



Geoscience ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (05): 1003-1014.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.05.07
• Petrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
TENG Chao( ), ZHANG Xiaofei, ZHOU Yi, FENG Junling, LI Shucai
), ZHANG Xiaofei, ZHOU Yi, FENG Junling, LI Shucai
Received:2018-04-07
Revised:2019-09-10
Online:2019-10-26
Published:2019-10-28
CLC Number:
TENG Chao, ZHANG Xiaofei, ZHOU Yi, FENG Junling, LI Shucai. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age and Geological Significance of the Early Cretaceous Monzogranite in Xiaowulangou, Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(05): 1003-1014.
| 点号 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | ||||
| 2 | 82 | 2 534 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.843 2 | 0.008 3 | 0.322 8 | 0.003 9 | 121 | 1 | 621 | 6 | 3 583 | 19 | |||
| 3 | 138 | 4 739 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.677 5 | 0.007 2 | 0.258 6 | 0.002 9 | 121 | 1 | 525 | 6 | 3 238 | 18 | |||
| 4 | 49 | 2 500 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.199 0 | 0.002 6 | 0.076 1 | 0.001 0 | 121 | 1 | 184 | 2 | 1 099 | 27 | |||
| 5 | 108 | 3 784 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.572 5 | 0.006 3 | 0.219 2 | 0.002 1 | 121 | 1 | 460 | 5 | 2 975 | 15 | |||
| 6 | 33 | 1 717 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.047 9 | 0.000 6 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 1 | 96 | 27 | |||
| 7 | 29 | 895 | 0.031 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.218 5 | 0.002 7 | 0.050 1 | 0.000 6 | 201 | 1 | 201 | 2 | 198 | 28 | |||
| 8 | 42 | 1 836 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.324 4 | 0.003 5 | 0.124 1 | 0.001 1 | 121 | 1 | 285 | 3 | 2 015 | 16 | |||
| 9 | 12 | 613 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.127 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.048 4 | 0.001 0 | 122 | 1 | 122 | 3 | 120 | 50 | |||
| 10 | 13 | 705 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 4 | 0.002 6 | 0.048 1 | 0.001 1 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 3 | 102 | 54 | |||
| 11 | 24 | 1 273 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 5 | 0.001 9 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 7 | 121 | 1 | 121 | 2 | 113 | 33 | |||
| 12 | 29 | 1 492 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 9 | 0.002 2 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 8 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 2 | 114 | 41 | |||
| 13 | 21 | 976 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.232 0 | 0.005 2 | 0.089 0 | 0.001 9 | 121 | 1 | 212 | 5 | 1 403 | 41 | |||
| 14 | 70 | 3 535 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 2 | 0.001 2 | 0.048 2 | 0.000 4 | 121 | 1 | 121 | 1 | 108 | 21 | |||
| 15 | 90 | 4 842 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 6 | 0.001 1 | 0.048 5 | 0.000 4 | 121 | 1 | 121 | 1 | 122 | 19 | |||
| 16 | 116 | 4 002 | 0.031 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.218 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.050 3 | 0.000 4 | 200 | 1 | 201 | 2 | 209 | 17 | |||
| 17 | 100 | 3 357 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.319 0 | 0.004 3 | 0.122 2 | 0.001 1 | 121 | 1 | 281 | 4 | 1 989 | 16 | |||
| 18 | 15 | 719 | 0.019 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 7 | 0.004 3 | 0.047 9 | 0.001 6 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 4 | 95 | 79 | |||
| 19 | 59 | 2 654 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.281 5 | 0.003 0 | 0.107 9 | 0.001 3 | 121 | 1 | 252 | 3 | 1 764 | 22 | |||
| 20 | 101 | 4 364 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.333 4 | 0.004 1 | 0.127 7 | 0.001 3 | 121 | 1 | 292 | 4 | 2 066 | 17 | |||
| 21 | 121 | 4 063 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.434 2 | 0.004 2 | 0.165 9 | 0.001 6 | 121 | 1 | 366 | 4 | 2 517 | 16 | |||
| 22 | 99 | 4 531 | 0.018 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 0 | 0.002 6 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 9 | 120 | 1 | 121 | 3 | 134 | 43 | |||
| 23 | 113 | 5 208 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.191 0 | 0.001 9 | 0.073 4 | 0.000 7 | 121 | 1 | 177 | 2 | 1 024 | 20 | |||
| 24 | 60 | 2 877 | 0.018 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.125 9 | 0.001 2 | 0.048 6 | 0.000 4 | 120 | 1 | 120 | 1 | 129 | 20 | |||
| 25 | 112 | 3 954 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.553 5 | 0.005 6 | 0.212 6 | 0.001 8 | 121 | 1 | 447 | 5 | 2 926 | 14 | |||
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data for the Early Cretaceous monzogranite
| 点号 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | ||||
| 2 | 82 | 2 534 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.843 2 | 0.008 3 | 0.322 8 | 0.003 9 | 121 | 1 | 621 | 6 | 3 583 | 19 | |||
| 3 | 138 | 4 739 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 2 | 0.677 5 | 0.007 2 | 0.258 6 | 0.002 9 | 121 | 1 | 525 | 6 | 3 238 | 18 | |||
| 4 | 49 | 2 500 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.199 0 | 0.002 6 | 0.076 1 | 0.001 0 | 121 | 1 | 184 | 2 | 1 099 | 27 | |||
| 5 | 108 | 3 784 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.572 5 | 0.006 3 | 0.219 2 | 0.002 1 | 121 | 1 | 460 | 5 | 2 975 | 15 | |||
| 6 | 33 | 1 717 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.047 9 | 0.000 6 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 1 | 96 | 27 | |||
| 7 | 29 | 895 | 0.031 6 | 0.000 2 | 0.218 5 | 0.002 7 | 0.050 1 | 0.000 6 | 201 | 1 | 201 | 2 | 198 | 28 | |||
| 8 | 42 | 1 836 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.324 4 | 0.003 5 | 0.124 1 | 0.001 1 | 121 | 1 | 285 | 3 | 2 015 | 16 | |||
| 9 | 12 | 613 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.127 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.048 4 | 0.001 0 | 122 | 1 | 122 | 3 | 120 | 50 | |||
| 10 | 13 | 705 | 0.019 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 4 | 0.002 6 | 0.048 1 | 0.001 1 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 3 | 102 | 54 | |||
| 11 | 24 | 1 273 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 5 | 0.001 9 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 7 | 121 | 1 | 121 | 2 | 113 | 33 | |||
| 12 | 29 | 1 492 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 9 | 0.002 2 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 8 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 2 | 114 | 41 | |||
| 13 | 21 | 976 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.232 0 | 0.005 2 | 0.089 0 | 0.001 9 | 121 | 1 | 212 | 5 | 1 403 | 41 | |||
| 14 | 70 | 3 535 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 2 | 0.001 2 | 0.048 2 | 0.000 4 | 121 | 1 | 121 | 1 | 108 | 21 | |||
| 15 | 90 | 4 842 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 6 | 0.001 1 | 0.048 5 | 0.000 4 | 121 | 1 | 121 | 1 | 122 | 19 | |||
| 16 | 116 | 4 002 | 0.031 5 | 0.000 2 | 0.218 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.050 3 | 0.000 4 | 200 | 1 | 201 | 2 | 209 | 17 | |||
| 17 | 100 | 3 357 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.319 0 | 0.004 3 | 0.122 2 | 0.001 1 | 121 | 1 | 281 | 4 | 1 989 | 16 | |||
| 18 | 15 | 719 | 0.019 2 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 7 | 0.004 3 | 0.047 9 | 0.001 6 | 122 | 1 | 121 | 4 | 95 | 79 | |||
| 19 | 59 | 2 654 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.281 5 | 0.003 0 | 0.107 9 | 0.001 3 | 121 | 1 | 252 | 3 | 1 764 | 22 | |||
| 20 | 101 | 4 364 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.333 4 | 0.004 1 | 0.127 7 | 0.001 3 | 121 | 1 | 292 | 4 | 2 066 | 17 | |||
| 21 | 121 | 4 063 | 0.019 0 | 0.000 1 | 0.434 2 | 0.004 2 | 0.165 9 | 0.001 6 | 121 | 1 | 366 | 4 | 2 517 | 16 | |||
| 22 | 99 | 4 531 | 0.018 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.126 0 | 0.002 6 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 9 | 120 | 1 | 121 | 3 | 134 | 43 | |||
| 23 | 113 | 5 208 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.191 0 | 0.001 9 | 0.073 4 | 0.000 7 | 121 | 1 | 177 | 2 | 1 024 | 20 | |||
| 24 | 60 | 2 877 | 0.018 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.125 9 | 0.001 2 | 0.048 6 | 0.000 4 | 120 | 1 | 120 | 1 | 129 | 20 | |||
| 25 | 112 | 3 954 | 0.018 9 | 0.000 1 | 0.553 5 | 0.005 6 | 0.212 6 | 0.001 8 | 121 | 1 | 447 | 5 | 2 926 | 14 | |||
| 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2545 | 78.05 | 0.05 | 12.03 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 3.36 |
| D2548 | 76.94 | 0.08 | 12.78 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.71 | 3.57 |
| D2529 | 74.51 | 0.14 | 13.82 | 1.05 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 3.24 |
| D2011 | 76.72 | 0.05 | 12.72 | 0.50 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 3.66 |
| D8348 | 76.15 | 0.09 | 12.51 | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 3.57 |
| D2504 | 76.50 | 0.09 | 12.74 | 0.33 | 0.93 | 0.018 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 3.51 |
| D2506 | 76.42 | 0.05 | 13.03 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.039 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 3.86 |
| 样号 | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | 烧失量 | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | FeOT/MgO | AR |
| D2545 | 4.89 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.56 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 7.04 | 5.11 |
| D2548 | 4.67 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 1.31 | 1.05 | 8.50 | 4.14 |
| D2529 | 5.21 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 1.61 | 1.17 | 6.60 | 3.88 |
| D2011 | 5.00 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 29.78 | 4.63 |
| D8348 | 5.22 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.60 | 1.46 | 1.01 | 19.01 | 5.20 |
| D2504 | 4.77 | 0.017 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 1.36 | 1.08 | 13.50 | 4.35 |
| D2506 | 4.57 | 0.017 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.42 | 1.18 | 1.07 | 12.57 | 4.30 |
Table 2 Major element oxide compositions of the monzogranite (%)
| 样号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2545 | 78.05 | 0.05 | 12.03 | 0.36 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 3.36 |
| D2548 | 76.94 | 0.08 | 12.78 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.71 | 3.57 |
| D2529 | 74.51 | 0.14 | 13.82 | 1.05 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 3.24 |
| D2011 | 76.72 | 0.05 | 12.72 | 0.50 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.70 | 3.66 |
| D8348 | 76.15 | 0.09 | 12.51 | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.47 | 3.57 |
| D2504 | 76.50 | 0.09 | 12.74 | 0.33 | 0.93 | 0.018 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 3.51 |
| D2506 | 76.42 | 0.05 | 13.03 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.039 | 0.07 | 0.51 | 3.86 |
| 样号 | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | H2O- | 烧失量 | K2O/Na2O | A/CNK | FeOT/MgO | AR |
| D2545 | 4.89 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.56 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 7.04 | 5.11 |
| D2548 | 4.67 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 1.31 | 1.05 | 8.50 | 4.14 |
| D2529 | 5.21 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.31 | 0.89 | 1.61 | 1.17 | 6.60 | 3.88 |
| D2011 | 5.00 | 0.02 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 1.36 | 1.00 | 29.78 | 4.63 |
| D8348 | 5.22 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.60 | 1.46 | 1.01 | 19.01 | 5.20 |
| D2504 | 4.77 | 0.017 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 1.36 | 1.08 | 13.50 | 4.35 |
| D2506 | 4.57 | 0.017 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.42 | 1.18 | 1.07 | 12.57 | 4.30 |
| 样号 | Cs | Rb | Sr | Ba | Ga | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2545 | 1.43 | 82.70 | 50.20 | 367.50 | 10.67 | 6.09 | 0.34 | 130.30 | 4.88 | 16.82 |
| D2548 | 15.00 | 251.30 | 56.90 | 158.70 | 17.36 | 2.31 | 2.46 | 64.00 | 2.93 | 32.51 |
| D2529 | 15.02 | 490.20 | 57.57 | 166.59 | 25.04 | 23.17 | 4.06 | 101.50 | 3.41 | 36.56 |
| D2011 | 17.12 | 312.38 | 26.94 | 56.78 | 23.94 | 39.46 | 3.97 | 58.64 | 3.03 | 21.44 |
| D8348 | 11.93 | 311.33 | 20.03 | 71.51 | 29.91 | 30.99 | 1.35 | 106.50 | 5.15 | 28.11 |
| D2504 | 11.62 | 376.10 | 7.44 | 28.47 | 32.48 | 25.07 | 1.46 | 130.20 | 5.36 | 58.21 |
| D2506 | 37.35 | 441.09 | 22.90 | 51.31 | 28.25 | 32.29 | 9.37 | 70.80 | 3.22 | 26.39 |
| 样号 | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Li | Sc | U | Th/U | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba |
| D2545 | 31.80 | 3.30 | 0.79 | 3.40 | 7.05 | 2.27 | 0.74 | 22.73 | 1.65 | 0.14 |
| D2548 | 34.00 | 3.90 | 0.79 | 1.80 | 36.56 | 2.72 | 1.59 | 20.45 | 4.42 | 0.36 |
| D2529 | 42.13 | 11.55 | 2.36 | 7.83 | 30.29 | 5.56 | 2.15 | 16.98 | 8.52 | 0.35 |
| D2011 | 12.21 | 10.51 | 0.39 | 3.91 | 13.13 | 2.42 | 1.72 | 12.49 | 11.60 | 0.47 |
| D8348 | 12.75 | 10.01 | 0.71 | 3.55 | 30.69 | 1.79 | 1.30 | 21.61 | 15.54 | 0.28 |
| D2504 | 40.87 | 8.91 | 0.46 | 7.03 | 51.96 | 2.97 | 3.60 | 16.19 | 50.57 | 0.26 |
| D2506 | 48.22 | 11.02 | 0.47 | 6.34 | 76.46 | 4.60 | 2.63 | 10.05 | 19.26 | 0.45 |
Table 3 Trace element compositions of the monzogranite (10-6)
| 样号 | Cs | Rb | Sr | Ba | Ga | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Th |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2545 | 1.43 | 82.70 | 50.20 | 367.50 | 10.67 | 6.09 | 0.34 | 130.30 | 4.88 | 16.82 |
| D2548 | 15.00 | 251.30 | 56.90 | 158.70 | 17.36 | 2.31 | 2.46 | 64.00 | 2.93 | 32.51 |
| D2529 | 15.02 | 490.20 | 57.57 | 166.59 | 25.04 | 23.17 | 4.06 | 101.50 | 3.41 | 36.56 |
| D2011 | 17.12 | 312.38 | 26.94 | 56.78 | 23.94 | 39.46 | 3.97 | 58.64 | 3.03 | 21.44 |
| D8348 | 11.93 | 311.33 | 20.03 | 71.51 | 29.91 | 30.99 | 1.35 | 106.50 | 5.15 | 28.11 |
| D2504 | 11.62 | 376.10 | 7.44 | 28.47 | 32.48 | 25.07 | 1.46 | 130.20 | 5.36 | 58.21 |
| D2506 | 37.35 | 441.09 | 22.90 | 51.31 | 28.25 | 32.29 | 9.37 | 70.80 | 3.22 | 26.39 |
| 样号 | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Li | Sc | U | Th/U | Rb/Sr | Sr/Ba |
| D2545 | 31.80 | 3.30 | 0.79 | 3.40 | 7.05 | 2.27 | 0.74 | 22.73 | 1.65 | 0.14 |
| D2548 | 34.00 | 3.90 | 0.79 | 1.80 | 36.56 | 2.72 | 1.59 | 20.45 | 4.42 | 0.36 |
| D2529 | 42.13 | 11.55 | 2.36 | 7.83 | 30.29 | 5.56 | 2.15 | 16.98 | 8.52 | 0.35 |
| D2011 | 12.21 | 10.51 | 0.39 | 3.91 | 13.13 | 2.42 | 1.72 | 12.49 | 11.60 | 0.47 |
| D8348 | 12.75 | 10.01 | 0.71 | 3.55 | 30.69 | 1.79 | 1.30 | 21.61 | 15.54 | 0.28 |
| D2504 | 40.87 | 8.91 | 0.46 | 7.03 | 51.96 | 2.97 | 3.60 | 16.19 | 50.57 | 0.26 |
| D2506 | 48.22 | 11.02 | 0.47 | 6.34 | 76.46 | 4.60 | 2.63 | 10.05 | 19.26 | 0.45 |
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2545 | 13.35 | 23.18 | 3.54 | 14.06 | 3.09 | 0.40 | 2.89 | 0.52 | 3.10 | 0.59 |
| D2548 | 17.46 | 38.90 | 5.57 | 21.22 | 4.85 | 0.38 | 3.62 | 0.60 | 3.30 | 0.58 |
| D2529 | 35.62 | 78.72 | 9.54 | 32.72 | 6.81 | 0.36 | 6.03 | 1.13 | 6.18 | 1.22 |
| D2011 | 10.93 | 27.34 | 3.46 | 13.56 | 4.09 | 0.14 | 3.55 | 0.80 | 4.52 | 0.79 |
| D8348 | 13.34 | 37.15 | 4.79 | 20.32 | 6.62 | 0.14 | 7.15 | 1.75 | 12.12 | 2.61 |
| D2504 | 21.32 | 90.23 | 9.31 | 41.68 | 14.89 | 0.08 | 15.03 | 3.09 | 17.46 | 3.43 |
| D2506 | 8.98 | 30.45 | 2.64 | 10.24 | 2.90 | 0.13 | 2.75 | 0.59 | 3.87 | 0.84 |
| 样号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ∑REE | LREE/HREE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | Sm/Nd |
| D2545 | 1.69 | 0.27 | 1.89 | 0.32 | 14.39 | 83.28 | 2.25 | 0.40 | 5.07 | 0.22 |
| D2548 | 1.74 | 0.30 | 2.10 | 0.36 | 15.31 | 116.29 | 3.17 | 0.27 | 5.96 | 0.23 |
| D2529 | 3.09 | 0.56 | 3.12 | 0.60 | 33.12 | 218.82 | 2.97 | 0.17 | 8.20 | 0.21 |
| D2011 | 2.27 | 0.42 | 2.65 | 0.53 | 19.85 | 94.90 | 1.68 | 0.11 | 2.96 | 0.30 |
| D8348 | 7.54 | 1.18 | 8.12 | 1.33 | 85.08 | 209.24 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 1.18 | 0.33 |
| D2504 | 8.30 | 1.29 | 6.46 | 1.11 | 73.50 | 307.20 | 1.37 | 0.02 | 2.37 | 0.36 |
| D2506 | 2.49 | 0.54 | 3.53 | 0.62 | 23.90 | 94.47 | 1.41 | 0.14 | 1.83 | 0.28 |
Table 4 REE compositions of the monzogranite (10-6)
| 样号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2545 | 13.35 | 23.18 | 3.54 | 14.06 | 3.09 | 0.40 | 2.89 | 0.52 | 3.10 | 0.59 |
| D2548 | 17.46 | 38.90 | 5.57 | 21.22 | 4.85 | 0.38 | 3.62 | 0.60 | 3.30 | 0.58 |
| D2529 | 35.62 | 78.72 | 9.54 | 32.72 | 6.81 | 0.36 | 6.03 | 1.13 | 6.18 | 1.22 |
| D2011 | 10.93 | 27.34 | 3.46 | 13.56 | 4.09 | 0.14 | 3.55 | 0.80 | 4.52 | 0.79 |
| D8348 | 13.34 | 37.15 | 4.79 | 20.32 | 6.62 | 0.14 | 7.15 | 1.75 | 12.12 | 2.61 |
| D2504 | 21.32 | 90.23 | 9.31 | 41.68 | 14.89 | 0.08 | 15.03 | 3.09 | 17.46 | 3.43 |
| D2506 | 8.98 | 30.45 | 2.64 | 10.24 | 2.90 | 0.13 | 2.75 | 0.59 | 3.87 | 0.84 |
| 样号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | ∑REE | LREE/HREE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | Sm/Nd |
| D2545 | 1.69 | 0.27 | 1.89 | 0.32 | 14.39 | 83.28 | 2.25 | 0.40 | 5.07 | 0.22 |
| D2548 | 1.74 | 0.30 | 2.10 | 0.36 | 15.31 | 116.29 | 3.17 | 0.27 | 5.96 | 0.23 |
| D2529 | 3.09 | 0.56 | 3.12 | 0.60 | 33.12 | 218.82 | 2.97 | 0.17 | 8.20 | 0.21 |
| D2011 | 2.27 | 0.42 | 2.65 | 0.53 | 19.85 | 94.90 | 1.68 | 0.11 | 2.96 | 0.30 |
| D8348 | 7.54 | 1.18 | 8.12 | 1.33 | 85.08 | 209.24 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 1.18 | 0.33 |
| D2504 | 8.30 | 1.29 | 6.46 | 1.11 | 73.50 | 307.20 | 1.37 | 0.02 | 2.37 | 0.36 |
| D2506 | 2.49 | 0.54 | 3.53 | 0.62 | 23.90 | 94.47 | 1.41 | 0.14 | 1.83 | 0.28 |

Fig.5 A/CNK-A/NK ((a),base map after MANIAR et al. [20]), ternary Q-A-P ((b),base map after LE MAITRE et al. [21]),TAS ((c),base map after MIDDLEMOST [22]), SiO2-K2O ((d),base map after PECCERILLOA et al. [23]) diagrams for the Early Cretaceous monzogranite
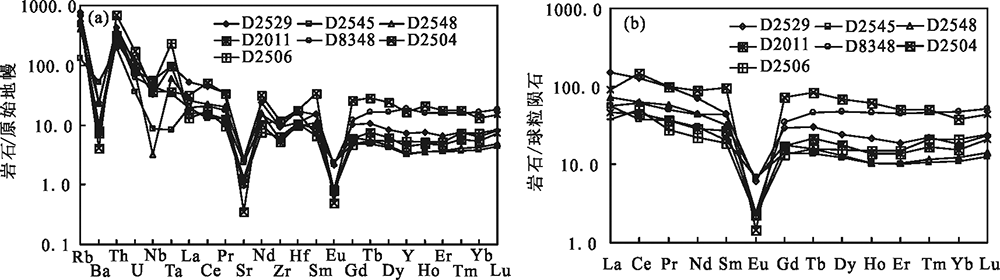
Fig.6 Primitive mantle-normalized multi-element diagram (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) for the Early Cretaceous monzogranite (normalizing values after SUN et al. [24])
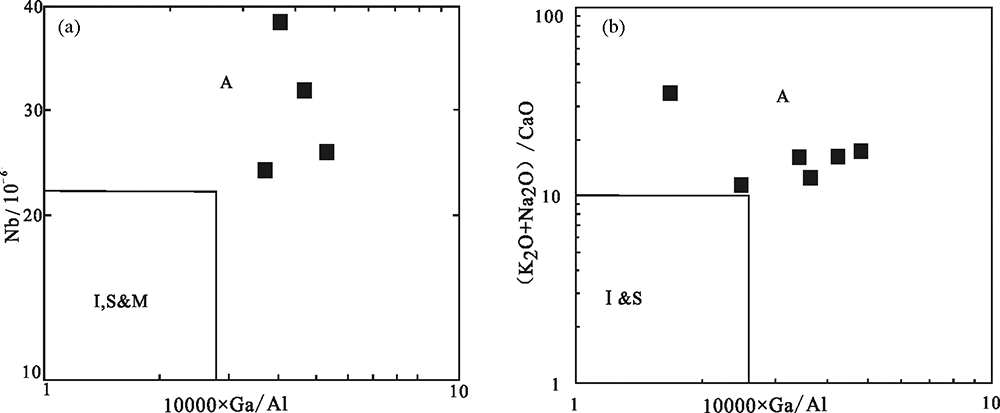
Fig.7 10000×Ga/Al-Nb (a) and 10000×Ga/Al-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO (b) discrimination diagrams for the Early Cretaceous monzogranite (base map after WHALEN et al. [30])
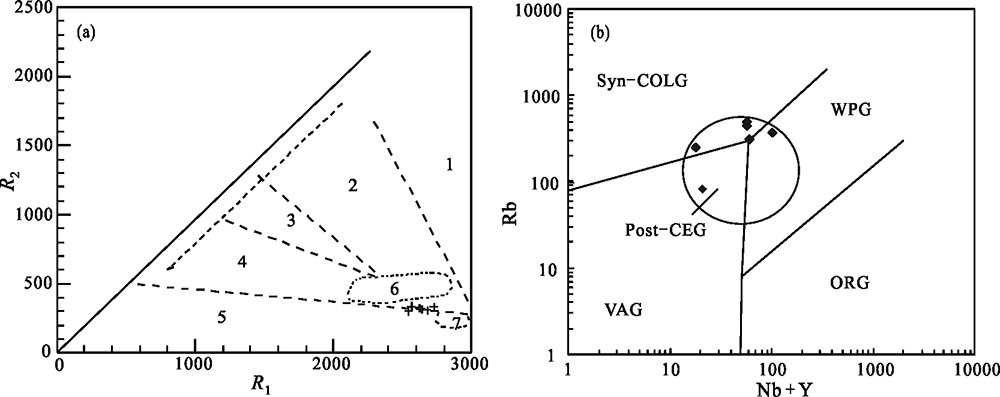
Fig. 9 R1-R2 diagram ((a),base map after BATCHELOR et al. [50]) and Rb-(Nb+Y) tectonic discrimination diagram ((b),base map after PEARCE et al. [51]) for the Early Cretaceous monzogranite
| [1] |
TANG K D. Tectonic development of Paleozoic foldbelts at the north margin of the Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Tectonics, 1990,9:249-260.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 邵济安. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1991: 1-135. |
| [3] | 徐备, 陈斌. 内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构及演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997,27(3):227-232. |
| [4] | 徐备, CHARCET J, 张福勤. 内蒙古北部苏尼特左旗蓝片岩岩石学和年代学研究[J]. 地质科学, 2001,36(4):424-434. |
| [5] |
XU B, CHARVET J, CHEN Y, et al. Middle Paleozoic convergent orogenic belts in western Inner Mongolia (China): Framework, kinematics, geochronology and implications for tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013,23:1342-1364.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
CHEN B, JAHN B M, WILDE S, et al. Two contrasting Paleozoic magmatic belts in northern Inner Mongolia, China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,328:157-182.
DOI URL |
| [7] | XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HAO J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003,22:1069-1088. |
| [8] | WINDLEY B F, ALEXELEW D, XIAO W J, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007,164(1):31-47. |
| [9] | WU F Y, ZHAO G C, SUN D Y, et al. The Hulan Group: Its role in the evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007,30:542-556. |
| [10] | 李大鹏, 陈岳龙, 王忠, 等. 内蒙古中—东部兴蒙造山带古生代沉积记录: 对物源特征及中亚造山带构造演化的指示[J]. 科学通报, 2012,57(7):550-559. |
| [11] | ZHOU J B, WILDE S A. The crustal accretion history and tectonic evolution of the NE China segment of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013,23:1365-1377. |
| [12] | MENG E, XU W L, PEI F P, et al. Permian bimodal volcanism in the Zhangguangcai Range of eastern Heilongjiang Province, NE China: Zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes and geochemical evidence[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011,41:119-132. |
| [13] | 刘洪涛, 翟明国, 刘建明, 等. 华北克拉通北缘中生代花岗岩: 从碰撞后到非造山[J]. 岩石学报, 2002,18(4):433-448. |
| [14] |
WU F, SUN D, GE W, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011,41(1):1-30.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 孟恩, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 满洲里地区灵泉盆地中生代火山岩的锆石U-Pb 年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(4):1209-1226. |
| [16] | XU W, JI W, PEI F, et al. Triassic volcanism in eastern Heilongjiang and Jilin provinces, NE China: Chronology, geochemistry, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009,34(3):392-402. |
| [17] | 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009,36(1):1-28. |
| [18] | LUDWIG K R. Isoplot/EX, Version 3.0 A—Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003:1-70. |
| [19] | ANDERSEN T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,192(1/2):59-79. |
| [20] | MANIAR P, PICCOL P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [21] | LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A, ZANETTIN B, et al. Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002:1-236. |
| [22] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37(3/4):215-224. |
| [23] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamomu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976,58(1):63-81.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 陈志广, 张连昌, 吴华英, 等. 内蒙古西拉木伦成矿带碾子沟钼矿区A 型花岗岩地球化学和构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2008,24(4):879-889. |
| [26] | 单强, 廖思平, 卢焕章, 等. 岩浆到热液演化的包裹体记录——以骑田岭花岗岩体为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(5):1511-1520. |
| [27] | 葛文春, 林强, 孙德有, 等. 大兴安岭中生代两类流纹岩成因的地球化学研究[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2000,25(2):172-178. |
| [28] | 张旗, 潘国强, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩结晶分离作用问题——关于花岗岩研究的思考之二[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(6):1239-1251. |
| [29] |
HARRIS C, MARSH J S, MILNER S C. Petrology of the alkaline core of the Messum igneous complex, Namibia: evidence for the progressively decreasing effect of crustal contamination[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1999,40:1377-1397.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WHALEN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,95(4):407-419.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
PATINO DOUCE A E. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997,25:743-746.
DOI URL |
| [32] | CLEMENS J D, HOLLOWAY J R, WHITE A J R. Origin of an A-type granites: experimental constraints[J]. American Mineralogist, 1986,71:317-324. |
| [33] | DIXON S S, RUTHERFORD M J. The origin of rhyolite and plagiogranite in oceanic crust: An experimental study[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1983,24:1-25. |
| [34] | TISCHENDOR F G, PAELCHEN W. Zur classification von granitoiden/classification of granitoids[J]. Zeitschrift fuer Geologische Wissenschaften, 1985,13(5):615-627. |
| [35] | 李超文, 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 等. 延吉地区晚中生代火山岩的Ar-Ar年代学格架及其大地构造背景[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2007,37(3):319-330. |
| [36] | 张连昌, 吴华英, 相鹏, 等. 中生代复杂构造体系的成矿过程与成矿作用——以华北大陆北缘西拉木伦钼铜多金属成矿带为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(5):1351-1362. |
| [37] | 刘翠, 邓晋福, 许立权, 等. 大兴安岭—小兴安岭地区中生代岩浆-构造-钼成矿地质事件序列的初步框架[J]. 地学前缘, 2011,18(3):166-178. |
| [38] | 张学斌, 周长红, 来林, 等. 锡林浩特东部早白垩世白音高老组岩石地球化学特征、LA-MC-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015,51(2) : 290-302. |
| [39] | 施光海, 苗来成, 张福勤, 等. 内蒙古锡林浩特A 型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004,49(4):384-389. |
| [40] | 程银行, 刘永顺, 滕学建, 等. 内蒙古莫合尔图中—晚侏罗世火山岩年代学、地球化学研究及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013,87(7):943-956. |
| [41] | 俞礽安, 胡鹏, 曾威, 等. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗东苏A型花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016,35(2):229-241. |
| [42] | 尚庆华. 北方造山带内蒙古中、东部地区二叠纪放射虫的发现及意义[J]. 科学通报, 2004,49(24):2574-2579. |
| [43] | 王玉净, 樊志勇. 内蒙古西拉木伦河北部蛇绿岩带中二叠纪放射虫的发现及其地质意义[J]. 古生物学报, 1997,36(1):58-69. |
| [44] | DAVIS G A, XU B, ZHENG Y, et al. Indosinian extension in the Solonker suture zone: the Sonid Zuoqi metamorphic core complex, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. 地学前缘, 2004,11(3):135-143. |
| [45] | 李可, 张志诚, 李建锋, 等. 内蒙古西乌珠穆沁旗地区中生代中酸性火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012,32(5):671-685. |
| [46] | 刘伟, 潘小菲, 谢烈文, 等. 大兴安岭南段林西地区花岗岩类的源岩: 地壳生长的时代和方式[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):441-459. |
| [47] |
LIU W, SIEBEL W, LI X J, et al. Petrogenesis of the Linxi granitoids, northern Inner Mongolia of china: constraints on basaltic underplating[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005,219:5-35.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 张吉衡. 大兴安岭中生代火山岩年代学及地球化学研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2009: 1-105. |
| [49] |
EBY G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992,20(7):641-644.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
BATCHELOR R A, BOWDEN P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985,48(1):43-55.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25(4):956-983.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||