



Geoscience ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (06): 1475-1485.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.06.03
• Ore Deposits • Previous Articles Next Articles
TANG Mingying1,2( ), HUA Lei1,2(
), HUA Lei1,2( ), DING Zhengjiang3,4,5, DONG Zhenkun1, WANG Weixiao1, ZHAI Xiaozhi1, WANG Rujie6, ZHENG Chenglong1
), DING Zhengjiang3,4,5, DONG Zhenkun1, WANG Weixiao1, ZHAI Xiaozhi1, WANG Rujie6, ZHENG Chenglong1
Received:2022-01-04
Revised:2022-03-01
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2023-01-11
Contact:
HUA Lei
CLC Number:
TANG Mingying, HUA Lei, DING Zhengjiang, DONG Zhenkun, WANG Weixiao, ZHAI Xiaozhi, WANG Rujie, ZHENG Chenglong. Geochemical Characteristics and Metallogenic Mechanism of the Wulade Graphite Deposit in the Qimantage Area, East Kunlun[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(06): 1475-1485.
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | TiO2 | CaO | MgO | MnO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 16.32 | 2.80 | 1.46 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 44.38 | 2.39 | 0.06 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 26.49 | 3.61 | 5.18 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 30.92 | 1.51 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.16 | 0.20 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 13.91 | 2.27 | 1.56 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 44.26 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.11 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 11.17 | 2.19 | 1.07 | 0.61 | 0.13 | 45.75 | 0.56 | 0.07 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 0.14 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 17.87 | 2.54 | 2.04 | 0.61 | 0.14 | 44.11 | 1.24 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.12 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | S | LOI | Rb | Sr | Ba | Nb | Ta | Cs | U | Th | Zr |
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 0.21 | 31.78 | 30.88 | 1 035.72 | 174.70 | 4.36 | 0.38 | 4.28 | 3.90 | 4.32 | 27.60 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 0.10 | 29.56 | 45.19 | 944.97 | 285.30 | 5.09 | 0.44 | 3.79 | 5.12 | 4.83 | 48.50 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 0.04 | 36.77 | 18.86 | 1 087.60 | 746.30 | 3.11 | 0.25 | 0.96 | 2.64 | 3.05 | 14.90 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 0.04 | 38.30 | 33.80 | 712.21 | 267.20 | 3.13 | 0.25 | 3.02 | 2.33 | 2.92 | 23.00 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 0.08 | 30.98 | 36.62 | 897.63 | 242.40 | 4.19 | 0.36 | 3.70 | 3.78 | 4.02 | 33.06 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Hf | V | Cr | Co | Ni | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 2.70 | 154.89 | 28.14 | 5.42 | 36.95 | 14.88 | 27.43 | 3.50 | 13.76 | 2.80 | 0.60 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 2.50 | 221.06 | 32.59 | 9.87 | 53.19 | 16.36 | 30.58 | 3.83 | 15.40 | 3.11 | 0.66 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 2.00 | 197.05 | 35.70 | 4.29 | 51.52 | 8.18 | 14.03 | 2.11 | 8.82 | 1.87 | 0.48 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 1.80 | 85.85 | 18.32 | 2.20 | 20.78 | 13.33 | 23.58 | 2.96 | 11.52 | 2.18 | 0.50 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 2.33 | 153.93 | 26.35 | 5.83 | 36.97 | 14.86 | 27.20 | 3.43 | 13.56 | 2.70 | 0.59 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba |
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 2.73 | 0.47 | 2.80 | 0.57 | 1.62 | 0.26 | 1.58 | 0.26 | 19.69 | 0.03 | 5.93 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 2.93 | 0.50 | 2.96 | 0.62 | 1.78 | 0.29 | 1.79 | 0.29 | 20.95 | 0.05 | 3.31 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 1.77 | 0.37 | 1.05 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 13.34 | 0.02 | 1.46 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 2.05 | 0.34 | 1.93 | 0.40 | 1.15 | 0.19 | 1.18 | 0.20 | 13.55 | 0.05 | 2.67 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 2.57 | 0.44 | 2.56 | 0.53 | 1.52 | 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.25 | 18.07 | 0.04 | 3.70 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | δCe | (La/Yb)N | ||||
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 73.26 | 62.97 | 10.29 | 6.12 | 0.65 | 0.89 | 6.37 | ||||
| ZKJD402H9 | 81.11 | 69.94 | 11.17 | 6.26 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 6.17 | |||||
| 16TC3H3 | 42.13 | 35.49 | 6.64 | 5.34 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 5.49 | |||||
| 16TC3H7 | 61.51 | 54.08 | 7.43 | 7.27 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 7.63 | |||||
| ZKJD402H15 | 71.96 | 62.33 | 9.63 | 6.47 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 6.62 | |||||
Table 1 Major and trace element composition of ore bearing rock of the Wulade graphite deposit
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | TiO2 | CaO | MgO | MnO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 16.32 | 2.80 | 1.46 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 44.38 | 2.39 | 0.06 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 26.49 | 3.61 | 5.18 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 30.92 | 1.51 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.16 | 0.20 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 13.91 | 2.27 | 1.56 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 44.26 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.11 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 11.17 | 2.19 | 1.07 | 0.61 | 0.13 | 45.75 | 0.56 | 0.07 | 0.66 | 0.11 | 0.14 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 17.87 | 2.54 | 2.04 | 0.61 | 0.14 | 44.11 | 1.24 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.14 | 0.12 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | S | LOI | Rb | Sr | Ba | Nb | Ta | Cs | U | Th | Zr |
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 0.21 | 31.78 | 30.88 | 1 035.72 | 174.70 | 4.36 | 0.38 | 4.28 | 3.90 | 4.32 | 27.60 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 0.10 | 29.56 | 45.19 | 944.97 | 285.30 | 5.09 | 0.44 | 3.79 | 5.12 | 4.83 | 48.50 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 0.04 | 36.77 | 18.86 | 1 087.60 | 746.30 | 3.11 | 0.25 | 0.96 | 2.64 | 3.05 | 14.90 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 0.04 | 38.30 | 33.80 | 712.21 | 267.20 | 3.13 | 0.25 | 3.02 | 2.33 | 2.92 | 23.00 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 0.08 | 30.98 | 36.62 | 897.63 | 242.40 | 4.19 | 0.36 | 3.70 | 3.78 | 4.02 | 33.06 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Hf | V | Cr | Co | Ni | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu |
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 2.70 | 154.89 | 28.14 | 5.42 | 36.95 | 14.88 | 27.43 | 3.50 | 13.76 | 2.80 | 0.60 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 2.50 | 221.06 | 32.59 | 9.87 | 53.19 | 16.36 | 30.58 | 3.83 | 15.40 | 3.11 | 0.66 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 2.00 | 197.05 | 35.70 | 4.29 | 51.52 | 8.18 | 14.03 | 2.11 | 8.82 | 1.87 | 0.48 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 1.80 | 85.85 | 18.32 | 2.20 | 20.78 | 13.33 | 23.58 | 2.96 | 11.52 | 2.18 | 0.50 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 2.33 | 153.93 | 26.35 | 5.83 | 36.97 | 14.86 | 27.20 | 3.43 | 13.56 | 2.70 | 0.59 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba |
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 2.73 | 0.47 | 2.80 | 0.57 | 1.62 | 0.26 | 1.58 | 0.26 | 19.69 | 0.03 | 5.93 |
| ZKJD402H9 | 2.93 | 0.50 | 2.96 | 0.62 | 1.78 | 0.29 | 1.79 | 0.29 | 20.95 | 0.05 | 3.31 | |
| 16TC3H3 | 1.81 | 0.31 | 1.77 | 0.37 | 1.05 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.16 | 13.34 | 0.02 | 1.46 | |
| 16TC3H7 | 2.05 | 0.34 | 1.93 | 0.40 | 1.15 | 0.19 | 1.18 | 0.20 | 13.55 | 0.05 | 2.67 | |
| ZKJD402H15 | 2.57 | 0.44 | 2.56 | 0.53 | 1.52 | 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.25 | 18.07 | 0.04 | 3.70 | |
| 样品编号 | 岩性 | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | δCe | (La/Yb)N | ||||
| ZKJD402H5 | 石墨 大理岩 | 73.26 | 62.97 | 10.29 | 6.12 | 0.65 | 0.89 | 6.37 | ||||
| ZKJD402H9 | 81.11 | 69.94 | 11.17 | 6.26 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 6.17 | |||||
| 16TC3H3 | 42.13 | 35.49 | 6.64 | 5.34 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 5.49 | |||||
| 16TC3H7 | 61.51 | 54.08 | 7.43 | 7.27 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 7.63 | |||||
| ZKJD402H15 | 71.96 | 62.33 | 9.63 | 6.47 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 6.62 | |||||
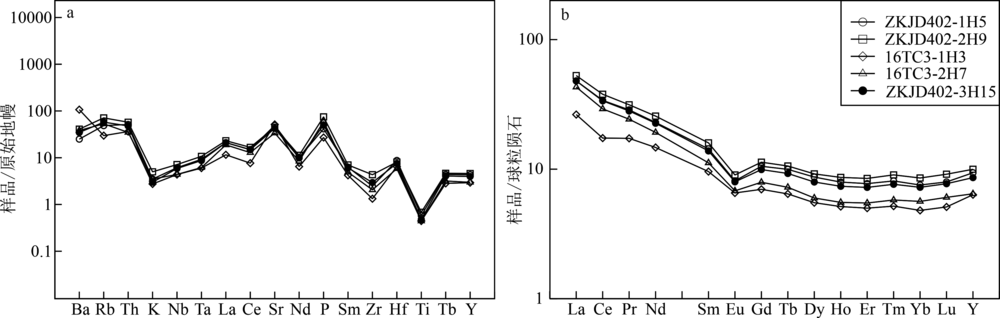
Fig.4 Primitive mantle normalized trace elements spide diagrams and chondrite normalized REE patterns of the Wulade graphite deposit(primitive mantle and chondrite normalized values according to reference[26])
| 样品编号 | 样品岩性 | 取样位置 | δ13CPDB/‰ |
|---|---|---|---|
| WLD-TW01 | 原生石墨大理岩 | ZKJD402H5 | -5.4 |
| WLD-TW02 | 原生石墨大理岩 | ZKJD402H9 | -5.8 |
| WLD-TW03 | 原生石墨大理岩 | 16TC3H5 | -5.4 |
| WLD-TW04 | 大理岩 | 16TC3H8 | 3.0 |
| WLD-TW05 | 大理岩 | ZKJD402H21 | 1.4 |
| WLD-TW06 | 大理岩 | 4线SM2矿体南侧 | 3.3 |
Table 2 Sampling locations and δ13C values of ore and marble samples of the Wulade graphite deposit
| 样品编号 | 样品岩性 | 取样位置 | δ13CPDB/‰ |
|---|---|---|---|
| WLD-TW01 | 原生石墨大理岩 | ZKJD402H5 | -5.4 |
| WLD-TW02 | 原生石墨大理岩 | ZKJD402H9 | -5.8 |
| WLD-TW03 | 原生石墨大理岩 | 16TC3H5 | -5.4 |
| WLD-TW04 | 大理岩 | 16TC3H8 | 3.0 |
| WLD-TW05 | 大理岩 | ZKJD402H21 | 1.4 |
| WLD-TW06 | 大理岩 | 4线SM2矿体南侧 | 3.3 |
| [1] | 陈其慎, 于汶加, 张艳飞, 等. 资源-产业“雁行式”演进规律[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(5): 871-882. |
| [2] | 肖克炎, 孙莉, 李思远, 等. 我国石墨矿产地质特征及资源潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37 (5): 607-614. |
| [3] | 陈军元, 刘艳飞, 颜玲亚, 等. 石墨、萤石等战略非金属矿产发展趋势研究[J]. 地球学报, 2021, 42 (2):287-296. |
| [4] | 徐新文, 段建华, 路耀祖, 等. 青海省石墨矿地质特征及可利用性评价[J]. 金属矿山, 2019, 48(1): 125-140. |
| [5] | 王永刚, 郁东良, 王雪萍, 等. 柴达木周缘晶质石墨矿成矿地质特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 青海大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 35(4): 21-25. |
| [6] | 刘恒轩, 刘鑫, 廖怡, 等. 青海格尔木市乌腊德铁矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 四川地质学报, 2017, 37(4): 573-577. |
| [7] | 付佳. 东昆仑那西郭勒地区石墨矿成矿地质特征及激电找矿效果研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020: 1-87. |
| [8] | 郭玮彭, 王琦, 王振琦, 等. 青海省格尔木市乌腊德地区铁铜及石墨矿详查报告[R]. 德阳: 四川省核工业地质局二八二大队, 2020:103-104. |
| [9] | 王盘喜, 郭峰, 王振宁. 东昆仑祁漫塔格鸭子沟地区花岗岩类岩石年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5): 987-1000. |
| [10] | 宋忠宝, 张雨莲, 贾群子, 等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区野马泉深部的华力西期花岗闪长岩U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1161-1169. |
| [11] | 杨兴科, 韩珂, 范阅, 等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格矿带典型矿田构造背景与岩浆-热力构造特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(2): 201-212. |
| [12] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 造山的高原——青藏高原的地体拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007:1-7. |
| [13] | 丰成友, 王松, 李国臣, 等. 青海祁漫塔格中晚三叠世花岗岩:年代学、地球化学及成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 665-678. |
| [14] | 赵一鸣, 丰成友, 李大新, 等. 青海西部祁漫塔格地区主要夕卡岩铁多金属矿床成矿地质背景和矿化蚀变特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(1): 1-19. |
| [15] | 毛景文, 周振华, 丰成友, 等. 初论中国三叠纪大规模成矿作用及其动力学背景[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6): 1437-1471. |
| [16] | 姚磊, 吕志成, 于晓飞, 等. 青海祁漫塔格地区夕卡岩型矿床花岗质岩石矿物学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(8): 2294-2306. |
| [17] | 杨宝凯, 徐美君, 苏旭亮, 等. 青海祁漫塔格成矿带骆驼峰铜钼矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(S1): 12-18. |
| [18] | 于淼, 丰成友, 保广英, 等. 青海尕林格铁矿床夕卡岩矿物学及蚀变分带[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(1): 55-76. |
| [19] | 李东生, 张文权, 田承盛, 等. 青海祁漫塔格地区主要矿床类型找矿方法探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2013, 46(4): 131-141. |
| [20] | 刘建楠, 丰成友, 赵一鸣, 等. 青海野马泉夕卡岩铁锌多金属矿区侵入岩、交代岩及矿化蚀变特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(1): 77-93. |
| [21] | 张爱奎, 刘光莲, 丰成友, 等. 青海虎头崖多金属矿床地球化学特征及成矿控矿因素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(1): 94-108. |
| [22] | 陈静, 谢智勇, 李彬, 等. 东昆仑拉陵灶火钼多金属矿床含矿岩体地质地球化学特征及其成矿意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2013, 49(5): 813-824. |
| [23] | 许庆林, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等. 东昆仑莫河下拉银多金属矿床花岗斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(2):421-433. |
| [24] | 刘智刚, 张爱奎, 夏友河, 等. 青海祁漫塔格那西郭勒BIF型铁矿床特征及意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(10):1841-1849. |
| [25] | 张鹏. 东昆仑成矿带那西郭勒铁矿矿床地质特征及成因[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018: 1-65. |
| [26] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]// SAUNDERSA D, NORRYM J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society, 1989, 42:313-345. |
| [27] | 刘敬党, 肖荣阁, 张艳飞, 等. 华北显晶质石墨矿床[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017:506-577. |
| [28] | 阎昆, 杨延伟, 王丽伟, 等. 北秦岭西峡龙王庙石墨矿床地球化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(3): 589-598. |
| [29] | WINCHERTER J A, PARK R G, HOLLAND J G. The geochemistry of Lewisian semipelitic schists from the Gairloch district, Wester Ross[J]. Scottish Journal of Geology, 1980, 16(2): 165-179. |
| [30] | ALLEGER C J, MINSTER J F. Quantitative models of trace element behavior in magmatic processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 38(1): 1-25. |
| [31] | SIMONEN A. Stratigraphy and sedimentation of the Svecofennidie,early Archean supracrustal rocks in southwestern Finland[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Finland, 1953, 160:1-64. |
| [32] | 林治家, 陈多福, 刘芊. 海相沉积氧化还原环境的地球化学识别指标[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(1): 72-80. |
| [33] | 王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 等. 变质岩原岩图解判别法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986:4-71,63-165. |
| [34] | SCHIDLOWSKI M. Application of stable carbon isotopes to early biochemical evolution on earth[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1987, 15: 47-72. |
| [35] | SCHIDLOWSKI M. Carbon isotopes as biogeochemical recorders of life over 3.8 Ga of earth history: Evolution of a concept[J]. Precambrian Research, 2001, 106(1/2): 117-134. |
| [36] | HOEFS J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry[M]. 6th ed. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2009: 53-107. |
| [37] | SHARP Z. Principles of Stable Isotope Geochemistry[M]. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2007: 1-344. |
| [38] | 刘松柏, 杨梅珍, 吴洪恩, 等. 新疆苏吉泉球状石墨矿床成矿模式[J]. 新疆地质, 2011, 29(2):178-182. |
| [39] | 白建科, 陈隽璐, 彭素霞. 新疆奇台县黄羊山岩浆热液型石墨矿床含矿岩体年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(8): 2327-2340. |
| [40] | 孙新浩, 任云生, 孙珍军, 等. 新疆奇台县黄羊山石墨矿床特征、物质来源及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(6): 1867-1882. |
| [41] | DOBNER A, GRAF W, WEINHEIMER P H, et al. Stable carbon isotopes of graphite from Bogala mine, Sri Lanka[J]. Lithos, 1978, 11(3):251-255. |
| [42] | KATZ M B, 李德荣. 斯里兰卡石墨矿床——麻粒岩相变质作用的产物[J]. 黑龙江地质情报, 1992(3):51-57. |
| [43] | RAY J S. Carbon isotopic variations in fluid-deposited graphite: Evidence for multicomponent Rayleigh isotopic fractionation[J]. International Geology Review, 2009, 51(1): 45-57. |
| [44] | LUQUE F J, CRESPO-FEO E, BARRENECHEA J F, et al. Carbon isotopes of graphite: Implications on fluid history[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2012, 3(2): 197-207. |
| [45] | 陈衍景, 刘丛强, 陈华勇, 等. 中国北方石墨矿床及赋矿孔达岩系碳同位素特征及有关问题讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 2000, 16(2): 233-244. |
| [46] | 朱建江, 刘福来, 刘福兴, 等. 胶—辽—吉造山带辽河群石墨矿碳同位素特征及成因分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(2): 599-618. |
| [47] | CRESPO E, LUQUE J, FERNÁNDEZ-RODRÍGU C, et al. Significance of graphite occurrences in the Aracena metamorphic belt, Iberian massif[J]. Geological Magazine, 2004, 141(6): 687-697. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||