



Geoscience ›› 2019, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (01): 121-136.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.01.12
• Ore Deposits • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Linnan1( ), HUANG Chunmei1,2, ZHANG Liang2, CHEN Binghan2,3, LI Ruihong2,4, LIU Yue2,5
), HUANG Chunmei1,2, ZHANG Liang2, CHEN Binghan2,3, LI Ruihong2,4, LIU Yue2,5
Received:2018-05-10
Revised:2018-09-12
Online:2019-02-26
Published:2019-02-28
CLC Number:
GUO Linnan, HUANG Chunmei, ZHANG Liang, CHEN Binghan, LI Ruihong, LIU Yue. Source of Ore-forming Fluids in the Luoshan Gold Deposit, Jiaodong: Constrains from REE and Trace Element Features of Auriferous Pyrite in the Altered-rock Type and Auriferous Quartz Vein Type Ores[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(01): 121-136.
| 序号 | 样品号 | 样品名称 | 采样位置 | 矿石类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LS13D020B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -400 m中段CM22穿脉口 | 石英脉型 |
| 2 | LS13D021B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -400 m中段CM22穿脉口附近 | 石英脉型 |
| 3 | LS13D029B2 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -400 m中段CM12穿脉口附近 | 石英脉型 |
| 4 | LS13D063B1 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段脉外巷B4测点附近 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 5 | LS13D066B1 | 硅化岩 | -560 m中段CM23穿脉内 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 6 | LS13D067B1 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段CM25穿脉内近主断裂处 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 7 | LS13D067B2 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段CM25穿脉内近主断裂处 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 8 | LS13D068B1 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段CM27穿脉内 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 9 | LS13D070B13 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -600 m中段1号竖井大巷N15测点附近 | 石英脉型 |
| 10 | LS13D071B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -600 m中段大巷M59测点 | 石英脉型 |
| 11 | LS13D071B2 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -600 m中段大巷M59测点 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 12 | LS13D073B1 | 硅化岩 | -600 m中段CM17穿脉内 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 13 | LS13D087B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -680 m中段盲主井大巷M2测点 | 石英脉型 |
Table 1 Location and type of ore samples for analysis of REE and trace elements in pyrites in the Luoshan gold deposit
| 序号 | 样品号 | 样品名称 | 采样位置 | 矿石类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LS13D020B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -400 m中段CM22穿脉口 | 石英脉型 |
| 2 | LS13D021B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -400 m中段CM22穿脉口附近 | 石英脉型 |
| 3 | LS13D029B2 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -400 m中段CM12穿脉口附近 | 石英脉型 |
| 4 | LS13D063B1 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段脉外巷B4测点附近 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 5 | LS13D066B1 | 硅化岩 | -560 m中段CM23穿脉内 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 6 | LS13D067B1 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段CM25穿脉内近主断裂处 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 7 | LS13D067B2 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段CM25穿脉内近主断裂处 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 8 | LS13D068B1 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -560 m中段CM27穿脉内 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 9 | LS13D070B13 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -600 m中段1号竖井大巷N15测点附近 | 石英脉型 |
| 10 | LS13D071B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -600 m中段大巷M59测点 | 石英脉型 |
| 11 | LS13D071B2 | 黄铁绢英岩 | -600 m中段大巷M59测点 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 12 | LS13D073B1 | 硅化岩 | -600 m中段CM17穿脉内 | 蚀变岩型 |
| 13 | LS13D087B1 | 石英-硫化物脉 | -680 m中段盲主井大巷M2测点 | 石英脉型 |
| 样品 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 2.94 | 4.96 | 0.50 | 1.67 | 0.24 | 0.037 | 0.215 | 0.014 | 0.079 | 0.011 | 0.032 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| LS13D066B1 | 11.60 | 21.20 | 2.29 | 7.73 | 1.12 | 0.101 | 0.816 | 0.082 | 0.310 | 0.033 | 0.113 | 0.011 | 0.106 | 0.014 | |||||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 5.06 | 8.99 | 0.89 | 2.95 | 0.40 | 0.046 | 0.353 | 0.038 | 0.157 | 0.023 | 0.050 | 0.009 | 0.048 | 0.011 | |||||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.57 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.025 | 0.053 | 0.012 | 0.030 | 0.005 | 0.011 | — | 0.008 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 4.81 | 8.80 | 0.93 | 3.57 | 0.52 | 0.077 | 0.393 | 0.051 | 0.231 | 0.035 | 0.085 | 0.013 | 0.071 | 0.014 | |||||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 6.71 | 11.90 | 1.35 | 4.86 | 0.62 | 0.082 | 0.455 | 0.048 | 0.214 | 0.029 | 0.080 | 0.010 | 0.064 | 0.011 | |||||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 3.58 | 6.40 | 0.64 | 2.24 | 0.32 | 0.031 | 0.221 | 0.019 | 0.074 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 1.92 | 3.16 | 0.35 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 0.023 | 0.128 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 0.009 | 0.021 | 0.004 | 0.021 | — | ||||||||
| LS13D021B1 | 5.47 | 8.89 | 1.00 | 3.56 | 0.59 | 0.049 | 0.484 | 0.046 | 0.171 | 0.020 | 0.048 | 0.005 | 0.039 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 5.06 | 8.71 | 1.00 | 3.71 | 0.63 | 0.208 | 0.506 | 0.072 | 0.314 | 0.057 | 0.154 | 0.022 | 0.159 | 0.019 | |||||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 2.44 | 5.04 | 0.57 | 2.21 | 0.39 | 0.075 | 0.202 | 0.018 | 0.069 | 0.007 | 0.021 | — | 0.008 | — | |||||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 6.73 | 11.70 | 1.22 | 4.18 | 0.60 | 0.092 | 0.444 | 0.050 | 0.152 | 0.017 | 0.054 | 0.005 | 0.047 | 0.005 | |||||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 1.48 | 2.72 | 0.31 | 1.12 | 0.17 | 0.021 | 0.124 | 0.013 | 0.061 | 0.013 | 0.039 | 0.004 | 0.029 | — | |||||||||
| 样品 | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Y/Ho | ||||||||||||
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.24 | 10.96 | 10.35 | 0.61 | 17.0 | 117.2 | 7.91 | 9.88 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 21.4 | |||||||||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.85 | 46.38 | 44.04 | 2.34 | 18.8 | 78.5 | 6.69 | 6.37 | 0.32 | 1.01 | 25.8 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 0.53 | 19.55 | 18.33 | 1.22 | 15.1 | 75.6 | 8.21 | 6.08 | 0.38 | 1.04 | 23.0 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.20 | 2.54 | 2.22 | 0.32 | 7.0 | 51.3 | 5.43 | 5.48 | 1.27 | 1.00 | 39.2 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 1.00 | 20.60 | 18.71 | 1.89 | 9.9 | 48.6 | 5.90 | 4.58 | 0.52 | 1.02 | 28.6 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.85 | 27.29 | 25.52 | 1.76 | 14.5 | 75.2 | 7.00 | 5.88 | 0.47 | 0.97 | 29.4 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.21 | 13.79 | 13.21 | 0.58 | 22.7 | 151.1 | 7.20 | 10.75 | 0.36 | 1.04 | 26.6 | ||||||||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.20 | 7.27 | 6.83 | 0.45 | 15.3 | 65.6 | 6.02 | 5.04 | 0.43 | 0.95 | 22.7 | |||||||||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.52 | 20.90 | 19.56 | 1.34 | 14.6 | 100.6 | 5.99 | 10.27 | 0.28 | 0.93 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 1.58 | 22.20 | 19.32 | 2.88 | 6.7 | 22.8 | 5.21 | 2.63 | 1.13 | 0.95 | 27.7 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.22 | 11.27 | 10.72 | 0.55 | 19.5 | 218.8 | 4.04 | 20.89 | 0.82 | 1.05 | 32.0 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.49 | 25.78 | 24.52 | 1.26 | 19.5 | 102.7 | 7.30 | 7.81 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 28.5 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.31 | 6.41 | 5.82 | 0.59 | 9.9 | 36.6 | 5.69 | 3.54 | 0.44 | 0.98 | 23.6 | ||||||||||||
Table 2 REE compositions (10-6) and characteristic values of gold-bearing pyrite in the Luoshan gold deposit
| 样品 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 2.94 | 4.96 | 0.50 | 1.67 | 0.24 | 0.037 | 0.215 | 0.014 | 0.079 | 0.011 | 0.032 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.003 | ||||||||
| LS13D066B1 | 11.60 | 21.20 | 2.29 | 7.73 | 1.12 | 0.101 | 0.816 | 0.082 | 0.310 | 0.033 | 0.113 | 0.011 | 0.106 | 0.014 | |||||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 5.06 | 8.99 | 0.89 | 2.95 | 0.40 | 0.046 | 0.353 | 0.038 | 0.157 | 0.023 | 0.050 | 0.009 | 0.048 | 0.011 | |||||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.57 | 1.04 | 0.11 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.025 | 0.053 | 0.012 | 0.030 | 0.005 | 0.011 | — | 0.008 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 4.81 | 8.80 | 0.93 | 3.57 | 0.52 | 0.077 | 0.393 | 0.051 | 0.231 | 0.035 | 0.085 | 0.013 | 0.071 | 0.014 | |||||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 6.71 | 11.90 | 1.35 | 4.86 | 0.62 | 0.082 | 0.455 | 0.048 | 0.214 | 0.029 | 0.080 | 0.010 | 0.064 | 0.011 | |||||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 3.58 | 6.40 | 0.64 | 2.24 | 0.32 | 0.031 | 0.221 | 0.019 | 0.074 | 0.008 | 0.024 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 1.92 | 3.16 | 0.35 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 0.023 | 0.128 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 0.009 | 0.021 | 0.004 | 0.021 | — | ||||||||
| LS13D021B1 | 5.47 | 8.89 | 1.00 | 3.56 | 0.59 | 0.049 | 0.484 | 0.046 | 0.171 | 0.020 | 0.048 | 0.005 | 0.039 | 0.003 | |||||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 5.06 | 8.71 | 1.00 | 3.71 | 0.63 | 0.208 | 0.506 | 0.072 | 0.314 | 0.057 | 0.154 | 0.022 | 0.159 | 0.019 | |||||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 2.44 | 5.04 | 0.57 | 2.21 | 0.39 | 0.075 | 0.202 | 0.018 | 0.069 | 0.007 | 0.021 | — | 0.008 | — | |||||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 6.73 | 11.70 | 1.22 | 4.18 | 0.60 | 0.092 | 0.444 | 0.050 | 0.152 | 0.017 | 0.054 | 0.005 | 0.047 | 0.005 | |||||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 1.48 | 2.72 | 0.31 | 1.12 | 0.17 | 0.021 | 0.124 | 0.013 | 0.061 | 0.013 | 0.039 | 0.004 | 0.029 | — | |||||||||
| 样品 | Y | ΣREE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | δEu | δCe | Y/Ho | ||||||||||||
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.24 | 10.96 | 10.35 | 0.61 | 17.0 | 117.2 | 7.91 | 9.88 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 21.4 | |||||||||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.85 | 46.38 | 44.04 | 2.34 | 18.8 | 78.5 | 6.69 | 6.37 | 0.32 | 1.01 | 25.8 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 0.53 | 19.55 | 18.33 | 1.22 | 15.1 | 75.6 | 8.21 | 6.08 | 0.38 | 1.04 | 23.0 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.20 | 2.54 | 2.22 | 0.32 | 7.0 | 51.3 | 5.43 | 5.48 | 1.27 | 1.00 | 39.2 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 1.00 | 20.60 | 18.71 | 1.89 | 9.9 | 48.6 | 5.90 | 4.58 | 0.52 | 1.02 | 28.6 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.85 | 27.29 | 25.52 | 1.76 | 14.5 | 75.2 | 7.00 | 5.88 | 0.47 | 0.97 | 29.4 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.21 | 13.79 | 13.21 | 0.58 | 22.7 | 151.1 | 7.20 | 10.75 | 0.36 | 1.04 | 26.6 | ||||||||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.20 | 7.27 | 6.83 | 0.45 | 15.3 | 65.6 | 6.02 | 5.04 | 0.43 | 0.95 | 22.7 | |||||||||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.52 | 20.90 | 19.56 | 1.34 | 14.6 | 100.6 | 5.99 | 10.27 | 0.28 | 0.93 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 1.58 | 22.20 | 19.32 | 2.88 | 6.7 | 22.8 | 5.21 | 2.63 | 1.13 | 0.95 | 27.7 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.22 | 11.27 | 10.72 | 0.55 | 19.5 | 218.8 | 4.04 | 20.89 | 0.82 | 1.05 | 32.0 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.49 | 25.78 | 24.52 | 1.26 | 19.5 | 102.7 | 7.30 | 7.81 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 28.5 | ||||||||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.31 | 6.41 | 5.82 | 0.59 | 9.9 | 36.6 | 5.69 | 3.54 | 0.44 | 0.98 | 23.6 | ||||||||||||
| 样品 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.124 | 0.091 | 0.356 | 1.39 | 1.53 | 105.0 | 486 | 648 | 805 | 0.69 | 2.04 | 6.65 | |||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.088 | 0.075 | 0.881 | 7.11 | 0.73 | 82.6 | 21.9 | 292 | 1 357 | 1.27 | 3.57 | 15.80 | ||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 0.172 | 0.059 | 0.634 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 15.8 | 28.2 | 515 | 1 076 | 0.95 | 4.22 | 6.09 | ||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.108 | 0.028 | 0.510 | 0.59 | 1.12 | 8.5 | 30.2 | 581 | 2 265 | 0.75 | 2.93 | 2.80 | ||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 0.089 | 0.056 | 0.912 | 2.07 | 7.03 | 71.8 | 254 | 545 | 529 | 0.77 | 4.18 | 11.50 | ||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.032 | 0.099 | 0.396 | 0.50 | 2.32 | 41.0 | 124 | 730 | 108 | 0.58 | 2.25 | 4.54 | ||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.070 | 0.043 | 0.622 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 34.9 | 171 | 461 | 55.4 | 0.50 | 1.95 | 10.60 | ||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.062 | 0.015 | 0.203 | 2.56 | 0.14 | 12.3 | 151 | 537 | 613 | 0.65 | 2.77 | 8.84 | |||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.053 | 0.042 | 0.187 | 5.26 | 0.30 | 52.1 | 76.8 | 309 | 1 504 | 0.63 | 2.46 | 5.55 | ||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 0.086 | 0.044 | 0.368 | 8.22 | 1.07 | 264.0 | 83.1 | 581 | 441 | 0.92 | 3.49 | 14.80 | ||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.115 | 0.103 | 0.328 | 0.31 | 0.92 | 21.2 | 33.0 | 481 | 44 | 0.33 | 0.83 | 7.44 | ||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.090 | 0.120 | 0.471 | 0.74 | 1.51 | 513.0 | 175 | 850 | 30 | 0.73 | 3.00 | 2.55 | ||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.079 | 0.101 | 0.259 | 0.32 | 1.18 | 312.0 | 292 | 1 809 | 191 | 0.33 | 0.81 | 3.73 | ||||||
| 华北陆壳 | 13 | 1.0 | 18 | 110 | 84 | 22 | 40 | 30 | 74 | 18.2 | 92 | 330 | ||||||
| 样品 | Y | Mo | Cd | In | Sb | Cs | Ba | W | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | ||||||
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 4.75 | 0.082 | 1.21 | 0.012 | 83.0 | 0.19 | 0.021 | 2 146 | 1.64 | 0.44 | |||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 11.60 | 0.256 | 1.72 | 0.020 | 15.5 | 0.60 | 0.027 | 1 955 | 1.61 | 3.88 | ||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 9.14 | 0.205 | 5.76 | 0.025 | 53.2 | 0.23 | 0.064 | 3 720 | 4.04 | 1.29 | ||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.20 | 1.39 | 18.60 | 0.218 | 2.71 | 0.016 | 38.4 | 0.05 | 0.033 | 6 228 | 2.36 | 0.11 | ||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 3.91 | 0.311 | 1.53 | 0.022 | 30.2 | 0.19 | 0.021 | 3 097 | 2.31 | 3.75 | ||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.85 | 1.15 | 0.33 | 0.185 | 0.69 | 0.010 | 6.7 | 0.10 | 0.016 | 609 | 6.30 | 1.92 | ||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.21 | 2.89 | 0.33 | 0.113 | 1.30 | 0.012 | 159.0 | 0.05 | 0.033 | 630 | 3.25 | 0.66 | ||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 4.61 | 0.143 | 2.14 | 0.017 | 21.9 | 2.29 | 0.024 | 3 716 | 2.76 | 0.58 | |||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.52 | 0.12 | 11.80 | 0.186 | 2.53 | 0.017 | 19.7 | 0.18 | 0.023 | 4 511 | 2.42 | 2.14 | ||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 1.58 | 0.28 | 3.28 | 0.034 | 1.04 | 0.028 | 179.0 | 0.24 | 0.035 | 4 604 | 50.00 | 0.82 | ||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.22 | 0.90 | 0.33 | 0.245 | 0.31 | 0.011 | 56.7 | 0.04 | 0.004 | 191 | 2.50 | 0.04 | ||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.49 | 1.68 | 0.16 | 0.136 | 0.73 | 0.017 | 9.0 | 0.06 | 0.020 | 147 | 5.34 | 0.94 | ||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.31 | 3.70 | 2.12 | 0.930 | 0.63 | 0.008 | 2.7 | 0.05 | 0.016 | 1 792 | 104.00 | 0.16 | ||||||
| 华北陆壳 | 17 | 0.5 | 80 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 1.4 | 690 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 13 | 0.14 | 5.0 | ||||||
| 样品 | U | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Co/Ni | Nb/Ta | Zr/Hf | Hf/Sm | Th/La | Nb/La | |||||||
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.38 | 0.045 | 0.002 | 3.20 | 0.127 | 0.22 | 22.5 | 25.2 | 0.53 | 0.15 | 0.02 | ||||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.55 | 0.579 | 0.021 | 8.32 | 0.391 | 3.77 | 27.6 | 21.3 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.05 | |||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 1.83 | 0.302 | 0.012 | 3.64 | 0.111 | 0.56 | 25.2 | 32.8 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.06 | |||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.04 | 0.040 | 0.003 | 0.85 | 0.026 | 0.28 | 13.3 | 32.5 | 0.38 | 0.20 | 0.07 | |||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 1.01 | 0.133 | 0.006 | 6.31 | 0.258 | 0.28 | 22.2 | 24.5 | 0.49 | 0.78 | 0.03 | |||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.37 | 0.046 | — | 3.77 | 0.107 | 0.33 | — | 35.2 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 0.01 | |||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.15 | 0.013 | — | 1.34 | 0.040 | 0.20 | — | 33.5 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.00 | |||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.20 | * | * | * | * | 0.08 | — | — | — | 0.30 | — | ||||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.34 | * | * | * | * | 0.68 | — | — | — | 0.39 | — | |||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 0.24 | * | * | * | * | 3.18 | — | — | — | 0.16 | — | |||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.02 | 0.013 | — | 0.18 | — | 0.64 | — | — | — | 0.02 | 0.01 | |||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.15 | 0.121 | 0.007 | 5.20 | 0.173 | 2.93 | 17.3 | 30.1 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.02 | |||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.62 | 0.129 | 0.010 | 0.47 | 0.019 | 1.07 | 12.9 | 24.9 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 华北陆壳 | 1.0 | 12 | 0.8 | 162 | 4.5 | |||||||||||||
Table 3 Trace element abundances (10-6) and characteristic values of gold-bearing pyrite in the Luoshan gold deposit
| 样品 | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.124 | 0.091 | 0.356 | 1.39 | 1.53 | 105.0 | 486 | 648 | 805 | 0.69 | 2.04 | 6.65 | |||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.088 | 0.075 | 0.881 | 7.11 | 0.73 | 82.6 | 21.9 | 292 | 1 357 | 1.27 | 3.57 | 15.80 | ||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 0.172 | 0.059 | 0.634 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 15.8 | 28.2 | 515 | 1 076 | 0.95 | 4.22 | 6.09 | ||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.108 | 0.028 | 0.510 | 0.59 | 1.12 | 8.5 | 30.2 | 581 | 2 265 | 0.75 | 2.93 | 2.80 | ||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 0.089 | 0.056 | 0.912 | 2.07 | 7.03 | 71.8 | 254 | 545 | 529 | 0.77 | 4.18 | 11.50 | ||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.032 | 0.099 | 0.396 | 0.50 | 2.32 | 41.0 | 124 | 730 | 108 | 0.58 | 2.25 | 4.54 | ||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.070 | 0.043 | 0.622 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 34.9 | 171 | 461 | 55.4 | 0.50 | 1.95 | 10.60 | ||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.062 | 0.015 | 0.203 | 2.56 | 0.14 | 12.3 | 151 | 537 | 613 | 0.65 | 2.77 | 8.84 | |||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.053 | 0.042 | 0.187 | 5.26 | 0.30 | 52.1 | 76.8 | 309 | 1 504 | 0.63 | 2.46 | 5.55 | ||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 0.086 | 0.044 | 0.368 | 8.22 | 1.07 | 264.0 | 83.1 | 581 | 441 | 0.92 | 3.49 | 14.80 | ||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.115 | 0.103 | 0.328 | 0.31 | 0.92 | 21.2 | 33.0 | 481 | 44 | 0.33 | 0.83 | 7.44 | ||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.090 | 0.120 | 0.471 | 0.74 | 1.51 | 513.0 | 175 | 850 | 30 | 0.73 | 3.00 | 2.55 | ||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.079 | 0.101 | 0.259 | 0.32 | 1.18 | 312.0 | 292 | 1 809 | 191 | 0.33 | 0.81 | 3.73 | ||||||
| 华北陆壳 | 13 | 1.0 | 18 | 110 | 84 | 22 | 40 | 30 | 74 | 18.2 | 92 | 330 | ||||||
| 样品 | Y | Mo | Cd | In | Sb | Cs | Ba | W | Tl | Pb | Bi | Th | ||||||
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 4.75 | 0.082 | 1.21 | 0.012 | 83.0 | 0.19 | 0.021 | 2 146 | 1.64 | 0.44 | |||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.85 | 0.76 | 11.60 | 0.256 | 1.72 | 0.020 | 15.5 | 0.60 | 0.027 | 1 955 | 1.61 | 3.88 | ||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 9.14 | 0.205 | 5.76 | 0.025 | 53.2 | 0.23 | 0.064 | 3 720 | 4.04 | 1.29 | ||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.20 | 1.39 | 18.60 | 0.218 | 2.71 | 0.016 | 38.4 | 0.05 | 0.033 | 6 228 | 2.36 | 0.11 | ||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 3.91 | 0.311 | 1.53 | 0.022 | 30.2 | 0.19 | 0.021 | 3 097 | 2.31 | 3.75 | ||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.85 | 1.15 | 0.33 | 0.185 | 0.69 | 0.010 | 6.7 | 0.10 | 0.016 | 609 | 6.30 | 1.92 | ||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.21 | 2.89 | 0.33 | 0.113 | 1.30 | 0.012 | 159.0 | 0.05 | 0.033 | 630 | 3.25 | 0.66 | ||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 4.61 | 0.143 | 2.14 | 0.017 | 21.9 | 2.29 | 0.024 | 3 716 | 2.76 | 0.58 | |||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.52 | 0.12 | 11.80 | 0.186 | 2.53 | 0.017 | 19.7 | 0.18 | 0.023 | 4 511 | 2.42 | 2.14 | ||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 1.58 | 0.28 | 3.28 | 0.034 | 1.04 | 0.028 | 179.0 | 0.24 | 0.035 | 4 604 | 50.00 | 0.82 | ||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.22 | 0.90 | 0.33 | 0.245 | 0.31 | 0.011 | 56.7 | 0.04 | 0.004 | 191 | 2.50 | 0.04 | ||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.49 | 1.68 | 0.16 | 0.136 | 0.73 | 0.017 | 9.0 | 0.06 | 0.020 | 147 | 5.34 | 0.94 | ||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.31 | 3.70 | 2.12 | 0.930 | 0.63 | 0.008 | 2.7 | 0.05 | 0.016 | 1 792 | 104.00 | 0.16 | ||||||
| 华北陆壳 | 17 | 0.5 | 80 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 1.4 | 690 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 13 | 0.14 | 5.0 | ||||||
| 样品 | U | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Co/Ni | Nb/Ta | Zr/Hf | Hf/Sm | Th/La | Nb/La | |||||||
| 蚀 变 岩 型 矿 石 | LS13D063B1 | 0.38 | 0.045 | 0.002 | 3.20 | 0.127 | 0.22 | 22.5 | 25.2 | 0.53 | 0.15 | 0.02 | ||||||
| LS13D066B1 | 0.55 | 0.579 | 0.021 | 8.32 | 0.391 | 3.77 | 27.6 | 21.3 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.05 | |||||||
| LS13D067B1 | 1.83 | 0.302 | 0.012 | 3.64 | 0.111 | 0.56 | 25.2 | 32.8 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.06 | |||||||
| LS13D067B2 | 0.04 | 0.040 | 0.003 | 0.85 | 0.026 | 0.28 | 13.3 | 32.5 | 0.38 | 0.20 | 0.07 | |||||||
| LS13D068B1 | 1.01 | 0.133 | 0.006 | 6.31 | 0.258 | 0.28 | 22.2 | 24.5 | 0.49 | 0.78 | 0.03 | |||||||
| LS13D071B2 | 0.37 | 0.046 | — | 3.77 | 0.107 | 0.33 | — | 35.2 | 0.17 | 0.29 | 0.01 | |||||||
| LS13D073B1 | 0.15 | 0.013 | — | 1.34 | 0.040 | 0.20 | — | 33.5 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.00 | |||||||
| 石 英 脉 型 矿 石 | LS13D020B1 | 0.20 | * | * | * | * | 0.08 | — | — | — | 0.30 | — | ||||||
| LS13D021B1 | 0.34 | * | * | * | * | 0.68 | — | — | — | 0.39 | — | |||||||
| LS13D029B2 | 0.24 | * | * | * | * | 3.18 | — | — | — | 0.16 | — | |||||||
| LS13D070B13 | 0.02 | 0.013 | — | 0.18 | — | 0.64 | — | — | — | 0.02 | 0.01 | |||||||
| LS13D071B1 | 0.15 | 0.121 | 0.007 | 5.20 | 0.173 | 2.93 | 17.3 | 30.1 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.02 | |||||||
| LS13D087B1 | 0.62 | 0.129 | 0.010 | 0.47 | 0.019 | 1.07 | 12.9 | 24.9 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.09 | |||||||
| 华北陆壳 | 1.0 | 12 | 0.8 | 162 | 4.5 | |||||||||||||

Fig.7 Spider diagrams of trace elements in gold-bearing pyrite from the Luoshan gold deposit (Trace element values of North China continental crust from reference[48])

Fig.9 Trace elements concentrations in gold-bearing pyrite from the Luoshan gold deposit (The diamond points in the middle of the bar and above the bar are the average values and far outliers, respectively. The triangle points and circle points are the average values of trace ele-ments contents in pyrite respectively from magmatic and metamorphic hydrothermal gold deposits, which are defined after reference[68])
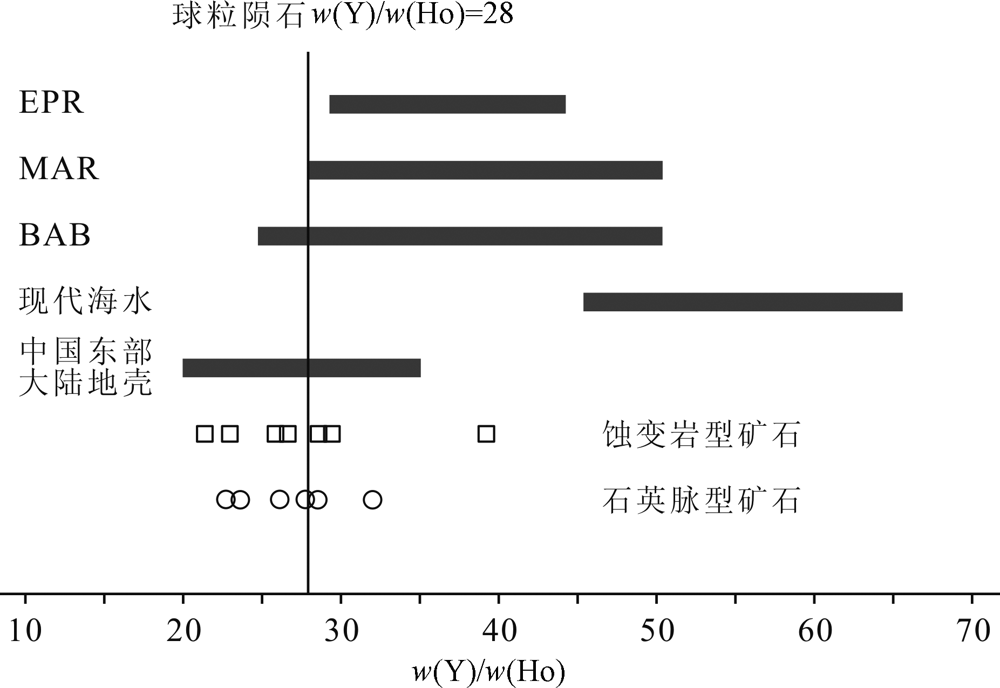
Fig.10 Y/Ho ratios of gold-bearing pyrite in Luoshan gold deposit, modern submarine hydrothermal fluids and seawater (Data of hydrothermal fluids, modern seawater and continental crust of East China are defined after refe-rences [48] and [71-73])
| [1] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, YANG L Q, et al. The structure of ore-controlling strain and stress fields in the Shangzhuang gold deposit in Shandong Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2008,82(4):769-780.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(9):2447-2467. |
| [3] |
GOLDFARB R J, SANTOSH M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2014,5(2):139-153.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DENG J, WANG Q F, LI G J, et al. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014,138:268-299.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
YANG L Q, DENG J, GUO R P, et al. World-class Xincheng gold deposit: an example from the giant Jiaodong gold province[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2016,7(3):419-430.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
DENG J, YANG L Q, SUN Z S, et al. A metallogenic model of gold deposits of the Jiaodong granite-greenstone belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2003,77(4):537-546.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI L, SANTOSH M, LI S R. The ‘Jiaodong type’ gold deposits: Characteristics, origin and prospecting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,65:589-611.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SONG M C, LI S Z, SANTOSH M, et al. Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,65:612-625.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
QIU Y, GROVES D I, MCNAUGHTON N J, et al. Nature, age, and tectonic setting of granitoid-hosted, orogenic gold deposits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China craton, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002,37(3):283-305.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YANG L Q, DENG J, GOLDFARB R J, et al. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit: New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014,25(4):1469-1483.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
YANG L Q, DENG J, WANG Z L, et al. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment[J]. Economic Geology, 2016,111(1):105-126.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
YANG L Q, DENG J, WANG Z L, et al. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong metamorphic core complex and implications for gold mineralization: A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016,72:165-178.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
WANG Z L, YANG L Q, GUO L N, et al. Fluid immiscibility and gold deposition in the Xincheng deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A fluid inclusion study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,65:701-717.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
DENG J, WANG Q F. Gold mineralization in China: Metalloge-nic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016,36:219-274.
DOI URL |
| [15] | HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers, 1984: 1-510. |
| [16] | THOMAS H V, LARGE R R, BULL S W, et al. Pyrite and pyrrhotite textures and composition in sediments, laminated quartz veins, and reefs at Bendigo gold mine, Australia: Insights for ore genesis[J]. Economic Geology, 2011,106(1):1-31. |
| [17] |
ZHENG Y, ZHANG L, CHEN Y J, et al. Metamorphosed Pb-Zn-(Ag) ores of the Keketale VMS deposit, NW China: Evidence from ore textures, fluid inclusions, geochronology and pyrite compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013,54(8):167-180.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
GUO L N, GOLDFARB R J, WANG Z L, et al. A comparison of Jiaojia-and Linglong-type gold deposit ore-forming fluids: do they differ?[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017,88:511-533.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WALLIS S, ENAMI M, BANNO S. The Sulu UHP terrane: A review of the petrology and structural geology[J]. International Geology Review, 1999,41(10):906-920.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
TANG J, ZHENG Y F, WU Y B, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane: Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogeny[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007,152(s1/2):48-82.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DENG J, WANG Q, WAN L, et al. A multifractal analysis of mineralization characteristics of the Dayingezhuang disseminated-veinlet gold deposit in the Jiaodong gold province of China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011,40(1):54-64.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
JAHN B, LIU D Y, WAN Y S, et al. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry[J]. American Journal of Science, 2008,308(3):232-269.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GENG Y S, DU L L, REN L D. Growth and reworking of the early Precambrian continental crust in the North China Craton: constraints from zircon Hf isotopes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012,21(2):517-529.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 董春艳, 王世进, 刘敦一, 等. 华北克拉通古元古代晚期地壳演化和荆山群形成时代制约——胶东地区变质中-基性侵入岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(6):1699-1706. |
| [25] | 李旭平, 刘云, 郭敬辉, 等. 胶北南山口古元古代高压基性麻粒岩和钙硅酸盐岩的岩石地球化学特征探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(7):2340-2352. |
| [26] |
TAM P Y, ZHAO G C, LIU F L, et al. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt: new SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites, gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011,19(1):150-162.
DOI URL |
| [27] | TAM P Y, ZHAO G, SUN M, et al. Metamorphic P-T, path and tectonic implications of medium-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2012,155(1):177-191. |
| [28] | 刘建辉, 刘福来, 丁正江, 等. 胶北~2.5 Ga岩浆热事件的锆石Hf同位素特征及其对地壳演化的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(9):2697-2704. |
| [29] | 初航, 陆松年, 王惠初, 等. 山东长岛地区蓬莱群辅子夼组碎屑锆石年龄谱研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011,27(4):1017-1028. |
| [30] |
FAURE M, LIN W, MONIE P, et al. Paleoproterozoic arc magmatism, collision in Liaodong Peninsula (north-east China)[J]. Terra Nova, 2004,16:75-80.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ZHANG J, ZHAO Z F, ZHENG Y F, et al. Postcollisional magmatism: geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen, China[J]. Lithos, 2010,119(3):512-536.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
WANG L G, QIU Y M, MCNAUGHTON N J, et al. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the Northwestern Jiao-dong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998,13(1):275-291.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, 等. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞—碰撞后构造过程:锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(4):1281-1301. |
| [34] |
HOU M L, JIANG Y H, JIANG S Y, et al. Contrasting origins of late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, east China: implications for crustal thickening to delamination[J]. Geological Magazine, 2007,144(4):619-631.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LI S R, SANTOSH M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: records from the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,56(1):376-414.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LI L, LI S R, SANTOSH M, et al. Dyke swarms and their role in the genesis of world-class gold deposits: insights from the Jiao-dong peninsula, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016,130, 2-22.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
WANG Z L, YANG L Q, DENG J, et al. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014,95:274-299.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 刘跃, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶西北新城金矿床二长花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(9):2559-2573. |
| [39] |
FAURE M, LIN W, CHEN Y. Is the Jurassic (Yanshanian) intraplate tectonics of North China due to westward indentation of the North China block?[J]. Terra Nova, 2012,24(6):456-466.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHU G, NIU M L, XIE C L, et al. Sinistral to normal faulting along the Tan-Lu fault zone: Evidence for geodynamic switching of the East China continental margin[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2010,118(3):277-293.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
DENG J, WANG C M, BAGAS L, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2015,50(8):987-1006.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
YANG L Q, DENG J, GUO L N, et al. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016,72:585-602.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
WEN B J, FAN H R, SANTOSH M, et al. Genesis of two diffe-rent types of gold mineralization in the Linglong gold field, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and stable isotope[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,65:643-658.
DOI URL |
| [44] | 陈光远, 孙岱生, 周珣若, 等. 胶东郭家岭花岗闪长岩成因矿物学与金矿化[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1993: 1-242. |
| [45] |
LU H Z, ARCHAMBAULT G, LI Y S, et al. Structural geochemistry of gold mineralization in the Linglong-Jiaojia district, Shandong Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2007,26(3):215-234.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
YANG Q Y, SHEN J F, LI S R, et al. Oxygen, boron, chromium and niobium enrichment in native Au and Ag grains: A case study from the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong, eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013,62:537-546.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systema-tics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345.
DOI URL |
| [48] | 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-114. |
| [49] |
WOOD S A, WILLIAMS-JONES A E. The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium: IV. Monazite solubility and REE mobility in exhalative massive sulfide-depositing environments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994,115(1/2):47-60.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
WANG Q F, DENG J, HUANG D H, et al. Deformation model for the Tongling ore cluster region,east-central China[J]. International Geology Review, 2011,53(5/6):562-579.
DOI URL |
| [51] | 李厚民, 沈远超, 毛景文, 等. 石英、黄铁矿及其包裹体的稀土元素特征——以胶东焦家式金矿为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2003,19(2):267-274. |
| [52] | MAO G, HUA R, GAO J, et al. Existing forms of REE in gold-bearing pyrite of the Jinshan gold deposit,Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Rare Earths (English Edition), 2009,27(6):1079-1087. |
| [53] | 韩吟文, 马振东, 张宏飞, 等. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 1-370. |
| [54] |
HAAS J R, SHOCK E L, SASSANI D C. Rare earth elements in hydrothermal systems: estimates of standard partial modal thermodynamic properties of aqueous complexes of the rare earth elements at high pressures and temperatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995,59:4329-4350.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
KEPPLER H. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction zone fluids[J]. Nature, 1996,380:237-240.
DOI URL |
| [56] | 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等. 黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体性质的指示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2004,23(1):1-4. |
| [57] |
ORESKES N, EINAUDI M T. Origin of rare earth element-enriched hematite breccias at the Olympic Dam Cu-U-Au-Ag deposit, Roxby Downs, South Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 1990,85:1-28.
DOI URL |
| [58] | 安芳, 朱永峰. 新疆西准噶尔包古图金矿微量元素地球化学研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014,33(2):329-342. |
| [59] |
DENG J, LIU X, WANG Q, et al. Origin of the Jiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,65:674-686.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
周国发, 吕古贤, 邓军, 等. 山东三山岛金矿床流体包裹体特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008,22(1):24-33.
DOI URL |
| [61] | 郭春影, 高帮飞, 张静, 等. 胶东半岛大磨曲家金矿床成矿流体物理化学条件演化[J]. 现代地质, 2008,22(5):743-750. |
| [62] | BRILL B A. Trace-element contents and partitioning of elements in ore minerals from the CSA Cu-Pb-Zn deposit, Australia[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 1989,27(7):263-274. |
| [63] | BRALIA A, SABATINI G, TROJA F. A revaluation of the Co/Ni ratio in pyrite as geochemical tool in ore genesis problems[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1979,14(3):353-374. |
| [64] |
FAN H R, ZHAI M G, XIE Y H, et al. Ore-forming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003,38(6):739-750.
DOI URL |
| [65] | 郭林楠, 张潮, 宋宇宙, 等. 胶东望儿山金矿床氢-氧同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014,30(9):2481-2494. |
| [66] |
YANG L Q, GUO L N, WANG Z L, et al. Timing and mechanism of gold mineralization at the Wang’ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017,88:491-510.
DOI URL |
| [67] | 严育通, 李胜荣, 贾宝剑, 等. 中国不同成因类型金矿床的黄铁矿成分标型特征及统计分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2012,19(4):214-226. |
| [68] |
YAN Y T, ZHANG N, LI S R, et al. Mineral chemistry and isotope geochemistry of pyrite from the Heilangou gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2014,5(2):205-213.
DOI URL |
| [69] | BAJWAH Z U, SECCOMBE P K, OFFLER R. Trace element distribution, Co∶Ni ratios and genesis of the Big Cadia iron-copper deposit, New South Wales, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1987,22(4):292-300. |
| [70] | 郭林楠. 胶东型金矿床成矿机理[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2016: 1-182. |
| [71] |
BAU M, DULSKI P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995,119(2):213-223.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
BAU M, MÕLER P, DULSKI P. Yttrium and lanthanides in eastern Mediterranean seawater and their fractionation during redox-cycling[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1997,56(1/2):123-131.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
DOUVILLE E, BIENVENU P, CHARLOU J L, et al. Yttrium and rare-earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999,63(5):627-643.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
NOZAKI Y, ZHANG J, AMAKAWA H. The fractionation between Y and Ho in the marine environment[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997,148(1/2):329-340.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
GOLDFARB R J, GROVES D I, GARDOLL S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: a global synjournal[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001,18(1):1-75.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
QIU Y M, GROVES D I, MCNAUGHTON N J, et al. Nature, age, and tectonic setting of granitoid-hosted, orogenic gold depo-sits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern North China craton, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002,37(3/4):283-305.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
GOLDFARB R J, HART C, DAVIS G, et al. East Asian gold: deciphering the anomaly of Phanerozoic gold in Precambrian cratons[J]. Economic Geology, 2007,102(3):341-345.
DOI URL |
| [78] | 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2015,45(8):1153-1168. |
| [79] |
LI S R, SANTOSH M. Geodynamics of heterogeneous gold minera-lization in the North China Craton and its relationship to lithospheric destruction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017,50, 267-292.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
YAXLEY G M, GREEN D H, KAMENETSKY V. Carbonatite metasomatism in the southeastern Australian lithosphere[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998,39(11/12):1917-1930.
DOI URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||