



现代地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (04): 931-946.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2025.021
孙世强( ), 陈翠华*(
), 陈翠华*( ), 赖翔, 辜鹰, 赵文皓, 张海军, 马天祺, 陈宵杰, 宋志娇
), 赖翔, 辜鹰, 赵文皓, 张海军, 马天祺, 陈宵杰, 宋志娇
出版日期:2025-08-10
发布日期:2025-08-27
通信作者:
*陈翠华,女,教授,1972年出生,主要从事矿床学、矿相学、地球化学研究工作。Email:chencuihua@cdut.edu.cn。作者简介:孙世强,男,硕士研究生,1999年出生,主要从事矿物学、岩石学、矿床学、矿产普查与勘探研究工作。Email:2284726172@qq.com。
基金资助:
SUN Shiqiang( ), CHEN Cuihua*(
), CHEN Cuihua*( ), LAI Xiang, GU Ying, ZHAO Wenhao, ZHANG Haijun, MA Tianqi, CHEN Xiaojie, SONG Zhijiao
), LAI Xiang, GU Ying, ZHAO Wenhao, ZHANG Haijun, MA Tianqi, CHEN Xiaojie, SONG Zhijiao
Published:2025-08-10
Online:2025-08-27
摘要:
乌斯河大型铅锌矿床是川滇黔成矿带内典型的富锗(Ge)铅锌矿床,前人对其成矿流体特征及Ge的赋存状态、替代机制的研究有了深入的认识,但影响Ge富集的关键物理化学条件还不明确,限制了对Ge的富集机制的理解。为综合研究该矿床成矿流体与Ge的富集条件,进行了岩矿学分析、LA-ICP-MS测试、流体包裹体显微测温分析。认为该矿床中发育两个阶段的闪锌矿,LA-ICP-MS测试结果显示第Ⅰ 阶段闪锌矿中Ge含量(均值为221.0×10-6)高于第 Ⅱ 阶段(均值为72.9×10-6)。流体包裹体显微测温显示热液期各个阶段均一温度平均值分别为220℃、180℃,pH值相差不大,平均盐度w(NaCleq)分别为8.0%、5.9%,成矿压力分别为43×105~283×105 Pa、120×105~236×105 Pa。综合Ge的富集规律、赋存方式和成矿流体特征,结合热力学相图计算,得出第 Ⅰ 阶段闪锌矿中Ge的富集条件为:log
中图分类号:
孙世强, 陈翠华, 赖翔, 辜鹰, 赵文皓, 张海军, 马天祺, 陈宵杰, 宋志娇. 四川乌斯河铅锌矿床成矿流体特征及Ge富集物理化学条件[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(04): 931-946.
SUN Shiqiang, CHEN Cuihua, LAI Xiang, GU Ying, ZHAO Wenhao, ZHANG Haijun, MA Tianqi, CHEN Xiaojie, SONG Zhijiao. Characteristics of Ore-Forming Fluids and Physicochemical Conditions for Ge Enrichment in the Wusihe Lead-Zinc Deposit, Sichuan[J]. Geoscience, 2025, 39(04): 931-946.

图1 华南大地构造背景(a)及川滇黔铅锌矿成矿带区域地质图(b)(据文献[8]修改)
Fig.1 Tectonic setting of South China (a) and regional geological map of the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Pb-Zn metallogenic belt (b) (modified after Ref.[8])

图3 乌斯河矿床坑道、手标本及镜下照片 (a)呈层状分布的矿体;(b)脉状闪锌矿穿插早阶段闪锌矿;(c)层状矿石,分布大颗粒闪锌矿(Sp1),下方白云石分布着细脉闪锌矿(Sp2);(d)浸染状矿石;(e)小颗粒的Sp2交代颗粒较大Sp1和Py(反射光);(f)Sp1局部呈褐色,可见环带结构(透射光);(g)Sp2颜色较浅呈浅棕黄色(透射光);(h)Gn1包含Py,与后形成的Sp2呈包含结构(反射光);(i)Gn2受应力发育揉皱结构,与Sp2伴生(反射光);(j)Gn2与Bit沿Sp裂隙填充;Sp.闪锌矿;Py.黄铁矿;Gn.方铅矿;Ma.白铁矿;Qz.石英;Bit.沥青;Dol.白云石
Fig.3 Photos of tunnels, hand specimens and microscopic images from the Wusihe Deposit
| 成矿阶段 | 样品编号 | Mn | Fe | Cu | Ga | Ge | Ag | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第Ⅰ阶段 | WSH-10-1-(1)-1 | 59.5 | 27189 | 103.0 | 0.19 | 180.0 | 94.9 | 2863.0 |
| WSH-10-1-(1)-2 | 59.2 | 27225 | 101.0 | 1.21 | 148.0 | 84.3 | 2931.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(1)-3 | 65.3 | 27234 | 103.0 | 1.39 | 163.0 | 91.9 | 2954.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(1)-4 | 54.6 | 29176 | 115.0 | 0.47 | 155.0 | 95.7 | 3206.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(2)-1 | 50.5 | 14035 | 82.6 | 0.41 | 195.0 | 50.2 | 2714.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(2)-2 | 53.0 | 4385 | 33.6 | 0.29 | 110.0 | 30.1 | 3589.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(1)-1 | 10.7 | 6462 | 154.0 | 24.80 | 98.4 | 49.1 | 881.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(1)-2 | 6.58 | 4184 | 262.0 | 14.10 | 225.0 | 60.7 | 803.0 | |
| WSH-2-(1)-1 | 39.7 | 21318 | 146.0 | 15.10 | 113.0 | 42.5 | 1556.0 | |
| WSH-2-(1)-2 | 37.2 | 14776 | 147.0 | 19.10 | 118.0 | 40.1 | 1562.0 | |
| WSH-2-(5)-1 | 16.4 | 12249 | 858.0 | 0.30 | 624.0 | 92.8 | 78.7 | |
| WSH-2-(5)-2 | 11.3 | 10440 | 666.0 | 0.65 | 511.0 | 73.6 | 54.7 | |
| WSH-2-(5)-3 | 24.5 | 9151 | 229.0 | 0.05 | 246.0 | 33.0 | 55.3 | |
| 第Ⅱ阶段 | WSH-10-1-(3)-1 | 5.86 | 1073 | 60.0 | 3.93 | 50.1 | 61.8 | 4618.0 |
| WSH-10-1-(3)-2 | 6.34 | 1437 | 240.0 | 0.59 | 169.0 | 95.7 | 3269.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(2)-1 | 41.80 | 6517 | 115.0 | 2.64 | 78.4 | 47.6 | 3786.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(2)-2 | 43.20 | 7807 | 79.0 | 4.70 | 77.7 | 52.6 | 3750.0 | |
| WSH-2-1-(1)-1 | - | 361 | 411.0 | 12.19 | 204.0 | 78.4 | 1850.0 | |
| WSH-2-1-(1)-2 | - | 534 | 163.0 | 0.69 | 109.0 | 53.8 | 1926.0 | |
| WSH-2-1-(2)-2 | 2.77 | 1357 | 128.0 | 83.7 | 40.6 | 16.9 | 2839.0 | |
| WSH-2-(2)-1 | 3.22 | 1059 | 64.1 | 17.5 | 7.90 | 61.7 | 7530.0 | |
| WSH-2-(2)-2 | 3.58 | 1218 | 4.96 | 0.44 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 9062.0 | |
| WSH-2-(3)-1 | 12.10 | 7560 | 96.0 | 36.1 | 53.1 | 39.7 | 1965.0 | |
| WSH-2-(3)-2 | 13.90 | 6693 | 80.7 | 29.1 | 49.3 | 37.3 | 2009.0 | |
| WSH-2-(4)-3 | 8.26 | 5620 | 85.6 | 28.2 | 35.8 | 34.8 | 1555.0 | |
| WSH10-1-3 | 2.23 | 210 | 155.0 | 20.0 | 73.6 | 144.0 | 2568.0 | |
| WSH3-1-4 | 80.60 | 4220 | 97.7 | 1.43 | 70.0 | 81.3 | 2766.0 |
表1 乌斯河矿床闪锌矿LA-ICP-MS实验结果(10-6)
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS analytical results of sphalerite from the Wusihe Deposit (10-6)
| 成矿阶段 | 样品编号 | Mn | Fe | Cu | Ga | Ge | Ag | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第Ⅰ阶段 | WSH-10-1-(1)-1 | 59.5 | 27189 | 103.0 | 0.19 | 180.0 | 94.9 | 2863.0 |
| WSH-10-1-(1)-2 | 59.2 | 27225 | 101.0 | 1.21 | 148.0 | 84.3 | 2931.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(1)-3 | 65.3 | 27234 | 103.0 | 1.39 | 163.0 | 91.9 | 2954.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(1)-4 | 54.6 | 29176 | 115.0 | 0.47 | 155.0 | 95.7 | 3206.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(2)-1 | 50.5 | 14035 | 82.6 | 0.41 | 195.0 | 50.2 | 2714.0 | |
| WSH-10-1-(2)-2 | 53.0 | 4385 | 33.6 | 0.29 | 110.0 | 30.1 | 3589.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(1)-1 | 10.7 | 6462 | 154.0 | 24.80 | 98.4 | 49.1 | 881.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(1)-2 | 6.58 | 4184 | 262.0 | 14.10 | 225.0 | 60.7 | 803.0 | |
| WSH-2-(1)-1 | 39.7 | 21318 | 146.0 | 15.10 | 113.0 | 42.5 | 1556.0 | |
| WSH-2-(1)-2 | 37.2 | 14776 | 147.0 | 19.10 | 118.0 | 40.1 | 1562.0 | |
| WSH-2-(5)-1 | 16.4 | 12249 | 858.0 | 0.30 | 624.0 | 92.8 | 78.7 | |
| WSH-2-(5)-2 | 11.3 | 10440 | 666.0 | 0.65 | 511.0 | 73.6 | 54.7 | |
| WSH-2-(5)-3 | 24.5 | 9151 | 229.0 | 0.05 | 246.0 | 33.0 | 55.3 | |
| 第Ⅱ阶段 | WSH-10-1-(3)-1 | 5.86 | 1073 | 60.0 | 3.93 | 50.1 | 61.8 | 4618.0 |
| WSH-10-1-(3)-2 | 6.34 | 1437 | 240.0 | 0.59 | 169.0 | 95.7 | 3269.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(2)-1 | 41.80 | 6517 | 115.0 | 2.64 | 78.4 | 47.6 | 3786.0 | |
| WSH-3-1-(2)-2 | 43.20 | 7807 | 79.0 | 4.70 | 77.7 | 52.6 | 3750.0 | |
| WSH-2-1-(1)-1 | - | 361 | 411.0 | 12.19 | 204.0 | 78.4 | 1850.0 | |
| WSH-2-1-(1)-2 | - | 534 | 163.0 | 0.69 | 109.0 | 53.8 | 1926.0 | |
| WSH-2-1-(2)-2 | 2.77 | 1357 | 128.0 | 83.7 | 40.6 | 16.9 | 2839.0 | |
| WSH-2-(2)-1 | 3.22 | 1059 | 64.1 | 17.5 | 7.90 | 61.7 | 7530.0 | |
| WSH-2-(2)-2 | 3.58 | 1218 | 4.96 | 0.44 | 1.54 | 5.49 | 9062.0 | |
| WSH-2-(3)-1 | 12.10 | 7560 | 96.0 | 36.1 | 53.1 | 39.7 | 1965.0 | |
| WSH-2-(3)-2 | 13.90 | 6693 | 80.7 | 29.1 | 49.3 | 37.3 | 2009.0 | |
| WSH-2-(4)-3 | 8.26 | 5620 | 85.6 | 28.2 | 35.8 | 34.8 | 1555.0 | |
| WSH10-1-3 | 2.23 | 210 | 155.0 | 20.0 | 73.6 | 144.0 | 2568.0 | |
| WSH3-1-4 | 80.60 | 4220 | 97.7 | 1.43 | 70.0 | 81.3 | 2766.0 |

图6 乌斯河矿床流体包裹体特征 (a)、(b)闪锌矿中L+V型次生包裹体(第一类);(c)、(d)闪锌矿中L+V型原生包裹体(第二类);(e)石英中L+V型负晶型原生包裹体(第一类);(f)石英中V+L型原生包裹体(第二类);(g)石英中L型包裹体沿长轴方向一致定向排列;(h)石英中孤立分布的L型负晶型原生包裹体;(i)、(j)白云石中呈群状分布的L+V型类负晶型原生包裹体(第一类);(k)、(l)白云石中L+V型次生包裹体(第一类)
Fig.6 Characteristics of fluid inclusions in the Wusihe Deposit
| 热液期成矿阶段 | 寄主矿物 | 测试个数 | 大小(μm) | 均一相态 | 均一温度(℃) | 冰点(℃) | 盐度w(NaCleq) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 闪锌矿 | 22 | 3~15 | L | 154.0~269.0 | -9.8~-3.2 | 5.3~13.7 | 5.42~5.66 |
| 石英 | 14 | 7~40 | L | 153.2~290.0 | -7.1~-0.9 | 1.6~10.6 | 5.44~5.66 | |
| 白云石 | 18 | 3~13 | L | 150.1~254.2 | -9.0~-2.3 | 3.9~12.8 | 5.44~5.66 | |
| Ⅱ | 闪锌矿 | 17 | 3~15 | L | 144.6~210.8 | -3.9~-0.8 | 1.4~6.3 | 5.47~5.70 |
| 石英 | 14 | 6~40 | L | 160.0~236.9 | -8.6~-1.5 | 2.6~12.4 | 5.46~5.63 | |
| 白云石 | 16 | 3~10 | L | 152.7~203.5 | -9.4~-3.0 | 5.0~13.3 | 5.48~5.66 |
表2 热液期各成矿阶段流体包裹体显微测温数据
Table 2 Microthermometric data of fluid inclusions from each mineralization stage of the hydrothermal period
| 热液期成矿阶段 | 寄主矿物 | 测试个数 | 大小(μm) | 均一相态 | 均一温度(℃) | 冰点(℃) | 盐度w(NaCleq) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 闪锌矿 | 22 | 3~15 | L | 154.0~269.0 | -9.8~-3.2 | 5.3~13.7 | 5.42~5.66 |
| 石英 | 14 | 7~40 | L | 153.2~290.0 | -7.1~-0.9 | 1.6~10.6 | 5.44~5.66 | |
| 白云石 | 18 | 3~13 | L | 150.1~254.2 | -9.0~-2.3 | 3.9~12.8 | 5.44~5.66 | |
| Ⅱ | 闪锌矿 | 17 | 3~15 | L | 144.6~210.8 | -3.9~-0.8 | 1.4~6.3 | 5.47~5.70 |
| 石英 | 14 | 6~40 | L | 160.0~236.9 | -8.6~-1.5 | 2.6~12.4 | 5.46~5.63 | |
| 白云石 | 16 | 3~10 | L | 152.7~203.5 | -9.4~-3.0 | 5.0~13.3 | 5.48~5.66 |

图7 流体包裹体均一温度直方图 (a)热液期第 Ⅰ 阶段,闪锌矿、石英和白云石中流体包裹体均一温度直方图;(b)热液期第 Ⅱ 阶段,闪锌矿、石英和白云石中流体包裹体均一温度直方图
Fig.7 Histograms of homogenization temperatures of fluid inclusions
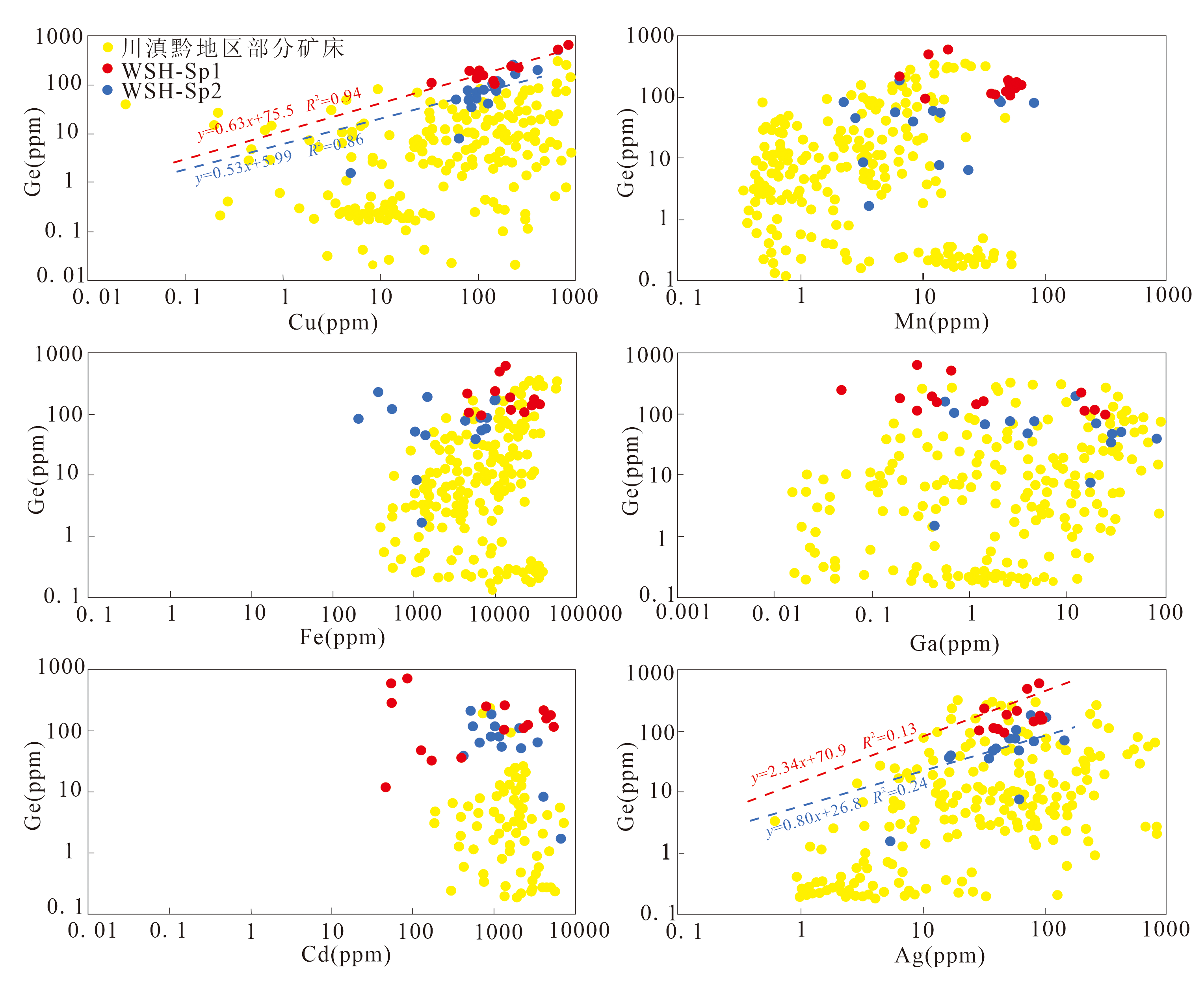
图9 乌斯河矿床闪锌矿微量元素含量对比图(川滇黔地区部分矿床数据引自文献[6][31]) WSH-Sp1,热液期第 Ⅰ 阶段闪锌矿;WSH-Sp2,热液期第 Ⅱ 阶段闪锌矿
Fig.9 Comparison of trace element contents in sphalerite from the Wusihe deposit (data of some deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou region are cited from references [6] and [31])

图10 成矿流体的盐度与闪锌矿中Ge富集程度的关系(其它矿床的数据引自文献[41-48])
Fig.10 Relationship between salinity of ore-forming fluids and Ge enrichment in sphalerite (data from other deposits are cited from references [41-48])
| 序号 | 反应方程式 | 序号 | 反应方程式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ge+O2=GeO2 | 2 | Ge+S2=GeS2 |
| 3 | GeS2+O2=GeO2+S2 | 4 | Zn+1/2O2=ZnO |
| 5 | Zn+1/2S2=ZnS | 6 | ZnS+1/2O2=ZnO+1/2S2 |
| 7 | Pb+ 1/2O2=PbO | 8 | 3Pb+2O2=Pb3O4 |
| 9 | Pb+O2=PbO2 | 10 | Pb+1/2S2=PbS |
| 11 | PbS+1/2O2=PbO+1/2S2 | 12 | 3PbS+ 2O2=Pb3O4+3/2S2 |
| 13 | PbS+O2=PbO2+1/2S2 | 14 | 4S2=S8 |
| 15 | 3Fe+2O2=Fe3O4 | 16 | Fe3O4+1/2O2=3Fe2O3 |
| 17 | Fe+1/2S2=FeS | 18 | FeS+1/2S2=FeS2 |
| 19 | 3FeS+2O2=Fe3O4+3/2S2 | 20 | 3FeS2+2O2=Fe3O4+3S2 |
| 21 | 3FeS2+3/2O2=Fe2O3+2S2 |
表3 相关化学反应化学式
Table 3 Chemical formulas of relevant reactions
| 序号 | 反应方程式 | 序号 | 反应方程式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ge+O2=GeO2 | 2 | Ge+S2=GeS2 |
| 3 | GeS2+O2=GeO2+S2 | 4 | Zn+1/2O2=ZnO |
| 5 | Zn+1/2S2=ZnS | 6 | ZnS+1/2O2=ZnO+1/2S2 |
| 7 | Pb+ 1/2O2=PbO | 8 | 3Pb+2O2=Pb3O4 |
| 9 | Pb+O2=PbO2 | 10 | Pb+1/2S2=PbS |
| 11 | PbS+1/2O2=PbO+1/2S2 | 12 | 3PbS+ 2O2=Pb3O4+3/2S2 |
| 13 | PbS+O2=PbO2+1/2S2 | 14 | 4S2=S8 |
| 15 | 3Fe+2O2=Fe3O4 | 16 | Fe3O4+1/2O2=3Fe2O3 |
| 17 | Fe+1/2S2=FeS | 18 | FeS+1/2S2=FeS2 |
| 19 | 3FeS+2O2=Fe3O4+3/2S2 | 20 | 3FeS2+2O2=Fe3O4+3S2 |
| 21 | 3FeS2+3/2O2=Fe2O3+2S2 |
| 温度(K) | 413.15 | 453.15 | 493.15 | 533.15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| log | log | log | log | log |
| log fS2 | -21.53≤log | -18.64≤log | -15.75≤log | -13.62≤log fS2≤-3.94 |
表4 不同温度下富Ge闪锌矿-方铅矿-黄铁矿沉淀的log f O 2-log f S 2
Table 4 log f O 2-log f S 2 for precipitation of Ge-rich sphalerite-galena-pyrite at different temperatures
| 温度(K) | 413.15 | 453.15 | 493.15 | 533.15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| log | log | log | log | log |
| log fS2 | -21.53≤log | -18.64≤log | -15.75≤log | -13.62≤log fS2≤-3.94 |

图11 不同温度下矿物的 log f O 2-log f S 2 相图蓝色实线为Zn的凝聚线;黄色实线为Pb的凝聚线;绿色实线为Fe的凝聚线;黑色实线为S的凝聚线;黄色区域为Ge;红色区域为GeS2;绿色区域为GeO2;Sp.闪锌矿; Spa.红锌矿; Py.黄铁矿; Po.磁黄铁矿; Mt.磁铁矿; Hm.赤铁矿; Gn.方铅矿; Li.铅黄; Pl.块黑铅矿; Mi.铅丹
Fig.11 log f O 2-log f S 2 phase diagrams of minerals at different temperatures
| 序号 | 反应方程式 | 序号 | 反应方程式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2S=HS-+H+ | 2 | HS-=S2-+H+ |
| 3 | Zn2++H2S=ZnS+2H+ | 4 | Zn2++HS-=ZnS+H+ |
| 5 | Zn2++S2-=ZnS | 6 | Ge4++2H2S=GeS2+4H+ |
| 7 | Ge4++2HS-=GeS2+2H+ | 8 | Ge4++2S2-=GeS2 |
| 9 | Ge(OH)4+2H2S= GeS2+4H2O | 10 | Ge(OH)4+2HS-= GeS2+2H2O+2OH- |
| 11 | Ge(OH)4+2S2-= GeS2+4OH- | 12 | ZnC ZnS+4Cl-+2H+ |
| 13 | ZnC ZnS+4Cl-+H+ | 14 | ZnC ZnS+4Cl- |
表5 相关化学反应方程式
Table 5 Relevant chemical reaction equations
| 序号 | 反应方程式 | 序号 | 反应方程式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H2S=HS-+H+ | 2 | HS-=S2-+H+ |
| 3 | Zn2++H2S=ZnS+2H+ | 4 | Zn2++HS-=ZnS+H+ |
| 5 | Zn2++S2-=ZnS | 6 | Ge4++2H2S=GeS2+4H+ |
| 7 | Ge4++2HS-=GeS2+2H+ | 8 | Ge4++2S2-=GeS2 |
| 9 | Ge(OH)4+2H2S= GeS2+4H2O | 10 | Ge(OH)4+2HS-= GeS2+2H2O+2OH- |
| 11 | Ge(OH)4+2S2-= GeS2+4OH- | 12 | ZnC ZnS+4Cl-+2H+ |
| 13 | ZnC ZnS+4Cl-+H+ | 14 | ZnC ZnS+4Cl- |

图12 不同温度下的pH-log[a]相图(引自文献[5]) 蓝色实线为Zn的凝聚线;红色实线为Ge的凝聚线;黑色实线为S的凝聚线;黑色虚线为Zn、Ge的凝聚线
Fig.12 pH-log[a] phase diagrams at different temperatures (cited from reference [5])
| [1] | 胡瑞忠, 苏文超, 戚华文, 等. 锗的地球化学, 赋存状态和成矿作用[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2000, 19(4): 215-217. |
| [2] | 周墨, 梁晓红, 张明, 等. 南京市溧水区表层土壤锗地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(1): 217-226. |
| [3] | European Commission Critical Raw Materials for the EU. Report of the Ad Hoc Working Group on Defining Critical Raw Materials. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. |
| [4] | COOK N J, CIOBANU C L, PRING A, et al. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(16): 4761-4791. |
| [5] | LIU W H, MEI Y, ETSCHMANN B, et al. Germanium speciation in experimental and natural sphalerite: Implications for critical metal enrichment in hydrothermal Zn-Pb ores[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2023, 342: 198-214. |
| [6] | YUAN B, ZHANG C Q, YU H J, et al. Element enrichment characteristics: Insights from element geochemistry of sphalerite in Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 186: 187-201. |
| [7] | 魏宇, 杨永峰, 柳维, 等. 四川甘洛铅锌矿集区闪锌矿Rb-Sr等时线年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2024, 60(3):482-493. |
| [8] | 罗开, 周家喜, 徐畅, 等. 四川乌斯河大型锗铅锌矿床锗超常富集特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(9): 2761-2777. |
| [9] | MENG Y M, GU X P, MENG S N, et al. Ruizhongite, (Ag2O)Pb3Ge2S8, a thiogermanate mineral from the Wusihe Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan Province, Southwest China[J]. American Mineralogist, 2023, 108(9): 1818-1823. |
| [10] | FRENZEL M, HIRSCH T, GUTZMER J. Gallium, germanium, indium, and other trace and minor elements in sphalerite as a function of deposit type—a meta-analysis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 76: 52-78. |
| [11] | BAUER M E, BURISCH M, OSTENDORF J, et al. Trace element geochemistry of sphalerite in contrasting hydrothermal fluid systems of the Freiberg district, Germany: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analysis, near-infrared light microthermometry of sphalerite-hosted fluid inclusions, and sulfur isotope geochemistry[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2019, 54(2): 237-262. |
| [12] | NIU P P, MUÑOZ M, MATHON O, et al. Mechanism of germanium enrichment in the world-class Huize MVT Pb-Zn deposit, southwestern China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2024, 59(5): 995-1016. |
| [13] | 吉晓佳. 会泽铅锌矿闪锌矿中锗的赋存状态研究和元素替代机制探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. |
| [14] | 周家喜, 孟庆田, 任厚州, 等. 贵州黄丝背斜地区发现特大型共(伴)生锗矿床[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(5): 1025-1026. |
| [15] | ZHANG J K, SHAO Y J, LIU Z F, et al. Sphalerite as a record of metallogenic information using multivariate statistical analysis: Constraints from trace element geochemistry[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 232: 106883. |
| [16] | 韦晨, 叶霖, 李珍立, 等. 四川乌斯河铅锌矿床成矿物质来源及矿床成因: 来自原位 S-Pb 同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(12): 3783-3796. |
| [17] | 熊索菲, 姚书振, 宫勇军, 等. 四川乌斯河铅锌矿床成矿流体特征及 TSR 作用初探[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(1): 105-120. |
| [18] | ZHANG H J, FAN H F, XIAO C Y, et al. The mixing of multi-source fluids in the Wusihe Zn-Pb ore deposit in Sichuan Province, Southwestern China[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2019, 38(5): 642-653. |
| [19] | 王雅萍, 鲍志东, 张连进, 等. 四川盆地蓬莱地区埃迪卡拉系灯影组二段微生物岩储层成岩作用:对优质储层形成与演化的启示[J]. 地质力学学报, 2024, 30(4):579-594. |
| [20] | LUO K, ZHOU J X, HUANG Z L, et al. New insights into the evolution of Mississippi Valley-Type hydrothermal system: A case study of the Wusihe Pb-Zn deposit, South China, using quartz in situ trace elements and sulfides in situ S-Pb isotopes[J]. American Mineralogist, 2020, 105(1): 35-51. |
| [21] | ZHOU J X, XIANG Z Z, ZHOU M F, et al. The giant Upper Yangtze Pb-Zn Province in SW China: Reviews, new advances and a new genetic model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 154: 280-315. |
| [22] | QIU Y M, GAO S, MCNAUGHTON N J, et al. First evidence of >3.2 Ga continental crust in the Yangtze craton of South China and its implications for Archean crustal evolution and Phanerozoic tectonics[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(1): 11-14. |
| [23] | GAO S, YANG J, ZHOU L, et al. Age and growth of the Archean Kongling terrain, South China, with emphasis on 3.3 Ga granitoid gneisses[J]. American Journal of Science, 2011, 311(2): 153-182. |
| [24] | 孙自明, 卞昌蓉, 刘光祥. 峨眉山地幔柱主要研究进展及四川盆地二叠纪成盆动力学机制[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1089-1099. |
| [25] | 王亮, 张嘉玮, 向坤鹏, 等. 黔西北地区地球物理特征与铅锌矿控矿构造分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(2): 325-336. |
| [26] | 杨兴玉, 任厚州, 刘雨, 等. 黔西北五指山地区叠加构造变形特征对铅锌矿成矿的控制[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(4): 739-749. |
| [27] | 林方成. 扬子地台西缘大渡河谷超大型层状铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(4): 540-556. |
| [28] | HALL D L, STERNER S M, BODNAR R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(1): 197-202. |
| [29] | 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. |
| [30] | 刘斌. 简单体系水溶液包裹体pH和Eh的计算[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1533-1542. |
| [31] | LIU J J, SPIRO B F, DAI S F, et al. Strontium isotopes in high- and low-Ge coals from the Shengli Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, Northern China: New indicators for Ge source[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2021, 233: 103642. |
| [32] | BERNSTEIN L R. Germanium geochemistry and mineralogy[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49(11): 2409-2422. |
| [33] | 邵洁涟. 金矿找矿矿物学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1988. |
| [34] | 王晓虎, 薛春纪, 李智明, 等. 扬子陆块北缘马元铅锌矿床地质和地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2008, 27(1): 37-48. |
| [35] | 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984. |
| [36] | LAI X, CHEN C H, YANG Y L, et al. Constraints on metallogenic temperature and mineralization style from reflection color of sphalerite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2023, 161: 105634. |
| [37] | YANG Y L, CHEN C H, QIN S P, et al. Mineral textures, mineral chemistry and S isotopes of sulphides from the Tianbaoshan Pb-Zn-Cu deposit in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou triangle: Implications for mineralization process[J]. Geological Magazine, 2023, 160(3): 471-489. |
| [38] | 张雪琴, 徐登峰, 赵云, 等. 新疆东天山照壁山金铅锌多金属矿床地质特征及矿床成因[J]. 矿床地质, 2023, 42(6): 1121-1138. |
| [39] | KELLEY K D. Textural, compositional, and sulfur isotope variations of sulfide minerals in the red dog Zn-Pb-Ag deposits, Brooks range, Alaska: Implications for ore formation[J]. Economic Geology, 2004, 99(7): 1509-1532. |
| [40] | 卢焕章, 池国祥, 王中刚. 典型金属矿床的成因及其构造环境[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995. |
| [41] | 王健, 张均, 仲文斌, 等. 川滇黔地区天宝山, 会泽铅锌矿床成矿流体来源初探: 来自流体包裹体及氦氩同位素的证据[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(6): 2076-2099. |
| [42] | 陈锌. 四川会东大梁子铅锌矿床成矿模式综合研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2021. |
| [43] | 余冲, 魏美丽, 胡广灿. 四川会理县天宝山铅锌矿流体包裹体地球化学特征[J]. 云南地质, 2015, 34(4): 531-538. |
| [44] | 杨清, 张均, 王健, 等. 四川天宝山大型铅锌矿床成矿流体及同位素地球化学[J]. 矿床地质, 2018, 37(4): 816-834. |
| [45] | 王海, 王京彬, 祝新友, 等. 扬子地台西缘大梁子铅锌矿床成因: 流体包裹体及同位素地球化学约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(4): 681-698. |
| [46] | 王海, 祝新友, 王京彬, 等. 四川天宝山铅锌矿成矿物质来源与成矿机制: 来自流体包裹体及同位素地球化学制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(6): 1830-1846. |
| [47] | 黎洪秩. 陕西马元地区楠木树铅锌矿床有机流体成矿的包裹体证据[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017. |
| [48] | 张艳. 滇东北矿集区会泽超大型铅锌矿床流体混合成矿机制[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2016. |
| [49] | 张振亮. 云南会泽铅锌矿床成矿流体性质和来源: 来自流体包裹体和水岩反应实验的证据[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院地球化学研究所, 2006. |
| [50] | 林传仙, 白正华, 张哲儒. 矿物及有关化合物热力学数据手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985. |
| [51] | 叶大伦, 胡建华. 实用无机物热力学数据手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002. |
| [52] | 刘金波. 广东凡口铅锌矿床闪锌矿矿物学和地球化学研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2023. |
| [1] | 郑博, 李成禄, 于雷, 杨文鹏, 徐国战, 史冬岩, 杨元江, 符安宗, 赵瑞君. 黑龙江二道坎银铅锌矿床黄铁矿标型特征及其S、Pb同位素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2025, 39(03): 648-666. |
| [2] | 胡生平, 韩善楚, 张洪求, 张勇, 潘家永, 钟福军, 卢建研, 李惟鑫. 庐枞盆地西湾铅锌矿床黄铁矿微量元素组成特征及成矿启示[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 183-197. |
| [3] | 杜保峰, 张荣臻, 杨长青, 李山坡, 谭和勇, 朱红运. 西藏则不吓铅锌矿床硫、铅同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的指示[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(04): 1138-1145. |
| [4] | 周桐, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 王承洋, 刘广虎. 内蒙古浩布高铅锌矿床小罕山岩体年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(01): 282-294. |
| [5] | 毛俊莉, 张金川, 丁江辉, 尚灿, 陈世敬, 苏泽昕. 辽河坳陷清水洼陷沙三段页岩气富集条件[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(06): 1252-1262. |
| [6] | 王亮, 张嘉玮, 向坤鹏, 陈囯勇, 胡从亮, 张琛. 黔西北地区地球物理特征与铅锌矿控矿构造分析[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(02): 325-336. |
| [7] | 宋志娇, 陈翠华, 尹力, 张燕. 陕西马元铅锌矿床中有机质的存在及其对成矿的作用[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(06): 1272-1282. |
| [8] | 邬秋敏, 陈翠华, 涂宗林, 张燕, 宋志娇, 赖翔. 西藏蒙亚啊铅锌矿床矽卡岩矿物特征及其意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(05): 874-886. |
| [9] | 杨兴玉, 任厚州, 刘雨, 单永波, 杨坤光, 安琦, 兰安平, 谭华, 吴才进, 肖凯, 莫璐璐. 黔西北五指山地区叠加构造变形特征对铅锌矿成矿的控制[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(04): 739-749. |
| [10] | 郜臻臻, 张招崇, 程志国, MIRZAEV A U, NURTAEV B S, KODIROV O. 乌兹别克斯坦Uchkulach铅锌矿流体包裹体特征及矿床成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(03): 429-437. |
| [11] | 王继春 ,王银宏 ,张梅 ,刘家军 ,彭润民 ,王建平 ,宋崇宇 ,周路路. 内蒙古高尔旗银铅锌矿区花岗岩的岩石成因:地球化学、锆石UPb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 961-980. |
| [12] | 吕豫辉,韩润生,任涛,邱文龙,让昊,高原. 滇东北矿集区云南富乐厂铅锌矿区断裂构造控矿特征及其与成矿的关系[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(3): 563-575. |
| [13] | 尹远,梁维,谢锦程,张继军. 藏南吉松铅锌矿流体包裹体特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(3): 553-562. |
| [14] | 王建荣,薛传东,黄河远,靳纪娟. 滇西保山核桃坪铅锌矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及其成因意义[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 721-730. |
| [15] | 彭义伟,顾雪祥,王新利,章永梅,刘溪溪,于晓亮. 新疆伊宁县塔北铅锌矿床地质特征和S、Pb、C、O同位素组成[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 674-685. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||