



Geoscience ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (04): 772-782.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.04.08
• Geochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Shengchao1( ), XIAO Gaoqiang1(
), XIAO Gaoqiang1( ), GONG Qingjie2, LIU Ningqiang2, YANG Tianyi1, DAO Yan1, XIANG Longzhou1, LI Zhong1
), GONG Qingjie2, LIU Ningqiang2, YANG Tianyi1, DAO Yan1, XIANG Longzhou1, LI Zhong1
Received:2019-03-20
Revised:2019-05-08
Online:2019-08-20
Published:2019-09-05
Contact:
XIAO Gaoqiang
CLC Number:
XU Shengchao, XIAO Gaoqiang, GONG Qingjie, LIU Ningqiang, YANG Tianyi, DAO Yan, XIANG Longzhou, LI Zhong. Anomalies and Prospecting Directions of Regional Geochemistry Survey in the Lanping Basin of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(04): 772-782.
| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素和氧化物 | 分析方法 | 检出限 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | ES | 20 | Cu | ICP-OES | 1 | Pb | XRF | 2 | Y | XRF | 1 |
| As | AFS | 1 | F | ISE | 100 | Rb | XRF | 3 | Zn | XRF | 4 |
| Au | ICP-MS | 0.3 | Hg | AFS | 0.003 | Sb | AFS | 0.05 | Zr | XRF | 2 |
| B | ES | 1 | La | ICP-OES | 2 | Sn | ES | 0.5 | SiO2 | XRF | 0.1 |
| Ba | ICP-OES | 10 | Li | ICP-OES | 1 | Sr | XRF | 4 | Al2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Be | ICP-OES | 0.3 | Mn | ICP-OES | 5 | Th | XRF | 2 | TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Bi | AFS | 0.05 | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.2 | Ti | XRF | 10 | K2O | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cd | ICP-MS | 0.03 | Nb | XRF | 2 | U | ICP-MS | 0.1 | Na2O | XRF | 0.1 |
| Co | ICP-OES | 0.5 | Ni | ICP-OES | 1.5 | V | ICP-OES | 3 | CaO | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cr | XRF | 2.5 | P | XRF | 10 | W | POL | 0.3 | MgO | XRF | 0.05 |
Table 1 Analytical methods and detection limits for 39 elements or major oxides
| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素和氧化物 | 分析方法 | 检出限 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | ES | 20 | Cu | ICP-OES | 1 | Pb | XRF | 2 | Y | XRF | 1 |
| As | AFS | 1 | F | ISE | 100 | Rb | XRF | 3 | Zn | XRF | 4 |
| Au | ICP-MS | 0.3 | Hg | AFS | 0.003 | Sb | AFS | 0.05 | Zr | XRF | 2 |
| B | ES | 1 | La | ICP-OES | 2 | Sn | ES | 0.5 | SiO2 | XRF | 0.1 |
| Ba | ICP-OES | 10 | Li | ICP-OES | 1 | Sr | XRF | 4 | Al2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Be | ICP-OES | 0.3 | Mn | ICP-OES | 5 | Th | XRF | 2 | TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05 |
| Bi | AFS | 0.05 | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.2 | Ti | XRF | 10 | K2O | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cd | ICP-MS | 0.03 | Nb | XRF | 2 | U | ICP-MS | 0.1 | Na2O | XRF | 0.1 |
| Co | ICP-OES | 0.5 | Ni | ICP-OES | 1.5 | V | ICP-OES | 3 | CaO | XRF | 0.05 |
| Cr | XRF | 2.5 | P | XRF | 10 | W | POL | 0.3 | MgO | XRF | 0.05 |
| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 富集系数 | 西南三江水系 沉积物背景值 | 边界品位/ 10-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 22 800 | 31 | 83 | 254 | 993 | 3.30 | 77 | 40 000 |
| As | 2 146 | 2.06 | 12.6 | 28.2 | 90 | 2.41 | 11.7 | 13 100 |
| Au | 57.7 | 0.15 | 0.93 | 1.10 | 2.23 | 0.87 | 1.27 | 1 000 |
| B | 300 | 5.04 | 66 | 68.3 | 31.7 | 1.22 | 56.2 | 9 316 |
| Ba | 13 895 | 73.8 | 440 | 562 | 596 | 1.44 | 389 | 139 172 |
| Be | 12.80 | 0.30 | 2.23 | 2.20 | 0.67 | 1.08 | 2.04 | 144.00 |
| Bi | 182 | 0.064 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 5.58 | 2.73 | 0.33 | 500 |
| Cd | 301 | 0.038 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 10.4 | 6.67 | 0.15 | 100 |
| Co | 175 | 2.09 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 7.46 | 1.07 | 12.4 | 200 |
| Cr | 568 | 4.3 | 74.2 | 72.6 | 32.0 | 1.22 | 59.4 | 171 000 |
| Cu | 6 544 | 1.07 | 22.0 | 46.5 | 231 | 2.00 | 23.2 | 2 000 |
| F | 1 743 | 108 | 593 | 593 | 155 | 1.16 | 510 | 97 311 |
| Hg | 165 | 0.003 | 0.040 | 0.40 | 4.21 | 13.3 | 0.030 | 400 |
| La | 130 | 3.92 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 8.25 | 0.98 | 35.6 | 853 |
| Li | 283 | 8.36 | 46.4 | 51.5 | 27.7 | 1.49 | 34.5 | 1 858 |
| Mo | 18.7 | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 1.23 | 0.65 | 300 |
| Nb | 42.3 | 2.5 | 15.1 | 14.9 | 3.93 | 0.96 | 15.5 | 350 |
| Ni | 189 | 2.24 | 30.7 | 29.7 | 13.4 | 1.13 | 26.4 | 2 000 |
| Pb | 16 382 | 4.26 | 25.8 | 118 | 833 | 5.06 | 23.3 | 3 000 |
| Sb | 793 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 5.20 | 34.4 | 6.05 | 0.86 | 5 000 |
| Sn | 42 | 0.99 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 1.16 | 1.02 | 2.94 | 1 000 |
| Sr | 3 206 | 13.8 | 92.3 | 137 | 176 | 1.49 | 92 | 47 701 |
| Th | 65.6 | 2.3 | 13.1 | 13.1 | 4.68 | 1.20 | 10.9 | 879 |
| U | 9.66 | 0.46 | 2.68 | 2.80 | 0.85 | 1.27 | 2.20 | 300 |
| V | 200 | 13.6 | 97.4 | 93.0 | 30.8 | 1.09 | 85.5 | 2 801 |
| W | 181 | 0.15 | 1.72 | 1.90 | 3.93 | 1.12 | 1.70 | 507 |
| Y | 208 | 4.4 | 22.9 | 23.4 | 10.6 | 0.98 | 23.8 | 394 |
| Zn | 44 331 | 4.1 | 75 | 192 | 1 388 | 2.69 | 71.5 | 5 000 |
| Zr | 1 451 | 66 | 187 | 193 | 74 | 0.83 | 233 | 2 221 |
| SiO2 | 93.9 | 20.4 | 67.5 | 67.9 | 6.70 | 1.06 | 64.0 | |
| Al2O3 | 20.9 | 2.24 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 2.35 | 1.08 | 13.1 | |
| TFe2O3 | 16.3 | 0.05 | 5.48 | 5.30 | 1.54 | 1.08 | 4.90 | |
| MgO | 10.9 | 0.08 | 1.46 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.18 | 1.27 | |
| CaO | 44.2 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 2.82 | 2.15 | 0.79 | |
| Na2O | 5.85 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 1.14 | 0.79 | |
| K2O | 6.63 | 0.41 | 3.06 | 3.10 | 0.81 | 1.27 | 2.45 | |
| Ti | 8 373 | 978 | 4 022 | 3 827 | 920 | 0.97 | 3 959 | |
| Mn | 12 265 | 128 | 630 | 687 | 397 | 1.00 | 684 | |
| P | 1 959 | 134 | 495 | 508 | 136 | 0.85 | 599 |
Table 2 Statistical parameters of elemental contents in stream sediments in the Lanping basin
| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 标准离差 | 富集系数 | 西南三江水系 沉积物背景值 | 边界品位/ 10-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 22 800 | 31 | 83 | 254 | 993 | 3.30 | 77 | 40 000 |
| As | 2 146 | 2.06 | 12.6 | 28.2 | 90 | 2.41 | 11.7 | 13 100 |
| Au | 57.7 | 0.15 | 0.93 | 1.10 | 2.23 | 0.87 | 1.27 | 1 000 |
| B | 300 | 5.04 | 66 | 68.3 | 31.7 | 1.22 | 56.2 | 9 316 |
| Ba | 13 895 | 73.8 | 440 | 562 | 596 | 1.44 | 389 | 139 172 |
| Be | 12.80 | 0.30 | 2.23 | 2.20 | 0.67 | 1.08 | 2.04 | 144.00 |
| Bi | 182 | 0.064 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 5.58 | 2.73 | 0.33 | 500 |
| Cd | 301 | 0.038 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 10.4 | 6.67 | 0.15 | 100 |
| Co | 175 | 2.09 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 7.46 | 1.07 | 12.4 | 200 |
| Cr | 568 | 4.3 | 74.2 | 72.6 | 32.0 | 1.22 | 59.4 | 171 000 |
| Cu | 6 544 | 1.07 | 22.0 | 46.5 | 231 | 2.00 | 23.2 | 2 000 |
| F | 1 743 | 108 | 593 | 593 | 155 | 1.16 | 510 | 97 311 |
| Hg | 165 | 0.003 | 0.040 | 0.40 | 4.21 | 13.3 | 0.030 | 400 |
| La | 130 | 3.92 | 35.6 | 34.9 | 8.25 | 0.98 | 35.6 | 853 |
| Li | 283 | 8.36 | 46.4 | 51.5 | 27.7 | 1.49 | 34.5 | 1 858 |
| Mo | 18.7 | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 1.23 | 0.65 | 300 |
| Nb | 42.3 | 2.5 | 15.1 | 14.9 | 3.93 | 0.96 | 15.5 | 350 |
| Ni | 189 | 2.24 | 30.7 | 29.7 | 13.4 | 1.13 | 26.4 | 2 000 |
| Pb | 16 382 | 4.26 | 25.8 | 118 | 833 | 5.06 | 23.3 | 3 000 |
| Sb | 793 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 5.20 | 34.4 | 6.05 | 0.86 | 5 000 |
| Sn | 42 | 0.99 | 2.96 | 3.00 | 1.16 | 1.02 | 2.94 | 1 000 |
| Sr | 3 206 | 13.8 | 92.3 | 137 | 176 | 1.49 | 92 | 47 701 |
| Th | 65.6 | 2.3 | 13.1 | 13.1 | 4.68 | 1.20 | 10.9 | 879 |
| U | 9.66 | 0.46 | 2.68 | 2.80 | 0.85 | 1.27 | 2.20 | 300 |
| V | 200 | 13.6 | 97.4 | 93.0 | 30.8 | 1.09 | 85.5 | 2 801 |
| W | 181 | 0.15 | 1.72 | 1.90 | 3.93 | 1.12 | 1.70 | 507 |
| Y | 208 | 4.4 | 22.9 | 23.4 | 10.6 | 0.98 | 23.8 | 394 |
| Zn | 44 331 | 4.1 | 75 | 192 | 1 388 | 2.69 | 71.5 | 5 000 |
| Zr | 1 451 | 66 | 187 | 193 | 74 | 0.83 | 233 | 2 221 |
| SiO2 | 93.9 | 20.4 | 67.5 | 67.9 | 6.70 | 1.06 | 64.0 | |
| Al2O3 | 20.9 | 2.24 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 2.35 | 1.08 | 13.1 | |
| TFe2O3 | 16.3 | 0.05 | 5.48 | 5.30 | 1.54 | 1.08 | 4.90 | |
| MgO | 10.9 | 0.08 | 1.46 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.18 | 1.27 | |
| CaO | 44.2 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 2.82 | 2.15 | 0.79 | |
| Na2O | 5.85 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 1.14 | 0.79 | |
| K2O | 6.63 | 0.41 | 3.06 | 3.10 | 0.81 | 1.27 | 2.45 | |
| Ti | 8 373 | 978 | 4 022 | 3 827 | 920 | 0.97 | 3 959 | |
| Mn | 12 265 | 128 | 630 | 687 | 397 | 1.00 | 684 | |
| P | 1 959 | 134 | 495 | 508 | 136 | 0.85 | 599 |
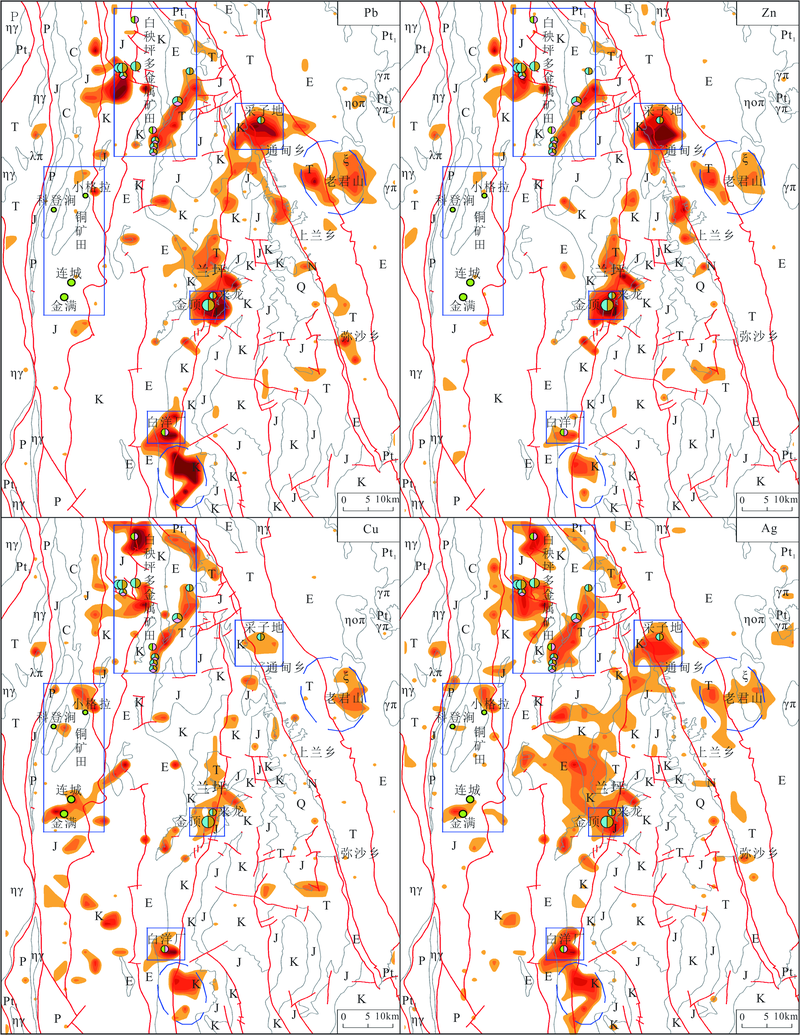
Fig.2 The geochemical anomaly maps of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Ag determined on the method of seven levels’ classification in the Lanping basin of Yunnan province, China

Fig.3 (The geochemical anomaly maps of As, Sb, Bi, and B determined on the method of seven levels’ classification in the Lanping basin of Yunnan province, China
| 矿田/矿区 | Pb | Zn | Cu | Ag | As | Sb | Bi | B | 异常平均强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白秧坪多金属矿田 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5.9 |
| 金顶铅多金属矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 菜子地铅锌矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 中西部铜矿田 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3.8 |
| 白洋厂铜银矿区 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4.6 |
| 老君山预测区 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3.1 |
| 白洋厂南预测区 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4.0 |
Table 3 Anomaly levels of 8 elements on regional geochemistry survey in Lanping basin
| 矿田/矿区 | Pb | Zn | Cu | Ag | As | Sb | Bi | B | 异常平均强度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白秧坪多金属矿田 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5.9 |
| 金顶铅多金属矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 菜子地铅锌矿区 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3.9 |
| 中西部铜矿田 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3.8 |
| 白洋厂铜银矿区 | 7 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4.6 |
| 老君山预测区 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3.1 |
| 白洋厂南预测区 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4.0 |
| [1] | 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 杨建民, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地构造体制和成矿背景分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2002,21(1):36-44. |
| [2] | 徐启东, 李建威. 云南兰坪北部铜多金属矿化成矿流体流动与矿化分带:流体包裹体和稳定同位素依据[J]. 矿床地质, 2003,22(4):365-376. |
| [3] | 杨伟光, 喻学惠, 李文昌, 等. 云南白秧坪银多金属矿集区成矿流体特征及成矿机制[J]. 现代地质, 2003,17(1):27-33. |
| [4] | 朱志军, 郭福生, 宋玉财, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地古近系构造-沉积演化与成矿的关系[J]. 沉积学报, 2014,32(6):997-1006. |
| [5] | 沈青强, 曹凯, 王国灿, 等. 剑川—兰坪盆地古近系沉积-构造变革及其区域构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017,41(1):23-41. |
| [6] | 王安建, 曹殿华, 高兰, 等. 论云南兰坪金顶超大型铅锌矿床的成因[J]. 地质学报, 2009,83(1):43-54. |
| [7] | 黄玉凤, 曹殿华, 王志军, 等. 云南兰坪盆地北部东缘铅锌矿床喷流沉积成因的厘定:来自矿物学和硫同位素证据[J]. 地质力学学报, 2011,17(1):91-102. |
| [8] | 李小明. 滇西金满铜矿床成矿年龄测定[J]. 现代地质, 2001,15(4):405-408. |
| [9] | 王晓虎, 宋玉财, 张洪瑞, 等. 白秧坪铅锌多金属矿集区东矿带成矿地球化学作用与成矿年龄[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016,22(2):294-309. |
| [10] | 徐墨寒, 薛传东, 杨天南, 等. 兰坪盆地西缘大宗铜矿区容矿火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学及地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016,35(5):735-750. |
| [11] | 朱华平, 范文玉, 高大发, 等. 西南三江成矿带中南段铅锌矿床成矿系列[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2008,28(4):62-68. |
| [12] | 朱多录. 云南兰坪矿集区成矿系列及成矿规律[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2013,28(2):224-229. |
| [13] | 江彪, 邓军, 张长青. 西南三江地区沉积岩容矿型铅锌矿成矿特征和成矿规律[J]. 地质学报, 2014,88(12):2532-2544. |
| [14] | 肖高强, 张小兵, 李忠, 等. 因子分析在1∶25万丽江市幅区域地球化学数据解释中的应用[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017,29(S2):175-179. |
| [15] | 徐志刚, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 中国成矿区带划分方案[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 1-138. |
| [16] | 张锦让, 温汉捷, 裘愉卓, 等. 兰坪盆地西缘沉积岩容矿脉状Cu-Ag(±Pb-Zn)多金属矿床成矿流体特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2015,34(3):497-520. |
| [17] | 赵海滨. 滇西兰坪盆地中北部铜多金属矿床成矿特征及地质条件[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2006: 11. |
| [18] | 牟传龙, 王剑, 余谦, 等. 兰坪中新生代沉积盆地演化[J]. 矿物岩石, 1999,19(3):30-36. |
| [19] | 付修根. 兰坪陆相盆地演化与金属矿床的形成[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2005,27(2):26-32. |
| [20] | 刘俊来, 王安建, 曹殿华, 等. 三江造山带后碰撞断裂构造带的结构与演化:以新生代剑川—兰坪盆地为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2004,10(4):488-499. |
| [21] | 张乾, 绍树勋, 刘家军, 等. 兰坪盆地大型矿集区多金属矿床的铅同位素组成及铅的来源[J]. 矿物学报, 2002,22(2):147-154. |
| [22] | 苏学军, 张家云, 肖玲, 等. 1∶25万福贡县幅、丽江市幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 昆明:云南省地质调查院, 2008: 1-314. |
| [23] | 陈开旭, 何龙清, 杨振强, 等. 云南兰坪三山—白秧坪铜银多金属成矿富集区的碳氧同位素地球化学[J]. 华南地质与成矿, 2000(4):1-8. |
| [24] | 何龙清, 陈开旭, 魏君奇. 云南白秧坪地区东成矿带矿床地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2005,24(1):61-70. |
| [25] | 刘家军, 翟德高, 李志明, 等. 兰坪盆地白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区中银、钴、铋、镍的赋存状态与成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(6):1646-1660. |
| [26] | 王晓虎, 侯增谦, 宋玉财, 等. 兰坪盆地白秧坪铅锌铜银多金属矿床:成矿年代及区域成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(9):2625-2634. |
| [27] | 王光辉, 宋玉财, 侯增谦, 等. 兰坪盆地连城脉状铜矿床辉钼矿Re-Os定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2009,28(4):413-424. |
| [28] | 刘家军, 李志明, 刘玉平, 等. 滇西金满脉状铜矿床成矿年龄讨论[J]. 现代地质, 2003,17(1):34-39. |
| [29] | 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 滇西北金顶和白秧坪矿床:地质和He,Ne,Xe同位素组成及成矿时代[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2003,33(4):315-322. |
| [30] | 牟传龙, 余谦. 金顶铅锌矿床相关地质问题及成因探讨[J]. 矿物岩石, 2004,24(1):48-51. |
| [31] | 史长义, 梁萌, 冯斌. 中国水系沉积物39种元素系列背景值[J]. 地球科学, 2016,41(2):234-251. |
| [32] |
GONG Q J, LI J Z, XIANG Y C, et al. Determination and classification of geochemical anomalies based on backgrounds and cutoff grades of trace elements: A case study in South Nanling Range, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018,194:44-51.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
GONG Q J, DENG J, WANG C M, et al. Element behaviors due to rock weathering and its implication to geochemical anomaly re-cognition: A case study on Linglong biotite granite in Jiaodong peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013,128:14-24.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 马云涛, 龚庆杰, 韩东昱, 等. 安山岩风化过程中元素行为——以豫西熊耳山地区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2015,51(3):545-554. |
| [35] |
LI J Z, GONG Q J, YAN T T, et al. Quantitative description of geochemical backgrounds of gold due to rock weathering in Jiao-dong peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018,192:155-162.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 向运川, 牟绪赞, 任天祥, 等. 全国矿产资源潜力评价化探资料应用研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 1-445. |
| [37] | 许胜超. 南岭东段区域化探异常分析[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2016: 5. |
| [38] |
GONG Q J, DENG J, JIA Y J, et al. Empirical equations to describe trace element behaviors due to rock weathering in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015,152:110-117.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Wei, AN Maoguo, WANG Zhipeng, YANG Qi, CHEN Huaixin, MA Xiaofeng, ZHI Chenglong, XING Qitao, PEI Changshi, WANG Na, LIU Ming. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting in the Middle Reach of the Nalinggele River, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 690-707. |
| [2] | LIANG Dong, HUA Bei, ZHAO Dehuai, WU Hao, WAN Shengnan, TAN Chaoxin, ZHAO Xiaojian, YANG Zhipeng. Geochemical Characteristics of River Sediment and Ore Prediction in the Malashan Area of the Karakoram Region [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(03): 708-721. |
| [3] | CHEN Shiming, YANG Zhenxi, LEI Ziqiang, KANG Weiliang, ZHANG Jing, ZHAO Qinghu. Geochemical Characteristics and Prospecting on Stream Sediment Survey in Qianhongquan Area of Beishan in Gansu Province, China [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(06): 1513-1524. |
| [4] | WANG Bin, REN Tao, SONG Yiwei, YANG Ke, WANG Zhanbin, SUN Yake. Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Stream Sediments in Changjiashan Region, Western Qinling Orogen [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(03): 911-922. |
| [5] | LI Chao, LUO Xianrong, QIU Wei, WANG Yuhui, ZHAO Xinyi, ZHENG Chaojie, LIU Panfeng. Geochemical Anomalies Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Ore-Search Prospect in Jinshuikou Area of Dulan County, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1397-1410. |
| [6] | ZENG Kai, LIU Hai, HUANG Dejiang, GUO Wei, QI Shuanglin, SI Xiaohua, YANG Yuzhen. Anomaly Characteristics of 1:50,000 Stream Sediments Survey and Analysis on Prospecting Effect in Mengweng Area, Yunnan [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(01): 270-280. |
| [7] | HUANG Yonggao, XIONG Changli, LUO Gai, ZHANG Tong, JIA Xiaochuan, YANG Xuejun, YE Chunlin, WANG Yi. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting Implications in Shangri-La Wengshui Area, NW Yunnan [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(05): 897-907. |
| [8] | LIU Kunfeng, FENG Changrong, ZHAI Liming, XU Lei, ZHANG Jiasheng, WANG Shaohua, KOU Xin. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting Direction in the Wuheshalu Area, Wuqia County, Xinjiang [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(04): 759-771. |
| [9] | WEI Bin, HOU Qingye, TANG Zhimin, ZONG Qingxia, YAN Shuai, HE Haiyun. Estimation of Background Values and Contamination Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sediments of the Pearl River, China [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(02): 293-304. |
| [10] | WANG Tao, ZHANG Jing, TONG Zida, LI Tengjian. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry Characteristics of the Lianhuashan Alkaline-rich Porphyry Intrusion in Western Yunnan Province [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(03): 438-452. |
| [11] | GAO Yongwei, GUO Zhouping, ZHAO Xinmin, WANG Yuxi, LI Xiangmin, XUE Baolin. Geochemical Characteristics and Anomalies Identification of Elements in the Stream Sediments from the Lenglongling Area of North Qilian Mountains, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(03): 468-480. |
| [12] | HU Zhaoguo, ZHANG Shaopeng, LIAN Guojian, WANG Lei, LI Xujiao, LI Shiyuan, ZHANG Zhiwu, YANG Shengfei, HU Jiabin, WANG Xiaoyu, ZHAO Xiaobo, ZHANG Yang. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting in the Narizong Area, Qinghai Province [J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(03): 481-492. |
| [13] | WANG Lei, YANG Jianguo, WANG Xiaohong, QI Qi, ZHANG Zhouyuan, ZHANG Le. Geochemical Characteristics of Stream Sediments and Prospecting Direction in the Tanshanzi-Huangcaoquan Area of Beishan, Gansu Province [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(6): 1276-1284. |
| [14] | YANG Fan , SONG Yuntao, ZHANG Shunyao, HAO Zhihong, GUO Zhijuan,. Regional Geochemical Distribution Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in the Dashizhai Area, Inner Mongolia [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(4): 802-810. |
| [15] | . Tracing the Stream Sediment of the Ganjiang River(Nanchang Section):Constraint from the Detrital Zircon U-Pb Isotope Evidence [J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(3): 514-527. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||