



Geoscience ›› 2022, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (02): 406-417.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527
• Water Resources and Environmental Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
AN Guoying( ), GUO Zhaocheng, YE Pei
), GUO Zhaocheng, YE Pei
Received:2021-03-15
Revised:2021-06-08
Online:2022-04-10
Published:2022-06-01
CLC Number:
AN Guoying, GUO Zhaocheng, YE Pei. Climatic Changes and Impacts on Water Quality of Erhai Lake in Dali Area, Yunnan Province over the Period from 1989 to 2019[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(02): 406-417.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.geoscience.net.cn/EN/10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527
| 参数 | chla | TP | TN | SD | CODMn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.84 | 0.82 | -0.83 | 0.83 | |
| 1 | 0.705 6 | 0.672 4 | 0.688 9 | 0.688 9 |
Table 1 Correlation coefficients (rij and γ2ij) between chla and some parameters of lakes in China
| 参数 | chla | TP | TN | SD | CODMn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.84 | 0.82 | -0.83 | 0.83 | |
| 1 | 0.705 6 | 0.672 4 | 0.688 9 | 0.688 9 |
| 年代际 | 年均/℃ | 春季/℃ | 夏季/℃ | 秋季/℃ | 冬季/℃ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | |||||
| 1991—2000 | 15.7 | -0.1 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 21.0 | -0.1 | 15.9 | -0.1 | 9.0 | -0.3 | ||||
| 2001—2010 | 16.0 | 0.2 | 17.0 | 0.3 | 21.2 | 0.1 | 16.1 | 0.1 | 9.7 | 0.4 | ||||
| 2011—2019 | 16.4 | 0.6 | 17.6 | 0.9 | 21.6 | 0.5 | 16.5 | 0.5 | 10.1 | 0.8 | ||||
| 1989—2019 | 16.0 | 0.2 | 17.0 | 0.3 | 21.2 | 0.1 | 16.2 | 0.2 | 9.6 | 0.3 | ||||
Table 2 Decadal means and anomalies of annual and seasonal temperatures in Dali area from 1989 to 2019
| 年代际 | 年均/℃ | 春季/℃ | 夏季/℃ | 秋季/℃ | 冬季/℃ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | 平均值 | 距平 | |||||
| 1991—2000 | 15.7 | -0.1 | 16.7 | 0.0 | 21.0 | -0.1 | 15.9 | -0.1 | 9.0 | -0.3 | ||||
| 2001—2010 | 16.0 | 0.2 | 17.0 | 0.3 | 21.2 | 0.1 | 16.1 | 0.1 | 9.7 | 0.4 | ||||
| 2011—2019 | 16.4 | 0.6 | 17.6 | 0.9 | 21.6 | 0.5 | 16.5 | 0.5 | 10.1 | 0.8 | ||||
| 1989—2019 | 16.0 | 0.2 | 17.0 | 0.3 | 21.2 | 0.1 | 16.2 | 0.2 | 9.6 | 0.3 | ||||
| 年代际 | 1991—2000 | 2001—2010 | 2011—2019 | 1989—2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最低 气温/℃ | 不同站点 (剑川) | 11.8 (1992) | 12.3 (2004) | 12.9 (2011) | 11.8 (1992) |
| 全区平均 | 15.0 | 15.6 | 16.0 | 15.0 | |
| 最高 气温/℃ | 不同站点 (南涧) | 19.9 (1998) | 19.7 (2006) | 20.4 (2019) | 20.4 (2019) |
| 全区平均 | 16.4 | 16.6 | 16.8 | 16.8 | |
Table 3 Decadal minimum and maximum temperatures for individual stations and averages of Dali area from 1989 to 2019
| 年代际 | 1991—2000 | 2001—2010 | 2011—2019 | 1989—2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最低 气温/℃ | 不同站点 (剑川) | 11.8 (1992) | 12.3 (2004) | 12.9 (2011) | 11.8 (1992) |
| 全区平均 | 15.0 | 15.6 | 16.0 | 15.0 | |
| 最高 气温/℃ | 不同站点 (南涧) | 19.9 (1998) | 19.7 (2006) | 20.4 (2019) | 20.4 (2019) |
| 全区平均 | 16.4 | 16.6 | 16.8 | 16.8 | |
| 年代际 | 年均 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | |||||
| 1991—2000 | 880.0 | 5.26 | 94.5 | -9.16 | 500.8 | 7.93 | 247.0 | 5.55 | 39.6 | 16.61 | ||||
| 2001—2010 | 847.0 | 1.32 | 132.5 | 27.40 | 463.1 | -0.19 | 222.1 | -5.08 | 28.6 | -15.93 | ||||
| 2011—2019 | 725.4 | -13.22 | 80.1 | -22.95 | 440.0 | -5.17 | 169.7 | -27.50 | 35.1 | 3.14 | ||||
| 1989—2019 | 822.2 | -1.65 | 104.8 | 0.74 | 465.5 | 0.31 | 218.0 | -6.85 | 34.3 | 0.97 | ||||
Table 4 Decadal means and precipitation anomalies in percentage in Dali area from 1989 to 2019
| 年代际 | 年均 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | 平均值 /mm | 距平 /% | |||||
| 1991—2000 | 880.0 | 5.26 | 94.5 | -9.16 | 500.8 | 7.93 | 247.0 | 5.55 | 39.6 | 16.61 | ||||
| 2001—2010 | 847.0 | 1.32 | 132.5 | 27.40 | 463.1 | -0.19 | 222.1 | -5.08 | 28.6 | -15.93 | ||||
| 2011—2019 | 725.4 | -13.22 | 80.1 | -22.95 | 440.0 | -5.17 | 169.7 | -27.50 | 35.1 | 3.14 | ||||
| 1989—2019 | 822.2 | -1.65 | 104.8 | 0.74 | 465.5 | 0.31 | 218.0 | -6.85 | 34.3 | 0.97 | ||||
| 年代际 | 1991—2000 | 2001—2010 | 2011—2019 | 1989—2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小降 水量/mm | 不同站点 | 474.7 | 416.0 | 357.0 | 357.0 |
| 全区平均 | 758.6 | 662.5 | 621.0 | 621.0 | |
| 最大降 水量/mm | 不同站点 | 1 300.0 | 1 417.0 | 1 216.8 | 1 417.0 |
| 全区平均 | 1 009.3 | 1 039.4 | 884.0 | 1 039.4 | |
Table 5 Decadal minimum and maximum precipitation amount for individual stations and their mean in Dali area from 1989 to 2019
| 年代际 | 1991—2000 | 2001—2010 | 2011—2019 | 1989—2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小降 水量/mm | 不同站点 | 474.7 | 416.0 | 357.0 | 357.0 |
| 全区平均 | 758.6 | 662.5 | 621.0 | 621.0 | |
| 最大降 水量/mm | 不同站点 | 1 300.0 | 1 417.0 | 1 216.8 | 1 417.0 |
| 全区平均 | 1 009.3 | 1 039.4 | 884.0 | 1 039.4 | |
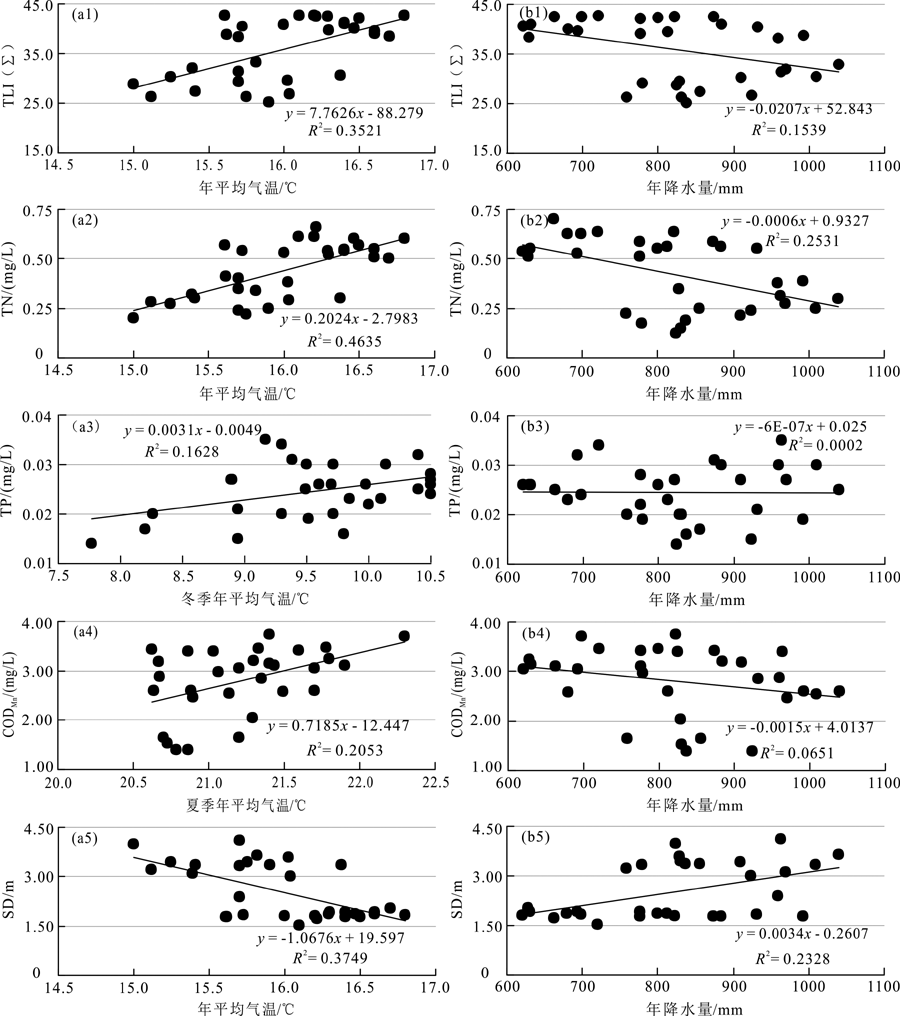
Fig.9 Correlations between annual mean air temperature, annual precipitation amount in Dali area and water quality parameters of Erhai Lake from 1989 to 2019
| [1] | 刘翔卿, 王雷, 刘阳, 等. 1951-2010年云贵高原大理和丽江气温、降水的气候特征分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2018, 23(5):513-523. |
| [2] | 翟羽佳, 周常春, 刘春学. 苍山十八溪流域近60年降水量时空分布特征分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 39(4):618-623. |
| [3] | 李芸, 李宝芬, 张坤, 等. 云南高原湖泊洱海流域年降水量时空分布特征研究[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2017, 15(3):234-240. |
| [4] | 丁文荣. 环洱海地区气候变化特征研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2016, 25(4):599-605. |
| [5] | 夏范燕, 吴巩胜, 李丽, 等. 近50年内滇西北极端气候变化[J]. 云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(3):64-69. |
| [6] | 申文斌, 王龙, 杨蕊, 等. 大理地区极端气候事件长期变化特征研究[J]. 人民珠江, 2018, 39(7):45-50. |
| [7] | 黄慧君, 王永平, 李庆红. 洱海流域近50年气候变化特征及其对洱海水资源的影响[J]. 气象, 2013, 39(4): 436-442. |
| [8] | 王永平, 黄慧君, 李庆红. 洱海净入水量与降水量关系分析[J]. 大理科技, 2006(1):29-33. |
| [9] | 王祖兴, 黄慧君. 洱海流域降水量及旱涝变化对洱海水资源的影响[J]. 大理科技, 2005(2):34-38. |
| [10] | 彭文启, 王世岩, 刘晓波. 洱海水质评价[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2005, 3(3):192-198. |
| [11] | 郑国强, 于兴修, 江南, 等. 洱海水质的演变过程及趋势[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2004, 32(1):99-102. |
| [12] | 唐建明. 洱海水质分析及预测[M]//中国环境科学学会,中国环境保护产业协会. 第十三届世界湖泊大会论文集. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2010:1675-1682. |
| [13] | 王杰, 赵茜, 谢永红, 等. 2008-2014年洱海水质变化特征[M]//中国水利学会2017学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国水利学会, 2017:1061-1066. |
| [14] | 大理州政府. 气候公报[EB/OL]. http://www.dali.gov.cn/dlrmzf/c100639/common_list.shtml[2020-03-12]-[2019-06-24]. |
| [15] | 林芸, 唐亚松, 刘刚, 等. 洱海流域水资源量变化趋势分析[J]. 云南水力发电, 2018, 34(6):4-7. |
| [16] | 大理白族自治州地方志编纂委员会. 大理州年鉴[M]. 昆明: 云南民族出版社, 1989-2019. |
| [17] | 杜宝汉. 亲历洱海保护二十年[M]. 政协大理白族自治州委员会文史和学习委员会. 大理州文史资料第十四辑洱海保护. 昆明: 云南民族出版社, 2010:114-141. |
| [18] | 梁袁华. 洱海网箱养鱼始末[M].政协大理白族自治州委员会文史和学习委员会. 大理州文史资料第十四辑洱海保护. 昆明: 云南民族出版社, 2010:90-93. |
| [19] | 杜宝汉. 洱海富营养化研究[J]. 云南环境科学, 1997, 16(2):30-33. |
| [20] | 颜昌宙, 金相灿, 赵景柱, 等. 云南洱海的生态保护及可持续利用对策[J]. 环境科学, 2005, 26(5):38-42. |
| [21] | 董云仙, 李杰君, 左永福, 等. 洱海水环境现状与治理对策[J]. 云南环境科学, 2004, 23(增1): 101-103. |
| [22] | 施贵兴. 央视《新闻联播》聚焦洱海保护治理成效[N]. 大理日报(汉),2019-09-11(1). |
| [23] | 云南省生态环境厅. 云南省环境状况公报[EB/OL]. http://sthjt.yn.gov.cn. |
| [24] | 大理州环境生态局. 环境状况公报[EB/OL]. http://www.dali.gov.cn/dlrmzf/c100638/common_list.shtml[2020-06-05]-[2019-06-24]. |
| [25] | 郭宏龙. 洱海水环境历史变化规律探讨[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2018, 37(4):22-25. |
| [26] | 王显丽. 基于水生态承载力的洱海流域TMDL总量研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2015. |
| [27] | 王明翠, 刘雪芹, 张建辉. 湖泊富营养化评价方法及分级标准[J]. 中国环境监测, 2002, 18(5):47-49. |
| [28] | 金相灿. 中国湖泊环境(第一册)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1995:275-278. |
| [29] | 林学椿, 于淑秋. 近40年我国气候趋势[J]. 气象, 1990, 16(10):16-22. |
| [30] | 龙红. 气候变暖对云南省冬作物影响[J]. 云南农业科技, 2006, 21(5):9-11. |
| [31] | 大理州人民政府. 水污染防治州级考核断面水质情况[EB/OL]. http://zs.kaipuyun.cn/s[2020-04-24]-[2019-02-11]. |
| [32] | 大理水务局. 水资源公报[EB/OL]. http://www.dali.gov.cn/dlrmzf/c102607/common_list.shtml[2020-08-13]-[2020-08-04]. |
| [33] | 中国气象局. 中国气候变化蓝皮书(2020):我国生态气候总体趋好[EB/OL]. http://www.cma.gov.cn/kppd/kppdqxyr/kppdjsqx/202008/t20200828_561907.html |
| [34] | 杜宝汉. 洱海水理化特性及其变化探讨[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1989, 20(6):538-543. |
| [1] | WANG Xianglian, HUANG Ting, XIAO He, WU Daishe, ZHANG Xiaolong, CHENG Shenggao, MAO Xumei. Magnetic Susceptibility of Hani Peat Sediments in Northeast China and Its Paleoclimate Significance [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1323-1331. |
| [2] | XU Keke, YANG Zhenjing, NING Kai, HAN Qiangqiang, BI Zhiwei, ZHAO Nannan. MIS6-MIS5 Climate Change of Yinchuan Basin Based on End-member Method [J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(05): 1311-1322. |
| [3] | LU Jingfang, ZHANG Kexin, SONG Bowen, XU Yadong, ZHANG Jianyu, HUANG Wei, ZHANG Daolai. Paleogene-Neogene Pollen and Climate Change in Dahonggou Region of Qaidam Basin [J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(04): 732-744. |
| [4] | DING Yingying, ZHANG Xujiao, HE Zexin, HU Daogong, WANG Chaoqun. River Incision Behavior Response to Climate Change During the Last Glacial Period [J]. Geoscience, 2017, 31(02): 394-405. |
| [5] | WANG Jian-yong,ZHANG Xu-jiao,HE Ze-xin,ZHAO Qiu-chen,HE Xiang-li,SHENG Yu-ying. Discovery of Ice-wedge Casts in the Northern Margin of Loess Plateau and Their Implications [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(4): 816-824. |
| [6] | WANG Jin-cui, ZHANG Ying, WEN Ji-li, SUN Ji-chao. Temporal and Spatial Changing Features of Climate in North China Plain [J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(2): 299-306. |
| [7] | DIAO Dun-Xiang, XU Shen-E, LIU Zhi-Rong. Grain Size Characteristics and Deposit Environment of Strata in Hujiagang River Terrace in Yingxian, Shanxi Province [J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(4): 716-722. |
| [8] | CHEN Xi-1, 2 , WANG Cheng-Shan-1, 2 , HUANG Yong-Jian-1, 2. Progress in the Study of Cretaceous Rapid Climate Change— Evidence of Glaciation in a Greenhouse World [J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(3): 409-418. |
| [9] | ZHAO Hai-bin,YIN Zhi-gang,WAN Xiao-qiao,YU Qing-wen,NIU Yan-hong. Influence of Late Cretaceous Climate Change to Extinction of Dinosaurs in Jiayin Area of Heilongjiang, Analyzed by Spore and Pollen [J]. Geoscience, 2006, 20(2): 216-224. |
| [10] | WANG Yong,CAO Ying-chang,ZHENG Wen-tao,ZHAO Jian,CHEN xiao-hong. THE PRIMARY STUDY ON HOW TO DIVIDE SQUENCES AND SYSTEM TRACTS OF THE LACUSTRINE DEEP WATER ENVIRONMENTAL STRATA —— A CASE STUDY OF WELL NIU 38 IN DONGYING DEPRESSION [J]. Geoscience, 2004, 18(2): 180-186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||