



Geoscience ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (05): 1194-1205.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2021.065
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Zhiping1,2( ), ZHONG Kanghui1, SHAN Shucheng1, ZHENG Xin1,3, HUANG Haozhen1, YAN Zhao1
), ZHONG Kanghui1, SHAN Shucheng1, ZHENG Xin1,3, HUANG Haozhen1, YAN Zhao1
Received:2020-02-24
Revised:2021-02-15
Online:2021-10-10
Published:2021-11-04
CLC Number:
ZHANG Zhiping, ZHONG Kanghui, SHAN Shucheng, ZHENG Xin, HUANG Haozhen, YAN Zhao. Late Cretaceous Evolution of the Neo-Tethys:Evidence from Geochronology, Geochemistry, and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Gongguori Monzogranite in Zedang[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1194-1205.
| 分析 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th232 | U238 | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | |||
| 01 | 892 | 580 | 1.54 | 0.047 9(0.001 3) | 0.095 3(0.002 6) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 96(37) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 02 | 469 | 231 | 2.03 | 0.047 9(0.001 9) | 0.094 7(0.003 8) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 92(61) | 92(4) | 92(2) | |
| 04 | 291 | 169 | 1.72 | 0.048 0(0.002 6) | 0.096 2(0.005 1) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 98(85) | 93(5) | 93(2) | |
| 05 | 1 427 | 1 036 | 1.38 | 0.047 9(0.001 1) | 0.093 8(0.002 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 93(32) | 91(2) | 91(1) | |
| 07 | 2 140 | 1 240 | 1.73 | 0.047 9(0.001 5) | 0.090 2(0.002 8) | 0.013 7(0.000 2) | 92(45) | 88(3) | 88(1) | |
| 08 | 513 | 425 | 1.21 | 0.047 8(0.001 9) | 0.092 4(0.003 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(58) | 90(3) | 90(2) | |
| 09 | 986 | 549 | 1.80 | 0.046 1(0.006 8) | 0.091 4(0.013 5) | 0.014 4(0.000 3) | (270) | 89(13) | 92(2) | |
| 10 | 2 390 | 1 091 | 2.19 | 0.047 9(0.001 0) | 0.094 5(0.002 1) | 0.014 3(0.000 2) | 95(27) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 11 | 200 | 174 | 1.15 | 0.048 0(0.003 0) | 0.094 7(0.005 9) | 0.014 3(0.000 3) | 97(101) | 92(5) | 92(2) | |
| 12 | 809 | 499 | 1.62 | 0.061 9(0.002 8) | 0.121 5(0.005 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 3) | 671(61) | 116(5) | 91(2) | |
| 13 | 187 | 159 | 1.18 | 0.047 8(0.002 9) | 0.091 5(0.005 4) | 0.013 9(0.000 3) | 89(97) | 89(5) | 89(2) | |
| 14 | 369 | 306 | 1.20 | 0.046 1(0.004 8) | 0.089 6(0.009 3) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | (213) | 87(9) | 90(1) | |
| 15 | 444 | 393 | 1.13 | 0.054 1(0.003 3) | 0.104 3(0.006 2) | 0.014 0(0.000 3) | 376(91) | 101(6) | 89(2) | |
| 16 | 883 | 409 | 2.16 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 5(0.002 8) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 90(43) | 90(3) | 90(1) | |
| 18 | 904 | 604 | 1.50 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 6(0.002 7) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | 90(40) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 19 | 575 | 431 | 1.34 | 0.047 8(0.001 5) | 0.091 2(0.003 0) | 0.013 8(0.000 2) | 91(48) | 89(3) | 88(1) | |
| 20 | 1 575 | 733 | 2.15 | 0.047 8(0.001 3) | 0.092 6(0.002 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(38) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 21 | 447 | 286 | 1.56 | 0.048 3(0.002 8) | 0.097 2(0.005 5) | 0.014 6(0.000 3) | 115(90) | 94(5) | 93(2) | |
| 23 | 1 025 | 756 | 1.36 | 0.047 7(0.001 9) | 0.095 3(0.003 9) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 85(58) | 92(4) | 93(2) | |
| 24 | 1 977 | 1 220 | 1.62 | 0.060 0(0.001 8) | 0.117 7(0.003 6) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 604(37) | 113(3) | 91(2) | |
| 25 | 594 | 474 | 1.25 | 0.046 1(0.008 5) | 0.089 2(0.016 4) | 0.014 1(0.000 3) | (317) | 87(15) | 90(2) | |
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results of the Gongguori monzogranite sample(17-40)
| 分析 点号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th232 | U238 | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | 207Pb/ 206Pb(1σ) | 207Pb/ 235U(1σ) | 206Pb/ 238U(1σ) | |||
| 01 | 892 | 580 | 1.54 | 0.047 9(0.001 3) | 0.095 3(0.002 6) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 96(37) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 02 | 469 | 231 | 2.03 | 0.047 9(0.001 9) | 0.094 7(0.003 8) | 0.014 4(0.000 2) | 92(61) | 92(4) | 92(2) | |
| 04 | 291 | 169 | 1.72 | 0.048 0(0.002 6) | 0.096 2(0.005 1) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 98(85) | 93(5) | 93(2) | |
| 05 | 1 427 | 1 036 | 1.38 | 0.047 9(0.001 1) | 0.093 8(0.002 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 93(32) | 91(2) | 91(1) | |
| 07 | 2 140 | 1 240 | 1.73 | 0.047 9(0.001 5) | 0.090 2(0.002 8) | 0.013 7(0.000 2) | 92(45) | 88(3) | 88(1) | |
| 08 | 513 | 425 | 1.21 | 0.047 8(0.001 9) | 0.092 4(0.003 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(58) | 90(3) | 90(2) | |
| 09 | 986 | 549 | 1.80 | 0.046 1(0.006 8) | 0.091 4(0.013 5) | 0.014 4(0.000 3) | (270) | 89(13) | 92(2) | |
| 10 | 2 390 | 1 091 | 2.19 | 0.047 9(0.001 0) | 0.094 5(0.002 1) | 0.014 3(0.000 2) | 95(27) | 92(2) | 92(1) | |
| 11 | 200 | 174 | 1.15 | 0.048 0(0.003 0) | 0.094 7(0.005 9) | 0.014 3(0.000 3) | 97(101) | 92(5) | 92(2) | |
| 12 | 809 | 499 | 1.62 | 0.061 9(0.002 8) | 0.121 5(0.005 4) | 0.014 2(0.000 3) | 671(61) | 116(5) | 91(2) | |
| 13 | 187 | 159 | 1.18 | 0.047 8(0.002 9) | 0.091 5(0.005 4) | 0.013 9(0.000 3) | 89(97) | 89(5) | 89(2) | |
| 14 | 369 | 306 | 1.20 | 0.046 1(0.004 8) | 0.089 6(0.009 3) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | (213) | 87(9) | 90(1) | |
| 15 | 444 | 393 | 1.13 | 0.054 1(0.003 3) | 0.104 3(0.006 2) | 0.014 0(0.000 3) | 376(91) | 101(6) | 89(2) | |
| 16 | 883 | 409 | 2.16 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 5(0.002 8) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 90(43) | 90(3) | 90(1) | |
| 18 | 904 | 604 | 1.50 | 0.047 8(0.001 4) | 0.092 6(0.002 7) | 0.014 1(0.000 2) | 90(40) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 19 | 575 | 431 | 1.34 | 0.047 8(0.001 5) | 0.091 2(0.003 0) | 0.013 8(0.000 2) | 91(48) | 89(3) | 88(1) | |
| 20 | 1 575 | 733 | 2.15 | 0.047 8(0.001 3) | 0.092 6(0.002 6) | 0.014 0(0.000 2) | 91(38) | 90(2) | 90(1) | |
| 21 | 447 | 286 | 1.56 | 0.048 3(0.002 8) | 0.097 2(0.005 5) | 0.014 6(0.000 3) | 115(90) | 94(5) | 93(2) | |
| 23 | 1 025 | 756 | 1.36 | 0.047 7(0.001 9) | 0.095 3(0.003 9) | 0.014 5(0.000 3) | 85(58) | 92(4) | 93(2) | |
| 24 | 1 977 | 1 220 | 1.62 | 0.060 0(0.001 8) | 0.117 7(0.003 6) | 0.014 2(0.000 2) | 604(37) | 113(3) | 91(2) | |
| 25 | 594 | 474 | 1.25 | 0.046 1(0.008 5) | 0.089 2(0.016 4) | 0.014 1(0.000 3) | (317) | 87(15) | 90(2) | |
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 73.12 | 0.18 | 13.45 | 6.67 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 1.79 | 4.45 | 3.87 | 0.05 | 1.04 | 100.31 | 1.17 |
| 17-40 | 68.43 | 0.21 | 14.65 | 2.03 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 1.73 | 4.78 | 3.76 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 99.68 | 1.23 |
| 17-42 | 73.37 | 0.19 | 13.83 | 6.14 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 2.26 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 0.06 | 0.90 | 99.71 | 1.27 |
| 7885-1 | 73.21 | 0.14 | 14.23 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.05 | 5.42 | 3.98 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 100.15 | 1.08 |
| 7890-1 | 71.74 | 0.21 | 14.60 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 1.23 | 5.71 | 3.13 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 99.95 | 1.14 |
| 7891-2 | 71.46 | 0.23 | 14.77 | 0.56 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 6.21 | 2.84 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 100.15 | 1.11 |
| 7892-2 | 69.66 | 0.23 | 15.76 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 1.41 | 4.65 | 5.12 | 0.07 | 0.91 | 99.88 | 1.20 |
| 样品编号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | Mg# | K2O/Na2O | Rb | Sr | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr |
| 17-36 | 0.91 | 89.66 | 3.40 | 37.21 | 0.87 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 558.20 | 9.48 | 1.96 | 5.65 | 0.46 | 71.72 |
| 17-40 | 0.97 | 87.48 | 3.18 | 39.06 | 0.79 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 528.52 | 11.97 | 1.57 | 6.52 | 0.61 | 102.21 |
| 17-42 | 0.92 | 87.50 | 2.75 | 36.70 | 0.50 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 385.91 | 8.44 | 1.64 | 4.78 | 0.45 | 83.58 |
| 7885-1 | 0.94 | 94.23 | 4.19 | 30.11 | 0.73 | 86.45 | 113.25 | 481.03 | 8.21 | 1.55 | 6.09 | 0.48 | 70.09 |
| 7890-1 | 0.97 | 90.32 | 3.53 | 35.64 | 0.55 | 68.68 | 237.23 | 402.11 | 8.43 | 1.84 | 5.49 | 0.49 | 77.57 |
| 7891-2 | 0.95 | 91.08 | 3.60 | 34.77 | 0.46 | 58.79 | 257.73 | 347.18 | 9.06 | 1.36 | 5.55 | 0.46 | 71.28 |
| 7892-2 | 1.00 | 88.95 | 3.36 | 39.20 | 1.10 | 101.48 | 176.18 | 555.27 | 9.09 | 1.60 | 5.51 | 0.50 | 82.61 |
| 样品编号 | Hf | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Sc | Li | Cs | Be | Ga | Tl | Pb | As |
| 17-36 | 2.01 | 1.82 | 0.29 | 4.59 | 16.45 | 4.11 | 6.68 | 3.79 | 1.71 | 13.67 | 0.49 | 14.93 | 1.32 |
| 17-40 | 2.99 | 2.31 | 3.01 | 8.17 | 19.54 | 4.42 | 13.81 | 2.11 | 1.76 | 15.50 | 0.49 | 17.52 | 1.92 |
| 17-42 | 2.33 | 2.31 | 2.66 | 8.17 | 17.10 | 3.61 | 12.19 | 1.46 | 1.70 | 12.65 | 0.33 | 12.79 | 2.65 |
| 7885-1 | 2.26 | 0.27 | 0.77 | 2.78 | 7.85 | 6.35 | 3.95 | 1.86 | 1.73 | 12.86 | 0.46 | 19.44 | 3.69 |
| 7890-1 | 2.62 | 1.79 | 0.95 | 3.11 | 18.16 | 6.02 | 7.11 | 2.37 | 2.50 | 13.48 | 0.37 | 12.56 | 7.72 |
| 7891-2 | 2.23 | 1.78 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 23.55 | 5.38 | 3.61 | 1.58 | 0.93 | 12.99 | 0.29 | 16.98 | 6.65 |
| 7892-2 | 2.35 | 1.90 | 1.43 | 3.53 | 18.42 | 5.99 | 6.86 | 3.49 | 2.29 | 14.04 | 0.56 | 15.53 | 2.04 |
| 样品编号 | Bi | Ge | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er |
| 17-36 | 0.10 | 1.04 | 18.99 | 35.58 | 3.48 | 11.68 | 2.15 | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.29 | 0.87 |
| 17-40 | 0.04 | 1.17 | 23.11 | 44.67 | 4.26 | 15.22 | 2.64 | 0.54 | 2.04 | 0.32 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 1.10 |
| 17-42 | 0.04 | 1.09 | 18.02 | 34.24 | 3.49 | 11.95 | 2.18 | 0.43 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| 7885-1 | 0.02 | 1.20 | 17.01 | 35.46 | 3.16 | 11.13 | 2.15 | 0.40 | 1.61 | 0.26 | 1.51 | 0.35 | 0.94 |
| 7890-1 | 0.02 | 1.27 | 18.36 | 36.22 | 3.25 | 9.76 | 1.97 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 1.36 | 0.31 | 0.82 |
| 7891-2 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 20.48 | 40.00 | 3.69 | 11.86 | 2.17 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 1.46 | 0.32 | 0.88 |
| 7892-2 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 21.02 | 37.74 | 3.68 | 10.72 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 1.65 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 0.95 |
| 样品编号 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | La/Nb | Nb/Ta | Sm/Nd | REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | δEu | δCe |
| 17-36 | 0.14 | 0.93 | 0.16 | 9.39 | 3.36 | 12.16 | 0.18 | 78.11 | 12.48 | 13.44 | 5.37 | 0.69 | 1.02 |
| 17-40 | 0.18 | 1.29 | 0.22 | 12.21 | 3.55 | 10.67 | 0.17 | 97.76 | 12.34 | 11.80 | 5.34 | 0.71 | 1.05 |
| 17-42 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 9.97 | 3.77 | 10.65 | 0.18 | 76.17 | 11.99 | 11.71 | 5.03 | 0.70 | 1.01 |
| 7885-1 | 0.14 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 11.66 | 2.79 | 12.76 | 0.19 | 75.47 | 11.28 | 9.71 | 4.82 | 0.67 | 1.13 |
| 7890-1 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 10.86 | 3.34 | 11.31 | 0.20 | 75.48 | 12.67 | 12.91 | 5.69 | 0.70 | 1.10 |
| 7891-2 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 11.28 | 3.69 | 12.03 | 0.18 | 84.43 | 13.53 | 13.24 | 5.76 | 0.70 | 1.08 |
| 7892-2 | 0.14 | 1.05 | 0.16 | 10.77 | 3.81 | 10.94 | 0.20 | 81.76 | 12.67 | 13.23 | 6.03 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
Table 2 Analysis results of major elements, REE and trace elements of the monzogranite samples
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | TFe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | A/NK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 73.12 | 0.18 | 13.45 | 6.67 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 1.79 | 4.45 | 3.87 | 0.05 | 1.04 | 100.31 | 1.17 |
| 17-40 | 68.43 | 0.21 | 14.65 | 2.03 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 1.73 | 4.78 | 3.76 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 99.68 | 1.23 |
| 17-42 | 73.37 | 0.19 | 13.83 | 6.14 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 2.26 | 5.00 | 2.50 | 0.06 | 0.90 | 99.71 | 1.27 |
| 7885-1 | 73.21 | 0.14 | 14.23 | 0.54 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 1.05 | 5.42 | 3.98 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 100.15 | 1.08 |
| 7890-1 | 71.74 | 0.21 | 14.60 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.46 | 1.23 | 5.71 | 3.13 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 99.95 | 1.14 |
| 7891-2 | 71.46 | 0.23 | 14.77 | 0.56 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 6.21 | 2.84 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 100.15 | 1.11 |
| 7892-2 | 69.66 | 0.23 | 15.76 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 1.41 | 4.65 | 5.12 | 0.07 | 0.91 | 99.88 | 1.20 |
| 样品编号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | Mg# | K2O/Na2O | Rb | Sr | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr |
| 17-36 | 0.91 | 89.66 | 3.40 | 37.21 | 0.87 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 558.20 | 9.48 | 1.96 | 5.65 | 0.46 | 71.72 |
| 17-40 | 0.97 | 87.48 | 3.18 | 39.06 | 0.79 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 528.52 | 11.97 | 1.57 | 6.52 | 0.61 | 102.21 |
| 17-42 | 0.92 | 87.50 | 2.75 | 36.70 | 0.50 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 385.91 | 8.44 | 1.64 | 4.78 | 0.45 | 83.58 |
| 7885-1 | 0.94 | 94.23 | 4.19 | 30.11 | 0.73 | 86.45 | 113.25 | 481.03 | 8.21 | 1.55 | 6.09 | 0.48 | 70.09 |
| 7890-1 | 0.97 | 90.32 | 3.53 | 35.64 | 0.55 | 68.68 | 237.23 | 402.11 | 8.43 | 1.84 | 5.49 | 0.49 | 77.57 |
| 7891-2 | 0.95 | 91.08 | 3.60 | 34.77 | 0.46 | 58.79 | 257.73 | 347.18 | 9.06 | 1.36 | 5.55 | 0.46 | 71.28 |
| 7892-2 | 1.00 | 88.95 | 3.36 | 39.20 | 1.10 | 101.48 | 176.18 | 555.27 | 9.09 | 1.60 | 5.51 | 0.50 | 82.61 |
| 样品编号 | Hf | Co | Ni | Cr | V | Sc | Li | Cs | Be | Ga | Tl | Pb | As |
| 17-36 | 2.01 | 1.82 | 0.29 | 4.59 | 16.45 | 4.11 | 6.68 | 3.79 | 1.71 | 13.67 | 0.49 | 14.93 | 1.32 |
| 17-40 | 2.99 | 2.31 | 3.01 | 8.17 | 19.54 | 4.42 | 13.81 | 2.11 | 1.76 | 15.50 | 0.49 | 17.52 | 1.92 |
| 17-42 | 2.33 | 2.31 | 2.66 | 8.17 | 17.10 | 3.61 | 12.19 | 1.46 | 1.70 | 12.65 | 0.33 | 12.79 | 2.65 |
| 7885-1 | 2.26 | 0.27 | 0.77 | 2.78 | 7.85 | 6.35 | 3.95 | 1.86 | 1.73 | 12.86 | 0.46 | 19.44 | 3.69 |
| 7890-1 | 2.62 | 1.79 | 0.95 | 3.11 | 18.16 | 6.02 | 7.11 | 2.37 | 2.50 | 13.48 | 0.37 | 12.56 | 7.72 |
| 7891-2 | 2.23 | 1.78 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 23.55 | 5.38 | 3.61 | 1.58 | 0.93 | 12.99 | 0.29 | 16.98 | 6.65 |
| 7892-2 | 2.35 | 1.90 | 1.43 | 3.53 | 18.42 | 5.99 | 6.86 | 3.49 | 2.29 | 14.04 | 0.56 | 15.53 | 2.04 |
| 样品编号 | Bi | Ge | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er |
| 17-36 | 0.10 | 1.04 | 18.99 | 35.58 | 3.48 | 11.68 | 2.15 | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.29 | 0.87 |
| 17-40 | 0.04 | 1.17 | 23.11 | 44.67 | 4.26 | 15.22 | 2.64 | 0.54 | 2.04 | 0.32 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 1.10 |
| 17-42 | 0.04 | 1.09 | 18.02 | 34.24 | 3.49 | 11.95 | 2.18 | 0.43 | 1.62 | 0.25 | 1.40 | 0.30 | 0.97 |
| 7885-1 | 0.02 | 1.20 | 17.01 | 35.46 | 3.16 | 11.13 | 2.15 | 0.40 | 1.61 | 0.26 | 1.51 | 0.35 | 0.94 |
| 7890-1 | 0.02 | 1.27 | 18.36 | 36.22 | 3.25 | 9.76 | 1.97 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 0.25 | 1.36 | 0.31 | 0.82 |
| 7891-2 | 0.05 | 1.02 | 20.48 | 40.00 | 3.69 | 11.86 | 2.17 | 0.42 | 1.60 | 0.26 | 1.46 | 0.32 | 0.88 |
| 7892-2 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 21.02 | 37.74 | 3.68 | 10.72 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 1.65 | 0.27 | 1.44 | 0.32 | 0.95 |
| 样品编号 | Tm | Yb | Lu | Y | La/Nb | Nb/Ta | Sm/Nd | REE | LREE/ HREE | (La/ Yb)N | (La/ Sm)N | δEu | δCe |
| 17-36 | 0.14 | 0.93 | 0.16 | 9.39 | 3.36 | 12.16 | 0.18 | 78.11 | 12.48 | 13.44 | 5.37 | 0.69 | 1.02 |
| 17-40 | 0.18 | 1.29 | 0.22 | 12.21 | 3.55 | 10.67 | 0.17 | 97.76 | 12.34 | 11.80 | 5.34 | 0.71 | 1.05 |
| 17-42 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.18 | 9.97 | 3.77 | 10.65 | 0.18 | 76.17 | 11.99 | 11.71 | 5.03 | 0.70 | 1.01 |
| 7885-1 | 0.14 | 1.16 | 0.18 | 11.66 | 2.79 | 12.76 | 0.19 | 75.47 | 11.28 | 9.71 | 4.82 | 0.67 | 1.13 |
| 7890-1 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 10.86 | 3.34 | 11.31 | 0.20 | 75.48 | 12.67 | 12.91 | 5.69 | 0.70 | 1.10 |
| 7891-2 | 0.14 | 1.02 | 0.14 | 11.28 | 3.69 | 12.03 | 0.18 | 84.43 | 13.53 | 13.24 | 5.76 | 0.70 | 1.08 |
| 7892-2 | 0.14 | 1.05 | 0.16 | 10.77 | 3.81 | 10.94 | 0.20 | 81.76 | 12.67 | 13.23 | 6.03 | 0.80 | 1.00 |
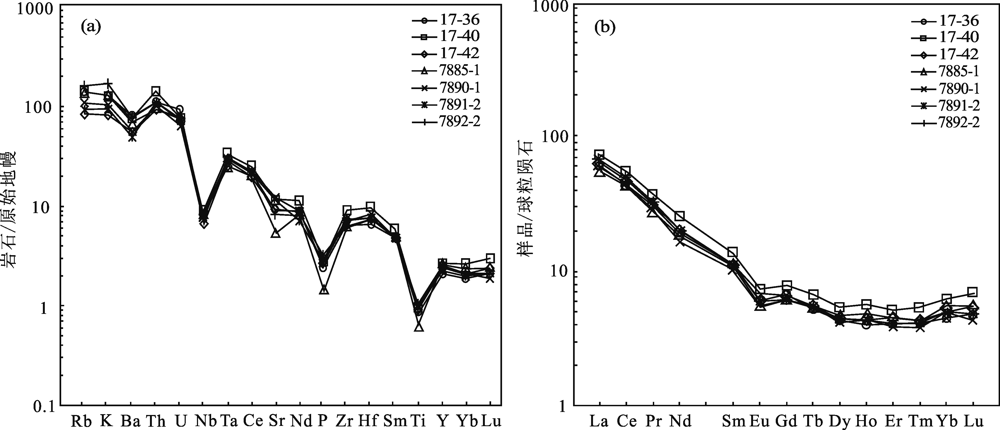
Fig.10 Primitive-mantle-normalized trace element patterns (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Gongguori monzogranite (b) (base map after refs.[19] and [20],respectively)
| 样号 编号 | t/Ma | Rb | Sr | Sm | Nd | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd | εNd(t) | TDM/Ma | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr | ISr | INd | εSr(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 90.67 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 2.15 | 11.68 | 0.111 5 | 0.512 716 | 2.51 | 650 | 1.315 2 | 0.706 284 | 0.704 59 | 0.512 650 | 2.8 |
| 17-40 | 90.67 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 2.64 | 15.22 | 0.104 9 | 0.512 708 | 2.43 | 621 | 1.085 1 | 0.706 084 | 0.704 69 | 0.512 646 | 4.2 |
| 17-42 | 90.67 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 2.18 | 11.95 | 0.110 5 | 0.512 689 | 2.00 | 684 | 0.830 2 | 0.705 708 | 0.704 64 | 0.512 624 | 3.5 |
Table 3 Sr-Nd isotopic parameters of the Gongguori monzogranite samples
| 样号 编号 | t/Ma | Rb | Sr | Sm | Nd | 147Sm/ 144Nd | 143Nd/ 144Nd | εNd(t) | TDM/Ma | 87Rb/ 86Sr | 87Sr/ 86Sr | ISr | INd | εSr(t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17-36 | 90.67 | 89.29 | 196.59 | 2.15 | 11.68 | 0.111 5 | 0.512 716 | 2.51 | 650 | 1.315 2 | 0.706 284 | 0.704 59 | 0.512 650 | 2.8 |
| 17-40 | 90.67 | 90.90 | 242.56 | 2.64 | 15.22 | 0.104 9 | 0.512 708 | 2.43 | 621 | 1.085 1 | 0.706 084 | 0.704 69 | 0.512 646 | 4.2 |
| 17-42 | 90.67 | 53.68 | 187.21 | 2.18 | 11.95 | 0.110 5 | 0.512 689 | 2.00 | 684 | 0.830 2 | 0.705 708 | 0.704 64 | 0.512 624 | 3.5 |
| [1] | 吴福元, 刘传周, 张亮亮, 等. 雅鲁藏布蛇绿岩——事实与臆想[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2):293-325. |
| [2] | 张进, 邓晋福, 肖庆辉, 等. 蛇绿岩研究的最新进展[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(1):1-12. |
| [3] | 鲍佩声, 苏犁, 王军, 等. 雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015:1-74. |
| [4] | 王成善, 李亚林, 刘志飞, 等. 雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩再研究:从地质调查到矿物记录[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(3):323-330. |
| [5] | 梁凤华, 许志琴, 巴登珠, 等. 西藏罗布莎—泽当蛇绿岩体的构造产出与侵位机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11):3255-3268. |
| [6] | 李文霞, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 等. 西藏日喀则地区雅鲁藏布蛇绿岩地球化学特征及其源区性质[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(2):294-302. |
| [7] |
COLEMAN R G, PETERMAN Z E. Oceanic plagiogranite[J]. Geophysical Research, 1975, 80(8):1099-1108.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 韦栋梁, 夏斌, 周国庆, 等. 西藏泽当英云闪长岩的地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素特征:特提斯洋内俯冲的新证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2007, 42(5):1515-1534. |
| [9] | 赵珍, 吴珍汉, 胡道功, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯带南缘泽当多金属矿田多期岩浆活动及年代意义[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(6):703-712. |
| [10] | LUDWIG K R. ISOPLOT3.0:A Geochronological Tool Kit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 39. |
| [11] |
STEIGER R H, JAGER E. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geochronology and cosmochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36:359-362.
DOI URL |
| [12] | WILLIARNS I S. Some observations on the use of zircon U-Pb geochronology in the study of granitic rocks[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Edinburgh-Earth Sciences, 1992, 83:447-458. |
| [13] | HU D G, WW Z H, JIANG W. et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ale and Nd isotopic study on the Nyainqentanghab Group[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2005, 48(9):1377-1386. |
| [14] |
BELOUSOVA E A, GRIFFIN W L, O’REILLY S Y, et al. Igneous zircon: trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37:215-224.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PECCERILLO J, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58:63-81.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101:635-643.
DOI URL |
| [18] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Magas and Magmatic Rocks[M]. London: Longman, 1985:1-266. |
| [19] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25:656-682. |
| [20] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:528-548. |
| [21] | TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985:1-312. |
| [22] | 韩吟文, 马振东. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003. |
| [23] | 王中刚. 稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992. |
| [24] |
JIANG Ziqi, WANG Qiang, WYMAN DEREK A, et al. Transition from oceanic to continental lithosphere subduction in southern Tibet: Evidence from the Late Cretaceous-Early Oligocene (~91-30 Ma) intrusive rocks in the Chanang-Zedong area, southern Gangdese[J]. Lithos, 2014, 196/197:213-231.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 张丽莹, 黄丰, 许继峰, 等. 西藏山南地区花岗质岩石成因及其对地壳结构变化的记录[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 44(6):1822-1833. |
| [26] | 纪伟强, 吴福元, 锺孙霖, 等. 西藏南部冈底斯岩基花岗岩时代与岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 2009, 39(7):849-871. |
| [27] | SETSUYA Nakada, MASAKI Takahashi. Regional variation in chemistry of the Miocene intermediate to felsic magmas in the Outer Zone and the Setouchi Province of Southwest Japan[J]. The Geological Society of Japan, 1979, 85(9):571-582. |
| [28] |
COLLINS W, BEAMS S, WHITE A, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2):189-200.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 肖庆辉, 邱瑞照, 邢作云, 等. 花岗岩成因研究前沿的认识[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(增):18-27. |
| [30] | 李昌年. 火成岩微量元素岩石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992. |
| [31] |
TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(2):241-265.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PFANDER J A, MUINKER C, STRACKE A, et al. Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf in ocean island basalts-Implications for crust-mantle differentiation and the fate of Niobium[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 254(1):158-172.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 陈德潜, 陈刚. 实用稀土元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1990. |
| [34] |
MCKENZIE D, BICKLE M J. The volume and composition of melt generated by extension of the lithosphere[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1988, 29:625-679.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
FOLEY S, TIEPOLO M, VANNUCCI R. Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones[J]. Nature, 2002, 417:837-840.
DOI URL |
| [36] | 黄泽森, 江巴多吉, 达瓦次仁, 等. 西藏切穷地区早白垩世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4):703-714. |
| [37] |
PATIÑO DOUCE A E. What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of granitic magmas?[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1999, 168:55-75.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 许庆林, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等. 东昆仑莫河下拉银多金属矿床花岗斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(2):421-433. |
| [39] | FAURE G. Principle of Isotope Geology[M]. New York:Wiley, 1987:117-247. |
| [40] | 邱瑞照, 肖润, 周肃, 等. 藏北班公湖—怒江带中段舍玛拉沟蛇绿岩中辉长岩Sm-Nd同位素年龄和Sr、Nd同位素特征[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(增):64-68. |
| [41] | 邱瑞照, 邓晋福, 周肃, 等. 青藏高原中新生代花岗岩Sr、Nd同位素研究[J]. 地球科学, 2003, 24(6):611-617. |
| [42] | 洪大卫, 王式光, 谢锡林, 等. 兴蒙造山带正εNd(t)值花岗岩的成因和大陆地壳生长[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(2):441-456. |
| [43] |
HARRIS N B W, PEARCE J A, TINDLE A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1986, 19:67-81.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoid[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643.
DOI URL |
| [45] | 梁华英, 魏启荣, 许继峰, 等. 西藏冈底斯矿带南缘矽卡岩型铜矿床含矿岩体锆石U-Pb年龄及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(6):1692-1698. |
| [46] | 董瀚, 张志平, 魏学平, 等. 西藏泽当蛇绿岩物质组成、年代格架及地质意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(6):1265-1273. |
| [47] | 杨鑫朋, 张振利, 张泽国, 等. 西藏冈底斯南缘中侏罗世辉长闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年和Lu-Hf位素组成及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1):63-72. |
| [48] | 代作文, 李光明, 丁俊, 等. 西藏努日晚白垩世埃达克岩:洋脊俯冲的产物[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8):2727-2741. |
| [49] | 岳相元, 杨波, 周雄, 等. 川西地区热达门石英闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学特征:岩石成因与构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(5):1015-1024. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||