



Geoscience ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (01): 118-129.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.198
• Marine Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Yangdong1( ), LIN Heming1, WANG Xudong1, QIU Xinwei1, QUE Xiaoming1, LI Min1, ZHAO Zeying2, CHEN Yan2(
), LIN Heming1, WANG Xudong1, QIU Xinwei1, QUE Xiaoming1, LI Min1, ZHAO Zeying2, CHEN Yan2( )
)
Received:2021-02-15
Revised:2021-06-18
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2022-03-08
Contact:
CHEN Yan
CLC Number:
GAO Yangdong, LIN Heming, WANG Xudong, QIU Xinwei, QUE Xiaoming, LI Min, ZHAO Zeying, CHEN Yan. Geochemical Constraints on the Sedimentary Environment of Wenchang Formation in Pearl River Mouth Basin and Its Paleoenvironmental Implications[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(01): 118-129.
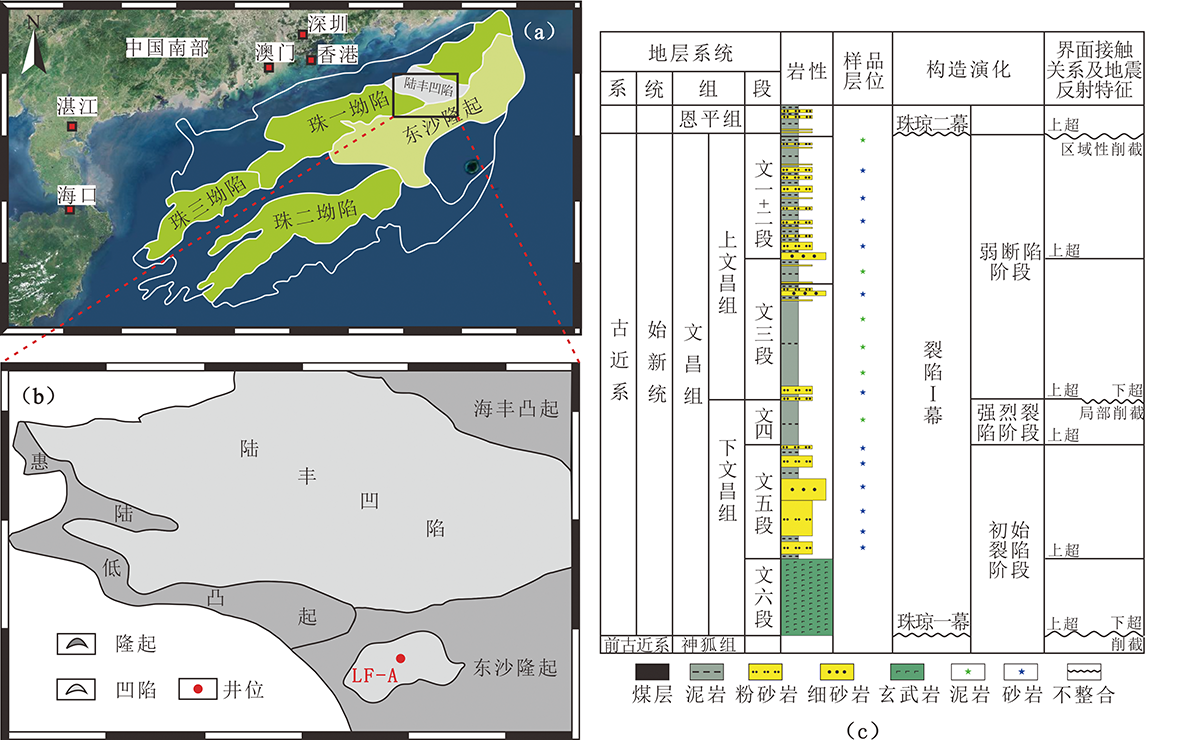
Fig.1 Geotectonic and geographical map, showing the location of Pearl River Mouth Basin and sampling well ((a), (b)), and stratigraphic column showing the lithology and stratigraphic age of the Lufeng sag (c)
| 层位 | 样品号 | 岩性 | 主量元素/% | 微量元素/10-6 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | MnO | MgO | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | SiO2 | V | Cr | Cu | Sr | Ba | |||
| 文一+二段 | M-T-01 | 泥岩 | 20.22 | 0.41 | 2.37 | 0.03 | 1.04 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 63.13 | 106.74 | 51.43 | 33.02 | 94.80 | 8 211.19 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-02 | 砂岩 | 16.11 | 0.43 | 2.22 | 0.03 | 0.94 | 0.52 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 69.18 | 76.48 | 39.60 | 27.39 | 186.64 | 21 223.92 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-03 | 砂岩 | 14.82 | 1.02 | 2.17 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 70.59 | 75.32 | 32.92 | 23.58 | 174.25 | 18 640.58 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-04 | 砂岩 | 14.81 | 0.38 | 2.22 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 71.79 | 79.97 | 32.98 | 26.19 | 131.23 | 12 130.18 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-05 | 砂岩 | 14.50 | 1.08 | 2.17 | 0.10 | 0.96 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 71.43 | 67.87 | 23.86 | 22.31 | 143.73 | 13 044.07 |
| 文三段 | M-T-06 | 泥岩 | 15.88 | 0.72 | 2.47 | 0.08 | 1.30 | 1.61 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 68.96 | 74.06 | 21.68 | 23.19 | 117.87 | 7 821.06 |
| 文三段 | M-T-07 | 砂岩 | 14.03 | 0.71 | 2.15 | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1.39 | 0.01 | 0.46 | 72.46 | 68.20 | 18.81 | 21.68 | 118.48 | 9 795.21 |
| 文三段 | M-T-08 | 泥岩 | 19.02 | 0.66 | 2.87 | 0.15 | 1.52 | 1.05 | 0.05 | 0.69 | 60.40 | 117.35 | 36.90 | 37.37 | 101.30 | 1 920.01 |
| 文三段 | M-T-09 | 泥岩 | 21.44 | 0.44 | 2.85 | 0.21 | 1.48 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.70 | 56.41 | 134.64 | 45.52 | 44.04 | 114.52 | 7 532.64 |
| 文三段 | M-T-10 | 泥岩 | 18.55 | 1.14 | 2.55 | 0.35 | 1.44 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 57.71 | 111.02 | 40.67 | 36.51 | 155.20 | 9 391.07 |
| 文三段 | M-T-11 | 砂岩 | 16.93 | 0.61 | 1.91 | 0.07 | 1.87 | 1.78 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 65.83 | 89.64 | 26.68 | 31.18 | 129.69 | 10 134.67 |
| 文四段 | M-T-12 | 泥岩 | 19.99 | 0.66 | 2.27 | 0.14 | 1.82 | 1.01 | 0.12 | 0.65 | 57.32 | 119.72 | 35.60 | 43.96 | 105.59 | 2 006.32 |
| 文五段 | M-T-13 | 砂岩 | 17.67 | 2.72 | 2.60 | 0.25 | 1.68 | 1.19 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 57.49 | 105.27 | 33.64 | 36.66 | 174.26 | 5 893.50 |
| 文五段 | M-T-14 | 砂岩 | 14.42 | 3.03 | 2.47 | 0.10 | 1.34 | 1.08 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 64.14 | 99.64 | 32.97 | 27.58 | 166.21 | 8 330.13 |
| 文五段 | M-T-15 | 砂岩 | 12.24 | 1.83 | 2.68 | 0.07 | 1.23 | 1.14 | 0.05 | 0.47 | 70.57 | 77.85 | 28.80 | 22.25 | 187.79 | 13 471.05 |
| 文五段 | M-T-16 | 砂岩 | 12.13 | 1.91 | 2.82 | 0.07 | 1.15 | 1.02 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 71.11 | 79.37 | 28.72 | 19.93 | 161.19 | 8 646.96 |
| 文五段 | M-T-17 | 砂岩 | 10.25 | 2.10 | 2.36 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 75.26 | 70.85 | 24.74 | 17.32 | 147.72 | 8 658.22 |
| 文五段 | M-T-18 | 砂岩 | 8.74 | 2.35 | 1.71 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 0.71 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 78.01 | 65.86 | 25.95 | 16.96 | 146.60 | 12 542.45 |
Table 1 Major oxide and trace element contents in the samples of the Wenchang Formation from well LF-A
| 层位 | 样品号 | 岩性 | 主量元素/% | 微量元素/10-6 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | CaO | K2O | MnO | MgO | Na2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | SiO2 | V | Cr | Cu | Sr | Ba | |||
| 文一+二段 | M-T-01 | 泥岩 | 20.22 | 0.41 | 2.37 | 0.03 | 1.04 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.73 | 63.13 | 106.74 | 51.43 | 33.02 | 94.80 | 8 211.19 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-02 | 砂岩 | 16.11 | 0.43 | 2.22 | 0.03 | 0.94 | 0.52 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 69.18 | 76.48 | 39.60 | 27.39 | 186.64 | 21 223.92 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-03 | 砂岩 | 14.82 | 1.02 | 2.17 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 70.59 | 75.32 | 32.92 | 23.58 | 174.25 | 18 640.58 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-04 | 砂岩 | 14.81 | 0.38 | 2.22 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.59 | 71.79 | 79.97 | 32.98 | 26.19 | 131.23 | 12 130.18 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-05 | 砂岩 | 14.50 | 1.08 | 2.17 | 0.10 | 0.96 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 71.43 | 67.87 | 23.86 | 22.31 | 143.73 | 13 044.07 |
| 文三段 | M-T-06 | 泥岩 | 15.88 | 0.72 | 2.47 | 0.08 | 1.30 | 1.61 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 68.96 | 74.06 | 21.68 | 23.19 | 117.87 | 7 821.06 |
| 文三段 | M-T-07 | 砂岩 | 14.03 | 0.71 | 2.15 | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1.39 | 0.01 | 0.46 | 72.46 | 68.20 | 18.81 | 21.68 | 118.48 | 9 795.21 |
| 文三段 | M-T-08 | 泥岩 | 19.02 | 0.66 | 2.87 | 0.15 | 1.52 | 1.05 | 0.05 | 0.69 | 60.40 | 117.35 | 36.90 | 37.37 | 101.30 | 1 920.01 |
| 文三段 | M-T-09 | 泥岩 | 21.44 | 0.44 | 2.85 | 0.21 | 1.48 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.70 | 56.41 | 134.64 | 45.52 | 44.04 | 114.52 | 7 532.64 |
| 文三段 | M-T-10 | 泥岩 | 18.55 | 1.14 | 2.55 | 0.35 | 1.44 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 57.71 | 111.02 | 40.67 | 36.51 | 155.20 | 9 391.07 |
| 文三段 | M-T-11 | 砂岩 | 16.93 | 0.61 | 1.91 | 0.07 | 1.87 | 1.78 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 65.83 | 89.64 | 26.68 | 31.18 | 129.69 | 10 134.67 |
| 文四段 | M-T-12 | 泥岩 | 19.99 | 0.66 | 2.27 | 0.14 | 1.82 | 1.01 | 0.12 | 0.65 | 57.32 | 119.72 | 35.60 | 43.96 | 105.59 | 2 006.32 |
| 文五段 | M-T-13 | 砂岩 | 17.67 | 2.72 | 2.60 | 0.25 | 1.68 | 1.19 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 57.49 | 105.27 | 33.64 | 36.66 | 174.26 | 5 893.50 |
| 文五段 | M-T-14 | 砂岩 | 14.42 | 3.03 | 2.47 | 0.10 | 1.34 | 1.08 | 0.08 | 0.59 | 64.14 | 99.64 | 32.97 | 27.58 | 166.21 | 8 330.13 |
| 文五段 | M-T-15 | 砂岩 | 12.24 | 1.83 | 2.68 | 0.07 | 1.23 | 1.14 | 0.05 | 0.47 | 70.57 | 77.85 | 28.80 | 22.25 | 187.79 | 13 471.05 |
| 文五段 | M-T-16 | 砂岩 | 12.13 | 1.91 | 2.82 | 0.07 | 1.15 | 1.02 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 71.11 | 79.37 | 28.72 | 19.93 | 161.19 | 8 646.96 |
| 文五段 | M-T-17 | 砂岩 | 10.25 | 2.10 | 2.36 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 75.26 | 70.85 | 24.74 | 17.32 | 147.72 | 8 658.22 |
| 文五段 | M-T-18 | 砂岩 | 8.74 | 2.35 | 1.71 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 0.71 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 78.01 | 65.86 | 25.95 | 16.96 | 146.60 | 12 542.45 |
| 样品号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | 样品号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | 样品号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC-1 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.32 | TOC-36 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-71 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.95 |
| TOC-2 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 1.35 | TOC-37 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.21 | TOC-72 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.96 |
| TOC-3 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.50 | TOC-38 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.23 | TOC-73 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 3.75 |
| TOC-4 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.61 | TOC-39 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.11 | TOC-74 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 3.21 |
| TOC-5 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.68 | TOC-40 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-75 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.72 |
| TOC-6 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.70 | TOC-41 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-76 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 3.47 |
| TOC-7 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.57 | TOC-42 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.24 | TOC-77 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.90 |
| TOC-8 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.51 | TOC-43 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-78 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.32 |
| TOC-9 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.52 | TOC-44 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.25 | TOC-79 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.25 |
| TOC-10 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 2.71 | TOC-45 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-80 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.25 |
| TOC-11 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 2.75 | TOC-46 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.29 | TOC-81 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.26 |
| TOC-12 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 2.86 | TOC-47 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-82 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.17 |
| TOC-13 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-48 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.21 | TOC-83 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.99 |
| TOC-14 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-49 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.23 | TOC-84 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.19 |
| TOC-15 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.28 | TOC-50 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.32 | TOC-85 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 0.95 |
| TOC-16 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.24 | TOC-51 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.29 | TOC-86 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 1.41 |
| TOC-17 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.24 | TOC-52 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.46 | TOC-87 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.41 |
| TOC-18 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-53 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.99 | TOC-88 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.57 |
| TOC-19 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-54 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.12 | TOC-89 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.24 |
| TOC-20 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-55 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.87 | TOC-90 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 1.18 |
| TOC-21 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-56 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.11 | TOC-91 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.46 |
| TOC-22 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-57 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.30 | TOC-92 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.60 |
| TOC-23 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.21 | TOC-58 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.49 | TOC-93 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.75 |
| TOC-24 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.22 | TOC-59 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.59 | TOC-94 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.77 |
| TOC-25 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-60 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.31 | TOC-95 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.38 |
| TOC-26 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-61 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.38 | TOC-96 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.36 |
| TOC-27 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-62 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.53 | TOC-97 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.16 |
| TOC-28 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.34 | TOC-63 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.83 | TOC-98 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.19 |
| TOC-29 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.39 | TOC-64 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.76 | TOC-99 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.73 |
| TOC-30 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.34 | TOC-65 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.11 | TOC-100 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 2.57 |
| TOC-31 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-66 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.60 | TOC-101 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 2.57 |
| TOC-32 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-67 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.90 | TOC-102 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.29 |
| TOC-33 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-68 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.85 | TOC-103 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.04 |
| TOC-34 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-69 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.26 | TOC-104 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.29 |
| TOC-35 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.17 | TOC-70 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.62 | TOC-105 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.08 |
Table 2 Content of TOC in the samples of the Wenchang Formation from well LF-A
| 样品号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | 样品号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% | 样品号 | 层位 | 岩性 | TOC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC-1 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.32 | TOC-36 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-71 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.95 |
| TOC-2 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 1.35 | TOC-37 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.21 | TOC-72 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.96 |
| TOC-3 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.50 | TOC-38 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.23 | TOC-73 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 3.75 |
| TOC-4 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.61 | TOC-39 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.11 | TOC-74 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 3.21 |
| TOC-5 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.68 | TOC-40 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-75 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.72 |
| TOC-6 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.70 | TOC-41 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-76 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 3.47 |
| TOC-7 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.57 | TOC-42 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.24 | TOC-77 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.90 |
| TOC-8 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.51 | TOC-43 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-78 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.32 |
| TOC-9 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.52 | TOC-44 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.25 | TOC-79 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.25 |
| TOC-10 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 2.71 | TOC-45 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-80 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.25 |
| TOC-11 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 2.75 | TOC-46 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.29 | TOC-81 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.26 |
| TOC-12 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 2.86 | TOC-47 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-82 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.17 |
| TOC-13 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-48 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.21 | TOC-83 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.99 |
| TOC-14 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-49 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.23 | TOC-84 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.19 |
| TOC-15 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.28 | TOC-50 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.32 | TOC-85 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 0.95 |
| TOC-16 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.24 | TOC-51 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.29 | TOC-86 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 1.41 |
| TOC-17 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.24 | TOC-52 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.46 | TOC-87 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.41 |
| TOC-18 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-53 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.99 | TOC-88 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.57 |
| TOC-19 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-54 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.12 | TOC-89 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.24 |
| TOC-20 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-55 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 0.87 | TOC-90 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 1.18 |
| TOC-21 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-56 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.11 | TOC-91 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.46 |
| TOC-22 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-57 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.30 | TOC-92 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.60 |
| TOC-23 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.21 | TOC-58 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.49 | TOC-93 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.75 |
| TOC-24 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.22 | TOC-59 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.59 | TOC-94 | 文四段 | 泥岩 | 2.77 |
| TOC-25 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.20 | TOC-60 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.31 | TOC-95 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.38 |
| TOC-26 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-61 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.38 | TOC-96 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.36 |
| TOC-27 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-62 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.53 | TOC-97 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.16 |
| TOC-28 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.34 | TOC-63 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.83 | TOC-98 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.19 |
| TOC-29 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.39 | TOC-64 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.76 | TOC-99 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 3.73 |
| TOC-30 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.34 | TOC-65 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.11 | TOC-100 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 2.57 |
| TOC-31 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.26 | TOC-66 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.60 | TOC-101 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 2.57 |
| TOC-32 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.27 | TOC-67 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.90 | TOC-102 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.29 |
| TOC-33 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-68 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 2.85 | TOC-103 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.04 |
| TOC-34 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.19 | TOC-69 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.26 | TOC-104 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.29 |
| TOC-35 | 文一+二段 | 泥岩 | 0.17 | TOC-70 | 文三段 | 泥岩 | 1.62 | TOC-105 | 文五段 | 泥岩 | 1.08 |
| 层位 | 样品号 | 岩性 | Sr/Cu | (Mn/Al)/10-2 | V/Cr | (Sr/Ba)/10-2 | (Ti/Al)/10-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文一+二段 | M-T-01 | 泥岩 | 2.87 | 0.20 | 2.08 | 1.15 | 4.12 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-02 | 砂岩 | 6.81 | 0.27 | 1.93 | 0.88 | 4.26 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-03 | 砂岩 | 7.39 | 0.47 | 2.29 | 0.93 | 4.31 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-04 | 砂岩 | 5.01 | 0.44 | 2.43 | 1.08 | 4.48 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-05 | 砂岩 | 6.44 | 0.97 | 2.84 | 1.10 | 3.75 |
| 文三段 | M-T-06 | 泥岩 | 5.08 | 0.72 | 3.42 | 1.51 | 4.04 |
| 文三段 | M-T-07 | 砂岩 | 5.46 | 0.53 | 3.63 | 1.21 | 3.75 |
| 文三段 | M-T-08 | 泥岩 | 2.71 | 1.18 | 3.18 | 5.28 | 4.10 |
| 文三段 | M-T-09 | 泥岩 | 2.60 | 1.45 | 2.96 | 1.52 | 3.71 |
| 文三段 | M-T-10 | 泥岩 | 4.25 | 2.75 | 2.73 | 1.65 | 3.34 |
| 文三段 | M-T-11 | 砂岩 | 4.16 | 0.57 | 3.36 | 1.28 | 4.06 |
| 文四段 | M-T-12 | 泥岩 | 2.40 | 1.03 | 3.36 | 5.26 | 3.67 |
| 文五段 | M-T-13 | 砂岩 | 4.75 | 2.11 | 3.13 | 2.96 | 3.96 |
| 文五段 | M-T-14 | 砂岩 | 6.03 | 1.04 | 3.02 | 2.00 | 4.62 |
| 文五段 | M-T-15 | 砂岩 | 8.44 | 0.85 | 2.70 | 1.39 | 4.39 |
| 文五段 | M-T-16 | 砂岩 | 8.09 | 0.79 | 2.76 | 1.86 | 4.48 |
| 文五段 | M-T-17 | 砂岩 | 8.53 | 0.75 | 2.86 | 1.71 | 4.61 |
| 文五段 | M-T-18 | 砂岩 | 8.65 | 0.84 | 2.54 | 1.17 | 5.11 |
Table 3 Paleoclimate/paleo-environment index of Wenchang Formation from well LF-A
| 层位 | 样品号 | 岩性 | Sr/Cu | (Mn/Al)/10-2 | V/Cr | (Sr/Ba)/10-2 | (Ti/Al)/10-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文一+二段 | M-T-01 | 泥岩 | 2.87 | 0.20 | 2.08 | 1.15 | 4.12 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-02 | 砂岩 | 6.81 | 0.27 | 1.93 | 0.88 | 4.26 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-03 | 砂岩 | 7.39 | 0.47 | 2.29 | 0.93 | 4.31 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-04 | 砂岩 | 5.01 | 0.44 | 2.43 | 1.08 | 4.48 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-05 | 砂岩 | 6.44 | 0.97 | 2.84 | 1.10 | 3.75 |
| 文三段 | M-T-06 | 泥岩 | 5.08 | 0.72 | 3.42 | 1.51 | 4.04 |
| 文三段 | M-T-07 | 砂岩 | 5.46 | 0.53 | 3.63 | 1.21 | 3.75 |
| 文三段 | M-T-08 | 泥岩 | 2.71 | 1.18 | 3.18 | 5.28 | 4.10 |
| 文三段 | M-T-09 | 泥岩 | 2.60 | 1.45 | 2.96 | 1.52 | 3.71 |
| 文三段 | M-T-10 | 泥岩 | 4.25 | 2.75 | 2.73 | 1.65 | 3.34 |
| 文三段 | M-T-11 | 砂岩 | 4.16 | 0.57 | 3.36 | 1.28 | 4.06 |
| 文四段 | M-T-12 | 泥岩 | 2.40 | 1.03 | 3.36 | 5.26 | 3.67 |
| 文五段 | M-T-13 | 砂岩 | 4.75 | 2.11 | 3.13 | 2.96 | 3.96 |
| 文五段 | M-T-14 | 砂岩 | 6.03 | 1.04 | 3.02 | 2.00 | 4.62 |
| 文五段 | M-T-15 | 砂岩 | 8.44 | 0.85 | 2.70 | 1.39 | 4.39 |
| 文五段 | M-T-16 | 砂岩 | 8.09 | 0.79 | 2.76 | 1.86 | 4.48 |
| 文五段 | M-T-17 | 砂岩 | 8.53 | 0.75 | 2.86 | 1.71 | 4.61 |
| 文五段 | M-T-18 | 砂岩 | 8.65 | 0.84 | 2.54 | 1.17 | 5.11 |
| 指数 | 原始文献 | 计算方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 化学蚀变指数(CIA) | Nesbitt[ | [Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)]×100 |
| Vogt残差指数(V) | Vogt[ | (Al2O3+K2O)/(MgO+CaO+Na2O) |
| R指数(R) | Ruxton[ | SiO2/Al2O3 |
| Parker风化指数(WIP) | Parker[ | (2Na2O/0.35+MgO/0.9+2K2O/0.25+CaO*/0.7)×100 |
| 天气化学指数(CIW) | Harnois[ | [Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O)]×100 |
| 二氧化钛指数(STI) | Jayawardena[ | [(SiO2/TiO2)/((SiO2/TiO2)+(SiO2/Al2O3)+(Al2O3/TiO2))]×100 |
| 斜长石蚀变指数(PIA) | Fedo等[ | [(Al2O3-K2O)/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O-K2O)]×100 |
Table 4 Chemical weathering indices
| 指数 | 原始文献 | 计算方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 化学蚀变指数(CIA) | Nesbitt[ | [Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)]×100 |
| Vogt残差指数(V) | Vogt[ | (Al2O3+K2O)/(MgO+CaO+Na2O) |
| R指数(R) | Ruxton[ | SiO2/Al2O3 |
| Parker风化指数(WIP) | Parker[ | (2Na2O/0.35+MgO/0.9+2K2O/0.25+CaO*/0.7)×100 |
| 天气化学指数(CIW) | Harnois[ | [Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O)]×100 |
| 二氧化钛指数(STI) | Jayawardena[ | [(SiO2/TiO2)/((SiO2/TiO2)+(SiO2/Al2O3)+(Al2O3/TiO2))]×100 |
| 斜长石蚀变指数(PIA) | Fedo等[ | [(Al2O3-K2O)/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O-K2O)]×100 |
| 层位 | 样品号 | 岩性 | CIA | CIW | V | PIA | WIP | STI | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文一+二段 | M-T-01 | 泥岩 | 84.86 | 94.14 | 5.81 | 93.34 | 26.70 | 80.99 | 5.31 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-02 | 砂岩 | 79.90 | 90.76 | 4.57 | 89.31 | 27.42 | 84.40 | 7.30 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-03 | 砂岩 | 76.97 | 83.65 | 3.43 | 81.14 | 28.06 | 85.33 | 8.10 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-04 | 砂岩 | 76.16 | 86.91 | 3.65 | 84.76 | 31.13 | 85.34 | 8.24 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-05 | 砂岩 | 69.61 | 78.50 | 2.62 | 75.35 | 35.16 | 86.10 | 8.38 |
| 文三段 | M-T-06 | 泥岩 | 70.51 | 80.03 | 2.55 | 76.91 | 41.34 | 84.68 | 7.38 |
| 文三段 | M-T-07 | 砂岩 | 70.40 | 79.67 | 2.61 | 76.58 | 35.77 | 86.50 | 8.78 |
| 文三段 | M-T-08 | 泥岩 | 76.00 | 86.66 | 3.26 | 84.46 | 39.97 | 81.21 | 5.40 |
| 文三段 | M-T-09 | 泥岩 | 82.24 | 92.90 | 4.52 | 91.80 | 34.04 | 79.03 | 4.47 |
| 文三段 | M-T-10 | 泥岩 | 79.63 | 85.83 | 3.16 | 83.76 | 32.62 | 81.52 | 5.29 |
| 文三段 | M-T-11 | 砂岩 | 73.54 | 80.78 | 2.16 | 78.68 | 39.33 | 83.54 | 6.61 |
| 文四段 | M-T-12 | 泥岩 | 79.21 | 87.46 | 2.99 | 85.94 | 35.32 | 80.23 | 4.87 |
| 文五段 | M-T-13 | 砂岩 | 72.42 | 71.88 | 1.83 | 68.23 | 40.49 | 81.61 | 5.53 |
| 文五段 | M-T-14 | 砂岩 | 69.83 | 66.39 | 1.59 | 61.66 | 37.19 | 84.44 | 7.56 |
| 文五段 | M-T-15 | 砂岩 | 64.74 | 70.11 | 1.81 | 64.14 | 39.40 | 86.85 | 9.80 |
| 文五段 | M-T-16 | 砂岩 | 65.41 | 70.20 | 1.88 | 63.79 | 38.93 | 86.90 | 9.97 |
| 文五段 | M-T-17 | 砂岩 | 65.56 | 66.16 | 1.63 | 59.45 | 32.82 | 88.34 | 12.48 |
| 文五段 | M-T-18 | 砂岩 | 67.56 | 61.58 | 1.38 | 55.82 | 25.14 | 89.01 | 15.17 |
Table 5 Chemical weathering intensity of the Wenchang Formation from well LF-A
| 层位 | 样品号 | 岩性 | CIA | CIW | V | PIA | WIP | STI | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文一+二段 | M-T-01 | 泥岩 | 84.86 | 94.14 | 5.81 | 93.34 | 26.70 | 80.99 | 5.31 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-02 | 砂岩 | 79.90 | 90.76 | 4.57 | 89.31 | 27.42 | 84.40 | 7.30 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-03 | 砂岩 | 76.97 | 83.65 | 3.43 | 81.14 | 28.06 | 85.33 | 8.10 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-04 | 砂岩 | 76.16 | 86.91 | 3.65 | 84.76 | 31.13 | 85.34 | 8.24 |
| 文一+二段 | M-T-05 | 砂岩 | 69.61 | 78.50 | 2.62 | 75.35 | 35.16 | 86.10 | 8.38 |
| 文三段 | M-T-06 | 泥岩 | 70.51 | 80.03 | 2.55 | 76.91 | 41.34 | 84.68 | 7.38 |
| 文三段 | M-T-07 | 砂岩 | 70.40 | 79.67 | 2.61 | 76.58 | 35.77 | 86.50 | 8.78 |
| 文三段 | M-T-08 | 泥岩 | 76.00 | 86.66 | 3.26 | 84.46 | 39.97 | 81.21 | 5.40 |
| 文三段 | M-T-09 | 泥岩 | 82.24 | 92.90 | 4.52 | 91.80 | 34.04 | 79.03 | 4.47 |
| 文三段 | M-T-10 | 泥岩 | 79.63 | 85.83 | 3.16 | 83.76 | 32.62 | 81.52 | 5.29 |
| 文三段 | M-T-11 | 砂岩 | 73.54 | 80.78 | 2.16 | 78.68 | 39.33 | 83.54 | 6.61 |
| 文四段 | M-T-12 | 泥岩 | 79.21 | 87.46 | 2.99 | 85.94 | 35.32 | 80.23 | 4.87 |
| 文五段 | M-T-13 | 砂岩 | 72.42 | 71.88 | 1.83 | 68.23 | 40.49 | 81.61 | 5.53 |
| 文五段 | M-T-14 | 砂岩 | 69.83 | 66.39 | 1.59 | 61.66 | 37.19 | 84.44 | 7.56 |
| 文五段 | M-T-15 | 砂岩 | 64.74 | 70.11 | 1.81 | 64.14 | 39.40 | 86.85 | 9.80 |
| 文五段 | M-T-16 | 砂岩 | 65.41 | 70.20 | 1.88 | 63.79 | 38.93 | 86.90 | 9.97 |
| 文五段 | M-T-17 | 砂岩 | 65.56 | 66.16 | 1.63 | 59.45 | 32.82 | 88.34 | 12.48 |
| 文五段 | M-T-18 | 砂岩 | 67.56 | 61.58 | 1.38 | 55.82 | 25.14 | 89.01 | 15.17 |
| 分段 | (Mn/Al)/10-2 | V/Cr | (Sr/Ba)/10-2 | CIA | (Ti/Al)/10-2 | Sr/Cu | P2O5/% | TOC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阶段一 | 0.81 | 2.72 | 1.53 | 65.82 | 4.65 | 8.43 | 0.05 | 1.64 |
| 阶段二 | 1.45 | 3.11 | 2.85 | 76.12 | 3.92 | 3.84 | 0.17 | 2.25 |
| 阶段三 | 0.67 | 3.08 | 1.23 | 71.67 | 4.01 | 5.50 | 0.01 | 0.49 |
| 阶段四 | 0.31 | 2.10 | 0.99 | 80.58 | 4.23 | 5.69 | 0.02 | 0.60 |
Table 6 Average values of paleoclimate/paleo-environment and organic matter content in different stages of the Wenchang Formation from well LF-A
| 分段 | (Mn/Al)/10-2 | V/Cr | (Sr/Ba)/10-2 | CIA | (Ti/Al)/10-2 | Sr/Cu | P2O5/% | TOC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阶段一 | 0.81 | 2.72 | 1.53 | 65.82 | 4.65 | 8.43 | 0.05 | 1.64 |
| 阶段二 | 1.45 | 3.11 | 2.85 | 76.12 | 3.92 | 3.84 | 0.17 | 2.25 |
| 阶段三 | 0.67 | 3.08 | 1.23 | 71.67 | 4.01 | 5.50 | 0.01 | 0.49 |
| 阶段四 | 0.31 | 2.10 | 0.99 | 80.58 | 4.23 | 5.69 | 0.02 | 0.60 |
| [1] | 施和生, 朱俊章, 姜正龙, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气资源再评价[J]. 中国海上油气, 2009, 21(1): 9-14. |
| [2] | 施和生, 代一丁, 刘丽华, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷油气藏地质特征与分布发育基本模式[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(增):120-133, 155. |
| [3] | 葛家旺, 朱筱敏, 张向涛, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷文昌组构造-沉积演化模式[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(2): 308-322. |
| [4] |
HE J H, DING W L, JIANG Z X, et al. Mineralogical and chemical distribution of the Es3L oil shale in the Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin (E China): Implications for paleoenvironmental reconstruction and organic matter accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 81: 196-219.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LEYTHAEUSER D. Effects of weathering on organic matter in shales[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, 37(1): 113-120.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
TYSON R V. Sedimentation rate, dilution, preservation and total organic carbon: some results of a modelling study[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2001, 32(2): 333-339.
DOI URL |
| [7] | 樊馥, 蔡进功, 张永生, 等. 泥质烃源岩有机质保存研究[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2011, 32(6): 686-689. |
| [8] |
ZHAI L N, WU C D, YE Y T, et al. Fluctuations in chemical weathering on the Yangtze Block during the Ediacaran-Cambrian transition: Implications for paleoclimatic conditions and the marine carbon cycle[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 490: 280-292.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WU J, LIANG C, HU Z Q, et al. Sedimentation mechanisms and enrichment of organic matter in the Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 556-565.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
QUAN Y B, HAO F, LIU J Z, et al. Source rock deposition controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate in the western Pearl River Mouth Basin, China: Evidence from organic and inorganic geochemistry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 79:1-17.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
NIU Z C, LIU G.D, GE J W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and depositional environment of Paleogene lacustrine source rocks in the Lufeng Sag, Pearl River Mouth basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 171: 60-77.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 张林晔, 湖相烃源岩研究进展[J]. 石油实验地质, 2008, 30(6): 591-595. |
| [13] |
MORFORD J L, EMERSON S. The geochemistry of redox sensitive trace metals in sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(11/12): 1735-1750.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MORFORD J L, RUSSELL A D, EMERSON S. Trace metal evidence for changes in the redox environment associated with the transition from terrigenous clay to diatomaceous sediment, Saanich Inlet, BC[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 174(1/4): 355-369.
DOI URL |
| [15] | 王福国, 梅廉夫, 施和生, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷古近系构造样式分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2008, 32(4): 448-454. |
| [16] | 施和生, 何敏, 张丽丽, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)油气地质特征、成藏规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3):11-22. |
| [17] | 舒誉, 施和生, 杜家元, 等. 珠一坳陷古近系油气成藏特征及勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3): 37-42. |
| [18] | 郭刚, 吴景富, 吴克强, 等. 珠江口盆地隆起区残留洼陷地质特征与石油勘探新领域[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(增): 39-47. |
| [19] | 孙珍, 周蒂, 庞雄, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地白云凹陷构造演化动力学研究[M]// 中国地球物理第二十一届年会. 长春: 中国地球物理学会, 2005. |
| [20] | 张丽丽, 舒梁锋, 冯轩, 等. 再论珠江口盆地恩平组时代归属[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(5): 9-18. |
| [21] |
WEI X S, YAN D T, LUO P, et al. Astronomically forced climate cooling across the Eocene-Oligocene transition in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Paleogeography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology, 2020, 558:109945.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 汪旭东, 张向涛, 林鹤鸣. 珠江口盆地陆丰13洼陷中央背斜带地质构造特征及对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(1): 56-66. |
| [23] | 王良忱, 张金亮. 沉积环境和沉积相[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1996: 146-147. |
| [24] | LERMAN A. 湖泊的化学地质学和物理学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 197-236. |
| [25] | 刘刚, 周东升. 微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用--以江汉盆地潜江组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3): 307-310, 314. |
| [26] | 王随继, 黄杏珍, 妥进才, 等. 泌阳凹陷核桃园组微量元素演化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(1): 66-71. |
| [27] |
NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of Intites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299: 715-717.
DOI URL |
| [28] | VOGT T. Sulitjelmafeltets Geologiog Petrografi[M]. Norway: Norges Geologiske Undersokelse, 1927: 1-560. |
| [29] |
RUXTON B P. Measures of the degree of chemical weathering of rocks[J]. Journal of Geology, 1968, 76(5): 518-527.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
PARKER A. An index of weathering for silicate rocks[J]. Geological Magazine, 1970, 107(6): 501-504.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
HARNOIS L. The CIW index:A new chemical index of weathering[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1988, 55(3): 319-322.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
JAYAWARDENA U D S, IZAWA E. A new chemical index of weathering for metamorphic silicate rocks in tropical regions: A study from Sri Lanka[J]. Engineering Geology, 1994, 36(3/4): 303-310.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
FEDO C M, NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleo-sols, with implications for paleo-weathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10): 921-924.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
TOYODA K. Geochemical history of ancient Lake Biwa in Japan-chemical indicators of sedimentary paleo-environments in a drilled core[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1993, 101(1/2): 169-184.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
OLSEN P E, KENT D V, CORNET B, et al. High-resolution stratigraphy of the Newark rift basin (Early Mesozoic, eastern North America)[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1996, 108(1): 40-77.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 高远. 晚白垩世松辽盆地古气候演化--来自松科1井大陆科学钻探的证据[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015. |
| [37] | 杨晓宇. 渤海湾盆地南部莱州湾凹陷新近纪时期湖平面重建研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. |
| [38] | CONVERS L C. Paleoenvironment reconstruction of the Eocene Southeastern Tethys using geochemistry of sedimentary rocks[D]. New Jersey: Montclair State University, 2020. |
| [39] |
HATCH J R, LEVENTHAL J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U.S.A[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/3): 65-82.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
MA Y Q, LU Y C, LIU X F, et al. Depositional environment and organic matter enrichment of the lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in western Hubei Province, South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 381-393.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
JONES B, MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
RIMMER S M. Geochemical paleo-redox indicators in Devonian-Mississippian black shales, Central Appalachian Basin (USA)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 373-391.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 钱凯, 时华星. 资源评价工作中古盐度测定法的选择[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1982(3): 32-38. |
| [44] | 邓宏文, 钱凯. 沉积地球化学与环境分析[M]. 兰州: 甘肃科学技术出版社, 1993:4-31. |
| [45] | 郑荣才, 柳梅青. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组古盐度研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(1): 22-27. |
| [46] | MURPHYA E, SAGEMAN B B, HOLLANDER D J, et al. Black shale deposition and faunal overturn in Devonian Appalachian basin: clastic starvation, seasonal water-column mixing, and efficient biolimiting nutrient recycling[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2000, 15(3): 280-291. |
| [47] |
TRIBOVILLARD N P, DESPRAIRIES A, VERGES E L. Geochemical study of organic-matter rich cycles from the Kimmeridge Clay Formation of Yorkshire (UK): productivity versus anoxia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1994, 108(1/2): 165-181.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
HEDGES J I., PARKER P L. Land-derived organic matter in surface sediments from the Gulf of Mexico[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1976, 40(9): 1019-1029.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
TRIBOVILLARD N, ALGEO T J, LYONS T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1/2): 12-32.
DOI URL |
| [50] | 许怀先. 生油地球化学层测试技术与应用[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001:49-118. |
| [51] | HUNT J M, JAMIESON G W. Oil and organic matter in source rocks of petroleum[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geo-logists Bulletin, 1956, 40(3): 477-488. |
| [52] | 陈果. 滨浅湖细粒沉积烃源岩有机质富集机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019. |
| [53] |
HARRIS N B, FREEMAN K H, PANCOST R D, et al. The character and origin of lacustrine source rocks in the Lower Cretaceous synrift section,Congo Basin,west Africa[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 2004, 88(8): 1163-1184.
DOI URL |
| [54] | ALGEO T J, SCHECKLER S E. Terrestrial-marine teleconnections in the Devonian: links between the evolution of land plants, weathering processes, and marine anoxic events[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London (Series B, Biological Sciences), 1998, 353: 113-130. |
| [55] |
CHEN G, GANG W Z, LIU Y Z, et al. High-resolution sediment accumulation rate determined by cyclostratigraphy and its impact on the organic matter abundance of the hydrocarbon source rock in the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 103: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
CHEN X, SAGEMAN B B, YAO H W, et al. Zinc isotope evidence for paleoenvironmental changes during Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2[J]. Geology, 2021, 49(4): 412-416.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
GELPI E, SCHNEIDER H, MANN J, et al. Hydrocarbons of geochemical significance in microscopic algae[J]. Phytochemistry, 1970, 9(3): 603-612.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
CAO J, YANG R F, HU G, et al. Hydrocarbon potential of the Lower Cretaceous mudstones in coastal southeastern China[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 2018, 102(2): 333-366.
DOI URL |
| [59] | MOLDOWAN J M, SEIFERT W K, GALLEGOS E J. Relationship Between Petroleum Composition and Depositional Environment of Petroleum Source Rocks[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1985, 69(8): 1255-1268. |
| [60] | TYSON R V. The “productivity versus preservation” controversy: cause, flaws, and resolution[J]. Society for Sedimentary Geology, Special Publications of SEPM, 2005, 82: 17-33. |
| [61] |
CARROLL A R, BOHACS K M. Stratigraphic classification of ancient lakes; balancing tectonic and climatic controls[J]. Geology, 1999, 27(2): 99-102.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
LIANG C, JIANG Z X, CAO Y C, et al. Sedimentary charac-teristics and origin of lacustrine organic-rich shales in the salinized Eocene Dongying Depression[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2018, 130(1/2): 154-174.
DOI URL |
| [1] | KE Xing, ZHAO Qingfang, WU Piao, YANG Chuansheng, LIAO Jing, GONG Jianming. Characteristics and Evaluation of Cretaceous Source Rocks in the Northeastern Jiaolai Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1358-1368. |
| [2] | YANG Xiongbing, WANG Hongyu, SU Yushan, GUAN Chao. Source Rock Characteristics and Its Accumulation Contribution in the Lower Congo Basin, South Atlantic [J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(05): 1369-1384. |
| [3] | GAN Jun, JI Hongquan, LIANG Gang, HE Xiaohu, XIONG Xiaofeng, LI Xing. Gas Accumulation Model of Mesozoic Buried Hill in Qiongdongnan Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(05): 1242-1253. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yingzhao, HU Senqing, LIU Jinshui, JIANG Yiming, CHEN Zhongyun, QIN Jun, DIAO Hui, WANG Chao. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Oil and Gas in the Lishuixi Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(05): 1382-1390. |
| [5] | ZHENG Qinghua, LIU Xingjun, ZHANG Xiaolong, WANG Hongjun, LIAO Yongle, AN Erliang, LIU Tao, ZHANG Jianna, ZUO Qin. Review of the High Natural Gamma Sandstones Associated With Source Rocks in the Chang 73 Submember of the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 1087-1094. |
| [6] | FAN Yan, WANG Xulong, XIANG Caifu, WANG Qianjun, LIU Jia, LIAO Jiande, XU Huaimin. Enrichment Patterns and Main Controlling Factors of Source Rocks in the Permian Pingdiquan Formation, Eastern Junggar Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(04): 1105-1117. |
| [7] | LI Yan, DENG Yunhua, LI Youchuan. Characteristics and Mechanism of Source Rock Development Controlled by Sedimentary Microfacies in River-delta System: Case Study of Coal-measure Source Rock in Enping Formation in Pearl River Estuary Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 1065-1077. |
| [8] | QI Peng, GUO Gang, REN Yaping, CUI Min, WANG Xin. Geological Characterization of the Eocene Pinghu Movement in the Xihu Sag and Its Hydrocarbon Geological Significance [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(04): 1098-1105. |
| [9] | SHEN Hua, LIU Zhen, SHI Yuanpeng, XU Zeyang, LI Yongjun, CHEN Shuguang, WANG Huilai, WANG Zhicheng, WANG Biao, LIU Chang. Hydrocarbon Accumulation Process and Exploration Potential in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(03): 871-882. |
| [10] | JIANG Wei, GAO Zhiqian, HU Zongquan, ZHAO Yongqiang, CHU Chenglin. Sedimentary Filling Evolution and Hydrocarbon Control of High Frequency Sequence in Yurtus Formation, Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 349-364. |
| [11] | LUO Ze, YAN Zhenghe, XIE Mingying, LIANG Jie, WU Jing. Paleogeomorphologic Reconstruction, Evolution, and Sedimentary System Control on Wenchang Formation in Enping 12 Sub-sag, Eastern Pearl River Estuary Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(04): 710-717. |
| [12] | ZHAO Yande, DENG Xiuqing, QI Yalin, SHAO Xiaozhou, YANG Bin, LU Xinchuan, LUO Anxian, XIE Xiankui. Geochemical Characteristics of Source Rocks of M53 Well and Chang-8 Member Oil-source in Pingliangbei Exploration Area, Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(04): 800-811. |
| [13] | ZHANG He, JIANG Zhenglong, LI Yajun, LIANG Shuang, FU Wenkai. Hydrocarbon Generation Conditions and Regional Comparison of the Lower Jurassic Kangsu Formation in Washixia Sag, Tarim Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(06): 1241-1251. |
| [14] | QI Yulin, ZHANG Zhihuan, XIA Dongling, ZHANG Huimin, HUANG Caixia, ZHENG Duo, JIN Xiao, CAO Yongle, ZHU Lei. Comparative Analysis of Hydrocarbon Generation Kinetics of Dark Shale and Black Shale of Chang 7 in Southern Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(04): 863-871. |
| [15] | XI Shengli, GANG Wenzhe, YANG Qingyu, CHEN Guo, LIU Yazhou, WANG Ning, LIU Lan. Organic Geochemistry and Sedimentary Paleoenvironment of Chang 7 Source Rocks in Yanchi-Dingbian Area, Ordos Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(04): 890-901. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||