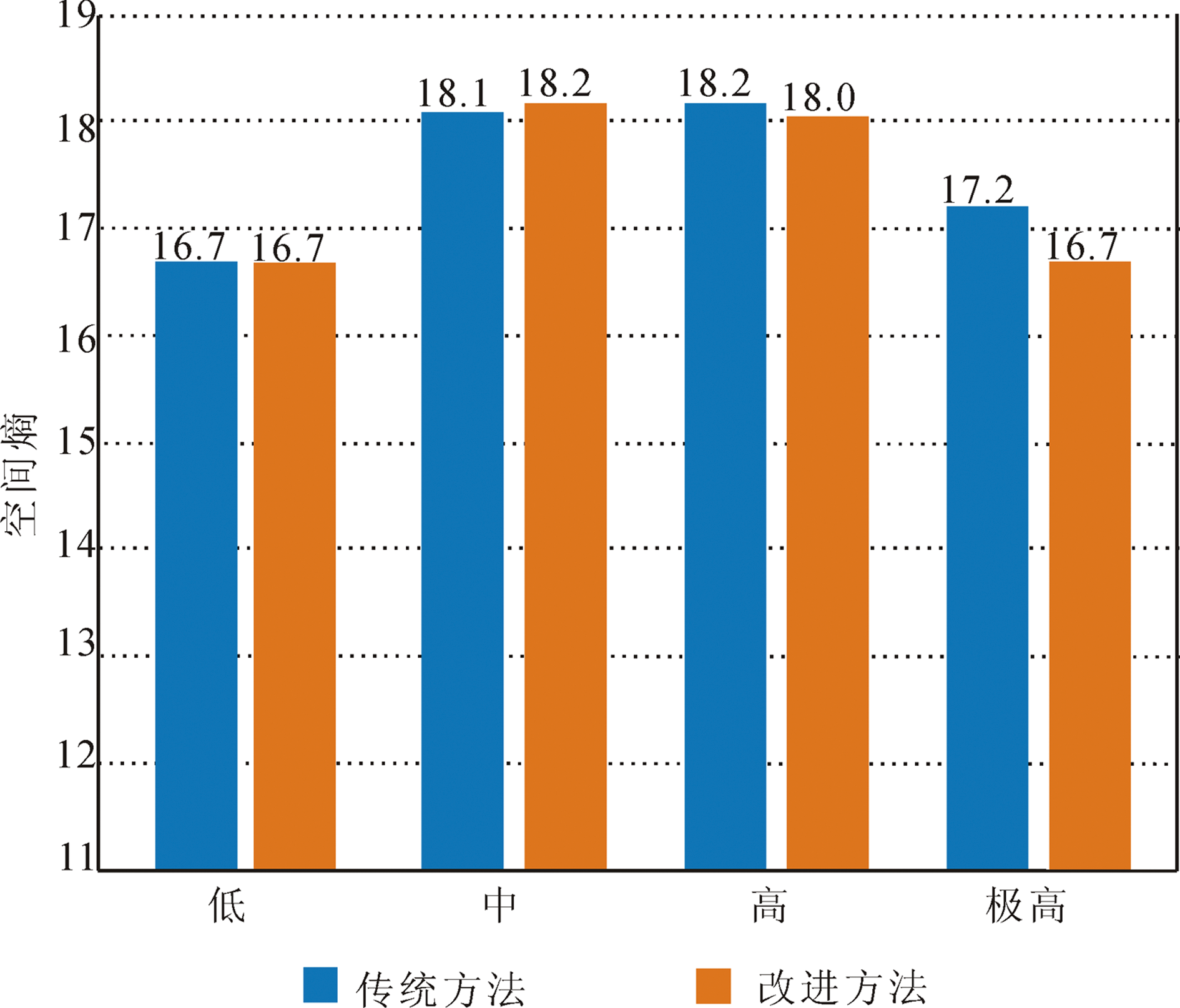
Fig.20 Spatial entropies of the geohazard susceptibilities along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and its adjacent area assessed using the traditional and improved frequency ratio methods
| 易发性分区 | 面积/km2 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|
| 极高 | 43 195.03 | 5.10 |
| 高 | 319 051.66 | 37.68 |
| 中 | 265 797.75 | 31.39 |
| 低 | 218 675.56 | 25.83 |
| 合计 | 846 720 | 100 |
Table 1 Areas and ratios of different geohazard susceptibility zones along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and its adjacent area
| 易发性分区 | 面积/km2 | 占比/% |
|---|---|---|
| 极高 | 43 195.03 | 5.10 |
| 高 | 319 051.66 | 37.68 |
| 中 | 265 797.75 | 31.39 |
| 低 | 218 675.56 | 25.83 |
| 合计 | 846 720 | 100 |
| [1] | 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. |
| [2] | 殷跃平. 西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡特征及减灾研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2000, 27(4): 8-11. |
| [3] | 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 佟元清, 等. 青藏高原东缘理塘乱石包高速远程滑坡发育特征与形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(8): 1332-1345. |
| [4] | 王东辉, 肖红勇, 李明辉. 滑坡滑前地质模型重建方法与思路——以鲜水河断裂带老虎嘴滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(5): 111-116. |
| [5] | 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 张永双, 等. 川西鲜水河断裂带地质灾害发育特征与典型滑坡形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(1): 9-22. |
| [6] | 王珂, 郭长宝, 马施民, 等. 基于证据权模型的川西鲜水河断裂带滑坡易发性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3): 705-715. |
| [7] | 蒋德明, 李益敏, 鲍华姝. 泸水县滑坡孕灾环境因素敏感性研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2016, 25(4): 109-119. |
| [8] | 白永健, 铁永波, 倪化勇, 等. 鲜水河流域地质灾害时空分布规律及孕灾环境研究[J]. 灾害学, 2014, 29(4): 69-75. |
| [9] | 王宇丰. 遥感技术在川藏及滇藏铁路可行性研究中的应用[J]. 铁路航测, 1998(2): 31-34. |
| [10] | 西藏自治区地质环境监测总站. 西藏自治区1∶50万区域环境地质调查报告[R]. 拉萨: 西藏自治区地质环境监测总站, 2004. |
| [11] | 四川省地质工程勘察院. 四川省1∶50万环境地质图[R]. 成都: 四川省地质工程勘察院, 1999. |
| [12] |
CLERICI A, PEREGO S, TELLINI C, et al. A GIS-based automated procedure for landslide susceptibility mapping by the Conditional Analysis method: the Baganza valley case study (Italian Northern Apennines)[J]. Environmental Geology, 2006, 50(7): 941-961.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GEMITZI A, FALALAKIS G, ESKIOGLOU P, et al. Evaluating landslide susceptibility using environmental factors, fuzzy membership functions and GIS[J]. Global NEST Journal, 2011, 13(1): 28-40.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CHOI J, OH H J, LEE H J, et al. Combining landslide susceptibility maps obtained from frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models using ASTER images and GIS[J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 124: 12-23.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
GUO C B, MONTGOMERY D R, ZHANG Y S, et al. Quantitative assessment of landslide susceptibility along the Xianshuihe fault zone, Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Geomorphology, 2015, 248: 93-110.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PRADHAN B, OH H J, BUCHROITHNER M. Weights-of-evidence model applied to landslide susceptibility mapping in a tropical hilly area[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2010, 1(3): 199-223.
DOI URL |
| [17] | LEE S, PRADHAN B. Landslide hazard mapping at Selangor, Malaysia using frequency ratio and logistic regression models[J]. Landslides, 2007, 4(1): 33-41. |
| [18] |
YALCIN A, REIS S, AYDINOGLU A C, et al. A GIS-based comparative study of frequency ratio, analytical hierarchy process, bivariate statistics and logistics regression methods for landslide susceptibility mapping in Trabzon, NE Turkey[J]. Catena, 2011, 85(3): 274-287.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
MONDAL S, MAITI R. Integrating the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and the frequency ratio (FR) model in landslide susceptibility mapping of Shiv-khola watershed, Darjeeling Himalaya[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science, 2013, 4(4): 200-212.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
YILMAZ I. Landslide susceptibility using frequency ratio, logistic regression, artificial neural networks and their comparison: a case study from Kat landslides (Tokat-Turkey)[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2009, 35(6): 1125-1138.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ANBALAGAN R, KUMAR R, LAKSHMANAN K, et al. Landslide hazard zonation mapping using frequency ratio and fuzzy logic approach, a case study of Lachung Valley, Sikkim[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 2015, 2: 6.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI L P, LAN H X, GUO C B, et al. A modified frequency ratio method for landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14:727-741.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
HANLEY J A, MCNEIL B J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve[J]. Radiology, 1982, 143: 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
MATHEW J, JHA V K, RAWAT G S. Landslide susceptibility zonation mapping and its validation in part of Garhwal Lesser Himalaya, India, using binary logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic curve method[J]. Landslides, 2009, 6: 17-26.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ERENER A, DÜZGÜN H S B. Improvement of statistical landslide susceptibility mapping by using spatial and global regression methods in the case of More and Romsdal (Norway)[J]. Landslides, 2010, 7: 55-68.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
AKGUN A. A comparison of landslide susceptibility maps produced by logistic regression, multi-criteria decision, and likelihood ratio methods: a case study at Zmir, Turkey[J]. Landslides, 2012, 9: 93-106.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
AHMED B. Landslide susceptibility mapping using multi-criteria evaluation techniques in Chittagong Metropolitan Area, Bangladesh[J]. Landslides, 2015, 12: 1077-1095.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 林宗涵. 热力学与统计物理学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2007: 39-58. |
| [29] | GRAY R M. Entropy and Information Theory[M]. Second Edition. New York: Springer Science and Business Media, 2011: 61-95. |
| [30] |
许冲, 戴福初, 姚鑫, 等. 汶川地震滑坡在两个典型区域内的分布研究[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2010, 27(5): 621-631.
DOI |
| [1] | LI Junlei, ZHANG Xujiao, WANG Yifan, ZHANG Xiangge, WANG Chongge, YUAN Xiaoning, LIU Xinlan, WANG Kaiya, RAO Haoshu, LIU Jiang, QIN Yuan. Route Planning and Ponder of Geoscience Study Travel in Hualong County, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1411-1422. |
| [2] | LIU Xinlan, ZHANG Xujiao, LI Junlei, WANG Yifan, ZHANG Xiangge, YUAN Xiaoning, WANG Kaiya, WANG Chongge, LIU Jiang, HOU Engang. Characteristics and Scientific Values of “Canyon and Danxia” Landform in Hualong County, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(01): 233-244. |
| [3] | HU Mengjun, JI Tianqi, ZHENG Dengyou, ZHUANG Jing, SUN Wenli, XU Aokang. Variation Characteristics of Chromatic Parameters of Eolian Sediments and Environmental Evolution on the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Since 9.4 ka [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 439-448. |
| [4] | CHEN Jing, LI Dapeng, KANG Huan, GENG Jianzhen, ZHANG Jingjing. Provenances and Tectonic Significance of Detrital Zircons from the Triassic to Jurassic Sedimentary Rocks in the Diancangshan Metamorphic Massif, Western Yunnan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 883-913. |
| [5] | GUO Changbao, WU Rui’an, JIANG Liangwen, ZHONG Ning, WANG Yang, WANG Dong, ZHANG Yongshuang, YANG Zhihua, MENG Wen, LI Xue, LIU Gui. Typical Geohazards and Engineering Geological Problems Along the Ya’an-Linzhi Section of the Sichuan-Tibet Railway,China [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 1-17. |
| [6] | WANG Jiazhu, GAO Yanchao, RAN Tao, TIE Yongbo, ZHANG Fan. Analysis of Genetic Mechanism and Failure Mode of a Large Paleo-landslide in Sichuan-Tibet Railway Transportation Corridor [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 18-25. |
| [7] | YAN Yiqiu, YANG Zhihua, ZHANG Xujiao, MENG Shaowei, GUO Changbao, WU Ruian, ZHANG Yiying. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Based on Weight-of-Evidence Modeling of the Batang Fault Zone, Eastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 26-37. |
| [8] | QUAN Xuerui, HUANG Yehuan, LIU Chun, GUO Changbao. Numerical Simulation Study on Seismic Magnification Effect of V-shaped Deep-cut Valley on Sichuan-Tibet Railway Line [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 38-46. |
| [9] | LI Xue, GUO Changbao, YANG Zhihua, LIAO Wei, WU Ruian, JIN Jijun, HE Yuanxiao. Development Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of the Xiongba Giant Ancient Landslide in the Jinshajiang Tectonic Zone [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 47-55. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jiajia, GAO Bo, LIU Jiankang, CHEN Long, HUANG Hai, LI Jie. Early Landslide Detection in the Lancangjiang Region Along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 64-73. |
| [11] | ZHOU Jie, DING Mingtao, HUANG Tao, CHEN Ningsheng. Optimization of Disaster-reduction Route Selection in Geological Disaster-Prone Region Along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Based on Virtual Reality: A Case Study of Luolong Station [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 92-102. |
| [12] | XIONG Xiaohui, BAI Yongjian, TIE Yongbo. Geological Structure and Rock Deformation Characteristics and Their Geohazard-Controlling Mechanism in Yajiang Area, West Sichuan [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 145-152. |
| [13] | WANG Lei, GUO Changbao, GUO Pengyu, JI Feng. Creep Characteristics and Constitutive Model of Gneiss in Zilashan Area Along Sichuan-Tibet Railway Line [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 153-160. |
| [14] | MENG Wen, GUO Changbao, MAO Bangyan, LU Haifeng, CHEN Qunce, XU Xueyuan. Tectonic Stress Field and Engineering Influence of China-Nepal Railway Corridor [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 167-179. |
| [15] | ZHAO Zhihong, XU Haoran, LIU Feng, WEI Shuaichao, ZHANG Wei, WANG Guiling. Preliminary Prediction of Temperature Field and Thermal Damage in Zheduoshan Region Along Sichuan-Tibet Railway [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 180-187. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||