



Geoscience ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (03): 460-473.
• Petrology and Mineral Deposits • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Jiangtao1,2( ), HE Xuefeng1(
), HE Xuefeng1( ), LIU Liang1,2, YANG Pengtao1, LIANG Bin1,2, SU Hua1, YANG Yudong1, HAN Hongming1, LIU Yingzhong3, DAI Zhihui4
), LIU Liang1,2, YANG Pengtao1, LIANG Bin1,2, SU Hua1, YANG Yudong1, HAN Hongming1, LIU Yingzhong3, DAI Zhihui4
Received:2016-05-12
Revised:2017-01-29
Online:2017-06-10
Published:2017-06-27
CLC Number:
LI Jiangtao, HE Xuefeng, LIU Liang, YANG Pengtao, LIANG Bin, SU Hua, YANG Yudong, HAN Hongming, LIU Yingzhong, DAI Zhihui. Ordovician Tectonic Evolution of Harlik in Eastern Tianshan of Xinjiang:Constraints from LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks[J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(03): 460-473.
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 总量 | Mg# | Σ | A/CNK | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 78.24 | 0.13 | 11.50 | 0.66 | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.83 | 2.14 | 5.26 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 15.12 | 1.55 | 1.07 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 71.75 | 0.71 | 13.22 | 4.33 | 1.25 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 1.93 | 3.03 | 1.48 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 41.52 | 0.71 | 1.31 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 77.88 | 0.12 | 11.31 | 0.54 | 2.10 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 3.22 | 4.50 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 8.87 | 1.71 | 1.09 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 73.29 | 0.97 | 12.19 | 2.03 | 2.28 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 3.41 | 4.24 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 100.00 | 29.20 | 0.66 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 63.12 | 0.62 | 17.07 | 1.62 | 3.88 | 0.13 | 2.19 | 2.43 | 6.35 | 2.46 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 42.27 | 3.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 68.97 | 1.00 | 14.04 | 1.70 | 3.71 | 0.18 | 1.20 | 4.07 | 4.57 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 100.00 | 28.95 | 0.91 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 49.12 | 0.93 | 20.86 | 5.36 | 6.95 | 0.35 | 3.38 | 10.68 | 1.06 | 1.15 | 0.15 | 100.00 | 33.88 | 0.80 | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 49.94 | 0.86 | 19.56 | 5.94 | 6.49 | 0.38 | 3.09 | 12.45 | 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 100.00 | 31.72 | 0.19 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 60.94 | 0.88 | 16.36 | 2.92 | 3.82 | 0.15 | 3.51 | 6.53 | 2.75 | 1.95 | 0.19 | 100.00 | 49.29 | 1.23 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Cr | Ni | Co | Rb | Cs | Sr | Ba | V | Sc | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | ||||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 6.43 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 134.34 | 8.95 | 113.69 | 389.62 | 4.18 | 2.19 | 19.40 | 1.94 | 163.61 | 5.27 | 7.34 | 30.02 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 17.98 | 6.46 | 11.13 | 31.59 | 5.37 | 248.28 | 411.88 | 58.59 | 15.38 | 9.13 | 0.78 | 138.03 | 3.92 | 0.74 | 4.01 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 12.81 | 3.84 | 1.66 | 137.60 | 2.27 | 54.68 | 113.85 | 4.39 | 1.67 | 22.17 | 1.79 | 564.04 | 13.97 | 5.66 | 21.41 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 16.02 | 2.78 | 13.86 | 5.66 | 0.70 | 147.18 | 50.98 | 108.97 | 26.49 | 2.42 | 0.17 | 106.85 | 9.27 | 0.83 | 1.72 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 35.35 | 9.00 | 16.51 | 55.68 | 3.91 | 164.98 | 401.47 | 104.04 | 18.01 | 5.60 | 0.46 | 179.66 | 5.08 | 2.37 | 8.06 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 14.58 | 1.33 | 18.26 | 6.11 | 0.73 | 177.22 | 55.86 | 133.44 | 27.28 | 2.57 | 0.19 | 113.14 | 12.15 | 0.88 | 1.77 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 122.23 | 52.95 | 29.04 | 28.27 | 3.02 | 289.83 | 601.59 | 220.87 | 37.11 | 2.41 | 0.19 | 67.96 | 2.59 | 0.56 | 0.94 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 114.37 | 49.11 | 25.46 | 8.33 | 0.85 | 322.56 | 172.00 | 194.88 | 38.58 | 1.99 | 0.15 | 63.78 | 2.08 | 0.66 | 0.83 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 22.80 | 10.80 | 20.60 | 36.60 | 2.43 | 710.00 | 1450.00 | 151.00 | 23.00 | 6.18 | 0.53 | 160.00 | 4.57 | 1.86 | 6.41 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | δEu | |||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 48.67 | 100.84 | 10.70 | 39.94 | 7.30 | 0.48 | 7.92 | 1.35 | 7.49 | 1.67 | 5.93 | 0.84 | 5.79 | 0.95 | 239.87 | 0.19 | |||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 29.39 | 61.62 | 6.49 | 29.95 | 6.10 | 1.62 | 5.74 | 0.91 | 4.91 | 1.03 | 2.98 | 0.42 | 2.89 | 0.47 | 154.54 | 0.84 | ||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 62.39 | 119.27 | 14.98 | 67.03 | 14.98 | 0.59 | 13.61 | 2.31 | 12.92 | 2.76 | 8.07 | 1.23 | 8.05 | 1.27 | 329.45 | 0.13 | |||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 13.83 | 29.63 | 4.22 | 22.40 | 5.60 | 1.34 | 5.59 | 0.98 | 5.63 | 1.19 | 3.46 | 0.51 | 3.28 | 0.52 | 98.17 | 0.73 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 17.94 | 38.00 | 4.67 | 20.81 | 4.16 | 1.25 | 3.94 | 0.65 | 3.68 | 0.80 | 2.42 | 0.37 | 2.55 | 0.41 | 101.64 | 0.95 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 15.54 | 27.92 | 4.06 | 21.77 | 5.55 | 1.48 | 5.73 | 1.04 | 5.87 | 1.29 | 3.66 | 0.54 | 3.62 | 0.60 | 98.66 | 0.80 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 8.91 | 16.16 | 2.67 | 13.85 | 3.63 | 1.52 | 4.13 | 0.73 | 4.47 | 0.98 | 2.80 | 0.41 | 2.86 | 0.46 | 68.59 | 1.20 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 8.21 | 18.01 | 2.39 | 12.90 | 3.48 | 1.40 | 4.01 | 0.77 | 4.70 | 1.02 | 2.97 | 0.44 | 2.92 | 0.47 | 63.68 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 17.20 | 37.20 | 4.89 | 19.70 | 4.52 | 1.43 | 4.58 | 0.86 | 6.06 | 1.24 | 3.65 | 0.58 | 3.60 | 0.56 | 106.07 | 0.96 | ||||||||||
Table 1 Major (%),rare earth and trace(10-6) element compositions of the Ordovician volcanic rocks in Harlik Mountain
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 总量 | Mg# | Σ | A/CNK | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 78.24 | 0.13 | 11.50 | 0.66 | 1.03 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.83 | 2.14 | 5.26 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 15.12 | 1.55 | 1.07 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 71.75 | 0.71 | 13.22 | 4.33 | 1.25 | 0.11 | 2.05 | 1.93 | 3.03 | 1.48 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 41.52 | 0.71 | 1.31 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 77.88 | 0.12 | 11.31 | 0.54 | 2.10 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 3.22 | 4.50 | 0.01 | 100.00 | 8.87 | 1.71 | 1.09 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 73.29 | 0.97 | 12.19 | 2.03 | 2.28 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 3.41 | 4.24 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 100.00 | 29.20 | 0.66 | 0.91 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 63.12 | 0.62 | 17.07 | 1.62 | 3.88 | 0.13 | 2.19 | 2.43 | 6.35 | 2.46 | 0.13 | 100.00 | 42.27 | 3.86 | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 68.97 | 1.00 | 14.04 | 1.70 | 3.71 | 0.18 | 1.20 | 4.07 | 4.57 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 100.00 | 28.95 | 0.91 | 0.92 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 49.12 | 0.93 | 20.86 | 5.36 | 6.95 | 0.35 | 3.38 | 10.68 | 1.06 | 1.15 | 0.15 | 100.00 | 33.88 | 0.80 | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 49.94 | 0.86 | 19.56 | 5.94 | 6.49 | 0.38 | 3.09 | 12.45 | 0.83 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 100.00 | 31.72 | 0.19 | 0.80 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 60.94 | 0.88 | 16.36 | 2.92 | 3.82 | 0.15 | 3.51 | 6.53 | 2.75 | 1.95 | 0.19 | 100.00 | 49.29 | 1.23 | 0.88 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | Cr | Ni | Co | Rb | Cs | Sr | Ba | V | Sc | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | U | Th | ||||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 6.43 | 2.60 | 1.41 | 134.34 | 8.95 | 113.69 | 389.62 | 4.18 | 2.19 | 19.40 | 1.94 | 163.61 | 5.27 | 7.34 | 30.02 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 17.98 | 6.46 | 11.13 | 31.59 | 5.37 | 248.28 | 411.88 | 58.59 | 15.38 | 9.13 | 0.78 | 138.03 | 3.92 | 0.74 | 4.01 | |||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 12.81 | 3.84 | 1.66 | 137.60 | 2.27 | 54.68 | 113.85 | 4.39 | 1.67 | 22.17 | 1.79 | 564.04 | 13.97 | 5.66 | 21.41 | ||||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 16.02 | 2.78 | 13.86 | 5.66 | 0.70 | 147.18 | 50.98 | 108.97 | 26.49 | 2.42 | 0.17 | 106.85 | 9.27 | 0.83 | 1.72 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 35.35 | 9.00 | 16.51 | 55.68 | 3.91 | 164.98 | 401.47 | 104.04 | 18.01 | 5.60 | 0.46 | 179.66 | 5.08 | 2.37 | 8.06 | |||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 14.58 | 1.33 | 18.26 | 6.11 | 0.73 | 177.22 | 55.86 | 133.44 | 27.28 | 2.57 | 0.19 | 113.14 | 12.15 | 0.88 | 1.77 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 122.23 | 52.95 | 29.04 | 28.27 | 3.02 | 289.83 | 601.59 | 220.87 | 37.11 | 2.41 | 0.19 | 67.96 | 2.59 | 0.56 | 0.94 | |||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 114.37 | 49.11 | 25.46 | 8.33 | 0.85 | 322.56 | 172.00 | 194.88 | 38.58 | 1.99 | 0.15 | 63.78 | 2.08 | 0.66 | 0.83 | |||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 22.80 | 10.80 | 20.60 | 36.60 | 2.43 | 710.00 | 1450.00 | 151.00 | 23.00 | 6.18 | 0.53 | 160.00 | 4.57 | 1.86 | 6.41 | |||||||||||
| 地层 | 岩性 | 样品号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | δEu | |||||||||
| 乌列 盖组 | 流纹岩 | WL-01 | 48.67 | 100.84 | 10.70 | 39.94 | 7.30 | 0.48 | 7.92 | 1.35 | 7.49 | 1.67 | 5.93 | 0.84 | 5.79 | 0.95 | 239.87 | 0.19 | |||||||||
| 英安岩 | WL-02 | 29.39 | 61.62 | 6.49 | 29.95 | 6.10 | 1.62 | 5.74 | 0.91 | 4.91 | 1.03 | 2.98 | 0.42 | 2.89 | 0.47 | 154.54 | 0.84 | ||||||||||
| 大柳 沟组 | 流纹岩 | DL-01 | 62.39 | 119.27 | 14.98 | 67.03 | 14.98 | 0.59 | 13.61 | 2.31 | 12.92 | 2.76 | 8.07 | 1.23 | 8.05 | 1.27 | 329.45 | 0.13 | |||||||||
| 流纹岩 | DL-02 | 13.83 | 29.63 | 4.22 | 22.40 | 5.60 | 1.34 | 5.59 | 0.98 | 5.63 | 1.19 | 3.46 | 0.51 | 3.28 | 0.52 | 98.17 | 0.73 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-03 | 17.94 | 38.00 | 4.67 | 20.81 | 4.16 | 1.25 | 3.94 | 0.65 | 3.68 | 0.80 | 2.42 | 0.37 | 2.55 | 0.41 | 101.64 | 0.95 | ||||||||||
| 英安岩 | DL-04 | 15.54 | 27.92 | 4.06 | 21.77 | 5.55 | 1.48 | 5.73 | 1.04 | 5.87 | 1.29 | 3.66 | 0.54 | 3.62 | 0.60 | 98.66 | 0.80 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-05 | 8.91 | 16.16 | 2.67 | 13.85 | 3.63 | 1.52 | 4.13 | 0.73 | 4.47 | 0.98 | 2.80 | 0.41 | 2.86 | 0.46 | 68.59 | 1.20 | ||||||||||
| 玄武岩 | DL-06 | 8.21 | 18.01 | 2.39 | 12.90 | 3.48 | 1.40 | 4.01 | 0.77 | 4.70 | 1.02 | 2.97 | 0.44 | 2.92 | 0.47 | 63.68 | 1.15 | ||||||||||
| 安山岩 | DL-07 | 17.20 | 37.20 | 4.89 | 19.70 | 4.52 | 1.43 | 4.58 | 0.86 | 6.06 | 1.24 | 3.65 | 0.58 | 3.60 | 0.56 | 106.07 | 0.96 | ||||||||||
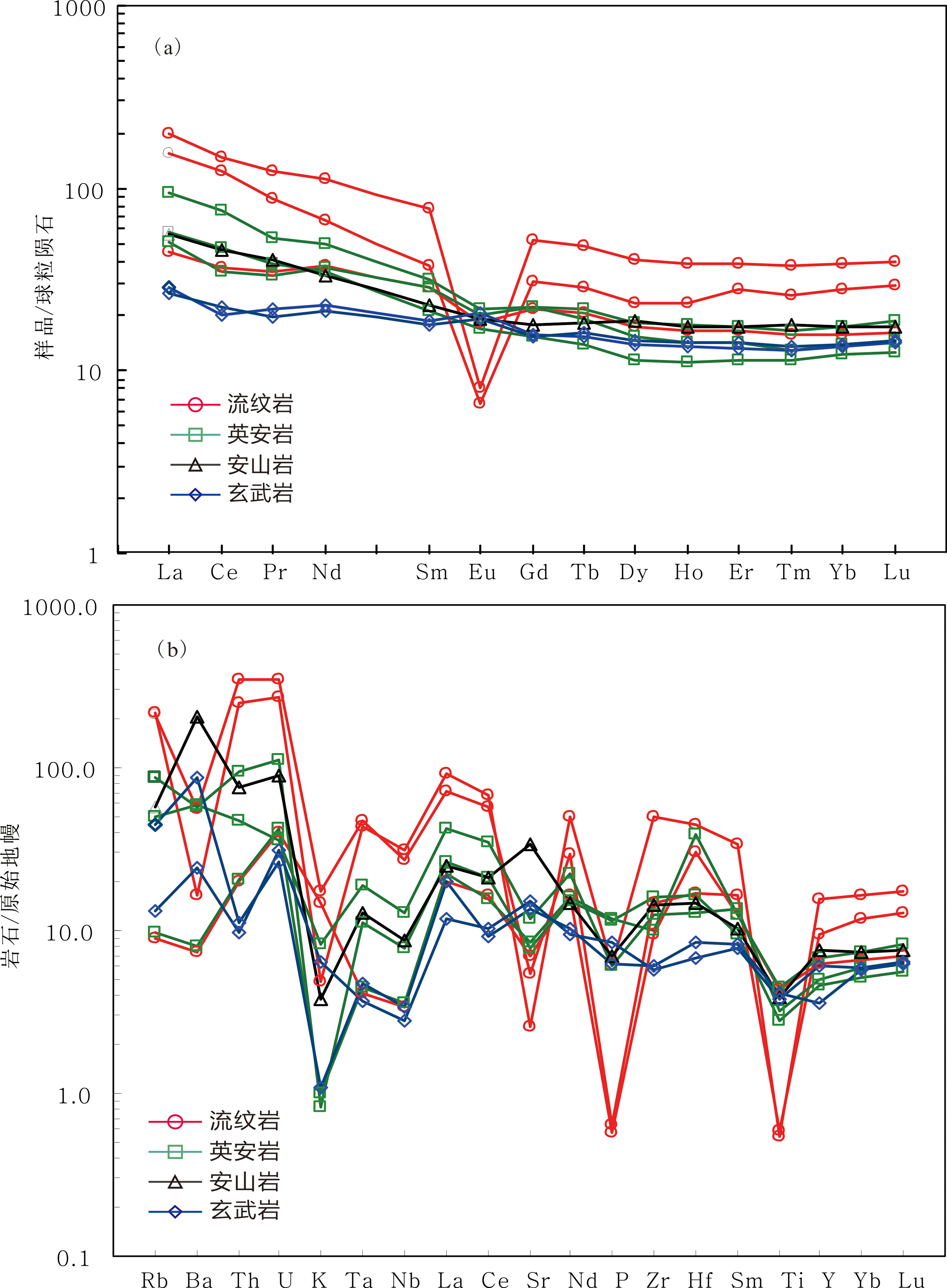
Fig.7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace element abundance spider diagram of the Ordovician volcanic rocks in Harlik Mountain
| 测点 编号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||
| 01(C) | 297 | 1 077 | 0.28 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.528 0 | 0.015 9 | 0.065 9 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 56.5 | 430.5 | 10.6 | 411.2 | 5.9 |
| 02(C) | 369 | 410 | 0.90 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 7 | 0.535 4 | 0.016 2 | 0.067 7 | 0.001 1 | 472.3 | 97.2 | 435.4 | 10.7 | 422.6 | 6.7 |
| 03 | 446 | 585 | 0.76 | 0.055 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.569 4 | 0.017 2 | 0.072 8 | 0.001 1 | 455.6 | 73.1 | 457.6 | 11.1 | 452.8 | 6.7 |
| 04(C) | 467 | 960 | 0.49 | 0.058 1 | 0.001 2 | 0.571 8 | 0.011 3 | 0.070 3 | 0.000 8 | 600.0 | 50.9 | 459.2 | 7.3 | 437.9 | 4.6 |
| 05 | 140 | 231 | 0.61 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 8 | 0.574 7 | 0.016 7 | 0.073 4 | 0.001 0 | 472.3 | 70.4 | 461.1 | 10.8 | 456.8 | 5.9 |
| 06 | 316 | 1 044 | 0.30 | 0.055 5 | 0.001 1 | 0.580 4 | 0.011 5 | 0.074 6 | 0.000 9 | 431.5 | 44.4 | 464.7 | 7.4 | 463.7 | 5.1 |
| 07 | 182 | 497 | 0.37 | 0.057 4 | 0.001 4 | 0.583 0 | 0.014 1 | 0.072 5 | 0.001 0 | 509.3 | 53.7 | 466.4 | 9.1 | 451.3 | 5.8 |
| 08 | 727 | 1 019 | 0.71 | 0.057 3 | 0.001 5 | 0.585 8 | 0.015 8 | 0.072 7 | 0.001 0 | 501.9 | 55.6 | 468.2 | 10.1 | 452.4 | 5.9 |
| 09 | 369 | 739 | 0.50 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.596 5 | 0.014 8 | 0.075 3 | 0.001 0 | 477.8 | 53.7 | 475.0 | 9.4 | 467.8 | 6.0 |
| 10 | 149 | 362 | 0.41 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 8 | 0.601 7 | 0.017 5 | 0.076 3 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 72.2 | 478.3 | 11.1 | 473.7 | 6.2 |
| 11 | 225 | 619 | 0.36 | 0.057 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.607 5 | 0.017 5 | 0.075 0 | 0.001 2 | 524.1 | 66.7 | 482.0 | 11.0 | 466.4 | 7.2 |
| 12(C) | 966 | 1 409 | 0.69 | 0.065 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.614 9 | 0.017 8 | 0.067 3 | 0.001 1 | 772.2 | 53.5 | 486.7 | 11.2 | 420.0 | 6.7 |
| 13 | 422 | 1 342 | 0.31 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 2 | 0.616 1 | 0.013 1 | 0.077 3 | 0.000 9 | 483.4 | 48.1 | 487.4 | 8.2 | 480.1 | 5.6 |
| 14 | 274 | 751 | 0.36 | 0.057 1 | 0.002 1 | 0.620 0 | 0.022 4 | 0.077 3 | 0.001 3 | 498.2 | 81.5 | 489.9 | 14.0 | 480.0 | 7.8 |
| 15 | 128 | 192 | 0.67 | 0.058 4 | 0.001 9 | 0.637 3 | 0.019 9 | 0.078 8 | 0.001 2 | 546.3 | 71.1 | 500.6 | 12.3 | 488.9 | 7.1 |
| 16 | 142 | 267 | 0.53 | 0.057 7 | 0.001 7 | 0.648 0 | 0.018 9 | 0.080 5 | 0.001 1 | 516.7 | 66.7 | 507.2 | 11.6 | 499.1 | 6.8 |
| 17 | 229 | 279 | 0.82 | 0.059 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.655 9 | 0.028 4 | 0.079 1 | 0.001 6 | 590.8 | 93.5 | 512.1 | 17.4 | 490.9 | 9.5 |
| 18(C) | 184 | 359 | 0.51 | 0.063 0 | 0.001 4 | 1.092 5 | 0.023 7 | 0.123 8 | 0.001 5 | 709.3 | 47.1 | 749.7 | 11.5 | 752.5 | 8.6 |
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb analyses of zircon for the rhyolite (DL-01) from the Harlik Mountain
| 测点 编号 | 含量/10-6 | Th/ U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/ 238U | 1σ | ||
| 01(C) | 297 | 1 077 | 0.28 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 6 | 0.528 0 | 0.015 9 | 0.065 9 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 56.5 | 430.5 | 10.6 | 411.2 | 5.9 |
| 02(C) | 369 | 410 | 0.90 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 7 | 0.535 4 | 0.016 2 | 0.067 7 | 0.001 1 | 472.3 | 97.2 | 435.4 | 10.7 | 422.6 | 6.7 |
| 03 | 446 | 585 | 0.76 | 0.055 8 | 0.001 7 | 0.569 4 | 0.017 2 | 0.072 8 | 0.001 1 | 455.6 | 73.1 | 457.6 | 11.1 | 452.8 | 6.7 |
| 04(C) | 467 | 960 | 0.49 | 0.058 1 | 0.001 2 | 0.571 8 | 0.011 3 | 0.070 3 | 0.000 8 | 600.0 | 50.9 | 459.2 | 7.3 | 437.9 | 4.6 |
| 05 | 140 | 231 | 0.61 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 8 | 0.574 7 | 0.016 7 | 0.073 4 | 0.001 0 | 472.3 | 70.4 | 461.1 | 10.8 | 456.8 | 5.9 |
| 06 | 316 | 1 044 | 0.30 | 0.055 5 | 0.001 1 | 0.580 4 | 0.011 5 | 0.074 6 | 0.000 9 | 431.5 | 44.4 | 464.7 | 7.4 | 463.7 | 5.1 |
| 07 | 182 | 497 | 0.37 | 0.057 4 | 0.001 4 | 0.583 0 | 0.014 1 | 0.072 5 | 0.001 0 | 509.3 | 53.7 | 466.4 | 9.1 | 451.3 | 5.8 |
| 08 | 727 | 1 019 | 0.71 | 0.057 3 | 0.001 5 | 0.585 8 | 0.015 8 | 0.072 7 | 0.001 0 | 501.9 | 55.6 | 468.2 | 10.1 | 452.4 | 5.9 |
| 09 | 369 | 739 | 0.50 | 0.056 5 | 0.001 4 | 0.596 5 | 0.014 8 | 0.075 3 | 0.001 0 | 477.8 | 53.7 | 475.0 | 9.4 | 467.8 | 6.0 |
| 10 | 149 | 362 | 0.41 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 8 | 0.601 7 | 0.017 5 | 0.076 3 | 0.001 0 | 483.4 | 72.2 | 478.3 | 11.1 | 473.7 | 6.2 |
| 11 | 225 | 619 | 0.36 | 0.057 9 | 0.001 7 | 0.607 5 | 0.017 5 | 0.075 0 | 0.001 2 | 524.1 | 66.7 | 482.0 | 11.0 | 466.4 | 7.2 |
| 12(C) | 966 | 1 409 | 0.69 | 0.065 0 | 0.001 8 | 0.614 9 | 0.017 8 | 0.067 3 | 0.001 1 | 772.2 | 53.5 | 486.7 | 11.2 | 420.0 | 6.7 |
| 13 | 422 | 1 342 | 0.31 | 0.056 8 | 0.001 2 | 0.616 1 | 0.013 1 | 0.077 3 | 0.000 9 | 483.4 | 48.1 | 487.4 | 8.2 | 480.1 | 5.6 |
| 14 | 274 | 751 | 0.36 | 0.057 1 | 0.002 1 | 0.620 0 | 0.022 4 | 0.077 3 | 0.001 3 | 498.2 | 81.5 | 489.9 | 14.0 | 480.0 | 7.8 |
| 15 | 128 | 192 | 0.67 | 0.058 4 | 0.001 9 | 0.637 3 | 0.019 9 | 0.078 8 | 0.001 2 | 546.3 | 71.1 | 500.6 | 12.3 | 488.9 | 7.1 |
| 16 | 142 | 267 | 0.53 | 0.057 7 | 0.001 7 | 0.648 0 | 0.018 9 | 0.080 5 | 0.001 1 | 516.7 | 66.7 | 507.2 | 11.6 | 499.1 | 6.8 |
| 17 | 229 | 279 | 0.82 | 0.059 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.655 9 | 0.028 4 | 0.079 1 | 0.001 6 | 590.8 | 93.5 | 512.1 | 17.4 | 490.9 | 9.5 |
| 18(C) | 184 | 359 | 0.51 | 0.063 0 | 0.001 4 | 1.092 5 | 0.023 7 | 0.123 8 | 0.001 5 | 709.3 | 47.1 | 749.7 | 11.5 | 752.5 | 8.6 |
| [1] |
BADARCH G, CUNNINGHAM W D, WINDLEY B F. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:Implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1):87-110.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
XIAO W J, ZHANG L C, QIN K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the eastern Tianshan (China):Implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4):370-395.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 刘亮, 何学锋, 李江涛, 等. 新疆东部哈尔里克沁城天生圈岩体岩石成因及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2):86-96. |
| [4] | 马星华, 陈斌, 王超, 等. 早古生代古亚洲洋俯冲作用:来自新疆哈尔里克侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(1):89-104. |
| [5] | 王赐银, 舒良树, 赵明, 等. 东天山北部哈尔里克晚古生代推覆构造与岩浆作用研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 1996, 2(2):198-206. |
| [6] | 李锦轶. 新疆东部新元古代晚期和古生代构造格局及其演变[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(3):304-322. |
| [7] | 张传恒, 刘典波, 张传林, 等. 新疆博格达山初始隆升时间的地层学标定[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(1):294-302. |
| [8] | 马瑞士, 王赐银, 叶尚夫. 东天山构造格架及地壳演化[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 1993:1-225. |
| [9] | 赵明, 舒良树, 王赐银. 东疆哈尔里克变质带变质作用特征及形成构造环境研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 1997, 3(1):40-50. |
| [10] | 成守德, 张湘江. 新疆大地构造基本格架[J]. 新疆地质, 2000, 18(4):293-296. |
| [11] | 靳刘圆, 张济, 朱志新, 等. 哈尔里克山古生代火山岩地质特征及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2013, 31(3):173-179. |
| [12] | 刘德权, 唐延龄, 周汝洪. 新疆北部古生代地壳演化及成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 1992, 11(4):307-314. |
| [13] | 王宗秀, 周高志, 李涛. 对新疆北部蛇绿岩及相关问题的思考和认识[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(4):683-691. |
| [14] | 李文明, 任秉琛, 杨兴科, 等. 东天山中酸性侵入岩浆作用及其地球动力学意义[J]. 西北地质, 2002, 35(4):41-64. |
| [15] | 李锦轶, 何国琦, 徐新, 等. 新疆北部及邻区地壳构造格架及其形成过程的初步探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(1):148-168. |
| [16] | 孙桂华, 李锦轶, 朱志新, 等. 新疆东部哈尔里克山片麻状黑云母花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2007, 25(1):4-10. |
| [17] | 李锦轶, 王克卓, 孙桂华, 等. 东天山吐哈盆地南缘古生代活动陆缘残片:中亚地区古亚洲洋板块俯冲的地质记录[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5):1087-1102. |
| [18] |
LE BAS M J, LE MAITRE R W, STRECKEISEN A. A chemical classification of volcanic rocks based on the total alkali-silica diagram[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1986, 27:745-750.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
WINCHESTER J A, FLOYD P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using im-mobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20:325-343.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
BINNS R A, DUGGAN M B, WILKINSON J F G. High pressure megacrysts in alkaline lavas from Northeastern New South Wales[J]. American Journal of Science, 1970, 269:132-168.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
EWART A, COLLERSON K D, REGELOUS M, et al. Geochemical evolution within the Tonga-Kermadec-Lau arc-back-arcsystems:The role of varying mantle wedge composition in space and time[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39(3):331-368.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
IRVINE T N, BARAGAR W R A. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Science, 1971, 8:523-548.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 潘桂堂, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 大地构造相的定义、划分、特征及其鉴别标志[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(10):1613-1637. |
| [24] | CULLERS R L, GRAF J L. Rare earth elements in igneous rocks of the continental crust:Intermediate and silicic rocks-ore petro-genesis[M]// HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1984:273-308. |
| [25] | BOYNTON W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorite studies[M]// HENDERSON P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1984:63-114. |
| [26] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]// SAUNDERS A D, NORRY M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society of London, 1989:313-345. |
| [27] | GILL J B. Orogenic Andesites and Plate Tectonic[M]. Berlin: Springer Verlag, 1981: 358. |
| [28] | PEARC E. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[M]// THORPE R S.Andesite. New York: John and Wiley Sons, 1982:525-548. |
| [29] |
SALTERS V T M, HART S R. The mantle sources of ocean ridges, island arcs:the Hf-isotope connection[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104:364-380.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
CONDIE K C. Geochemical changes in basalts and andesites across the Archaean-Proterozoic boundary:Identification and significance[J]. Lithos, 1989, 23:1-18.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
ANDERSON T. Correction of Pb in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Geochronology Center, 2003:1-10. |
| [33] |
KOSCHEK G. Origin and significance of the SEM cathodoluminescence from zircon[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1993, 171(3):223-232.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 周济元, 茅燕石, 黄志勋, 等. 东天山古大陆边缘火山地质[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社, 1994:1-90. |
| [35] | 曹福根, 涂其军, 张晓梅, 等. 哈尔里克山早古生代岩浆弧的初步确定——来自塔水河一带花岗质岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年的证据[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(8):923-927. |
| [36] | MESCHEDE M. A method of discriminating between different types of mid-ocean ridge basalts and continental tholeiites with the Nb-Zr-Y diagram[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 56:275-282. |
| [37] |
WOOD D A. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic Tertiary volcanic province[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1980, 50:11-30.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
PEARCE J A, HARRIS N, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 李曙光. εNd-La/Nb、Ba/Nb、Nb/Th图对地幔不均一性研究的意义——岛弧火山岩分类及EMII端元的分解[J]. 地球化学, 1994, 23(2):105-114. |
| [40] | 吴根耀, 邝国敦. 滇桂交界处古特提斯的洋岛和岛弧火山岩[J]. 现代地质, 2000, 14(4):393-400. |
| [41] |
KEPEZHINSKA S P, MCDERMOT T F, DEFANT M J. Trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints on a three-component model of Kamchatka arc petrogenesis[J]. Geochimica Cosmochimica, 1997, 61:577-600.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WOODHEAD J D, HERGT J M, DAVIDISON J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for “conservation” element mobility during subduction zone processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 192:331-346.
DOI URL |
| [43] | HANYU T, TATSUMI Y, NAKAI S, et al. Contribution of slab melting and slab dehydration to magmatism in the NE Japan arc for the last 25 Myr:Constraints from geochemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70:299. |
| [44] | 黄岗, 牛广智, 王新录, 等. 新疆东准噶尔早志留世弧岩浆岩:来自姜格尔库都克石英二长闪长岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(6):1219-1233. |
| [45] |
PLANK T. Constraints from thorium/lanthanum on sediment recycling at subduction zones and the evolution of the continents[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2005, 46(5):921-944.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
YOGODZINSKI G M, KEY R W, VOLYNETS O N, et al. Magnesian andesite in the Western Aleutian Komandorsky Region:Implications for slab melting and processes in the mantle wedge[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1995, 107(5):505-519.
DOI URL |
| [47] | 胡霭琴, 章振根, 张积斌. 天山东段中天山隆起带前寒武纪变质岩系时代及演化——据U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 地球化学, 1986, 15(1):23-25. |
| [48] | 孙桂华, 李锦轶, 朱志新, 等. 新疆东部哈尔里克山南麓石炭纪砂岩碎屑锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(5):778-789. |
| [49] | 郭华春, 钟莉, 李丽群. 新疆哈尔里克山口门子地区石英闪长岩年代研究及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(8):928-931. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||