



Geoscience ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (03): 466-482.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.023
• Petrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Di1,2( ), ZHAO Guochun1, SU Shangguo1(
), ZHAO Guochun1, SU Shangguo1( ), LI Hongxing3
), LI Hongxing3
Received:2019-03-23
Revised:2020-01-13
Online:2020-07-04
Published:2020-07-05
Contact:
SU Shangguo
CLC Number:
WANG Di, ZHAO Guochun, SU Shangguo, LI Hongxing. Spatial-temporal Distribution of Late Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks in South Daxing’anling Mountains and the Characteristic Contrast of Rocks in the Mid Ridge and the East Slope[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(03): 466-482.
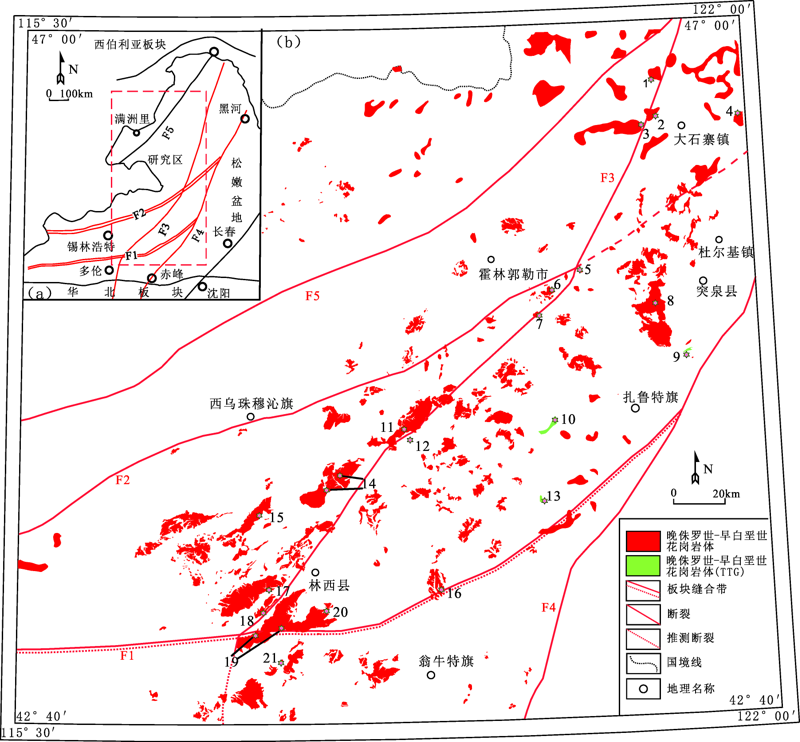
Fig.1 Tectonic location of the study area (a) and temporal-spatial distribution map of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous intrusive rocks of south Daxing’anling mountains(b) (modified after references [18-19])
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 75.75 | 0.13 | 12.63 | 0.52 | 1.03 | 0.070 | 0.21 | 0.61 | 4.04 | 4.53 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 99.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 75.58 | 0.12 | 12.54 | 0.42 | 1.26 | 0.070 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 4.18 | 4.26 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 99.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 73.13 | 0.19 | 13.61 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.070 | 0.35 | 1.09 | 4.28 | 4.34 | 0.05 | 0.78 | 99.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 75.66 | 0.13 | 11.72 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.036 | 0.15 | 0.71 | 3.82 | 4.73 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 99.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 77.44 | 0.11 | 10.69 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.037 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 3.85 | 4.34 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 99.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 77.20 | 0.08 | 11.34 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 3.63 | 4.58 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 99.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 76.22 | 0.08 | 12.54 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.060 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 4.45 | 4.14 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 99.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 71.53 | 0.34 | 14.01 | 0.49 | 2.08 | 0.100 | 0.68 | 1.63 | 4.49 | 4.04 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 99.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 74.30 | 0.13 | 13.18 | 0.16 | 1.60 | 0.060 | 0.18 | 0.82 | 4.31 | 4.72 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 99.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 71.35 | 0.25 | 14.29 | 0.10 | 2.45 | 0.070 | 0.37 | 1.37 | 4.47 | 4.54 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 99.73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 74.28 | 0.12 | 13.63 | 0.20 | 1.12 | 0.070 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 4.44 | 4.56 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 99.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 75.85 | 0.22 | 12.69 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.079 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 4.45 | 3.52 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 99.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 76.58 | 0.19 | 12.34 | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.103 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 4.55 | 3.36 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 99.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 0.998 | 94.13 | 4.67 | 24.80 | 66.80 | 5.84 | 20.20 | 3.78 | 0.25 | 3.68 | 0.56 | 3.22 | 0.64 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 0.974 | 93.45 | 4.47 | 24.60 | 62.60 | 5.87 | 19.60 | 3.57 | 0.20 | 3.52 | 0.52 | 2.98 | 0.59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 0.992 | 90.52 | 3.84 | 19.20 | 38.70 | 5.33 | 19.30 | 3.74 | 0.37 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 3.41 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 0.923 | 95.59 | 5.41 | 36.70 | 69.10 | 7.99 | 28.10 | 5.20 | 0.36 | 4.44 | 0.81 | 5.31 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 0.857 | 94.87 | 5.98 | 37.00 | 72.80 | 8.28 | 29.30 | 5.44 | 0.25 | 4.22 | 0.78 | 5.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 0.945 | 96.58 | 5.41 | 31.70 | 62.60 | 6.89 | 24.20 | 4.02 | 0.23 | 3.55 | 0.62 | 3.97 | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 0.997 | 95.45 | 4.92 | 22.60 | 82.00 | 6.58 | 22.80 | 4.04 | 0.05 | 3.74 | 0.46 | 2.26 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 0.952 | 86.94 | 3.40 | 24.70 | 44.80 | 5.81 | 19.80 | 3.88 | 0.49 | 3.36 | 0.53 | 3.20 | 0.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 0.963 | 93.10 | 4.63 | 28.10 | 85.20 | 7.46 | 27.70 | 5.42 | 0.28 | 4.76 | 0.72 | 3.88 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 0.968 | 88.22 | 3.71 | 40.30 | 68.40 | 9.81 | 34.20 | 5.92 | 0.65 | 5.31 | 0.77 | 4.27 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 0.984 | 93.08 | 4.26 | 30.20 | 66.80 | 8.82 | 33.00 | 7.76 | 0.29 | 6.30 | 1.10 | 6.73 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 0.979 | 92.84 | 3.79 | 20.32 | 44.11 | 5.09 | 18.45 | 3.73 | 0.57 | 3.09 | 0.50 | 2.90 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.057 | 95.42 | 4.34 | 20.50 | 43.51 | 4.97 | 18.02 | 3.43 | 0.55 | 3.04 | 0.53 | 3.10 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Pb | Sr | Zr | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 1.88 | 0.31 | 2.11 | 0.32 | 230.00 | 157.00 | 29.80 | 3.32 | 12.80 | 2.46 | 23.90 | 55.50 | 97.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 1.64 | 0.29 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 210.00 | 102.00 | 31.50 | 13.40 | 10.50 | 1.86 | 22.40 | 60.50 | 89.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 2.12 | 0.38 | 2.72 | 0.42 | 278.00 | 217.00 | 31.00 | 9.02 | 11.90 | 3.04 | 20.10 | 111.00 | 125.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 3.62 | 0.66 | 4.38 | 0.70 | 266.00 | 162.00 | 43.60 | 5.87 | 15.60 | 1.59 | 30.30 | 69.20 | 250.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 3.36 | 0.58 | 3.98 | 0.60 | 216.00 | 79.10 | 45.50 | 5.61 | 9.67 | 0.98 | 30.80 | 53.10 | 246.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 2.41 | 0.49 | 3.04 | 0.54 | 216.00 | 97.50 | 44.70 | 4.71 | 12.50 | 1.41 | 74.80 | 36.50 | 281.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 1.16 | 0.16 | 1.12 | 0.15 | 243.00 | 34.70 | 27.20 | 4.90 | 14.50 | 1.61 | 22.40 | 21.00 | 115.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 2.09 | 0.30 | 182.00 | 300.00 | 14.00 | 3.68 | 10.30 | 1.69 | 14.00 | 177.00 | 112.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 1.94 | 0.30 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 213.00 | 239.00 | 22.90 | 5.50 | 10.60 | 1.53 | 21.60 | 48.20 | 170.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 2.26 | 0.36 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 213.00 | 452.00 | 19.30 | 5.37 | 9.03 | 1.22 | 13.70 | 132.00 | 192.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 3.55 | 0.61 | 4.12 | 0.60 | 312.00 | 172.00 | 36.80 | 10.80 | 22.00 | 5.30 | 39.80 | 57.10 | 130.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 1.76 | 0.31 | 2.03 | 0.30 | 81.70 | 648.20 | 6.32 | 0.60 | 14.29 | 0.52 | 18.80 | 163.10 | 71.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.95 | 0.36 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 64.80 | 501.50 | 5.92 | 0.76 | 11.81 | 0.51 | 17.80 | 70.30 | 83.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Hf | Y | tzr | ∑REE | δEu | FeOT | FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) | Mg# | (LREE/HREE)N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 5.24 | 15.80 | 744.00 | 134.39 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.877 | 0.42 | 5.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 4.02 | 14.60 | 735.00 | 128.20 | 0.17 | 1.64 | 0.882 | 0.37 | 5.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 5.34 | 18.70 | 761.00 | 100.26 | 0.31 | 1.86 | 0.841 | 0.45 | 3.69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 11.30 | 33.80 | 818.00 | 168.40 | 0.22 | 1.44 | 0.906 | 0.42 | 4.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 9.10 | 31.70 | 810.00 | 172.67 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 0.927 | 0.42 | 4.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 10.70 | 22.80 | 834.00 | 145.01 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.899 | 0.56 | 4.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 5.62 | 7.68 | 758.00 | 147.53 | 0.04 | 1.48 | 0.914 | 0.35 | 8.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 4.37 | 16.70 | 744.00 | 111.72 | 0.41 | 2.52 | 0.788 | 0.62 | 4.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 7.00 | 16.00 | 785.00 | 168.65 | 0.16 | 1.74 | 0.906 | 0.25 | 6.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 6.47 | 20.50 | 791.00 | 175.71 | 0.35 | 2.54 | 0.873 | 0.33 | 5.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 6.52 | 33.10 | 764.00 | 171.16 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 0.867 | 0.38 | 3.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 4.65 | 16.91 | 718.00 | 103.76 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.816 | 0.80 | 4.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 4.49 | 18.53 | 739.00 | 103.29 | 0.51 | 1.14 | 0.812 | 1.07 | 4.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1 Major, REE and trace elements content of granite samples from the mid ridge and east slope of south Daxing’anling Mountains
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 75.75 | 0.13 | 12.63 | 0.52 | 1.03 | 0.070 | 0.21 | 0.61 | 4.04 | 4.53 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 99.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 75.58 | 0.12 | 12.54 | 0.42 | 1.26 | 0.070 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 4.18 | 4.26 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 99.85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 73.13 | 0.19 | 13.61 | 0.28 | 1.61 | 0.070 | 0.35 | 1.09 | 4.28 | 4.34 | 0.05 | 0.78 | 99.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 75.66 | 0.13 | 11.72 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.036 | 0.15 | 0.71 | 3.82 | 4.73 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 99.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 77.44 | 0.11 | 10.69 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.037 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 3.85 | 4.34 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 99.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 77.20 | 0.08 | 11.34 | 0.60 | 0.35 | 0.025 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 3.63 | 4.58 | 0.02 | 1.16 | 99.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 76.22 | 0.08 | 12.54 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.060 | 0.14 | 0.43 | 4.45 | 4.14 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 99.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 71.53 | 0.34 | 14.01 | 0.49 | 2.08 | 0.100 | 0.68 | 1.63 | 4.49 | 4.04 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 99.77 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 74.30 | 0.13 | 13.18 | 0.16 | 1.60 | 0.060 | 0.18 | 0.82 | 4.31 | 4.72 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 99.80 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 71.35 | 0.25 | 14.29 | 0.10 | 2.45 | 0.070 | 0.37 | 1.37 | 4.47 | 4.54 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 99.73 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 74.28 | 0.12 | 13.63 | 0.20 | 1.12 | 0.070 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 4.44 | 4.56 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 99.80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 75.85 | 0.22 | 12.69 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.079 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 4.45 | 3.52 | 0.07 | 0.37 | 99.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 76.58 | 0.19 | 12.34 | 0.88 | 0.36 | 0.103 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 4.55 | 3.36 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 99.58 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | A/CNK | DI | AR | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 0.998 | 94.13 | 4.67 | 24.80 | 66.80 | 5.84 | 20.20 | 3.78 | 0.25 | 3.68 | 0.56 | 3.22 | 0.64 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 0.974 | 93.45 | 4.47 | 24.60 | 62.60 | 5.87 | 19.60 | 3.57 | 0.20 | 3.52 | 0.52 | 2.98 | 0.59 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 0.992 | 90.52 | 3.84 | 19.20 | 38.70 | 5.33 | 19.30 | 3.74 | 0.37 | 3.33 | 0.54 | 3.41 | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 0.923 | 95.59 | 5.41 | 36.70 | 69.10 | 7.99 | 28.10 | 5.20 | 0.36 | 4.44 | 0.81 | 5.31 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 0.857 | 94.87 | 5.98 | 37.00 | 72.80 | 8.28 | 29.30 | 5.44 | 0.25 | 4.22 | 0.78 | 5.08 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 0.945 | 96.58 | 5.41 | 31.70 | 62.60 | 6.89 | 24.20 | 4.02 | 0.23 | 3.55 | 0.62 | 3.97 | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 0.997 | 95.45 | 4.92 | 22.60 | 82.00 | 6.58 | 22.80 | 4.04 | 0.05 | 3.74 | 0.46 | 2.26 | 0.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 0.952 | 86.94 | 3.40 | 24.70 | 44.80 | 5.81 | 19.80 | 3.88 | 0.49 | 3.36 | 0.53 | 3.20 | 0.63 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 0.963 | 93.10 | 4.63 | 28.10 | 85.20 | 7.46 | 27.70 | 5.42 | 0.28 | 4.76 | 0.72 | 3.88 | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 0.968 | 88.22 | 3.71 | 40.30 | 68.40 | 9.81 | 34.20 | 5.92 | 0.65 | 5.31 | 0.77 | 4.27 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 0.984 | 93.08 | 4.26 | 30.20 | 66.80 | 8.82 | 33.00 | 7.76 | 0.29 | 6.30 | 1.10 | 6.73 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 0.979 | 92.84 | 3.79 | 20.32 | 44.11 | 5.09 | 18.45 | 3.73 | 0.57 | 3.09 | 0.50 | 2.90 | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.057 | 95.42 | 4.34 | 20.50 | 43.51 | 4.97 | 18.02 | 3.43 | 0.55 | 3.04 | 0.53 | 3.10 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体 名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Pb | Sr | Zr | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 1.88 | 0.31 | 2.11 | 0.32 | 230.00 | 157.00 | 29.80 | 3.32 | 12.80 | 2.46 | 23.90 | 55.50 | 97.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 1.64 | 0.29 | 1.95 | 0.27 | 210.00 | 102.00 | 31.50 | 13.40 | 10.50 | 1.86 | 22.40 | 60.50 | 89.60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 2.12 | 0.38 | 2.72 | 0.42 | 278.00 | 217.00 | 31.00 | 9.02 | 11.90 | 3.04 | 20.10 | 111.00 | 125.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 3.62 | 0.66 | 4.38 | 0.70 | 266.00 | 162.00 | 43.60 | 5.87 | 15.60 | 1.59 | 30.30 | 69.20 | 250.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 3.36 | 0.58 | 3.98 | 0.60 | 216.00 | 79.10 | 45.50 | 5.61 | 9.67 | 0.98 | 30.80 | 53.10 | 246.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 2.41 | 0.49 | 3.04 | 0.54 | 216.00 | 97.50 | 44.70 | 4.71 | 12.50 | 1.41 | 74.80 | 36.50 | 281.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 1.16 | 0.16 | 1.12 | 0.15 | 243.00 | 34.70 | 27.20 | 4.90 | 14.50 | 1.61 | 22.40 | 21.00 | 115.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 1.83 | 0.30 | 2.09 | 0.30 | 182.00 | 300.00 | 14.00 | 3.68 | 10.30 | 1.69 | 14.00 | 177.00 | 112.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 1.94 | 0.30 | 1.92 | 0.27 | 213.00 | 239.00 | 22.90 | 5.50 | 10.60 | 1.53 | 21.60 | 48.20 | 170.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 2.26 | 0.36 | 2.33 | 0.35 | 213.00 | 452.00 | 19.30 | 5.37 | 9.03 | 1.22 | 13.70 | 132.00 | 192.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 3.55 | 0.61 | 4.12 | 0.60 | 312.00 | 172.00 | 36.80 | 10.80 | 22.00 | 5.30 | 39.80 | 57.10 | 130.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 1.76 | 0.31 | 2.03 | 0.30 | 81.70 | 648.20 | 6.32 | 0.60 | 14.29 | 0.52 | 18.80 | 163.10 | 71.10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 1.95 | 0.36 | 2.29 | 0.36 | 64.80 | 501.50 | 5.92 | 0.76 | 11.81 | 0.51 | 17.80 | 70.30 | 83.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 岩体名称 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Hf | Y | tzr | ∑REE | δEu | FeOT | FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) | Mg# | (LREE/HREE)N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 马勒根 坝岩体 | 斑状黑云母 二长花岗岩 | MLG02-2 | 5.24 | 15.80 | 744.00 | 134.39 | 0.20 | 1.50 | 0.877 | 0.42 | 5.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG03-1 | 4.02 | 14.60 | 735.00 | 128.20 | 0.17 | 1.64 | 0.882 | 0.37 | 5.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MLG14-2 | 5.34 | 18.70 | 761.00 | 100.26 | 0.31 | 1.86 | 0.841 | 0.45 | 3.69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BYN1* | 11.30 | 33.80 | 818.00 | 168.40 | 0.22 | 1.44 | 0.906 | 0.42 | 4.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-1* | 9.10 | 31.70 | 810.00 | 172.67 | 0.15 | 1.40 | 0.927 | 0.42 | 4.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BY09-2* | 10.70 | 22.80 | 834.00 | 145.01 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.899 | 0.56 | 4.89 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 朝阳沟 岩体 | 含晶洞花岗岩 | CY18-2 | 5.62 | 7.68 | 758.00 | 147.53 | 0.04 | 1.48 | 0.914 | 0.35 | 8.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 二长花岗岩 | CY27-2 | 4.37 | 16.70 | 744.00 | 111.72 | 0.41 | 2.52 | 0.788 | 0.62 | 4.71 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 正长花岗岩 | CY36-2 | 7.00 | 16.00 | 785.00 | 168.65 | 0.16 | 1.74 | 0.906 | 0.25 | 6.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY38-2 | 6.47 | 20.50 | 791.00 | 175.71 | 0.35 | 2.54 | 0.873 | 0.33 | 5.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CY46-2 | 6.52 | 33.10 | 764.00 | 171.16 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 0.867 | 0.38 | 3.50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 野猪沟 岩体 | 二长花岗岩 | YC10-1 | 4.65 | 16.91 | 718.00 | 103.76 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.816 | 0.80 | 4.65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YC08-1 | 4.49 | 18.53 | 739.00 | 103.29 | 0.51 | 1.14 | 0.812 | 1.07 | 4.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
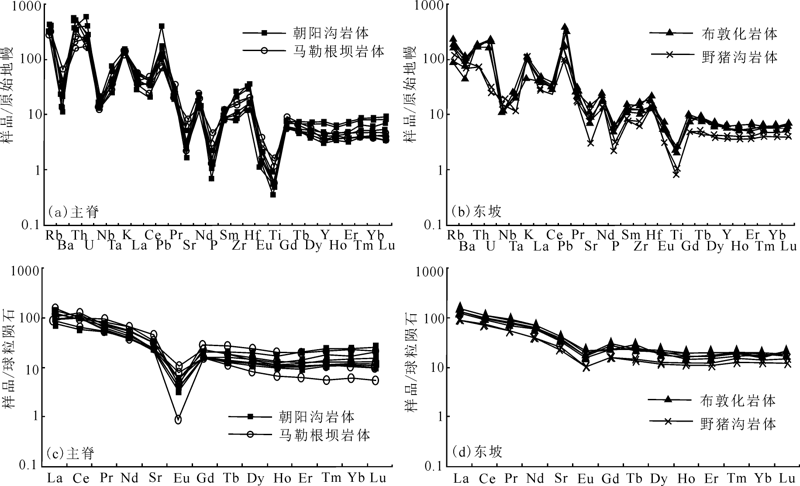
Fig.5 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram and chondrite-normalized REE patterns of granite samples from the main ridge and the east slope of Daxing’anling Mountains
| 测点号 | 岩 体 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||||||||
| MLG03-1/3 | 马勒根坝 | 16 | 687 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 0 | 0.153 0 | 0.003 3 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 153 | 48 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | |||||||
| MLG03-1/4 | 48 | 2 138 | 0.049 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.156 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 172 | 19 | 148 | 1 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/5 | 24 | 1 100 | 0.048 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 6 | 0.001 8 | 0.022 8 | 0.000 2 | 142 | 25 | 145 | 2 | 145 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/8 | 16 | 684 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 8 | 0.157 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 151 | 41 | 148 | 3 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/10 | 29 | 1 307 | 0.050 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.022 3 | 0.000 2 | 195 | 24 | 145 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/11 | 38 | 1 777 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.149 1 | 0.001 5 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 112 | 21 | 141 | 1 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/12 | 43 | 1 955 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.155 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 26 | 147 | 2 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/13 | 14 | 640 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 9 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 9 | 0.022 5 | 0.000 2 | 154 | 43 | 144 | 3 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/15 | 4 | 3 760 | 0.049 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.156 6 | 0.001 3 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 149 | 16 | 148 | 1 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/16 | 21 | 946 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 2 | 0.000 2 | 177 | 30 | 144 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/17 | 16 | 722 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 8 | 0.153 9 | 0.002 7 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 165 | 38 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/19 | 22 | 1 085 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 7 | 0.152 9 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 175 | 31 | 144 | 2 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/2 | 朝阳沟 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 3 | 0.003 1 | 0.169 3 | 0.010 6 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 145 | 159 | 10 | 158 | 1 | |||||||
| CY19-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 8 | 0.170 4 | 0.002 7 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 176 | 36 | 160 | 3 | 159 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/4 | 329 | 0.050 1 | 0.002 0 | 0.168 6 | 0.006 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 199 | 92 | 158 | 6 | 155 | 1 | |||||||||
| CY19-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.165 5 | 0.001 6 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 162 | 18 | 156 | 1 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/7 | 36 | 1 502 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.164 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 135 | 22 | 154 | 2 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/10 | 40 | 1 770 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.158 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 115 | 26 | 149 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.165 5 | 0.006 2 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 155 | 87 | 156 | 6 | 156 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/12 | 49 | 2 167 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 4 | 0.159 5 | 0.001 5 | 0.023 4 | 0.000 2 | 167 | 19 | 150 | 1 | 149 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.162 5 | 0.002 0 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 174 | 27 | 153 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.050 3 | 0.004 6 | 0.166 1 | 0.015 2 | 0.024 0 | 0.000 2 | 208 | 214 | 156 | 14 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/16 | 15 | 612 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 0 | 0.162 5 | 0.003 6 | 0.023 9 | 0.000 2 | 158 | 50 | 153 | 3 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.049 7 | 0.003 1 | 0.168 1 | 0.011 8 | 0.024 5 | 0.000 3 | 181 | 144 | 158 | 11 | 156 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/1 | 野猪沟 | 36 | 1 529 | 0.048 84 | 0.033 92 | 0.145 97 | 0.101 23 | 0.021 67 | 0.000 90 | 140 | 1 029 | 138 | 90 | 138 | 6 | |||||||
| YC10-1/2 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 19 | 0.044 43 | 0.152 67 | 0.137 66 | 0.022 50 | 0.001 22 | 157 | 1 147 | 144 | 121 | 143 | 8 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.048 61 | 0.004 23 | 0.139 87 | 0.012 07 | 0.020 86 | 0.000 42 | 129 | 155 | 133 | 11 | 133 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 06 | 0.002 34 | 0.154 95 | 0.007 37 | 0.022 90 | 0.000 38 | 151 | 80 | 146 | 6 | 146 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/6 | 44 | 1 904 | 0.048 70 | 0.003 43 | 0.145 72 | 0.010 14 | 0.021 69 | 0.000 42 | 133 | 120 | 138 | 9 | 138 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/8 | 12 | 496 | 0.048 61 | 0.023 62 | 0.127 96 | 0.061 88 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 97 | 129 | 754 | 122 | 56 | 122 | 6 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.051 63 | 0.001 86 | 0.161 37 | 0.005 85 | 0.022 66 | 0.000 35 | 269 | 55 | 152 | 5 | 144 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.048 88 | 0.004 97 | 0.142 63 | 0.014 46 | 0.021 16 | 0.000 39 | 142 | 192 | 135 | 13 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.048 94 | 0.003 60 | 0.141 00 | 0.010 31 | 0.020 89 | 0.000 38 | 145 | 130 | 134 | 9 | 133 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.048 60 | 0.007 98 | 0.149 71 | 0.024 43 | 0.022 33 | 0.000 56 | 129 | 283 | 142 | 22 | 142 | 4 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/18 | 12 | 486 | 0.048 63 | 0.003 04 | 0.141 83 | 0.008 81 | 0.021 15 | 0.000 38 | 130 | 106 | 135 | 8 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/19 | 8 | 341 | 0.048 64 | 0.004 12 | 0.142 12 | 0.011 95 | 0.021 19 | 0.000 40 | 131 | 153 | 135 | 11 | 135 | 3 | ||||||||
Table 2 Results of zircons LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of granite samples from Malegenba, Chaoyanggou and Yezhugou
| 测点号 | 岩 体 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | |||||||||
| MLG03-1/3 | 马勒根坝 | 16 | 687 | 0.000 1 | 0.001 0 | 0.153 0 | 0.003 3 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 153 | 48 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | |||||||
| MLG03-1/4 | 48 | 2 138 | 0.049 5 | 0.000 4 | 0.156 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 172 | 19 | 148 | 1 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/5 | 24 | 1 100 | 0.048 9 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 6 | 0.001 8 | 0.022 8 | 0.000 2 | 142 | 25 | 145 | 2 | 145 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/8 | 16 | 684 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 8 | 0.157 1 | 0.002 9 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 151 | 41 | 148 | 3 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/10 | 29 | 1 307 | 0.050 0 | 0.000 5 | 0.153 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.022 3 | 0.000 2 | 195 | 24 | 145 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/11 | 38 | 1 777 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.149 1 | 0.001 5 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 112 | 21 | 141 | 1 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/12 | 43 | 1 955 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.155 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 26 | 147 | 2 | 146 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/13 | 14 | 640 | 0.049 1 | 0.000 9 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 9 | 0.022 5 | 0.000 2 | 154 | 43 | 144 | 3 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/15 | 4 | 3 760 | 0.049 0 | 0.000 3 | 0.156 6 | 0.001 3 | 0.023 2 | 0.000 2 | 149 | 16 | 148 | 1 | 148 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/16 | 21 | 946 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.152 2 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 2 | 0.000 2 | 177 | 30 | 144 | 2 | 142 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/17 | 16 | 722 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 8 | 0.153 9 | 0.002 7 | 0.022 6 | 0.000 2 | 165 | 38 | 145 | 3 | 144 | 1 | ||||||||
| MLG03-1/19 | 22 | 1 085 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 7 | 0.152 9 | 0.002 1 | 0.022 4 | 0.000 2 | 175 | 31 | 144 | 2 | 143 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/2 | 朝阳沟 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 3 | 0.003 1 | 0.169 3 | 0.010 6 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 164 | 145 | 159 | 10 | 158 | 1 | |||||||
| CY19-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 8 | 0.170 4 | 0.002 7 | 0.024 9 | 0.000 2 | 176 | 36 | 160 | 3 | 159 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/4 | 329 | 0.050 1 | 0.002 0 | 0.168 6 | 0.006 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 199 | 92 | 158 | 6 | 155 | 1 | |||||||||
| CY19-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 4 | 0.165 5 | 0.001 6 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 162 | 18 | 156 | 1 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/7 | 36 | 1 502 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 5 | 0.164 0 | 0.001 7 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 135 | 22 | 154 | 2 | 155 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/10 | 40 | 1 770 | 0.048 3 | 0.000 5 | 0.158 3 | 0.001 9 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 115 | 26 | 149 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 8 | 0.165 5 | 0.006 2 | 0.024 4 | 0.000 2 | 155 | 87 | 156 | 6 | 156 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/12 | 49 | 2 167 | 0.049 4 | 0.000 4 | 0.159 5 | 0.001 5 | 0.023 4 | 0.000 2 | 167 | 19 | 150 | 1 | 149 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.049 6 | 0.000 6 | 0.162 5 | 0.002 0 | 0.023 8 | 0.000 2 | 174 | 27 | 153 | 2 | 151 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.050 3 | 0.004 6 | 0.166 1 | 0.015 2 | 0.024 0 | 0.000 2 | 208 | 214 | 156 | 14 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/16 | 15 | 612 | 0.049 2 | 0.001 0 | 0.162 5 | 0.003 6 | 0.023 9 | 0.000 2 | 158 | 50 | 153 | 3 | 153 | 1 | ||||||||
| CY19-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.049 7 | 0.003 1 | 0.168 1 | 0.011 8 | 0.024 5 | 0.000 3 | 181 | 144 | 158 | 11 | 156 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/1 | 野猪沟 | 36 | 1 529 | 0.048 84 | 0.033 92 | 0.145 97 | 0.101 23 | 0.021 67 | 0.000 90 | 140 | 1 029 | 138 | 90 | 138 | 6 | |||||||
| YC10-1/2 | 6 | 237 | 0.049 19 | 0.044 43 | 0.152 67 | 0.137 66 | 0.022 50 | 0.001 22 | 157 | 1 147 | 144 | 121 | 143 | 8 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/3 | 19 | 750 | 0.048 61 | 0.004 23 | 0.139 87 | 0.012 07 | 0.020 86 | 0.000 42 | 129 | 155 | 133 | 11 | 133 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/5 | 49 | 2 067 | 0.049 06 | 0.002 34 | 0.154 95 | 0.007 37 | 0.022 90 | 0.000 38 | 151 | 80 | 146 | 6 | 146 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/6 | 44 | 1 904 | 0.048 70 | 0.003 43 | 0.145 72 | 0.010 14 | 0.021 69 | 0.000 42 | 133 | 120 | 138 | 9 | 138 | 3 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/8 | 12 | 496 | 0.048 61 | 0.023 62 | 0.127 96 | 0.061 88 | 0.019 09 | 0.000 97 | 129 | 754 | 122 | 56 | 122 | 6 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/11 | 9 | 376 | 0.051 63 | 0.001 86 | 0.161 37 | 0.005 85 | 0.022 66 | 0.000 35 | 269 | 55 | 152 | 5 | 144 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/13 | 29 | 1 239 | 0.048 88 | 0.004 97 | 0.142 63 | 0.014 46 | 0.021 16 | 0.000 39 | 142 | 192 | 135 | 13 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/14 | 4 | 158 | 0.048 94 | 0.003 60 | 0.141 00 | 0.010 31 | 0.020 89 | 0.000 38 | 145 | 130 | 134 | 9 | 133 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/17 | 9 | 357 | 0.048 60 | 0.007 98 | 0.149 71 | 0.024 43 | 0.022 33 | 0.000 56 | 129 | 283 | 142 | 22 | 142 | 4 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/18 | 12 | 486 | 0.048 63 | 0.003 04 | 0.141 83 | 0.008 81 | 0.021 15 | 0.000 38 | 130 | 106 | 135 | 8 | 135 | 2 | ||||||||
| YC10-1/19 | 8 | 341 | 0.048 64 | 0.004 12 | 0.142 12 | 0.011 95 | 0.021 19 | 0.000 40 | 131 | 153 | 135 | 11 | 135 | 3 | ||||||||
| 编 号 | 岩体 位置 | 岩体名称 | 采样点 | 岩性 | 年龄/Ma | 测试方法 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 主脊 | 索伦 | 121°13'11″,46°40'58″ | 黑云母碱长花岗岩 | 125±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 周漪等[ | |
| 2 | 乌兰毛多 | 121°14'23″,46°24'42″ | 正长花岗岩 | 131±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 3 | 沙布台 | 121°05'32″,46°21'14″ | 二长花岗岩 | 129±2 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 5 | 巴尔哲 | 碱性花岗岩 | 122 | 锆石U-Pb | 赵振华等[ | |||
| 6 | 哈马尔乌拉 | 花岗斑岩 | 124.9±2.5 | 锆石U-Pb | 徐学纯等[ | |||
| 7 | 毛伊勒吐 | 石英闪长岩 | 147.97±0.95 | SHRIMP | 李雪菲等[ | |||
| 11 | 马勒根坝 | 118°49'53.31″,44°29'12.36″ | 黑云母正长花岗岩 | 145 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 12 | 白音诺尔 | 118°53'12.7″,44°26'52.3″ | 石英斑岩 | 129.0±1.4 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 14 | 朝阳沟岩体 | 118°05'12.59″,44°03'23.23″ | 含晶洞正长花岗岩 | 154 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 15 | 北大山 | 117°32'24″,43°57'15″ | 正长花岗岩 | 136±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 刘翼飞[ | ||
| 17 | 黄岗梁 | 117°37'27″,43°31'09″ | 正长花岗岩 | 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 18 | 大营子 | 117°36'34″,43°21'43″ | 二长花岗岩 | 132±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 19 | 经棚 | 117°32'30″,43°13'33″;117°44'55″, 43°15'50″;117°32'30″,43°13'33″ | 二长花岗岩 | 140±2; 140±2; 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 4 | 东坡 | 青山岩体 | 46°29'40.6″,122°07'28.6″ | 黑云母花岗闪长岩 | 134±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 葛文春等[ | |
| 8 | 杜尔基 | 121°08'57.4″,45°13'6.9″ | 正长花岗岩 | 154.5±0.5 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 9 | 布敦化 | 121°23'36″,44°55'14.8″ | 斜长花岗斑岩 | 154.1±1.6 | SHRIMP | 冯祥发[ | ||
| 10 | 敖仑花 | *120°13',44°33' | 二长花岗斑岩 | 134±4 | SHRIMP | 马星华等[ | ||
| 13 | 半砬山钼矿 | *120°07',44°03' | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 136.5±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 张晓静等[ | ||
| 16 | 野猪沟 | 119°20'14.43″,43°50'8.47 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 140.2±2.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 20 | 林西县小城子 | *118°10'00″,44°22'00″ | 石英斑岩脉 | 146.1±0.9 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 21 | 小东沟 | 117°44'30″-117°45', 43°00'-43°02'15″ | 斑状花岗岩 | 142.2±2.0 | SHRIMP | 覃锋等[ | ||
Table 3 Granite ages of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous in south Daxing’anling Mountains
| 编 号 | 岩体 位置 | 岩体名称 | 采样点 | 岩性 | 年龄/Ma | 测试方法 | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 主脊 | 索伦 | 121°13'11″,46°40'58″ | 黑云母碱长花岗岩 | 125±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 周漪等[ | |
| 2 | 乌兰毛多 | 121°14'23″,46°24'42″ | 正长花岗岩 | 131±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 3 | 沙布台 | 121°05'32″,46°21'14″ | 二长花岗岩 | 129±2 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 5 | 巴尔哲 | 碱性花岗岩 | 122 | 锆石U-Pb | 赵振华等[ | |||
| 6 | 哈马尔乌拉 | 花岗斑岩 | 124.9±2.5 | 锆石U-Pb | 徐学纯等[ | |||
| 7 | 毛伊勒吐 | 石英闪长岩 | 147.97±0.95 | SHRIMP | 李雪菲等[ | |||
| 11 | 马勒根坝 | 118°49'53.31″,44°29'12.36″ | 黑云母正长花岗岩 | 145 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 12 | 白音诺尔 | 118°53'12.7″,44°26'52.3″ | 石英斑岩 | 129.0±1.4 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 14 | 朝阳沟岩体 | 118°05'12.59″,44°03'23.23″ | 含晶洞正长花岗岩 | 154 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 15 | 北大山 | 117°32'24″,43°57'15″ | 正长花岗岩 | 136±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 刘翼飞[ | ||
| 17 | 黄岗梁 | 117°37'27″,43°31'09″ | 正长花岗岩 | 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 18 | 大营子 | 117°36'34″,43°21'43″ | 二长花岗岩 | 132±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 19 | 经棚 | 117°32'30″,43°13'33″;117°44'55″, 43°15'50″;117°32'30″,43°13'33″ | 二长花岗岩 | 140±2; 140±2; 141±1 | LA-ICP-MS | Wu等[ | ||
| 4 | 东坡 | 青山岩体 | 46°29'40.6″,122°07'28.6″ | 黑云母花岗闪长岩 | 134±2 | LA-ICP-MS | 葛文春等[ | |
| 8 | 杜尔基 | 121°08'57.4″,45°13'6.9″ | 正长花岗岩 | 154.5±0.5 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 9 | 布敦化 | 121°23'36″,44°55'14.8″ | 斜长花岗斑岩 | 154.1±1.6 | SHRIMP | 冯祥发[ | ||
| 10 | 敖仑花 | *120°13',44°33' | 二长花岗斑岩 | 134±4 | SHRIMP | 马星华等[ | ||
| 13 | 半砬山钼矿 | *120°07',44°03' | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 136.5±1.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 张晓静等[ | ||
| 16 | 野猪沟 | 119°20'14.43″,43°50'8.47 | 中粗粒二长花岗岩 | 140.2±2.7 | LA-ICP-MS | 本文 | ||
| 20 | 林西县小城子 | *118°10'00″,44°22'00″ | 石英斑岩脉 | 146.1±0.9 | LA-ICP-MS | 江思宏等[ | ||
| 21 | 小东沟 | 117°44'30″-117°45', 43°00'-43°02'15″ | 斑状花岗岩 | 142.2±2.0 | SHRIMP | 覃锋等[ | ||
| [1] | 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊. 大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J]. 地学前缘, 1999,6(4):339-346. |
| [2] | 邵济安, 赵国龙, 王忠, 等. 大兴安岭中生代火山活动构造背景[J]. 地质论评, 1999,45(增):422-430. |
| [3] | 邵济安, 刘福田, 陈辉, 等. 大兴安岭—燕山晚中生代岩浆活动与俯冲作用关系[J]. 地质学报, 2001,75(1):56-63. |
| [4] | 邵济安, 韩庆军, 李惠民. 华北克拉通早中生代麻粒岩捕虏体的发现[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2000,30(增):148-153. |
| [5] | 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊, 等. 大兴安岭的隆起与地球动力学背景[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 18-28. |
| [6] | METELKIN D V, GORDIENKO I V, KLIMUK V S. Paleomagnetism of Upper Jurassic basalts from Transbaikalia:New data on the time of closure of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean and Mesozoic intraplate tectonics of central Asia-Russian[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2007,48(10):825-834. |
| [7] | KRAVEHISKY V A, COGNE J P, HARBERT W P, et al. Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean as constrained by new palaeo-magnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suturezone, Siberia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2002,148(1):34-57. |
| [8] | 林强, 葛文春, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭中生代花岗岩类的地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2004,20(3):403-412. |
| [9] | 葛文春, 隋振民, 吴福元, 等. 大兴安岭东北部早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):423-440. |
| [10] | 赵国龙, 杨桂林, 王忠, 等. 大兴安岭中南部中生代火山岩[M]. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1989: 1-200. |
| [11] | 马家骏, 方大赫. 黑龙江省中生代火山岩初步研究[J]. 黑龙江地质, 1991,2(2):1-16. |
| [12] | 邓晋福, 赵海玲, 莫宣学, 等. 中国大陆根-柱构造——大陆动力学的钥匙[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-110. |
| [13] | 朱勤文, 路凤香, 谢意红, 等. 大陆边缘扩张型活动带火山岩组合——松辽盆地周边中生代火山岩研究[J]. 岩石学报, 1997,13(4) : 551-562. |
| [14] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 张广良, 等. 论燕山运动的深部地球动力学本质[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000,6(3):379-388. |
| [15] | WANG P J, LIU W Z, WANG S X, et al. 40Ar/39Ar and K/Ar dating on the volcanic rocks in the Songliao basin, NE China: constraints on stratigraphy and basin dynamics [J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002,91(2):331-340. |
| [16] | 吴福元, 孙德有, 林强. 东北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生[J]. 岩石学报, 1999,15(2):181-189. |
| [17] | FAN W M, GUO F, WANG Y J, et al. Late Mesozoic calc-alkaline volcanism of post-orogenic extension in the northern Da Hinggan mountains, northeastern China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2003,121(1):115-135. |
| [18] | 曹生儒. 对内蒙古板块构造轮廓的新认识[J]. 中国区域地质, 1993(3):211-215. |
| [19] | 辽宁省第二区域地质测量队. 协里府幅、巴林左旗幅1∶200000区域地质矿产报告书(地质部分)[R]. 大连:辽宁省第二区域地质测量队, 1971. |
| [20] | 武新丽. 内蒙古布敦化铜矿矿床地质特征与成矿研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2013. |
| [21] | 冯祥发. 内蒙古兴安盟布敦化铜矿地质与地球化学特征研究[D]. 内蒙古煤炭经济 2010(4):41-44. |
| [22] | LIU Y S, HU Z C, GAO S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,257(1/2):34-43. |
| [23] | 李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2009,29(1):600-601. |
| [24] | 张旗. 花岗岩Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006,22(9):2249-2269. |
| [25] | 冯艳芳, 邓晋福, 王世进, 等. 鲁西地区早前寒武纪花岗岩类中镁安山质岩石系列(MA)的识别及大陆地壳生长[J]. 中国地质, 2010,37(4):1119-1120. |
| [26] | 沈阳地质矿产研究所. 西乌珠穆沁旗幅1∶25万区域地质调查报告[R]. 沈阳:沈阳地质矿产研究所, 2005. |
| [27] | MILLER C F, MCDOWELL S M, MAPES R W. Hot and cold granites ? Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003,31(6):529-532. |
| [28] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [29] | EWART A, GRIFFIN W L. Application of proton-microprobe data to trace-element partitioning in volcanic rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994,117(1/4):251-284. |
| [30] | SUN S S, HANSON G N. Rare earth element evidence for differentiation of McMundo volcanics,Ross Island, Antarctica[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976,54(2):139-155. |
| [31] | 邓晋福, 罗照华, 苏尚国, 等. 岩石成因、构造环境与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 20-30. |
| [32] | WILSON M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London: Allen and Unwin, 1989: 1-10. |
| [33] | 徐学纯, 李雪菲, 赵庆英, 等. 内蒙古哈马尔乌拉花岗斑岩的锆石U-Pb定年及其岩石地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2011,20(3):161-166. |
| [34] | 赵振华, 熊小林, 韩小东, 等. 花岗岩稀土元素四分组效应形成机理探讨——以千里山和巴尔哲花岗岩为例[J]. 中国科学( D辑), 1999,29(4):331-338. |
| [35] | 周漪, 葛文春, 王清海. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的成因——地球化学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011,30(5):901-923. |
| [36] | 刘翼飞. 内蒙古克什克腾旗拜仁达坝银多金属矿床成因研究[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院, 2009. |
| [37] | WU F Y, SUN D Y, GE W C, et al. Geochronology of the phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011,41:1-30. |
| [38] | 李雪菲, 赵庆英, 王晓志, 等. 内蒙古扎鲁特地区毛伊勒吐岩体形成时代及构造环境[J]. 地质与资源, 2012,21(2):194-199. |
| [39] | 江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古孟恩陶勒盖银多金属矿床及其附近侵入岩的年代学[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011,41(6):1755-1769. |
| [40] | 张晓静, 张连昌, 靳新娣, 等. 内蒙古半砬山钼矿含矿斑岩U-Pb年龄和地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010,26(5):1411-1422. |
| [41] | 葛文春, 吴福元, 周长勇, 等. 大兴安岭中部乌兰浩特地区中生代花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2005,21(3):749-762. |
| [42] | 马星华, 陈斌, 赖勇, 等. 内蒙古敖仑花斑岩钼矿床成岩成矿年代学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(11):2939-2950. |
| [43] | 江思宏, 梁清玲, 刘翼飞, 等. 内蒙古大井矿区及外围岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其对成矿时间的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(2):495-507. |
| [44] | 覃锋, 刘建明, 曾庆栋, 等. 内蒙古克什克腾旗小东沟斑岩型钼矿床成岩成矿机制探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2009,25(12):3357-3368. |
| [45] | WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDER S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (I):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003,66(3/4):241-273. |
| [46] | CHAPPELL B W. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999,46(3):535-551. |
| [47] | 张旗. 花岗岩与地壳厚度关系探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011,35(2):259-269. |
| [48] | LIEGEOIS J P, NAVEZ J, HERTOGEN J, et al. Contrasting origin of post-collisional high-K calc-alkaline and shoshonitic versus alkaline and peralkaline granitoids the use of sliding normalization[J]. Lithos, 1998,45(1/4):1-28. |
| [49] | PEARCE J A. Source and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996,19(4):120-125. |
| [50] | ZHOU X M, LI W X. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern China: Implications for lithosphere subduction and underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000,326(3/4):269-287. |
| [51] | MARUYAMA S, SENO T. Orogeny and relative plate motions:Example of the Japanese Island[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986,127(3/4):305-329. |
| [52] | ENGEBRETSON D C, COX A, GORDON R G. Relative Motions Between Oceanic and Continental Plates in the Pacific Basin[M]. Washington:Geological Society of America Specical Paper, 1985: 1-59. |
| [53] | 包汉勇, 郭战峰, 张罗磊, 等. 太平洋板块形成以来的中国东部构造动力学背景[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013,28(3):337-346. |
| [54] | 张旗. 中国东部中生代岩浆活动与太平洋板块向西俯冲有关吗?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013,32(1):113-128. |
| [55] | MARUYAMA S, ISOZAKI Y, KIMURA G, et al. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic sysjournal from 750Ma to the present[J]. Island Arc, 1997,6:121-142. |
| [56] | ISOZAKI Y, KAZUMASA A, NAKAMA T, et al. New insight into a subduction-related orogen: A reappraisal of the geotectonic framework and evolution of the Japanese Islands[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010,18(1):82-105. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||