



Geoscience ›› 2020, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (06): 1277-1290.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.046
• Petrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Huan1,2( ), KANG Zhiqiang1,2(
), KANG Zhiqiang1,2( ), WU Jiachang3, LI Daixian1,2, CAO Yan1,2, WEI Tianwei1,2, WEI Naishao1,2, LIU Di1,2, ZHOU Tong1,2, LIU Dongmei1,2, LAN Haiyang4
), WU Jiachang3, LI Daixian1,2, CAO Yan1,2, WEI Tianwei1,2, WEI Naishao1,2, LIU Di1,2, ZHOU Tong1,2, LIU Dongmei1,2, LAN Haiyang4
Received:2019-06-05
Revised:2020-07-02
Online:2020-12-22
Published:2020-12-22
Contact:
KANG Zhiqiang
CLC Number:
CHEN Huan, KANG Zhiqiang, WU Jiachang, LI Daixian, CAO Yan, WEI Tianwei, WEI Naishao, LIU Di, ZHOU Tong, LIU Dongmei, LAN Haiyang. Geochronology, Petrogenesis and Geological Significance of the Puquan Granite Pluton in Dayaoshan Area, Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(06): 1277-1290.
| 测点 | wB/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | 207Pb/235U ±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | 207Pb/235U±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | |||
| 14PQ-06-1 | 488 | 82 | 0.17 | 0.547 4±0.002 2 | 0.070 8± 0.000 3 | 443±1.4 | 441±1.6 | |
| 14PQ-06-2 | 551 | 58 | 0.10 | 0.562 9±0.002 1 | 0.070 8± 0.000 3 | 453±1.4 | 441±1.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 518 | 69 | 0.13 | 0.553 9±0.004 3 | 0.070 8± 0.000 4 | 448±2.8 | 441±2.4 | |
| 14PQ-06-4 | 503 | 81 | 0.16 | 0.555 5±0.001 6 | 0.070 7± 0.000 1 | 449±1.1 | 440±0.5 | |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 570 | 62 | 0.11 | 0.540 1±0.003 0 | 0.070 7± 0.000 4 | 438±2.0 | 441±2.3 | |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 523 | 76 | 0.15 | 0.547 7±0.001 5 | 0.070 9± 0.000 2 | 444±1.0 | 441±1.1 | |
| 14PQ-06-7 | 480 | 89 | 0.19 | 0.572 3±0.003 4 | 0.070 7± 0.000 4 | 460±2.2 | 440±2.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-8 | 295 | 162 | 0.55 | 0.572 2±0.001 7 | 0.070 7± 0.000 2 | 459±1.1 | 440±1.1 | |
| 14PQ-06-9 | 444 | 97 | 0.22 | 0.575 0±0.002 4 | 0.070 8± 0.000 3 | 461±1.5 | 441±1.9 | |
| 14PQ-06-10 | 481 | 81 | 0.17 | 0.569 5±0.003 9 | 0.070 8± 0.000 5 | 458±2.5 | 441±3.2 | |
| 14PQ-06-11 | 558 | 69 | 0.12 | 0.546 6±0.002 3 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 443±1.5 | 441±1.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-12 | 422 | 113 | 0.27 | 0.550 1±0.002 6 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 445±1.7 | 442±1.8 | |
| 14PQ-06-13 | 571 | 57 | 0.10 | 0.563 5±0.001 7 | 0.070 9± 0.000 2 | 454±1.1 | 441±1.0 | |
| 14PQ-06-14 | 354 | 131 | 0.37 | 0.552 5±0.002 4 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 447±1.6 | 441±1.6 | |
| 14PQ-06-15 | 428 | 107 | 0.25 | 0.561 7±0.002 5 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 453±1.6 | 442±1.8 | |
| 14PQ-06-16 | 455 | 102 | 0.22 | 0.554 0±0.003 8 | 0.070 9± 0.000 5 | 448±2.5 | 442±2.9 | |
| 14PQ-06-17 | 439 | 107 | 0.24 | 0.573 7±0.001 2 | 0.070 8± 0.000 1 | 460±0.8 | 441±0.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-18 | 326 | 146 | 0.45 | 0.561 9±0.002 8 | 0.070 8± 0.000 2 | 453±1.8 | 441±1.5 | |
Table 1 LA-(MC)-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analysis results of Puquan granitic pluton
| 测点 | wB/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | Th | 207Pb/235U ±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | 207Pb/235U±σ | 206Pb/238U±σ | |||
| 14PQ-06-1 | 488 | 82 | 0.17 | 0.547 4±0.002 2 | 0.070 8± 0.000 3 | 443±1.4 | 441±1.6 | |
| 14PQ-06-2 | 551 | 58 | 0.10 | 0.562 9±0.002 1 | 0.070 8± 0.000 3 | 453±1.4 | 441±1.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 518 | 69 | 0.13 | 0.553 9±0.004 3 | 0.070 8± 0.000 4 | 448±2.8 | 441±2.4 | |
| 14PQ-06-4 | 503 | 81 | 0.16 | 0.555 5±0.001 6 | 0.070 7± 0.000 1 | 449±1.1 | 440±0.5 | |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 570 | 62 | 0.11 | 0.540 1±0.003 0 | 0.070 7± 0.000 4 | 438±2.0 | 441±2.3 | |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 523 | 76 | 0.15 | 0.547 7±0.001 5 | 0.070 9± 0.000 2 | 444±1.0 | 441±1.1 | |
| 14PQ-06-7 | 480 | 89 | 0.19 | 0.572 3±0.003 4 | 0.070 7± 0.000 4 | 460±2.2 | 440±2.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-8 | 295 | 162 | 0.55 | 0.572 2±0.001 7 | 0.070 7± 0.000 2 | 459±1.1 | 440±1.1 | |
| 14PQ-06-9 | 444 | 97 | 0.22 | 0.575 0±0.002 4 | 0.070 8± 0.000 3 | 461±1.5 | 441±1.9 | |
| 14PQ-06-10 | 481 | 81 | 0.17 | 0.569 5±0.003 9 | 0.070 8± 0.000 5 | 458±2.5 | 441±3.2 | |
| 14PQ-06-11 | 558 | 69 | 0.12 | 0.546 6±0.002 3 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 443±1.5 | 441±1.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-12 | 422 | 113 | 0.27 | 0.550 1±0.002 6 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 445±1.7 | 442±1.8 | |
| 14PQ-06-13 | 571 | 57 | 0.10 | 0.563 5±0.001 7 | 0.070 9± 0.000 2 | 454±1.1 | 441±1.0 | |
| 14PQ-06-14 | 354 | 131 | 0.37 | 0.552 5±0.002 4 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 447±1.6 | 441±1.6 | |
| 14PQ-06-15 | 428 | 107 | 0.25 | 0.561 7±0.002 5 | 0.070 9± 0.000 3 | 453±1.6 | 442±1.8 | |
| 14PQ-06-16 | 455 | 102 | 0.22 | 0.554 0±0.003 8 | 0.070 9± 0.000 5 | 448±2.5 | 442±2.9 | |
| 14PQ-06-17 | 439 | 107 | 0.24 | 0.573 7±0.001 2 | 0.070 8± 0.000 1 | 460±0.8 | 441±0.7 | |
| 14PQ-06-18 | 326 | 146 | 0.45 | 0.561 9±0.002 8 | 0.070 8± 0.000 2 | 453±1.8 | 441±1.5 | |
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O/ Na2O | A/NK | A/CNK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14PQ-06-2 | 72.83 | 0.18 | 13.66 | 2.69 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 3.58 | 4.77 | 0.04 | 0.94 | 99.73 | 1.33 | 1.24 | 1.18 |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 70.08 | 0.33 | 14.28 | 3.78 | 0.16 | 1.07 | 2.10 | 3.32 | 3.85 | 0.10 | 0.93 | 100.00 | 1.16 | 1.48 | 1.06 |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 69.75 | 0.34 | 14.42 | 3.50 | 0.09 | 1.08 | 2.58 | 3.55 | 3.65 | 0.10 | 1.16 | 100.22 | 1.03 | 1.47 | 1.00 |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 68.50 | 0.33 | 14.12 | 3.63 | 0.13 | 1.01 | 2.45 | 4.64 | 3.49 | 0.10 | 1.06 | 99.46 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.89 |
| 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Pb | Sr | Zr | Hf | Ti | Y | La | Ce | Pr |
| 14PQ-06-2 | 324.00 | 272.00 | 31.99 | 14.12 | 13.00 | 2.14 | 35.34 | 54.82 | 95.48 | 3.46 | 1 039.00 | 23.67 | 79.87 | 62.22 | 49.37 |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 255.00 | 360.00 | 32.14 | 15.42 | 16.22 | 2.29 | 66.87 | 113.00 | 159.00 | 4.83 | 1 897.00 | 30.99 | 149.00 | 116.00 | 91.05 |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 236.00 | 362.00 | 30.89 | 12.61 | 15.74 | 2.02 | 39.35 | 120.00 | 173.00 | 5.04 | 2 014.00 | 28.43 | 157.00 | 122.00 | 93.89 |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 238.00 | 322.00 | 30.65 | 14.38 | 16.66 | 2.71 | 40.87 | 111.00 | 172.00 | 5.22 | 1 952.00 | 33.36 | 149.00 | 117.00 | 90.53 |
| 样品编号 | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | LREE | HREE | REE | δEu |
| 14PQ-06-2 | 36.36 | 25.10 | 8.79 | 17.13 | 17.38 | 14.92 | 14.13 | 14.32 | 14.51 | 14.53 | 16.14 | 83.03 | 14.38 | 97.41 | 0.14 |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 67.19 | 42.48 | 12.07 | 27.30 | 25.13 | 20.47 | 18.73 | 17.70 | 16.86 | 16.41 | 17.72 | 154.00 | 19.41 | 173.00 | 0.12 |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 68.46 | 41.96 | 12.76 | 26.67 | 23.80 | 19.09 | 17.31 | 16.25 | 15.69 | 14.82 | 16.14 | 160.00 | 18.21 | 178.00 | 0.12 |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 67.19 | 42.29 | 12.93 | 28.13 | 25.94 | 20.98 | 19.43 | 18.61 | 18.43 | 18.06 | 19.69 | 154.00 | 20.29 | 174.00 | 0.12 |
Table 2 Major (%), trace element (10-6), and REE (10-6) contents of the Puquan granitic pluton
| 样品编号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | 烧失量 | 总量 | K2O/ Na2O | A/NK | A/CNK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14PQ-06-2 | 72.83 | 0.18 | 13.66 | 2.69 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 3.58 | 4.77 | 0.04 | 0.94 | 99.73 | 1.33 | 1.24 | 1.18 |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 70.08 | 0.33 | 14.28 | 3.78 | 0.16 | 1.07 | 2.10 | 3.32 | 3.85 | 0.10 | 0.93 | 100.00 | 1.16 | 1.48 | 1.06 |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 69.75 | 0.34 | 14.42 | 3.50 | 0.09 | 1.08 | 2.58 | 3.55 | 3.65 | 0.10 | 1.16 | 100.22 | 1.03 | 1.47 | 1.00 |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 68.50 | 0.33 | 14.12 | 3.63 | 0.13 | 1.01 | 2.45 | 4.64 | 3.49 | 0.10 | 1.06 | 99.46 | 0.75 | 1.24 | 0.89 |
| 样品编号 | Rb | Ba | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Pb | Sr | Zr | Hf | Ti | Y | La | Ce | Pr |
| 14PQ-06-2 | 324.00 | 272.00 | 31.99 | 14.12 | 13.00 | 2.14 | 35.34 | 54.82 | 95.48 | 3.46 | 1 039.00 | 23.67 | 79.87 | 62.22 | 49.37 |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 255.00 | 360.00 | 32.14 | 15.42 | 16.22 | 2.29 | 66.87 | 113.00 | 159.00 | 4.83 | 1 897.00 | 30.99 | 149.00 | 116.00 | 91.05 |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 236.00 | 362.00 | 30.89 | 12.61 | 15.74 | 2.02 | 39.35 | 120.00 | 173.00 | 5.04 | 2 014.00 | 28.43 | 157.00 | 122.00 | 93.89 |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 238.00 | 322.00 | 30.65 | 14.38 | 16.66 | 2.71 | 40.87 | 111.00 | 172.00 | 5.22 | 1 952.00 | 33.36 | 149.00 | 117.00 | 90.53 |
| 样品编号 | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | LREE | HREE | REE | δEu |
| 14PQ-06-2 | 36.36 | 25.10 | 8.79 | 17.13 | 17.38 | 14.92 | 14.13 | 14.32 | 14.51 | 14.53 | 16.14 | 83.03 | 14.38 | 97.41 | 0.14 |
| 14PQ-06-3 | 67.19 | 42.48 | 12.07 | 27.30 | 25.13 | 20.47 | 18.73 | 17.70 | 16.86 | 16.41 | 17.72 | 154.00 | 19.41 | 173.00 | 0.12 |
| 14PQ-06-5 | 68.46 | 41.96 | 12.76 | 26.67 | 23.80 | 19.09 | 17.31 | 16.25 | 15.69 | 14.82 | 16.14 | 160.00 | 18.21 | 178.00 | 0.12 |
| 14PQ-06-6 | 67.19 | 42.29 | 12.93 | 28.13 | 25.94 | 20.98 | 19.43 | 18.61 | 18.43 | 18.06 | 19.69 | 154.00 | 20.29 | 174.00 | 0.12 |
| 样品测点 | t/Ma | 176Lu/177Hf±1σ | 176Yb/177Hf±1σ | 176Hf/177Hf±1σ | εHf (0) | εHf (t) | tDM /Ma | /Ma | f(176Hf/ 177Hf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14PQ-6-1 | 441.0 | 0.001 113±0.000 075 | 0.034 595±0.003 795 | 0.282 379±0.000 017 | -13.91 | -4.53 | 1 237 | 1 704 | -0.97 |
| 14PQ-6-2 | 441.0 | 0.000 657±0.000 018 | 0.020 395±0.000 425 | 0.282 409±0.000 015 | -12.83 | -3.32 | 1 180 | 1 628 | -0.98 |
| 14PQ-6-3 | 440.9 | 0.001 380±0.000 033 | 0.042 456±0.001 245 | 0.282 459±0.000 020 | -11.06 | -1.76 | 1 132 | 1 530 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-4 | 440.4 | 0.002 461±0.000 011 | 0.075 485±0.000 503 | 0.282 480±0.000 017 | -10.33 | -1.36 | 1 136 | 1 505 | -0.93 |
| 14PQ-6-5 | 440.7 | 0.001 245±0.000 047 | 0.040 750±0.001 700 | 0.282 380±0.000 018 | -13.88 | -4.55 | 1 240 | 1 705 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-6 | 441.5 | 0.002 336±0.000 027 | 0.074 280±0.001 097 | 0.282 495±0.000 017 | -9.81 | -0.78 | 1 110 | 1 469 | -0.93 |
| 14PQ-6-7 | 440.2 | 0.001 102±0.000 010 | 0.033 945±0.000 598 | 0.282 488±0.000 019 | -10.04 | -0.67 | 1 083 | 1 461 | -0.97 |
| 14PQ-6-8 | 440.4 | 0.002 367±0.000 011 | 0.063 705±0.000 147 | 0.282 501±0.000 017 | -9.58 | -0.58 | 1 102 | 1 456 | -0.93 |
| 14PQ-6-9 | 440.9 | 0.002 038±0.000 073 | 0.054 017±0.001 510 | 0.282 540±0.000 020 | -8.19 | 0.92 | 1 035 | 1 362 | -0.94 |
| 14PQ-6-10 | 440.9 | 0.000 935±0.000 017 | 0.026 944±0.000 805 | 0.282 460±0.000 017 | -11.05 | -1.62 | 1 118 | 1 521 | -0.97 |
| 14PQ-6-11 | 441.5 | 0.001 372±0.000 014 | 0.037 329±0.000 375 | 0.282 454±0.000 015 | -11.23 | -1.92 | 1 139 | 1 541 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-12 | 441.5 | 0.001 372±0.000 007 | 0.044 861±0.000 117 | 0.282 445±0.000 015 | -11.55 | -2.24 | 1 151 | 1 561 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-13 | 441.5 | 0.002 688±0.000 015 | 0.067 995±0.000 601 | 0.282 098±0.000 021 | -23.83 | -14.92 | 1 700 | 2 351 | -0.92 |
| 14PQ-6-14 | 441.5 | 0.002 930±0.000 015 | 0.092 515±0.000 660 | 0.282 599±0.000 022 | -6.12 | 2.75 | 974 | 1 247 | -0.91 |
| 14PQ-6-15 | 441.5 | 0.001 564±0.000 021 | 0.045 459±0.000 903 | 0.282 456±0.000 019 | -11.19 | -1.93 | 1 143 | 1 541 | -0.95 |
| 14PQ-6-16 | 441.6 | 0.001 419±0.000 009 | 0.044 094±0.000 326 | 0.282 372±0.000 016 | -14.16 | -4.86 | 1 257 | 1 725 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-17 | 441.1 | 0.001 336±0.000 013 | 0.042 220±0.000 586 | 0.282 423±0.000 017 | -12.35 | -3.04 | 1 182 | 1 611 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-18 | 440.9 | 0.001 034±0.000 063 | 0.030 677±0.001 124 | 0.282 407±0.000 024 | -12.91 | -3.51 | 1 195 | 1 640 | -0.97 |
Table 3 Zircon Hf isotope data and related parameters
| 样品测点 | t/Ma | 176Lu/177Hf±1σ | 176Yb/177Hf±1σ | 176Hf/177Hf±1σ | εHf (0) | εHf (t) | tDM /Ma | /Ma | f(176Hf/ 177Hf) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14PQ-6-1 | 441.0 | 0.001 113±0.000 075 | 0.034 595±0.003 795 | 0.282 379±0.000 017 | -13.91 | -4.53 | 1 237 | 1 704 | -0.97 |
| 14PQ-6-2 | 441.0 | 0.000 657±0.000 018 | 0.020 395±0.000 425 | 0.282 409±0.000 015 | -12.83 | -3.32 | 1 180 | 1 628 | -0.98 |
| 14PQ-6-3 | 440.9 | 0.001 380±0.000 033 | 0.042 456±0.001 245 | 0.282 459±0.000 020 | -11.06 | -1.76 | 1 132 | 1 530 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-4 | 440.4 | 0.002 461±0.000 011 | 0.075 485±0.000 503 | 0.282 480±0.000 017 | -10.33 | -1.36 | 1 136 | 1 505 | -0.93 |
| 14PQ-6-5 | 440.7 | 0.001 245±0.000 047 | 0.040 750±0.001 700 | 0.282 380±0.000 018 | -13.88 | -4.55 | 1 240 | 1 705 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-6 | 441.5 | 0.002 336±0.000 027 | 0.074 280±0.001 097 | 0.282 495±0.000 017 | -9.81 | -0.78 | 1 110 | 1 469 | -0.93 |
| 14PQ-6-7 | 440.2 | 0.001 102±0.000 010 | 0.033 945±0.000 598 | 0.282 488±0.000 019 | -10.04 | -0.67 | 1 083 | 1 461 | -0.97 |
| 14PQ-6-8 | 440.4 | 0.002 367±0.000 011 | 0.063 705±0.000 147 | 0.282 501±0.000 017 | -9.58 | -0.58 | 1 102 | 1 456 | -0.93 |
| 14PQ-6-9 | 440.9 | 0.002 038±0.000 073 | 0.054 017±0.001 510 | 0.282 540±0.000 020 | -8.19 | 0.92 | 1 035 | 1 362 | -0.94 |
| 14PQ-6-10 | 440.9 | 0.000 935±0.000 017 | 0.026 944±0.000 805 | 0.282 460±0.000 017 | -11.05 | -1.62 | 1 118 | 1 521 | -0.97 |
| 14PQ-6-11 | 441.5 | 0.001 372±0.000 014 | 0.037 329±0.000 375 | 0.282 454±0.000 015 | -11.23 | -1.92 | 1 139 | 1 541 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-12 | 441.5 | 0.001 372±0.000 007 | 0.044 861±0.000 117 | 0.282 445±0.000 015 | -11.55 | -2.24 | 1 151 | 1 561 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-13 | 441.5 | 0.002 688±0.000 015 | 0.067 995±0.000 601 | 0.282 098±0.000 021 | -23.83 | -14.92 | 1 700 | 2 351 | -0.92 |
| 14PQ-6-14 | 441.5 | 0.002 930±0.000 015 | 0.092 515±0.000 660 | 0.282 599±0.000 022 | -6.12 | 2.75 | 974 | 1 247 | -0.91 |
| 14PQ-6-15 | 441.5 | 0.001 564±0.000 021 | 0.045 459±0.000 903 | 0.282 456±0.000 019 | -11.19 | -1.93 | 1 143 | 1 541 | -0.95 |
| 14PQ-6-16 | 441.6 | 0.001 419±0.000 009 | 0.044 094±0.000 326 | 0.282 372±0.000 016 | -14.16 | -4.86 | 1 257 | 1 725 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-17 | 441.1 | 0.001 336±0.000 013 | 0.042 220±0.000 586 | 0.282 423±0.000 017 | -12.35 | -3.04 | 1 182 | 1 611 | -0.96 |
| 14PQ-6-18 | 440.9 | 0.001 034±0.000 063 | 0.030 677±0.001 124 | 0.282 407±0.000 024 | -12.91 | -3.51 | 1 195 | 1 640 | -0.97 |
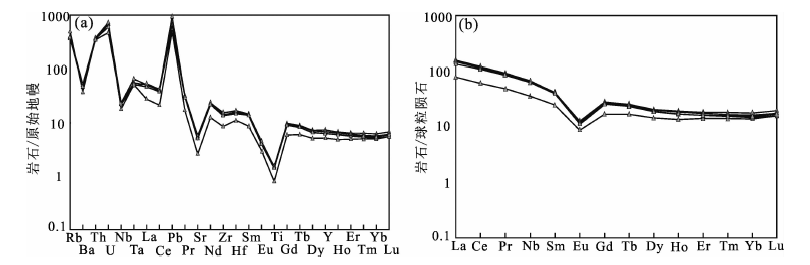
Fig.7 Primitive-mantle-normalized multi-element (a) and chondrite-normalized REE (b) patterns of the Puquan granitic pluton (normalizing values from reference [30])
| 岩体 | 岩性 | 测年结果/Ma | 资料来源 | 岩体 | 岩性 | 测年结果/Ma | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朴全 | 中-细粒花岗岩 | 441.1±1.2 | 本文资料 | 夏郢-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 452.5±1.7 | 文献[ |
| 平头背 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 432.0±1.7 | 文献[ | 大平 | 闪长岩 | 454.2±3.0 | 文献[ |
| 武界 | 花岗闪长岩 | 434.5±0.8 | 文献[ | 大村 | 英云闪长岩 | 456.9±2.0 | 文献[ |
| 社山 | 花岗闪长岩 | 435.5±1.3 | 文献[ | 大村 | 花岗闪长岩 | 451.5±1.3 | 文献[ |
| 大王冲(湾岛金矿) | 花岗斑岩 | 436.1±2.1 | 文献[ | 大进 | 二长花岗岩 | 457.7±1.2 | 文献[ |
| 大王冲(湾岛金矿) | 花岗斑岩 | 436.3±3.0 | 文献[ | 新坪 | 花岗斑岩 | 462.9±6.4 | 文献[ |
| 大王冲(湾岛金矿) | 花岗斑岩 | 436.4±2.4 | 文献[ | 龙新-1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 463.6±1.3 | 文献[ |
| 大王顶 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 463.0±5.0 | 文献[ | 龙新-2 | 花岗岩 | 463.7±1.7 | 文献[ |
| 古龙 | 石英闪长岩 | 445.9±1.2 | 文献[ | 路峒 | 闪长岩 | 465.1±2.3 | 文献[ |
| 莲峒 | 花岗闪长岩 | 445.5±2.2 | 文献[ | 上木水村 | 花岗闪长岩 | 465.5±2.3 | 文献[ |
| 大坡-1 | 闪长岩 | 451.9±3.3 | 文献[ | 上木水矿点 | 花岗闪长岩 | 466.3±4.0 | 文献[ |
| 大坡-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 451.4±2.8 | 文献[ | 夏郢-1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 468.2±1.2 | 文献[ |
Table 4 Age summary of Caledonian granites in the Dayaoshan uplift zone
| 岩体 | 岩性 | 测年结果/Ma | 资料来源 | 岩体 | 岩性 | 测年结果/Ma | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 朴全 | 中-细粒花岗岩 | 441.1±1.2 | 本文资料 | 夏郢-2 | 二长花岗岩 | 452.5±1.7 | 文献[ |
| 平头背 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 432.0±1.7 | 文献[ | 大平 | 闪长岩 | 454.2±3.0 | 文献[ |
| 武界 | 花岗闪长岩 | 434.5±0.8 | 文献[ | 大村 | 英云闪长岩 | 456.9±2.0 | 文献[ |
| 社山 | 花岗闪长岩 | 435.5±1.3 | 文献[ | 大村 | 花岗闪长岩 | 451.5±1.3 | 文献[ |
| 大王冲(湾岛金矿) | 花岗斑岩 | 436.1±2.1 | 文献[ | 大进 | 二长花岗岩 | 457.7±1.2 | 文献[ |
| 大王冲(湾岛金矿) | 花岗斑岩 | 436.3±3.0 | 文献[ | 新坪 | 花岗斑岩 | 462.9±6.4 | 文献[ |
| 大王冲(湾岛金矿) | 花岗斑岩 | 436.4±2.4 | 文献[ | 龙新-1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 463.6±1.3 | 文献[ |
| 大王顶 | 花岗闪长斑岩 | 463.0±5.0 | 文献[ | 龙新-2 | 花岗岩 | 463.7±1.7 | 文献[ |
| 古龙 | 石英闪长岩 | 445.9±1.2 | 文献[ | 路峒 | 闪长岩 | 465.1±2.3 | 文献[ |
| 莲峒 | 花岗闪长岩 | 445.5±2.2 | 文献[ | 上木水村 | 花岗闪长岩 | 465.5±2.3 | 文献[ |
| 大坡-1 | 闪长岩 | 451.9±3.3 | 文献[ | 上木水矿点 | 花岗闪长岩 | 466.3±4.0 | 文献[ |
| 大坡-2 | 花岗闪长岩 | 451.4±2.8 | 文献[ | 夏郢-1 | 花岗闪长岩 | 468.2±1.2 | 文献[ |
| [1] | 广西壮族自治区地质矿产局. 广西壮族自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 1-96. |
| [2] | 黄惠民, 和志军, 崔彬. 广西大瑶山地区花岗岩成矿系列[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003,39(4):12-16. |
| [3] | 陈懋弘, 李忠阳, 李青, 等. 初论广西大瑶山地区多期次花岗质岩浆活动与成矿系列[J]. 地学前缘, 2015,22(2):41-53. |
| [4] | 段瑞春, 凌文黎, 李青, 等. 华南燕山晚期构造-岩浆事件与成矿作用——来自广西大瑶山龙头山金矿床的地球化学约束[J]. 地质学报, 2011,85(10):1644-1658. |
| [5] | 陈富文, 李华芹, 梅玉萍. 广西龙头山斑岩型金矿成岩成矿锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2008(7):921-926. |
| [6] | 胡升奇, 朱强, 张先进, 等. 广东园珠顶铜钼矿床花岗斑岩年代学、地球化学特征及锆石Hf同位素[J]. 矿床地质, 2013,32(6):1139-1158. |
| [7] | 胡升奇, 周国发, 彭松柏, 等. 广西大黎铜钼矿石英二长(斑)岩年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2012,33(1):23-37. |
| [8] | 杨启军, 孙明行, 秦亚, 等. 广西大瑶山大黎花岗岩体年代学研究及地质意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 2017,31(5):843-853. |
| [9] | 陈懋弘, 黄智忠, 李斌, 等. 广西苍梧社洞钨钼矿床花岗岩类岩石的地球化学特征及其与成矿关系[J]. 岩石学报, 2012,28(1):199-212. |
| [10] | 崔彬, 翟裕生, 蒙义峰, 等 .广西大瑶山—西大明山金银成矿系统研究[J].地球科学, 2000,25(4):352-355+396. |
| [11] | LENHARO S L R, MOURA M A, BOTELHO N F. Petrogenetic and mineralization processes in Paleo-to Mesoproterozoic rapakivi granites: examples from Pitinga and Goias, Brazil[J]. Precambrian Research, 2002,119(1):277-299. |
| [12] | LENHARO S L R, POLLARD P J, BORN H. Petrology and textural evolution of granites associated with tin and rare-metals mineralization at the Pitinga mine, Amazonas, Brazil[J]. Lithos, 2003,66(1/2):37-61. |
| [13] | SAVEL’EVA V B, BAZAROVA E P. The Early Proterozoic Primorskii complex of rapakivi granites (western Cisbaikalia): Geochemistry, crystallization conditions, and ore potential[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2012,53(2):147-168. |
| [14] | 徐德明, 付建明, 陈希清, 等. 都庞岭环斑花岗岩的形成时代、成因及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017,41(3):561-576. |
| [15] | 孙涛. 新编华南花岗岩分布图及其说明[J]. 地质通报, 2006,25(3):332-335. |
| [16] | 陈懋弘, 莫次生, 黄智忠, 等. 广西苍梧县社洞钨钼矿床花岗岩类锆石LA-ICP-MS和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2011,30(6):963-978. |
| [17] | 陈懋弘, 郭云起, 梁宾, 等. 广西苍梧县武界钨钼矿点成岩成矿年龄及岩体地球化学特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2012,32(1):1-13. |
| [18] | 熊松泉, 康志强, 冯佐海, 等. 广西大瑶山地区大进岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015,35(4):736-746. |
| [19] | 李献华, 祁昌实, 刘颖, 等. 岩石样品快速Hf分离与MC-ICP-MS同素分析:一个改进的单柱提取色谱方法[J]. 地球化学, 2005,34(2):109-114. |
| [20] | LI X H, ZHOU H, CHUNG S L, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of Late Paleogene ultrapotassic magmatism in southeastern Tibet[J]. International Geology Review, 2002,44(6):559-574. |
| [21] | JACKSON S E, PEARSON N J, GRIFFIN W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004,211(1/2):47-69. |
| [22] | LIU Y S, GAO S, HU Z, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the trans-north China orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010,51:392-399. |
| [23] | LUDWIG K R. User’s Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 39. |
| [24] | ANDERSON T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,192(1/2) : 59-79. |
| [25] | YUAN H L, GAO S, DAI M N, et al. Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008,247(1/2):110-118. |
| [26] | 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(10):2595-2604. |
| [27] | MORRISON G W. Characteristics and tectonic setting of the sho-shonite rock association[J]. Lithos, 1980,13:97-108. |
| [28] | MIDDLEMOST E A K. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks: An Introduction to Igneous Petrology[M]. London:Longman, 1985: 1-266. |
| [29] | MANIAR P D, PICCOLI P M. Tectonic discrimination of grani-toids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989,101(5):635-643. |
| [30] | SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989,42(1):313-345. |
| [31] | 肖柳阳, 陈懋弘, 张志强, 等. 广西昭平湾岛金矿矿床类型、成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2015,22(2):118-130. |
| [32] | 叶鸣, 张青伟, 胡华清, 等. 广西大瑶山地区大王顶花岗闪长斑岩年代学和地球化学特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015,35(4):756-765. |
| [33] | 许华, 黄炳诚, 倪战旭, 等. 钦杭成矿带西段古龙花岗岩株群岩石学、地球化学及年代学[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2012,28(4):331-339. |
| [34] | 吴佳昌, 康志强, 冯佐海, 等. 广西大瑶山隆起区大村岩体年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015,35(4):747-755. |
| [35] | 王新宇, 刘名朝, 周国发, 等. 桂东大瑶山成矿带新坪矿区花岗斑岩与金多金属成矿作用关系[J]. 现代地质, 2013,27(3):585-592. |
| [36] | JIANG X, KANG Z, XU J, et al. Early Paleozoic granodioritic plutons in the Shedong W-Mo ore district, Guangxi, southern China: Products of re-melting of middle Proterozoic crust due to magma underplating[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016: S1367912016303212. |
| [37] | CHAPPELL B W, WHITE A J R. Two contrasting granite type[J]. Pacific Geology, 1974,8:173-174. |
| [38] | WHITE A J R. Sources of granite magmas[J]. Geological So-ciety of America Abstract with Programs, 1979,11:53. |
| [39] | WHALRN J B, CURRIE K L, CHAPPELL B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987,95:407-419. |
| [40] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):185-220. |
| [41] | WU F Y, JAHN B M, WILDE S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China(J):Geochronology and petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2003,66:241-27. |
| [42] | MILLER, CALVIN F. Are strongly peraluminous magmas derived from pelitic sedimentary sources?[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985,93(6):673-689. |
| [43] | SYLVESTER P J. Post-collision strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 1998,45:29-44. |
| [44] | CHAPPELLl B W. Aluminum saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999,46(3):535-551. |
| [45] | 周刚, 张招崇, 罗世宾, 等. 新疆阿尔泰山南缘玛因鄂博高温型强过铝花岗岩:年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(8):1909-1920. |
| [46] | 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(6):1217-1238. |
| [47] | 李献华, 李武显, 李正祥. 再论南岭燕山早期花岗岩的成因类型与构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 2007,52(9):981-991. |
| [48] | 刘腾飞. 桂东古里脑斑岩体地质及金矿化的地球化学特征[J]. 黄金地质科技, 1994(2):52-57. |
| [49] | SCANDOLARA J E, FUCK R A, DALL’AGNOL R, et al. Geochemistry and origin of the Early Mesoproterozoic mangerite charnockite rapakivi granite association of the Serra da Providência suite and associated gabbros, central-eastern Rondonia, SW Amazonian Craton, Brazil[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2013,45:166-193. |
| [50] | CHAPPELL B W, STEPHENS W E. Origin of infracrustal (I-type) granite magmas[J]. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh Earth Sciences, 1988,79(2/3):71-86. |
| [51] |
KEMP A I S, HAWKESWORTH C J, FOSTER G L. et al. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon[J]. Science, 2007,315:980-983.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] | COLLINS W J, RICHARDS S W. Geodynamic significance of S-type granites in circum-Pacific orogens[J]. Geology, 2008,36:559-562. |
| [53] | 朱弟成, 莫宣学, 王立全, 等. 西藏冈底斯东部察隅高分异I型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素约束[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2009,39(7):833-848. |
| [54] | VERVOORT J D, PATCHETT P J, GEHRELS G E, et al. Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J]. Nature, 1996,379:624-627. |
| [55] | GRIFFIN W L, WANG X, JACKSON S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002,61(3/4):237-269. |
| [56] | CONDIE K C. Plate Tectonics and Crustal Evolution[M]. London: Pergamon Press, 1997. |
| [57] | BROWNG C, THORPE R S, WEBB P C. The geochemical characteristics of granitoids in contrasting arcs and comments on magma sources[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1984,141(3):413-426. |
| [58] | DOUCE A E P, JOHNSTON A D. Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the pelitic system: implications for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1991,107(2):202-218. |
| [59] | DOUCE A E P, BEARD J S. Effects of p,f(O2) and Mg/Fe ratio on dehydration melting of model metagreywackes[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996,37(5):999-1024. |
| [60] | GREEN T H, PEARSON N J. An experimental study of Nb and Ta partitioning between Ti-rich minerals and silicate liquids at high pressure and temperature[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987,51(1):55-62. |
| [61] | BARTH M G, MEDONOUGH W F, RUDNIEK R L. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000,165(3/4):197-213. |
| [62] | 徐克勤, 胡受奚, 孙明志, 等. 论花岗岩的成因系列——以华南中生代花岗岩为例[J]. 地质学报, 1983,57(2):107-118. |
| [63] | 邱家骧. 应用岩浆岩岩石学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1991: 201-211. |
| [64] | 郑伟, 陈懋弘, 赵海杰, 等. 广东鹦鹉岭钨多金属矿床中黑云母花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(12):4121-4135. |
| [65] | CHARVET J, SHU L S, FAURE M, et al. Structural development of the Lower Paleozoic belt of South China: Genesis of an intracontinental orogen[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010,39:309-330. |
| [66] | COLLINS W J, BEAMS S D, WHITE A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to SE Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982,80(2):189-200. |
| [67] | LI Z X, LI X H, WARTHO J A, et al. Magmatic and metamorphic events during the Early Paleozoic Wuyi-Yunkai orogeny, southeastern South China: New age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010,122(5/6):772-793. |
| [68] | WAN Y, LIU D, WILDE S A, et al. Evolution of the Yunkai Terrane, South China: Evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and Nd isotope[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010,37(2):1-153. |
| [69] | ZHAO K D, JIANG S Y, SUN T, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating, trace element and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry of Paleozoic granites in the Miao’ershan-Yuechengling batholith, South China: Implication for petrogenesis and tectonic-magmatic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013,74:244-264. |
| [70] | WANG Y, FAN W, ZHANG G, et al. Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block: Key observations and controversies[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013,23(4):1273-1305. |
| [71] | PENG T P, FAN W M, ZHAO G, et al. Petrogenesis of the early Paleozoic strongly peraluminous granites in the Western South China Block and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015,98:399-420. |
| [72] | 吴浩若. 广西加里东运动构造古地理问题[J]. 古地理学报, 2000,45(5):70-76. |
| [73] | 杜远生, 徐亚军. 华南加里东运动初探[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012,31(5):43-49. |
| [74] | PEARCE J A, HARRIS N B W, TINDLE A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretations of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984,25:956-983. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||