



现代地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (02): 269-286.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2023.066
黄向青1,2( ), 梁开1,2, 马胜中1,2(
), 梁开1,2, 马胜中1,2( ), 袁晓婕1,2, 潘毅1
), 袁晓婕1,2, 潘毅1
收稿日期:2022-09-05
修回日期:2023-06-22
出版日期:2024-04-10
发布日期:2024-05-22
通讯作者:
马胜中,男,正高级工程师,1968年出生,地球物理探测专业,从事地质环境综合调查和研究。Email: sz-ma@163.com。
作者简介:黄向青,女,高级工程师,1964年出生,气象和气候专业,主要从事地质环境调查研究。Email: eegs2007@163.com。
基金资助:
HUANG Xiangqing1,2( ), LIANG Kai1,2, MA Shengzhong1,2(
), LIANG Kai1,2, MA Shengzhong1,2( ), YUAN Xiaojie1,2, PAN Yi1
), YUAN Xiaojie1,2, PAN Yi1
Received:2022-09-05
Revised:2023-06-22
Online:2024-04-10
Published:2024-05-22
摘要:
南海西北部北部湾在地质环境方面与狭义巽他陆架相似而成为一体构成泛巽他,同属青藏高原及其挤出阶梯地貌盆山体系。然而,关于其指示环境变化和碳循环的古泥沼分布及其气候-构造驱动机制、作用与联系等缺乏关注,其研究滞后于上述热点巽他陆架相关进展。为加强对这些内容的认识,本文的研究在北部湾北部华南陆缘沉降带进行了80.05 m进尺第四系全岩心钻取,立足于沉积物微体古生物、粒度、碎屑矿物组分、微量元素含量等基础沉积环境指标的实验测试、鉴定以及测年数据,并结合前人相关资料和结果进行综合分析。结果表明,岩心底部年龄为中更新世后期171.0 ka,孢粉化石呈热带和亚热带植被面貌,主要有栲属、栎属等以及鳞盖蕨属、水龙骨科等,其含量变化显示出3个主要气候变化阶段,与倒数第二冰盛期、末次间冰期、末次冰期以及冰消期等相联系,从56.0 ka始见有半咸水种硅藻化石条纹小环藻、柱状小环藻等,有孔虫化石出现于中全新世6.0 ka接受海进。总体上以砂为主,但局部粉砂和黏土(泥)含量较高,最高依次可达65.78%、59.71%,元素含量为2.6×10-6~347×10-6,碎屑矿物稳定出现石英、长石、风化矿物,以前者占优,平均含量88.57%,余下矿物相间出现,具有陆源性,各要素随气候阶段而变化。存在5个泥沼旋回,沉积环境有所差异,在冰期和间冰期均有分布,出现炭化腐木以及邻区炭化层。青藏高原隆起导致的区域强烈地形落差在中—晚更新世业已构建,盆山体系成为海洋暖湿气流与地形作用的水热有效利用地带,北部湾冰期出露地表古水系广布,森林和草地植被共存,有助于泥沼的维护发展。气候波动性是泥沼的本质驱动因素,除了间冰期之外,冰期的强烈暖阶振荡亦为其成因;泛巽他北部湾在冰期同样具有碳库意义,具有转移与弥补中高纬度生产力衰减之作用。
中图分类号:
黄向青, 梁开, 马胜中, 袁晓婕, 潘毅. 泛巽他盆山体系北部湾古泥沼旋回与古生态效应[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(02): 269-286.
HUANG Xiangqing, LIANG Kai, MA Shengzhong, YUAN Xiaojie, PAN Yi. Palaeo-peat Cycles in Beibu Gulf of Pan-Sunda and Their Palaeo-Ecological Significance Under Plateau-Mountain-Basin Complex Backgrounds[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(02): 269-286.

图1 巽他地块、建议扩展泛巽他部分以及ZK9钻孔取心位置示意图(据文献[1]修改)
Fig.1 Sundaland area, suggested expanded Pan-Sunda (slash lines) and the sediment core ZK9 position in Beibu Gulf (modified after reference [1])
| 样品编号 | 深度(m) | 材料 | 14C年龄(a BP) | 校正年龄(cal a BP) | 年龄范围(2σ)(cal a BP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.2~2.3 | 沉积物 | 8590 ± 220 | 9567 | 9075~10059 |
| 2 | 5.2~5.3 | 沉积物 | 10110 ± 210 | 11394 | 10890~11897 |
| 3 | 10.1~10.3 | 沉积物 | 11598 ± 510 | 13182 | 13039~13325 |
表1 北部湾ZK9岩心14C测年结果
Table 1 14C dating data of the sediment core ZK9 in Beibu Gulf
| 样品编号 | 深度(m) | 材料 | 14C年龄(a BP) | 校正年龄(cal a BP) | 年龄范围(2σ)(cal a BP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.2~2.3 | 沉积物 | 8590 ± 220 | 9567 | 9075~10059 |
| 2 | 5.2~5.3 | 沉积物 | 10110 ± 210 | 11394 | 10890~11897 |
| 3 | 10.1~10.3 | 沉积物 | 11598 ± 510 | 13182 | 13039~13325 |
| 样品 编号 | 深度 (m) | 材料 | 铀 (μg/g) | 钍 (μg/g) | K2O (%) | 年龄 (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 20.1~20.3 | 沉积物 | 1.97 | 7.31 | 1.2118 | 62±6 |
| 5 | 20.7~20.9 | 沉积物 | 3.74 | 10.40 | 1.5023 | 66±7 |
| 6 | 25.0~25.1 | 沉积物 | 3.28 | 20.50 | 1.494 | 103±10 |
| 7 | 45.2~45.3 | 沉积物 | 2.36 | 14.20 | 1.8592 | 120±12 |
| 8 | 54.1~54.2 | 沉积物 | 3.01 | 5.11 | 1.2107 | 150±15 |
| 9 | 79.7~79.8 | 沉积物 | 3.17 | 5.15 | 1.2201 | 171±17 |
表2 北部湾ZK9岩心OSL测年结果
Table 2 Luminescence dating data of the sediment core ZK9 in Beibu Gulf
| 样品 编号 | 深度 (m) | 材料 | 铀 (μg/g) | 钍 (μg/g) | K2O (%) | 年龄 (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 20.1~20.3 | 沉积物 | 1.97 | 7.31 | 1.2118 | 62±6 |
| 5 | 20.7~20.9 | 沉积物 | 3.74 | 10.40 | 1.5023 | 66±7 |
| 6 | 25.0~25.1 | 沉积物 | 3.28 | 20.50 | 1.494 | 103±10 |
| 7 | 45.2~45.3 | 沉积物 | 2.36 | 14.20 | 1.8592 | 120±12 |
| 8 | 54.1~54.2 | 沉积物 | 3.01 | 5.11 | 1.2107 | 150±15 |
| 9 | 79.7~79.8 | 沉积物 | 3.17 | 5.15 | 1.2201 | 171±17 |

图4 北部湾ZK9岩心有孔虫化石丰度(个/20g)和主要属种相对含量(%)分布
Fig.4 Foraminifera fossil abundance (Ind./20g) and relative concentration (%) of the sediment core ZK9 in Beibu Gulf
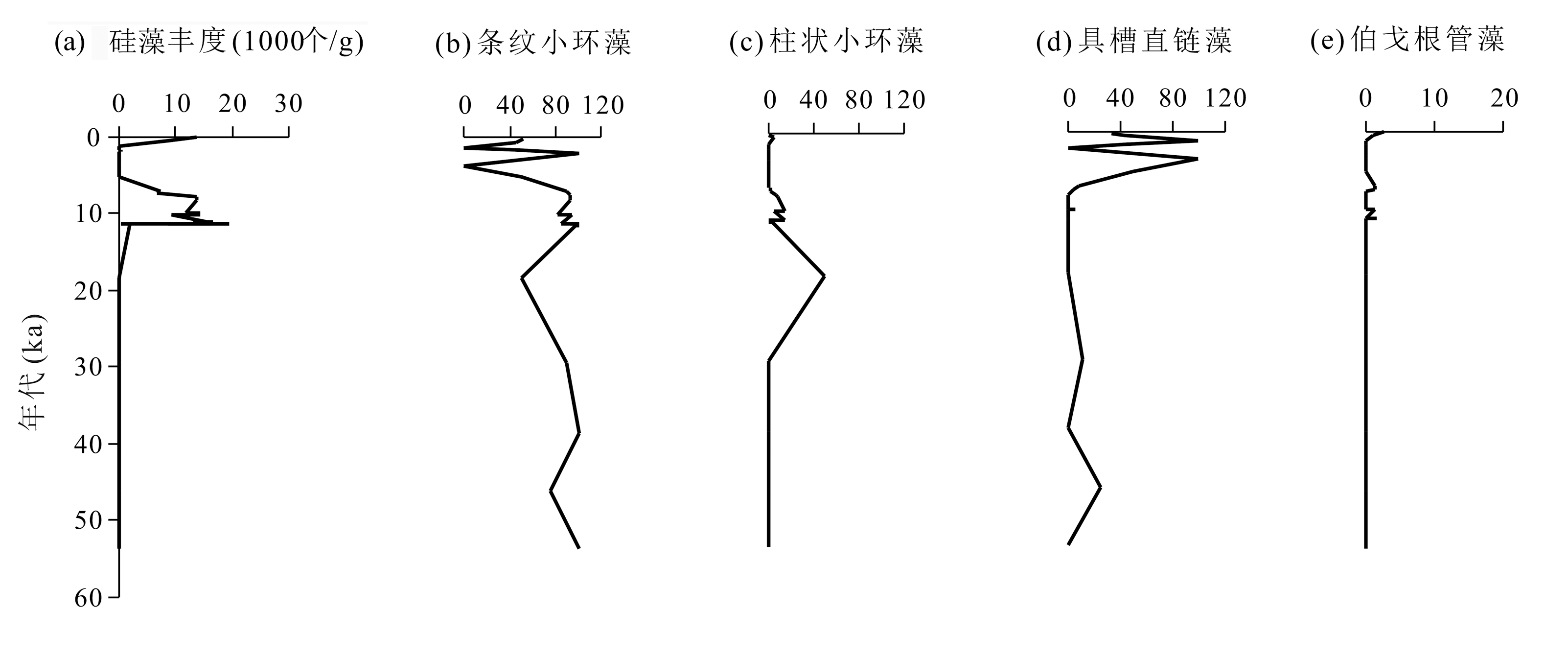
图5 北部湾ZK9岩心硅藻化石丰度(1000个/g)和主要属种含量(%)分布
Fig.5 Diatom fossil abundance (1000 Ind./g) and relative concentration (%) of the sediment core ZK9 in Beibu Gulf
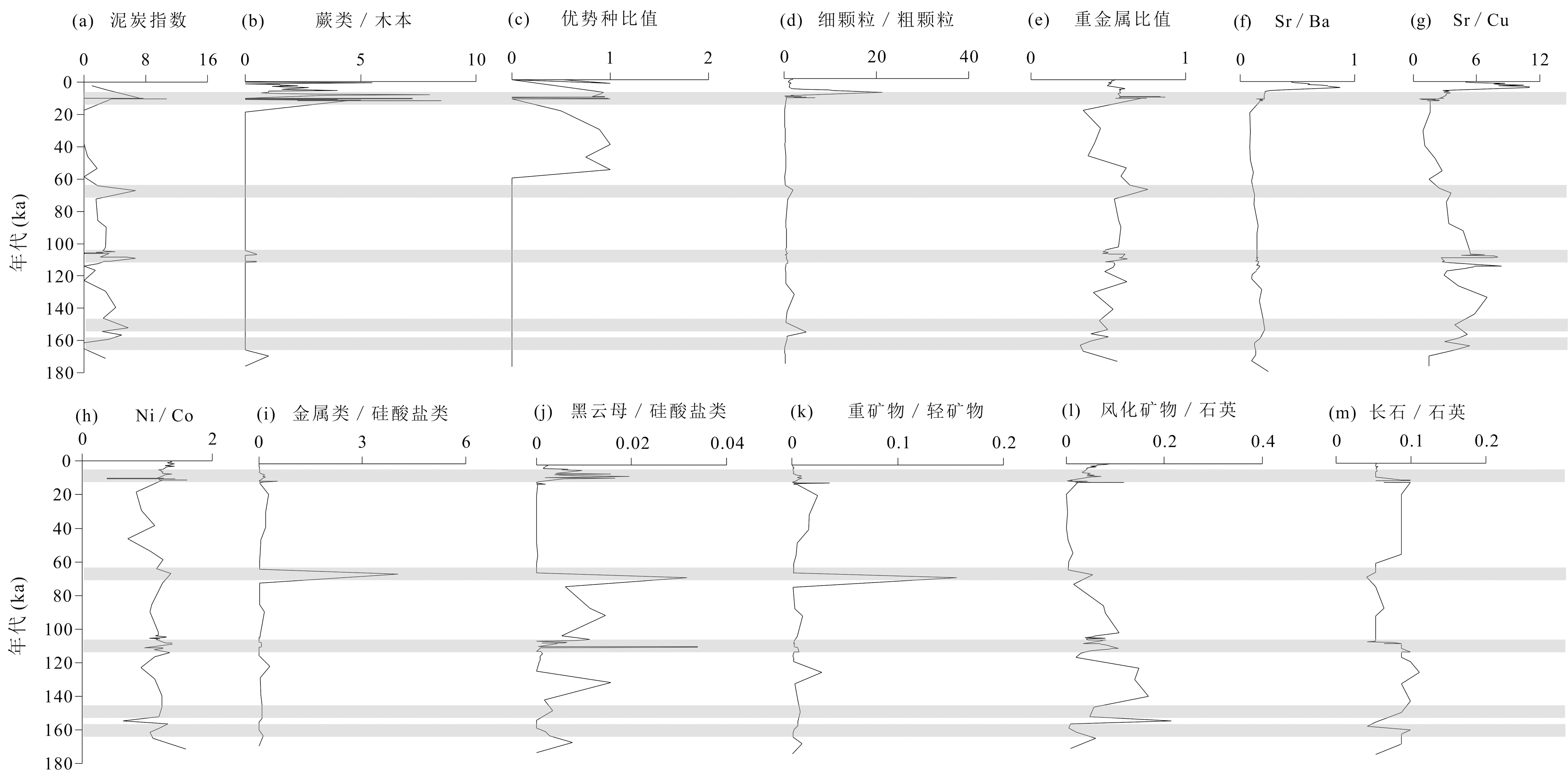
图9 北部湾ZK9岩心泥炭指数以及各比值分布(图中灰条指示泥沼旋回)
Fig.9 Peat index, fern/arboreal, dominant/whole species and other ratios of the sediment core ZK9 (gray bars indicaing peat cycle) in Beibu Gulf
| 泥沼旋回 | 地层岩性 | 要素变化特征 | 沉积环境 |
|---|---|---|---|
| P5 | 全新统底部与上更新统界面为强侵蚀面,自下往上为黏土质砂,再夹杂砂、粉砂、黏土,散见有砾石,往上颗粒总体趋细 | 粉砂、黏土明显升高,颗粒变细,泥沼水动力弱缓导致分选变差。微量元素除了Cr均增加,增幅最大的Ga、Zr平均超过50%,OM亦有较大增幅。褐铁矿和黄铁矿增幅依次为258.4%、77.8% | 孢粉化石有木本、草、藜科以及鳞盖蕨等,气候变暖恢复。Sr/Ba平均值偏低,仅为0.19,未见有孔虫,出现半咸水种条纹小环藻等,为陆相半咸水型河泽环境 |
| P4 | 上更新统以砂为主,间中出现粉砂和中粗砂层理,某些层次可见黑色腐木,以及河流冲积的土黄色粉土团块等 | 粉砂增幅为106.0%,但黏土略为降低,分选较差,峰值变化不大。大部分元素增加,增幅为225.6%~813.6%,Cr、Sr有所降低,OM增幅为223.0%。褐铁矿和黄铁矿显著上升 | 由于前述原因河流冲刷较强,只存有少量孢粉,为栲属、鳞盖蕨,仍可指示气候偏暖。Sr/Ba仅为0.12,见有条纹小环藻,为半咸水型河沼环境 |
| P3 | 砂、粉砂含量依次为47.5%、14.25%,砂、石夹杂并随后出现淤积。Pb、Ga最大增幅均接近73.0%,OM增幅为133.3%。褐铁矿和黄铁矿骤然增加,风化矿物增幅为203.7% | 孢粉有栎属、栲属与松属,见有挱椤属等,指示气候暖湿,未见硅藻和有孔虫,Sr/Ba为0.15,为陆相河沼环境 | |
| P2 | 沉积物底部有砂沉积物,杂有砾石和卵石,出现黏土、粉砂、粗砂互层,某些层段富含黑色有机质,偶见黑色腐木 | P2粉砂大幅增加,分选略为变好。Zn、Zr、Ga和Ba明显增加,最大增幅为62.3%,OM增幅为61.9%。褐铁矿、黄铁矿增幅依次为27.8%、82.5% | 孢粉均有栲属、栎属和蕨类水龙骨科,为阶段性暖湿气候,未见硅藻和有孔虫,Sr/Ba介于0.13~0.17之间,为陆相河沼环境 |
| P1 | P1粉砂增幅为22.5%,分选变差。Cr、Ba增加,增幅平均为39.0%,OM增幅为108.1%。鲕绿泥石、铁铝石榴石亦增加,长石增加了42.0%,石英略为降低 | ? |
表3 北部湾ZK9岩心泥沼旋回的沉积环境特征
Table 3 Sedimentary environment summary for peat series of the sediment core ZK9 in Beibu Gulf
| 泥沼旋回 | 地层岩性 | 要素变化特征 | 沉积环境 |
|---|---|---|---|
| P5 | 全新统底部与上更新统界面为强侵蚀面,自下往上为黏土质砂,再夹杂砂、粉砂、黏土,散见有砾石,往上颗粒总体趋细 | 粉砂、黏土明显升高,颗粒变细,泥沼水动力弱缓导致分选变差。微量元素除了Cr均增加,增幅最大的Ga、Zr平均超过50%,OM亦有较大增幅。褐铁矿和黄铁矿增幅依次为258.4%、77.8% | 孢粉化石有木本、草、藜科以及鳞盖蕨等,气候变暖恢复。Sr/Ba平均值偏低,仅为0.19,未见有孔虫,出现半咸水种条纹小环藻等,为陆相半咸水型河泽环境 |
| P4 | 上更新统以砂为主,间中出现粉砂和中粗砂层理,某些层次可见黑色腐木,以及河流冲积的土黄色粉土团块等 | 粉砂增幅为106.0%,但黏土略为降低,分选较差,峰值变化不大。大部分元素增加,增幅为225.6%~813.6%,Cr、Sr有所降低,OM增幅为223.0%。褐铁矿和黄铁矿显著上升 | 由于前述原因河流冲刷较强,只存有少量孢粉,为栲属、鳞盖蕨,仍可指示气候偏暖。Sr/Ba仅为0.12,见有条纹小环藻,为半咸水型河沼环境 |
| P3 | 砂、粉砂含量依次为47.5%、14.25%,砂、石夹杂并随后出现淤积。Pb、Ga最大增幅均接近73.0%,OM增幅为133.3%。褐铁矿和黄铁矿骤然增加,风化矿物增幅为203.7% | 孢粉有栎属、栲属与松属,见有挱椤属等,指示气候暖湿,未见硅藻和有孔虫,Sr/Ba为0.15,为陆相河沼环境 | |
| P2 | 沉积物底部有砂沉积物,杂有砾石和卵石,出现黏土、粉砂、粗砂互层,某些层段富含黑色有机质,偶见黑色腐木 | P2粉砂大幅增加,分选略为变好。Zn、Zr、Ga和Ba明显增加,最大增幅为62.3%,OM增幅为61.9%。褐铁矿、黄铁矿增幅依次为27.8%、82.5% | 孢粉均有栲属、栎属和蕨类水龙骨科,为阶段性暖湿气候,未见硅藻和有孔虫,Sr/Ba介于0.13~0.17之间,为陆相河沼环境 |
| P1 | P1粉砂增幅为22.5%,分选变差。Cr、Ba增加,增幅平均为39.0%,OM增幅为108.1%。鲕绿泥石、铁铝石榴石亦增加,长石增加了42.0%,石英略为降低 | ? |
| 泥沼旋回 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地层/沉积阶段 | 中更新统/陆相 | 上更新统/陆相 | 全新统/陆相 | ||
| 中更新世 | 晚更新世 | 全新世 | |||
| MIS阶段 | MIS6 | MIS5 | MIS3 | MIS1 | |
| 6c | 6b | 5e或者5c | 3d | ||
| 冰量 | 高 | 低 | 高 | 低 | |
| 60°N夏季太阳辐射 | 下降和低谷阶段的 阶段性小峰值回升 | 峰值区间 | 自低值上升阶段 | 峰值区间 | |
| GISP2冰心δ18O | —(未有数据) | D-O旋回24号 | D-O旋回19号或18号 | 大暖期 | |
| 南极古气温距平 | 低 | 低 | 高 | 低 | 高 |
| 全球古气温曲线 | 降低 | 低 | 高 | 低 | 高 |
表4 北部湾ZK9岩心泥沼旋回全球气候背景特征
Table 4 Peat series’ global climate background of the sediment core ZK9 in Beibu Gulf
| 泥沼旋回 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地层/沉积阶段 | 中更新统/陆相 | 上更新统/陆相 | 全新统/陆相 | ||
| 中更新世 | 晚更新世 | 全新世 | |||
| MIS阶段 | MIS6 | MIS5 | MIS3 | MIS1 | |
| 6c | 6b | 5e或者5c | 3d | ||
| 冰量 | 高 | 低 | 高 | 低 | |
| 60°N夏季太阳辐射 | 下降和低谷阶段的 阶段性小峰值回升 | 峰值区间 | 自低值上升阶段 | 峰值区间 | |
| GISP2冰心δ18O | —(未有数据) | D-O旋回24号 | D-O旋回19号或18号 | 大暖期 | |
| 南极古气温距平 | 低 | 低 | 高 | 低 | 高 |
| 全球古气温曲线 | 降低 | 低 | 高 | 低 | 高 |
| 岩心和位置 | 泥炭层 | 性状或特征 | 年龄(ka,OSL) | 泥沼旋回 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 深度(m) | 厚度(m) | ||||
| ZK8(东部) | 31.5 | 0.6 | 黑色炭化层,似煤炭 | 150±24 (35.1 m) | 与P1、P2接近 |
| ZK9(中部) | 23.0 | 2.4 | 含有黑色炭化腐木 | 66 ± 7 | 与P4接近 |
表5 北部湾北部所钻取岩心层序所显示的泥炭
Table 5 Peat sequence description of the drilling sediment cores in Beibu Gulf
| 岩心和位置 | 泥炭层 | 性状或特征 | 年龄(ka,OSL) | 泥沼旋回 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 深度(m) | 厚度(m) | ||||
| ZK8(东部) | 31.5 | 0.6 | 黑色炭化层,似煤炭 | 150±24 (35.1 m) | 与P1、P2接近 |
| ZK9(中部) | 23.0 | 2.4 | 含有黑色炭化腐木 | 66 ± 7 | 与P4接近 |
| 泥沼旋回 | P1和P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海平面/陆架状态 | 海退/出露 | 海进/淹没或半淹没 | 海退/出露 | 海进/淹没或半淹没 |
| 冰期/间冰期旋回 | 倒数第2冰期冰盛期 | 末次间冰期 | 末次冰期亚冰阶 | 全新世间冰期 |
| 生产力/南极EPICA冰心CO2 | 低值,但有所波动 | 高值 | 次低值,但有所波动 | 高值 |
| 全球CO2 | 低值 | 次高值 | 有阶段性低值 | 高值 |
表6 泥沼旋回的全球生产力背景
Table 6 Global productivity background of peat series
| 泥沼旋回 | P1和P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海平面/陆架状态 | 海退/出露 | 海进/淹没或半淹没 | 海退/出露 | 海进/淹没或半淹没 |
| 冰期/间冰期旋回 | 倒数第2冰期冰盛期 | 末次间冰期 | 末次冰期亚冰阶 | 全新世间冰期 |
| 生产力/南极EPICA冰心CO2 | 低值,但有所波动 | 高值 | 次低值,但有所波动 | 高值 |
| 全球CO2 | 低值 | 次高值 | 有阶段性低值 | 高值 |
| [1] | FRIEDERICH M C, MOORE T A, FLORES R M. A regional review and new insights into SE Asian Cenozoic coal-bearing sediments: Why does Indonesia have such extensive coal deposits?[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 166: 2-35. |
| [2] | GONG Y, PEASE V, WANG H, et al. Insights into evolution of a rift basin: Provenance of the middle Eocene-lower Oligocene strata of the Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea from detrital zircon[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2021, 419: 105908. |
| [3] | MANSOR M Y, RAHMAN A H A, MENIER D, et al. Structural evolution of Malay Basin, its link to Sunda Block tectonics[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 58: 736-748. |
| [4] | DOMMAIN R, COUWENBERG J, JOOSTEN H. Development and carbon sequestration of tropical peat domes in south-east Asia:Links to post-glacial sea-level changes and Holocene climate variability[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(7/8): 999-1010. |
| [5] | 李金澜, 田军. 末次冰期南海南部暴露的巽他陆架是大气碳汇?[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(4): 155-163. |
| [6] |
贾国东. 冰期出露的巽他陆架: 重要的陆地碳储库?[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(11): 1157-1162.
DOI |
| [7] | FILIPPELLI G M, LATIMER J C, MURRAY R W, et al. Productivity records from the Southern Ocean and the equatorial Pacific Ocean: Testing the glacial Shelf-Nutrient Hypothesis[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2007, 54(21/22): 2443-2452. |
| [8] | 崔振昂, 夏真, 林进清, 等. 南海北部湾全新世环境演变及人类活动影响研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2017: 30-165. |
| [9] | 夏真, 林进清, 郑志昌, 等. 北部湾广西近岸海洋地质环境综合研究[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2019: 123-258. |
| [10] | MA J, WANG Y, JIN C Z, et al. Isotopic evidence of foraging ecology of Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) in South China during the Late Pleistocene[J]. Quaternary International, 2017, 443: 160-167. |
| [11] | 杨士雄, 郑卓, 宗永强, 等. 田洋玛珥湖中更新世以来磁化率特征及其环境意义[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 51(3): 121-127. |
| [12] | 余建英, 何旭宏. 数据统计分析与SPSS应用[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2003: 1-200. |
| [13] | 李玲, 王嘉学, 黎亚波. 基于石笋记录的云贵高原古气候变化研究进展[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2013, 25(5): 96-103. |
| [14] | KARAS C, GOLDSTEIN S L. DE MENOCAL P B. Evolution of Antarctic Intermediate Water during the Plio-Pleistocene and implications for global climate: Evidence from the South Atlantic[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 223: 105945. |
| [15] | KREMER A, STEIN R, FAHL K, et al. Changes in sea ice cover and ice sheet extent at the Yermak Plateau during the last 160 ka-Reconstructions from biomarker records[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 182: 93-108. |
| [16] | DE DECKKER P, MOROS M, PERNER K, et al. Climatic evolution in the Australian region over the last 94 ka-spanning human occupancy, and unveiling the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 249: 106593. |
| [17] | WANG P X, LI Q Y, TIAN J. Pleistocene paleoceanography of the South China Sea: Progress over the past 20years[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 381-396. |
| [18] | WANG P X, LI Q Y, TIAN J, et al. Monsoon influence on planktonic δ18O records from the South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 142: 26-39. |
| [19] | THANH N T, CUONG D H, STATTEGGER K, et al. Depositional sequences of the Mekong river delta and adjacent shelf over the past 140 kyr, southern Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 206: 104634. |
| [20] | OBROCHTA S P, YOKOYAMA Y, MOREN J, et al. Conversion of GISP2-based sediment core age models to the GICC05 extended chronology[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2014, 20: 1-7. |
| [21] | NAIR A, MOHAN R, CROSTA X, et al. Southern Ocean sea ice and frontal changes during the Late Quaternary and their linkages to Asian summer monsoon[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 213: 93-104. |
| [22] | KUMAR K, BAND S T, RAMESH R, et al. Monsoon variability and upper ocean stratification during the last-66 ka over the Andaman Sea: Inferences from the δ18O records of planktonic foraminifera[J]. Quaternary International, 2018, 479: 12-18. |
| [23] | 贾惠兰, 李保生. 青海共和盆地东部晚更新世—全新世地层中元素分布与古气候[J]. 中国沙漠, 1991, 11(2): 27-32. |
| [24] | 石胜强, 袁道先, 罗伦德, 等. 晚更新世晚期以来滇西北高原的孢粉记录与我国南方石笋记录的气候变化对比研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(2): 119-127. |
| [25] | ZHAO M X, HUANG C Y, WANG C C, et al. A millennial-scale $U_{37}^{K'}$ sea-surface temperature record from the South China Sea (8°N) over the last 150 kyr: Monsoon and sea-level influence[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 236: 39-55. |
| [26] | XU Z K, WAN S M, COLIN C, et al. Enhanced terrigenous organic matter input and productivity on the western margin of the Western Pacific Warm Pool during the Quaternary sea-level lowstands: Forcingmechanisms and implications for the global carbon cycle[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 232: 106211. |
| [27] | 张美良, 朱晓燕, 吴夏, 等. 广西巴马县水晶宫洞穴沉积物特征及其沉积环境[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(3): 345-357. |
| [28] | 沈华东, 于革. 13万年以来温暖期气候模拟[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(6): 119-124. |
| [29] | 张岳桥, 李海龙, 李建. 青藏高原30—40 ka B.P. 暖湿气候事件对川西河谷地质环境的影响[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(4): 481-492. |
| [30] |
黄春长. 若尔盖盆地河流古洪水沉积及其对黄河水系演变问题的启示[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(3): 612-625.
DOI |
| [31] |
陈莹璐, 黄春长, 张玉柱, 等. 黄河源区玛曲段末次冰消期古洪水事件及其光释光测年研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2017, 39(3): 549-562.
DOI |
| [32] | 王娜, 查小春, 黄春长, 等. 汉江上游晚冰期以来古洪水事件发生的气候背景分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2020, 29(10): 2250-2260. |
| [33] | VIAGGI P. Quantitative impact of astronomical and sun-related cycles on the Pleistocene climate system from Antarctica records[J]. Quaternary Science Advances, 2021, 4: 100037. |
| [34] | 管清玉, 潘保田, 邬光剑, 等. 末次冰期东亚季风快速波动的模式与成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(3): 429-436. |
| [35] | 司月君, 李保生, 温小浩, 等. 萨拉乌苏河流域MGS4层段记录的末次冰期早冰阶气候波动[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(4): 938-946. |
| [36] | ZHANG J Y, YANG H L, JING L Z, et al. Reconstructing the incision of the Lancang River (Upper Mekong) in southeastern Tibet below its prominent knick zone using fluvial terraces and transient tributary profiles[J]. Geomorphology, 2021, 376: 107551. |
| [37] | 陈思宇, 王嘉学. 云贵高原隆升研究进展[J]. 云南地理环境研究, 2017, 29(3): 23-29, 40. |
| [38] | LIU Y, WANG S J, XU S, et al. New chronological constraints on the Plio-Pleistocene uplift of the Guizhou Plateau, SE margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2022, 67: 101237. |
| [39] | 王凌梓, 苗峻峰, 韩芙蓉. 近10年中国地区地形对降水影响研究进展[J]. 气象科技, 2018, 46(1): 64-75. |
| [40] |
郭永强, 葛永刚, 陈晓清, 等. 高山峡谷区古洪水事件重建研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2): 168-180.
DOI |
| [41] | WOODROFFE C D, WEBSTER J M. Coral reefs and sea-level change[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 248-267. |
| [42] | WANG M Y, ZHENG Z, HUANG K Y, et al. $U_{37}^{K'}$ temperature estimates from Eemian marine sediments in the southern coast of Hainan Island, tropical China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 127: 91-99. |
| [43] | DUNG B V, STATTEGGER K, UNVERRICHT D, et al. Late Pleistocene-Holocene seismic stratigraphy of the Southeast Vietnam Shelf[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2013, 110: 156-169. |
| [44] | BOROWKA R K, OSADCZUK A, LI Z, et al. Sedimentological and geochemical imprint of environmental changes in late Pleistocene palaeodelta-hosting deposits, southwest of the Hainan Island (South China Sea)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 201: 104502. |
| [45] | WETZEL A, FELDENS A, UNVERRICHT D, et al. Late Pleistocene sea-level changes and the formation and fill of bent valleys incised into the shelf of the western South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 206: 104626. |
| [46] | 丁莹莹, 张绪教, 何泽新, 等. 末次冰期河流下切行为对气候变化的响应模式[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(2): 394-405. |
| [47] | JIANG X L, GARDNER E M, MENG H H, et al. Land bridges in the Pleistocene contributed to flora assembly on the continental islands of South China: Insights from the evolutionary history of Quercus championii[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 2019, 132: 36-45. |
| [48] | DODSON J, LI J Y, LU F Y, et al. A Late Pleistocene and Ho-locene vegetation and environmental record from Shuangchi Maar, Hainan Province, South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 523: 89-96. |
| [49] | PUCHAŁA R J, POREBSKI S J, SLIWINSKI W R, et al. Pleistocene to Holocene transition in the central basin of the Gulf of Thailand, based on geoacoustic survey and radiocarbon ages[J]. Marine Geology, 2011, 288(1/2/3/4): 103-111. |
| [50] | PHILLIPS S, BUSTIN R M. Accumulation of organic rich sediments in a dendritic fluvial/lacustrine mire system at Tasik Bera, Malaysia: Implications for coal formation[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1998, 36(1/2): 31-61. |
| [51] | HANEBUTH T J J, VORIS H K, YOKOYAMA Y, et al. Formation and fate of sedimentary depocentres on Southeast Asia’s Sunda Shelf over the past sea-level cycle and biogeographic implications[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 104(1/2/3): 92-110. |
| [52] | HANEBUTH T J J, STATTEGGER K. Depositional sequences on a late Pleistocene-Holocene tropical siliciclastic shelf (Sunda Shelf, Southeast Asia)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(1): 113-126. |
| [53] | TAYLOR D, YEN O H, SANDERSON P G, et al. Late Quaternary peat formation and vegetation dynamics in a lowland tropical swamp: Nee Soon, Singapore[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2001, 171(3/4): 269-287. |
| [54] | SIA S G, ABDULLA W H, KONJING Z, et al. The age, palaeoclimate, palaeovegetation, coal seam architecture/mire types, paleodepositional environments and thermal maturity of syn-collision paralic coal from Mukah, Sarawak, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 81: 1-19. |
| [55] | TWAROGM R, CULVER S J, MALLINSON D J, et al. Depositional environments and sequence stratigraphy of post-last glacial maximum incised valley-fill, Malay Basin, northern Sunda Shelf[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 436: 106457. |
| [56] |
柯思茵, 张冬丽, 王伟涛, 等. 青藏高原东北缘晚更新世以来环境变化研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2021, 36(7): 727-739.
DOI |
| [57] | 郭喜运. 内蒙古朝克乌拉地区晚更新世—全新世早期孢粉特征及古气候指示意义[J]. 华北国土资源, 2015(5): 106-108. |
| [58] | 张晓飞, 王永立, 黄猛, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗中更新世晚期以来古环境变迁的孢粉记录[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 174-185. |
| [59] |
姜大膀, 田芝平, 王娜, 等. 末次冰盛期和中全新世气候模拟分析进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(1): 1-9.
DOI |
| [60] | 赵增友, 石胜强, 袁智郴, 等. 黔西高原末次冰期晚期古植被及西南季风演变[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(6): 1013-1024. |
| [61] | 王婷, 孙有斌, 刘星星. 中更新世气候转型: 特征、机制和展望[J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(33): 3861-3872. |
| [62] | HUYBER S P, LANGMUIR C H. Delayed CO2 emissions from mid-ocean ridge volcanism as a possible cause of late-Pleistocene glacial cycles[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 457: 238-249. |
| [63] | CHALK T B, FOSTER G L, WILSON P A. Dynamic storage of glacial CO2 in the Atlantic Ocean revealed by boron[CO32-]and pH records[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2019, 510: 1-11. |
| [64] | 贾奇. 70万年来西太平洋暖池的热带过程及其对上层水体pH和${{P}_{\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{2}}}}$的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018. |
| [65] | 柯婷, 韦刚健, 刘颖, 等. 南海北部珊瑚高分辨率硼同位素组成及其对珊瑚礁海水pH变化的指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 2015, 44(1): 1-8. |
| [66] | 郭景腾, 李铁刚, 熊志方, 等. MIS6期以来西菲律宾海表层营养物质水平演化及其控制因素: 浮游有孔虫Globigerinoidesruber的Cd/Ca证据[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(9): 81-87. |
| [67] | LIU S F, ZHANG H, CAO P, et al. Paleoproductivity evolution in the northeastern Indian Ocean since the last glacial maximum: Evidence from biogenic silica variations[J]. Deep Sea ResearchPart I: Oceanographic Research, 2021, 175: 103591. |
| [68] | PRIYADARSHANI W N C. 南海北部颗石藻沉降通量的季节、年际变化及其潜在环境驱动因子[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. |
| [1] | 刘国栋, 戴慧敏, 杨泽, 许江, 张一鹤, 魏明辉. 三江平原土壤碳库时空变化和影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 443-454. |
| [2] | 刘震,谭卓,蔡东升,刘明全,付东阳. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组岩性圈闭形成条件[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 239-246. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||