



Geoscience ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (01): 130-140.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.010
• Marine Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
SONG Bei1( ), SU Xin1(
), SU Xin1( ), LÜ Shihui1, NI Jianyu2, LIAO Shili2, TAO Chunhui2, HU Maokang1, LI Shiyun1, YU Chonghan1
), LÜ Shihui1, NI Jianyu2, LIAO Shili2, TAO Chunhui2, HU Maokang1, LI Shiyun1, YU Chonghan1
Received:2019-06-20
Revised:2019-09-20
Online:2020-03-05
Published:2020-03-07
Contact:
SU Xin
CLC Number:
SONG Bei, SU Xin, LÜ Shihui, NI Jianyu, LIAO Shili, TAO Chunhui, HU Maokang, LI Shiyun, YU Chonghan. Geochemical Contrast in Sediments from Active and Inactive hydrothermal Fields on the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(01): 130-140.
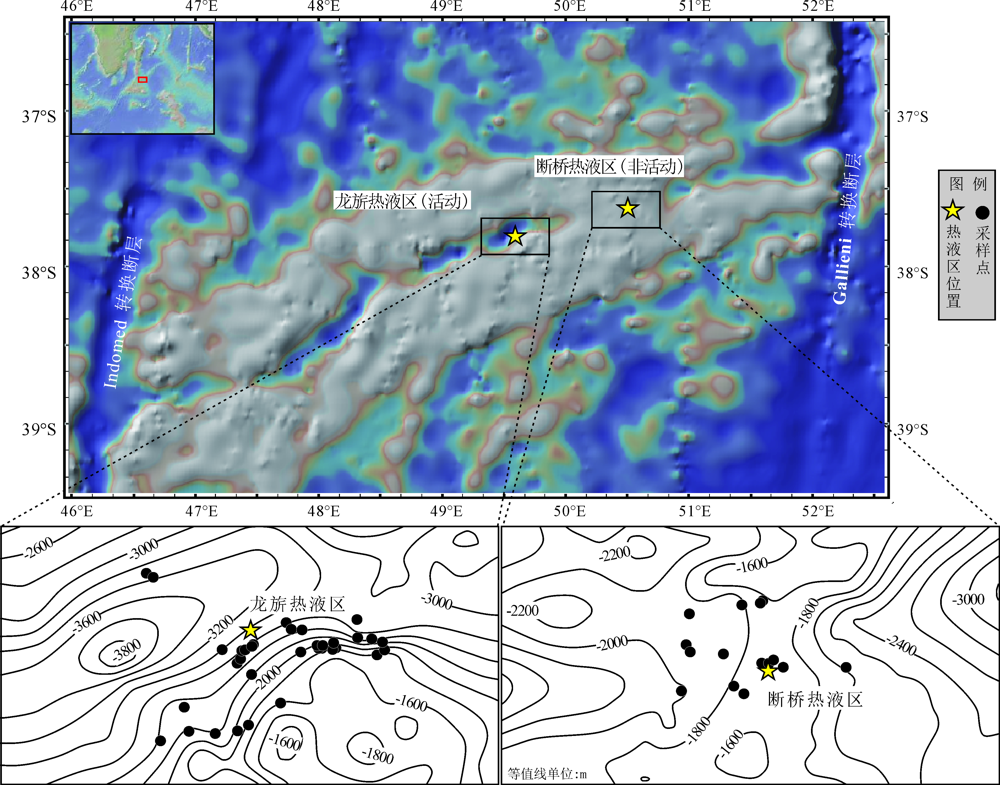
Fig.1 Maps showing tectonic settings of the study area and locations of samples(location of the hydrothermal fields from reference [6], base map of geotectonic setting from GeoMap App, topographic data from www.gebco.net)
| 元素 | 龙旂热液区 | 断桥热液区 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | ||
| SiO2 | 2.30 | 37.98 | 9.49 | 10.47 | 1.53 | 31.24 | 6.60 | 10.56 | |
| Al2O3 | 0.79 | 7.57 | 2.37 | 1.84 | 0.54 | 9.47 | 1.82 | 3.23 | |
| TFe2O3 | 0.61 | 9.03 | 2.05 | 2.57 | 0.29 | 7.84 | 1.21 | 2.78 | |
| MgO | 0.40 | 36.30 | 1.62 | 8.24 | 0.40 | 4.87 | 0.77 | 1.60 | |
| CaO | 2.01 | 50.03 | 43.24 | 13.26 | 25.42 | 53.05 | 47.61 | 9.49 | |
| Na2O | 0.41 | 2.10 | 1.46 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.48 | |
| K2O | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.05 | |
| MnO | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
| TiO2 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 0.31 | |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| Li | 2.57 | 12.05 | 6.35 | 2.04 | 3.33 | 11.10 | 4.58 | 1.86 | |
| Be | 0.03 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| V | 11.45 | 145.14 | 37.70 | 38.96 | 9.84 | 223.00 | 30.50 | 76.65 | |
| Cr | 0.11 | 1 814.70 | 37.70 | 477.80 | 6.02 | 153.00 | 17.50 | 47.33 | |
| Co | 6.10 | 125.00 | 19.80 | 26.50 | 6.76 | 152.00 | 27.70 | 38.15 | |
| Ni | 21.00 | 1 575.00 | 43.70 | 348.81 | 20.80 | 90.70 | 42.30 | 17.10 | |
| Cu | 19.87 | 1 238.00 | 69.40 | 213.56 | 9.67 | 148.00 | 31.60 | 38.05 | |
| Zn | 12.79 | 210.00 | 38.20 | 46.16 | 15.80 | 100.00 | 28.65 | 29.95 | |
| Sr | 101.00 | 1 694.00 | 1 239.00 | 418.12 | 658.45 | 1 540.00 | 1 248.00 | 263.45 | |
| Y | 1.52 | 25.80 | 13.40 | 4.37 | 5.53 | 30.10 | 12.25 | 7.04 | |
| Mo | 0.16 | 4.83 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 0.17 | 0.85 | 0.32 | 0.22 | |
| Cd | 0.03 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 0.15 | |
| Rb | 0.32 | 10.70 | 7.05 | 2.62 | 2.36 | 7.05 | 4.27 | 1.18 | |
| Cs | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.09 | |
| Ba | 6.41 | 735.00 | 409.00 | 170.60 | 46.70 | 381.00 | 206.50 | 92.87 | |
| W | 0.19 | 289.00 | 10.40 | 46.82 | 0.26 | 323.00 | 29.80 | 85.20 | |
| Pb | 0.72 | 7.04 | 3.89 | 1.35 | 3.64 | 44.80 | 9.23 | 8.95 | |
| Th | 0.04 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 1.11 | 0.66 | 0.19 | |
| U | 0.16 | 2.06 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.09 | |
| Zr | 3.29 | 52.70 | 15.00 | 10.62 | 5.44 | 72.70 | 14.75 | 22.27 | |
| LREE | 1.80 | 37.10 | 24.65 | 7.27 | 16.23 | 45.58 | 23.22 | 8.13 | |
| HREE | 0.98 | 14.09 | 7.01 | 2.45 | 3.32 | 19.05 | 6.20 | 4.89 | |
| REE | 2.78 | 48.60 | 31.15 | 8.90 | 20.20 | 55.39 | 30.63 | 11.22 | |
| LREE/HREE | 1.35 | 4.63 | 3.46 | 0.91 | 1.59 | 5.26 | 3.94 | 1.13 | |
| (La/Yb | 0.72 | 6.59 | 3.95 | 1.63 | 1.06 | 7.54 | 4.25 | 1.84 | |
| δEu* | 0.74 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 4.85 | 0.22 | 1.31 | |
| δCe* | 0.51 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| C | -0.36 | 0.03 | -0.27 | 0.06 | -0.28 | 0.18 | -0.18 | 0.11 | |
Table 1 Statistics of the element compositions of the sediment samples from the study area
| 元素 | 龙旂热液区 | 断桥热液区 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位数 | 标准差 | ||
| SiO2 | 2.30 | 37.98 | 9.49 | 10.47 | 1.53 | 31.24 | 6.60 | 10.56 | |
| Al2O3 | 0.79 | 7.57 | 2.37 | 1.84 | 0.54 | 9.47 | 1.82 | 3.23 | |
| TFe2O3 | 0.61 | 9.03 | 2.05 | 2.57 | 0.29 | 7.84 | 1.21 | 2.78 | |
| MgO | 0.40 | 36.30 | 1.62 | 8.24 | 0.40 | 4.87 | 0.77 | 1.60 | |
| CaO | 2.01 | 50.03 | 43.24 | 13.26 | 25.42 | 53.05 | 47.61 | 9.49 | |
| Na2O | 0.41 | 2.10 | 1.46 | 0.29 | 0.92 | 2.59 | 1.40 | 0.48 | |
| K2O | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.05 | |
| MnO | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.06 | |
| TiO2 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 0.31 | |
| P2O5 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 | |
| Li | 2.57 | 12.05 | 6.35 | 2.04 | 3.33 | 11.10 | 4.58 | 1.86 | |
| Be | 0.03 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| V | 11.45 | 145.14 | 37.70 | 38.96 | 9.84 | 223.00 | 30.50 | 76.65 | |
| Cr | 0.11 | 1 814.70 | 37.70 | 477.80 | 6.02 | 153.00 | 17.50 | 47.33 | |
| Co | 6.10 | 125.00 | 19.80 | 26.50 | 6.76 | 152.00 | 27.70 | 38.15 | |
| Ni | 21.00 | 1 575.00 | 43.70 | 348.81 | 20.80 | 90.70 | 42.30 | 17.10 | |
| Cu | 19.87 | 1 238.00 | 69.40 | 213.56 | 9.67 | 148.00 | 31.60 | 38.05 | |
| Zn | 12.79 | 210.00 | 38.20 | 46.16 | 15.80 | 100.00 | 28.65 | 29.95 | |
| Sr | 101.00 | 1 694.00 | 1 239.00 | 418.12 | 658.45 | 1 540.00 | 1 248.00 | 263.45 | |
| Y | 1.52 | 25.80 | 13.40 | 4.37 | 5.53 | 30.10 | 12.25 | 7.04 | |
| Mo | 0.16 | 4.83 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 0.17 | 0.85 | 0.32 | 0.22 | |
| Cd | 0.03 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.72 | 0.30 | 0.15 | |
| Rb | 0.32 | 10.70 | 7.05 | 2.62 | 2.36 | 7.05 | 4.27 | 1.18 | |
| Cs | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.09 | |
| Ba | 6.41 | 735.00 | 409.00 | 170.60 | 46.70 | 381.00 | 206.50 | 92.87 | |
| W | 0.19 | 289.00 | 10.40 | 46.82 | 0.26 | 323.00 | 29.80 | 85.20 | |
| Pb | 0.72 | 7.04 | 3.89 | 1.35 | 3.64 | 44.80 | 9.23 | 8.95 | |
| Th | 0.04 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 1.11 | 0.66 | 0.19 | |
| U | 0.16 | 2.06 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.09 | |
| Zr | 3.29 | 52.70 | 15.00 | 10.62 | 5.44 | 72.70 | 14.75 | 22.27 | |
| LREE | 1.80 | 37.10 | 24.65 | 7.27 | 16.23 | 45.58 | 23.22 | 8.13 | |
| HREE | 0.98 | 14.09 | 7.01 | 2.45 | 3.32 | 19.05 | 6.20 | 4.89 | |
| REE | 2.78 | 48.60 | 31.15 | 8.90 | 20.20 | 55.39 | 30.63 | 11.22 | |
| LREE/HREE | 1.35 | 4.63 | 3.46 | 0.91 | 1.59 | 5.26 | 3.94 | 1.13 | |
| (La/Yb | 0.72 | 6.59 | 3.95 | 1.63 | 1.06 | 7.54 | 4.25 | 1.84 | |
| δEu* | 0.74 | 1.25 | 1.03 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 4.85 | 0.22 | 1.31 | |
| δCe* | 0.51 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.05 | |
| C | -0.36 | 0.03 | -0.27 | 0.06 | -0.28 | 0.18 | -0.18 | 0.11 | |

Fig.3 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of sediments samples from the study area (data of chondrite-normalization from reference [48], basalt and peridotite from reference [52], and sulfide from reference [53])

Fig.4 Discriminant results of compositions of sediment samples from the study area (data of basalt from references[52] and [58], peridotite from references [52] and [59])
| [1] | BEAULIEU S E, BAKER E T, GERMAN C R, et al. An authoritative global database for active submarine hydrothermal vent fields[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013,14(11):4892-4905. |
| [2] | BAKER E T, GERMAN C R. On the global distribution of hydrothermal vent fields[M] // GERMANCR. Mid-Ocean Ridges: Hydrothermal Interactions Between the Lithosphere and Oceans. Washington: American Geophysical Union, 2004: 245-266. |
| [3] | SINGER D A. Base and precious metal resources in seafloor massive sulfide deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014,59(6):66-72. |
| [4] | HANNINGTON M, JAMIESON J, MONECKE T, et al. The abundance of seafloor massive sulfide deposits[J]. Geology, 2011,39(12):1155-1158. |
| [5] | BEAULIEU S E, BAKER E T, GERMAN C R. Where are the undiscovered hydrothermal vents on oceanic spreading ridges?[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2015,121:202-212. |
| [6] | TAO C, LI H, JIN X, et al. Seafloor hydrothermal activity and polymetallic sulfide exploration on the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014,59(19):2266-2276. |
| [7] | COLLINS P C, CROOT P, CARLSSON J, et al. A primer for the environmental impact assessment of mining at seafloor massive sulfide deposits[J]. Marine Policy, 2013,42(14):198-209. |
| [8] | FITZSIMMONS J N, JOHN S G, MARSAY C M, et al. Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved-particulate exchange[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2017,10(3):195-201. |
| [9] | DIAS Á S, BARRIGA F J A S. Mineralogy and geochemistry of hydrothermal sediments from the serpentinite-hosted Saldanha hydrothermal field (36°34'N, 33°26'W) at MAR[J]. Marine Geology, 2006,225(1/4):157-175. |
| [10] | FEELY R A, LEWISON M, MASSOTH G J, et al. Composition and dissolution of black smoker particulates from active vents on the Juan de Fuca Ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1987,92(11):11347-11363. |
| [11] | GERMAN C R, HIGGS N C, THOMSON J, et al. A geochemical study of metalliferous sediment from the TAG hydrothermal mound, 26°08'N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1993,98(6):9683-9692. |
| [12] | SHEARME S, CRONAN D S, RONA P A. Geochemistry of sediments from the TAG hydrothermal field, M.A.R. at latitude 26° N[J]. Marine Geology, 1983,51(3):269-291. |
| [13] | COOGAN L A, ATTAR A, MIHALY S F, et al. Near-vent chemical processes in a hydrothermal plume: Insights from an integrated study of the Endeavour segment[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017,18(4):1641-1660. |
| [14] | KUHN T, BURGER H, CASTRADORI D, et al. Volcanic and hydrothermal history of ridge segments near the Rodrigues Triple Junction (Central Indian Ocean) deduced from sediment geochemistry[J]. Marine Geology, 2000,169(3/4):391-409. |
| [15] | CAVE R R, GERMAN C R, THOMSON J, et al. Fluxes to sediments underlying the Rainbow hydrothermal plume at 36°14'N on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002,66(11):1905-1923. |
| [16] | HUMPHRIS S E, KLEIN F. Progress in deciphering the controls on the geochemistry of fluids in seafloor hydrothermal systems[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2018,10:315-343. |
| [17] | HANNINGTON M D, DE RONDE C D J, PETERSEN S. Sea-floor tectonics and submarine hydrothermal systems[M] // HEDENQUISTJ W.Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume. Littelton: Society of Economic Geologists, 2005: 111-141. |
| [18] |
DICK H J B, LIN J, SCHOUTEN H. An ultraslow-spreading class of ocean ridge[J]. Nature, 2003,426:405-412.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] | CANNAT M, SAUTER D, BEZOS A, et al. Spreading rate, spreading obliquity, and melt supply at the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008,9(4):1-26. |
| [20] | BAKER E T, CHEN Y J, MORGAN J P. The relationship between near-axis hydrothermal cooling and the spreading rate of mid-ocean ridges[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1996,142(1):137-145. |
| [21] | GERMAN C R, BAKER E T, MEVEL C, et al. Hydrothermal activity along the southwest Indian ridge[J]. Nature, 1998,395:490-493. |
| [22] | BAKER E T, EDMONDS H N, MICHAEL P J, et al. Hydrothermal venting in magma deserts: The ultraslow-spreading Gakkel and Southwest Indian Ridges[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2004,5(8):1-29. |
| [23] | SNOW J E, EDMONDS H N. Ultraslow-spreading ridges: rapid paradigm changes[J]. Oceanography, 2007,20(1):90-101. |
| [24] | 陈圆圆, 于炳松, 苏新, 等. 西南印度洋中脊钙质沉积物地球化学及矿物学特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013,32(1):107-113. |
| [25] | 黄大松, 张霄宇, 张国堙, 等. 西南印度洋中脊48.6°~51.7°E沉积物地球化学特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016,35(1):22-29. |
| [26] | VALLIER T L, KIDD R B. Volcanogenic sediments in the Indian Ocean[M] //HEIRTZLERJR. Indian Ocean Geology and Biostratigraphy.Washington: American Geophysical Union, 1977: 87-118. |
| [27] | PATTAN J N, PRATIMAJAUHAR I. Major, trace, and rare earth elements in the sediments of the Central Indian Ocean Basin: Their source and distribution[J]. Marine Geotechnology, 2001,19(2):85-106. |
| [28] | KOLLA V, HENDERSON L, BISCAYE P E. Clay mineralogy and sedimentation in the western Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research, 1976,23(10):949-961. |
| [29] | 林震, 于洪军, 徐兴永, 等. 西南印度洋中脊扩张轴部(34.9°S)西翼沉积物地球化学分析及物源探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018,38(5):14-29. |
| [30] | LI Z, CHU F, JIN L, et al. Major and trace element composition of surface sediments from the Southwest Indian Ridge: evidence for the incorporation of a hydrothermal component[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016,35(2):101-108. |
| [31] | GERMAN C R. Hydrothermal activity on the eastern SWIR (50°-70°E): Evidence from core-top geochemistry, 1887 and 1998[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003,4(7):1-13. |
| [32] | 曹凯君, 吴仲玮, 孙晓明, 等. 西南印度洋脊龙旂热液区富铝蚀变黏土矿物类型和地球化学特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018,37(6):607-617. |
| [33] | LIAO S, TAO C, LI H, et al. Surface sediment geochemistry and hydrothermal activity indicators in the Dragon Horn area on the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Marine Geology, 2018,398:22-34. |
| [34] | 贾琦, 范德江, 张文强, 等. 西南印度洋中脊表层沉积物中硫化物矿物学特征与地质意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2017,37(6):725-736. |
| [35] | PAN A, YANG Q, ZHOU H, et al. Geochemical impacts of hydrothermal activity on surface deposits at the Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2018,139:1-13. |
| [36] | LIAO S, TAO C, DIAS Á A, et al. Surface sediment composition and distribution of hydrothermal derived elements at the Duanqiao-1 hydrothermal field, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Marine Geology, 2019,416:105975. |
| [37] | DYMOND J. Geochemistry of Nazca plate surface sediments: An evaluation of hydrothermal, biogenic, detrital, and hydrogenous sources[J]. Geological Society of America Memoirs, 1981,154:133-174. |
| [38] | MARCHIG V, GUNDLACH H, MÖLLER P, et al. Some geochemical indicators for discrimination between diagenetic and hydrothermal metalliferous sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 1982,50(3):241-256. |
| [39] | KEITH M, HÄCKEL F, HAASE K M, et al. Trace element systematics of pyrite from submarine hydrothermal vents[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016,72:728-745. |
| [40] | TAO C, LIN J, GUO S, et al. First active hydrothermal vents on an ultraslow-spreading center: Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Geology, 2012,40(1):47-50. |
| [41] | ZHAO M, QIU X, LI J, et al. Three-dimensional seismic structure of the Dragon Flag oceanic core complex at the ultraslow spreading Southwest Indian Ridge (49°39'E)[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013,14(10):4544-4563. |
| [42] | 叶俊, 石学法, 杨耀民, 等. 西南印度洋超慢速扩张脊49.6°E热液区硫化物矿物学特征及其意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2011,31(1):17-29. |
| [43] | JI F, ZHOU H, YANG Q, et al. Geochemistry of hydrothermal vent fluids and its implications for subsurface processes at the active Longqi hydrothermal field, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017,122:41-47. |
| [44] | 杨伟芳. 西南印度洋中脊断桥热液区成矿作用研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2017. |
| [45] | 张俊, 李余生, 林曼利, 等. 淮南张集矿水文地球化学特征及水源识别[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014,41(6):32-37. |
| [46] | 安艳玲, 蒋浩, 吴起鑫, 等. 赤水河流域枯水期水环境质量评价研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014,23(10):1472-1478. |
| [47] | 庄作钦. B0X PLOT——描述统计的一个简便工具[J]. 统计与预测, 2003(2):56-57. |
| [48] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publication, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [49] | HASKIN L A, HASKIN M A, FREY F A, et al. Relative and absolute terrestrial abundances of the rare earths[M] //AHERENS L H.Origin and Distribution of the Elements. Oxford:Pergamon Press, 1968: 889-912. |
| [50] | WRIGHT J, SCHRADER H, HOLSER W T. Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987,51(3):631-644. |
| [51] | ELDERFIELD H, GREAVES M J. The rare earth elements in seawater[J]. Nature, 1982,296:214-219. |
| [52] | 韩宗珠, 张贺, 范德江, 等. 西南印度洋中脊50°E基性超基性岩石地球化学特征及其成因初探[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,42(9):69-76. |
| [53] | CAO Z, CAO H, TAO C, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012,31(2):62-69. |
| [54] | TOYODA K, MASUDA A. Sedimentary environments and chemical composition of Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1990,88(1):127-141. |
| [55] | 朱赖民, 高志友, 尹观, 等. 南海表层沉积物的稀土和微量元素的丰度及其空间变化[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(11):2963-2980. |
| [56] | MCMANUS J, BERELSON W M, KLINKHAMMER G P, et al. Geochemistry of barium in marine sediments: implications for its use as a paleoproxy[J]. Geochimistry et Cosmochimistry Acta, 1998,62(21/22):3453-3473. |
| [57] | PLANK T, LANGMUIR C H. The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998,145(3):325-394. |
| [58] | 于淼, 苏新, 陶春辉, 等. 西南印度洋中脊49.6°E和50.5°E区玄武岩岩石学及元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2013,27(3):497-508. |
| [59] | 陈灵. 西南印度洋中脊橄榄岩元素地球化学及其地幔动力学意义[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2016. |
| [60] | BLOEMSMA M R, ZABEL M, STUUT J B W, et al. Modeling the joint variability of grain size and chemical composition in sediments[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2012,280:135-148. |
| [61] | DYMOND J. Geochemistry of Nazca Plate surface sediments: An evaluation of hydrothermal, biogenic, detrital and hydrogeneous sources[J]. Geological Society of America Memoirs, 1981,154(12):133-173. |
| [62] | RAY D, BANERJEE R, IYER S D, et al. Glass and mineral chemistry of northern central Indian Ridge basalts: compositional diversity and petrogenetic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009,83(6):1122-1135. |
| [63] | CRONAN D S, HODKINSON R, MOORBY S A, et al. Hydrothermal and volcaniclastic sedimentation on the Tonga-Kermadec Ridge and in its adjacent marginal basins[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1984,16(1):137-149. |
| [64] | HEATH G R, DYMOND J. Genesis and transformation of metalliferous sediments from the East Pacific Rise, Bauer Deep, and Central Basin, northwest Nazca plate[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1977,88(5):723-733. |
| [65] | DYMOND J, CORLISS J B, HEATH G R, et al. Origin of metalliferous sediments from the Pacific Ocean[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1973,84(10):3355-3372. |
| [66] | WANYINGLI M, AHMADZAHARINARI S, ISMAIL T H. Spatial geochemical distribution and sources of heavy metals in the sediment of Langat River, Western Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Environmental Forensics, 2013,14(2):133-145. |
| [67] | SULTAN K, SHAZILI N A. Geochemical baselines of major, minor and trace elements in the tropical sediments of the Terengganu River basin, Malaysia[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2010,25(4):340-354. |
| [68] | WEDEPOHL K H. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1994,58(7):1217-1232. |
| [69] | BOSTROEM K, KRAEMER T, GARTNER S. Provenance and accumulation rates of opaline silica, Al, Ti, Fe, Mn, Cu, Ni and Co in Pacific pelagic sediments[J]. Chemical Geology, 1973,11(2):123-148. |
| [70] | MÜNCH U, LALOU C, HALBACH P, et al. Relict hydrothermal events along the super-slow Southwest Indian spreading ridge near 63°56'E-mineralogy, chemistry and chronology of sulfide samples[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001,177(3):341-349. |
| [71] | MÜNCH U, HALBACH P, FUJIMOTO H. Sea-floor hydrothermal mineralization from the Mt. Jourdanne, Southwest Indian Ridge[J]. JAMSTEC Journal of Deep Sea Research, 2000,16:125-132. |
| [72] | 李伟, 王建新. R型聚类分析在确定成矿岩体中的应用——以延边复兴—杜荒岭金矿化集中区为例[J]. 世界地质, 2003,22(2):147-151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||