



现代地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (02): 535-551.DOI: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.105
收稿日期:2020-09-23
修回日期:2020-10-15
出版日期:2021-04-25
发布日期:2021-05-25
作者简介:寇冠玉,女,硕士研究生,1995年出生,地质工程专业,主要从事矿床学与矿床地球化学研究。Email: kou_gy@163.com。
基金资助:
KOU Guanyu1( ), ZHOU Ye2, ZHENG Yuanchuan1, YU Jiaxing1
), ZHOU Ye2, ZHENG Yuanchuan1, YU Jiaxing1
Received:2020-09-23
Revised:2020-10-15
Online:2021-04-25
Published:2021-05-25
摘要:
伊朗马斯杰德达吉(Masjed Daghi)斑岩型矿床位于阿哈尔—乔勒法(Ahar-Julfa)/阿拉斯巴兰(Arasbaran)成矿带的西北部,目前针对该斑岩矿床的研究相对较少,许多地质问题有待解决。为了补充马斯杰德达吉斑岩型矿床成因的地球化学证据,更好地厘定斑岩形成时间,了解矿床形成过程,对矿区中钻孔采集的石英二长斑岩中的长石、石英和锆石等矿物进行了红外-拉曼光谱、同位素及U-Pb定年、主量和微量元素等测试,同时对斑岩全岩主微量元素进行了分析测试。光谱学测试结果显示斑岩样品中的长石斑晶主要为斜长石,少量为钾长石。锆石U-Pb定年结果显示其成岩年龄为(54.1±1.5) Ma (MSWD=0.48),属早始新世,为矿前斑岩。岩体内发育的斜长石具有较低的K2O(0.2%~1.8%)、较高的CaO(1.7%~8.7%)和Na2O(6.5%~9.7%)。这些斑岩中的长石具有相对过量的Al,反映了成岩岩浆具有较高的水含量。锆石Ce4+ / Ce3+比值为152~543,平均330,指示较高的氧逸度。斑岩SiO2含量高达63.4%,含有相对较高的K2O(4.9%)和Sr/Y值(120.0~121.6),显示为具有埃达克特征的钾玄质石英二长斑岩。锆石εHf(t)值为+4.5~+13.5,平均值+10.3,为正异常。另外,二阶段模型年龄(TDM=841~260 Ma)表明岩浆起源于亏损地幔物质。马斯杰德达吉始新世斑岩形成于碰撞前大洋俯冲环境,更可能来自基性岩浆,因经历了俯冲洋壳脱水和地幔楔部分熔融的过程,而具有高氧化和富水的特征。
中图分类号:
寇冠玉, 周晔, 郑远川, 于佳兴. 伊朗马斯杰德达吉(Masjed Daghi)始新世斑岩成因:来自光谱学与U-Pb年代学和地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(02): 535-551.
KOU Guanyu, ZHOU Ye, ZHENG Yuanchuan, YU Jiaxing. Genesis of Eocene Porphyry in Masjed Daghi, Iran: Evidence from Spectrographic, U-Pb Dating and Geochemical Characteristics[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(02): 535-551.
| 矿区 | 成矿带 | 吨位 /Mt | 品味 | 围岩 | 含矿斑岩 | 成矿类型 | 矿产 | 年龄/Ma | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马斯杰德达吉 (Masjed Daghi) | 阿哈尔— 乔勒法 (Ahar-Jolfa) 斑岩成矿带 | 340 | 0.27%Cu, 0.006%Mo, 0.32×10-6Au (20 Mt金矿体) | 始新世安山岩、 火山碎屑岩 | 二长闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状 | Cu+Mo+ Au | 20.46± 3.55 | [ |
| 松贡 (Sungun) | 阿哈尔— 乔勒法斑岩 成矿带 | 850 | 0.62% Cu, 0.01% Mo | 白垩纪沉积物、 始新世火山岩 | 二长岩-石 英二长岩, 花岗闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状, 矽卡岩 | Cu+Mo | 21 | [ |
| 萨尔切什梅 (Sar Cheshmeh) | 克尔曼 (Kerman) 斑岩成矿带 | 1 200 | 0.6% Cu, 0.02% Mo | 始新世安山岩、 玄武岩、火山 碎屑岩 | 花岗闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状 | Cu+Mo | 7~13 | [ |
| 梅杜克 (Meiduk) | 克尔曼斑岩 成矿带 | 500 | 0.8% Cu, 0.007% Mo | 始新世安山岩、玄 武岩、火山碎屑岩 | 花岗闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状 | Cu+Mo | 9~12 | [ |
表1 伊朗代表性斑岩型矿床概况及其成矿年龄
Table 1 Characteristics of major Iranian porphyry deposits and their ages
| 矿区 | 成矿带 | 吨位 /Mt | 品味 | 围岩 | 含矿斑岩 | 成矿类型 | 矿产 | 年龄/Ma | 参考 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 马斯杰德达吉 (Masjed Daghi) | 阿哈尔— 乔勒法 (Ahar-Jolfa) 斑岩成矿带 | 340 | 0.27%Cu, 0.006%Mo, 0.32×10-6Au (20 Mt金矿体) | 始新世安山岩、 火山碎屑岩 | 二长闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状 | Cu+Mo+ Au | 20.46± 3.55 | [ |
| 松贡 (Sungun) | 阿哈尔— 乔勒法斑岩 成矿带 | 850 | 0.62% Cu, 0.01% Mo | 白垩纪沉积物、 始新世火山岩 | 二长岩-石 英二长岩, 花岗闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状, 矽卡岩 | Cu+Mo | 21 | [ |
| 萨尔切什梅 (Sar Cheshmeh) | 克尔曼 (Kerman) 斑岩成矿带 | 1 200 | 0.6% Cu, 0.02% Mo | 始新世安山岩、 玄武岩、火山 碎屑岩 | 花岗闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状 | Cu+Mo | 7~13 | [ |
| 梅杜克 (Meiduk) | 克尔曼斑岩 成矿带 | 500 | 0.8% Cu, 0.007% Mo | 始新世安山岩、玄 武岩、火山碎屑岩 | 花岗闪长岩 | 脉状,散布状 | Cu+Mo | 9~12 | [ |
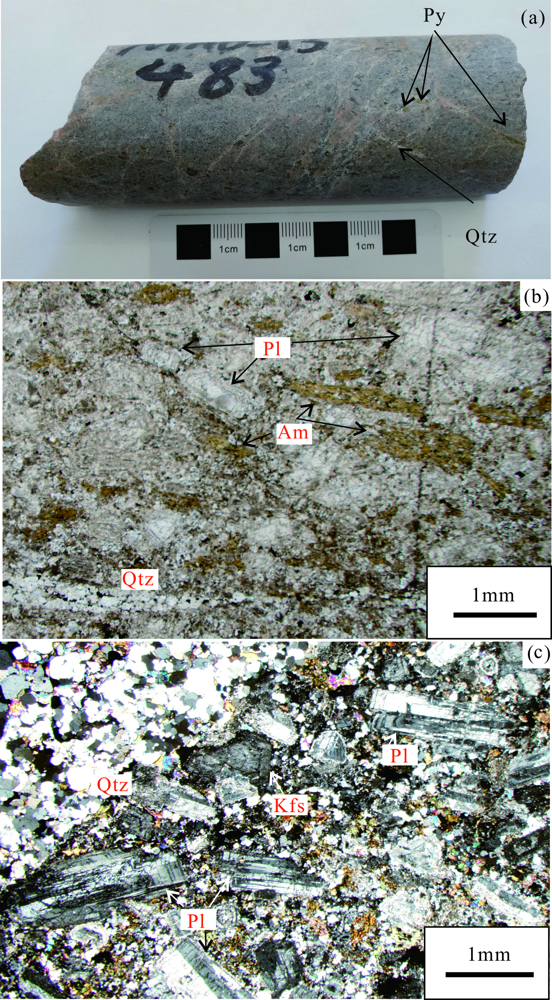
图3 马斯杰德达吉斑岩样品的岩相学特征(手标本及显微照片) (a)钻孔斑岩样品(MAD-13-483)照片,存在大量明显的长石斑晶,可见石英和黄铁矿;(b)岩石薄片的单偏光显微照片,可见长石和角闪石斑晶;(c)岩石薄片的正交偏光显微照片,可见石英和大量长石斑晶;Kfs. 钾长石; Pl. 斜长石; Py. 黄铁矿; Qtz. 石英; Am. 角闪石
Fig.3 Petrographic characteristics of the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample(hand specimen and thin-section micrographs)
| 编号 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | Pb | 207Pb/206Pb (1σ) | 207Pb/235U (1σ) | 206Pb/238U (1σ) | 207Pb/206Pb (1σ) | 207Pb/235U (1σ) | 206Pb/238U (1σ) | |||
| 1 | 75.40 | 153.40 | 1.91 | 0.194 8(0.030 5) | 0.207 8(0.029 0) | 0.008 7(0.000 5) | 2 783.65(259.26) | 191.70(24.37) | 56.16(3.37) | ||
| 2 | 68.81 | 171.28 | 1.98 | 0.187 4(0.049 7) | 0.184 5(0.039 0) | 0.008 1(0.000 3) | 2 720.38(451.70) | 171.89(33.43) | 52.30(1.92) | ||
| 3 | 69.74 | 135.25 | 1.76 | 0.293 1(0.064 7) | 0.327 9(0.071 2) | 0.008 6(0.000 4) | 3 434.27(349.00) | 287.94(54.50) | 55.33(2.25) | ||
| 4 | 76.72 | 249.94 | 3.35 | 0.235 8(0.071 6) | 0.344 1(0.124 7) | 0.009 8(0.001 0) | 3 091.67(504.76) | 300.31(94.44) | 63.14(6.53) | ||
| 5 | 146.88 | 348.51 | 3.77 | 0.069 5(0.005 5) | 0.079 8(0.006 4) | 0.008 7(0.000 3) | 922.22(195.37) | 78.00(6.01) | 55.90(1.78) | ||
| 6 | 94.40 | 172.80 | 2.76 | 0.240 8(0.036 7) | 0.292 2(0.034 0) | 0.010 0(0.000 7) | 3 125.01(245.07) | 260.33(26.74) | 63.85(4.29) | ||
| 7 | 140.27 | 215.30 | 2.34 | 0.179 8(0.048 1) | 0.196 7(0.066 2) | 0.007 8(0.000 3) | 2 650.31(458.34) | 182.37(56.21) | 50.23(2.09) | ||
| 8 | 96.24 | 170.61 | 1.83 | 0.010 8(0.015 2) | 0.012 2(0.015 9) | 0.008 4(0.000 3) | - | 12.33(15.91) | 53.91(1.93) | ||
| 9 | 293.68 | 538.35 | 5.80 | 0.059 9(0.010 4) | 0.068 9(0.011 9) | 0.008 2(0.000 3) | 611.13(381.44) | 67.69(11.33) | 52.87(2.08) | ||
| 10 | 121.63 | 318.14 | 5.06 | 0.206 5(0.071 8) | 0.250 4(0.077 3) | 0.009 4(0.000 4) | 2 878.7(596.43) | 226.92(62.83) | 60.06(2.43) | ||
| 11 | 146.05 | 368.76 | 3.64 | 0.148 1(0.060 6) | 0.140 4(0.049 9) | 0.007 9(0.000 2) | 2 324.39(761.88) | 133.44(44.44) | 50.92(1.55) | ||
| 12 | 119.76 | 263.15 | 2.83 | 0.080 8(0.006 3) | 0.097 0(0.009 0) | 0.008 4(0.000 3) | 1 216.67(155.09) | 93.96(8.37) | 54.09(2.05) | ||
| 13 | 79.83 | 163.51 | 1.70 | 0.246 7(0.041 0) | 0.242 9(0.035 5) | 0.008 3(0.000 3) | 3 164.82(266.67) | 220.76(28.99) | 53.01(2.12) | ||
| 14 | 113.20 | 331.29 | 3.34 | 0.095 5(0.012 7) | 0.103 4(0.011 1) | 0.008 8(0.000 5) | 1 536.73(251.85) | 99.89(10.23) | 56.37(3.35) | ||
| 15 | 133.43 | 282.62 | 3.01 | 0.100 5(0.016 6) | 0.106 5(0.015 0) | 0.008 5(0.000 4) | 1 633.02(311.11) | 102.80(13.81) | 54.35(2.27) | ||
表2 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)
| 编号 | 含量/10-6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Th | U | Pb | 207Pb/206Pb (1σ) | 207Pb/235U (1σ) | 206Pb/238U (1σ) | 207Pb/206Pb (1σ) | 207Pb/235U (1σ) | 206Pb/238U (1σ) | |||
| 1 | 75.40 | 153.40 | 1.91 | 0.194 8(0.030 5) | 0.207 8(0.029 0) | 0.008 7(0.000 5) | 2 783.65(259.26) | 191.70(24.37) | 56.16(3.37) | ||
| 2 | 68.81 | 171.28 | 1.98 | 0.187 4(0.049 7) | 0.184 5(0.039 0) | 0.008 1(0.000 3) | 2 720.38(451.70) | 171.89(33.43) | 52.30(1.92) | ||
| 3 | 69.74 | 135.25 | 1.76 | 0.293 1(0.064 7) | 0.327 9(0.071 2) | 0.008 6(0.000 4) | 3 434.27(349.00) | 287.94(54.50) | 55.33(2.25) | ||
| 4 | 76.72 | 249.94 | 3.35 | 0.235 8(0.071 6) | 0.344 1(0.124 7) | 0.009 8(0.001 0) | 3 091.67(504.76) | 300.31(94.44) | 63.14(6.53) | ||
| 5 | 146.88 | 348.51 | 3.77 | 0.069 5(0.005 5) | 0.079 8(0.006 4) | 0.008 7(0.000 3) | 922.22(195.37) | 78.00(6.01) | 55.90(1.78) | ||
| 6 | 94.40 | 172.80 | 2.76 | 0.240 8(0.036 7) | 0.292 2(0.034 0) | 0.010 0(0.000 7) | 3 125.01(245.07) | 260.33(26.74) | 63.85(4.29) | ||
| 7 | 140.27 | 215.30 | 2.34 | 0.179 8(0.048 1) | 0.196 7(0.066 2) | 0.007 8(0.000 3) | 2 650.31(458.34) | 182.37(56.21) | 50.23(2.09) | ||
| 8 | 96.24 | 170.61 | 1.83 | 0.010 8(0.015 2) | 0.012 2(0.015 9) | 0.008 4(0.000 3) | - | 12.33(15.91) | 53.91(1.93) | ||
| 9 | 293.68 | 538.35 | 5.80 | 0.059 9(0.010 4) | 0.068 9(0.011 9) | 0.008 2(0.000 3) | 611.13(381.44) | 67.69(11.33) | 52.87(2.08) | ||
| 10 | 121.63 | 318.14 | 5.06 | 0.206 5(0.071 8) | 0.250 4(0.077 3) | 0.009 4(0.000 4) | 2 878.7(596.43) | 226.92(62.83) | 60.06(2.43) | ||
| 11 | 146.05 | 368.76 | 3.64 | 0.148 1(0.060 6) | 0.140 4(0.049 9) | 0.007 9(0.000 2) | 2 324.39(761.88) | 133.44(44.44) | 50.92(1.55) | ||
| 12 | 119.76 | 263.15 | 2.83 | 0.080 8(0.006 3) | 0.097 0(0.009 0) | 0.008 4(0.000 3) | 1 216.67(155.09) | 93.96(8.37) | 54.09(2.05) | ||
| 13 | 79.83 | 163.51 | 1.70 | 0.246 7(0.041 0) | 0.242 9(0.035 5) | 0.008 3(0.000 3) | 3 164.82(266.67) | 220.76(28.99) | 53.01(2.12) | ||
| 14 | 113.20 | 331.29 | 3.34 | 0.095 5(0.012 7) | 0.103 4(0.011 1) | 0.008 8(0.000 5) | 1 536.73(251.85) | 99.89(10.23) | 56.37(3.35) | ||
| 15 | 133.43 | 282.62 | 3.01 | 0.100 5(0.016 6) | 0.106 5(0.015 0) | 0.008 5(0.000 4) | 1 633.02(311.11) | 102.80(13.81) | 54.35(2.27) | ||
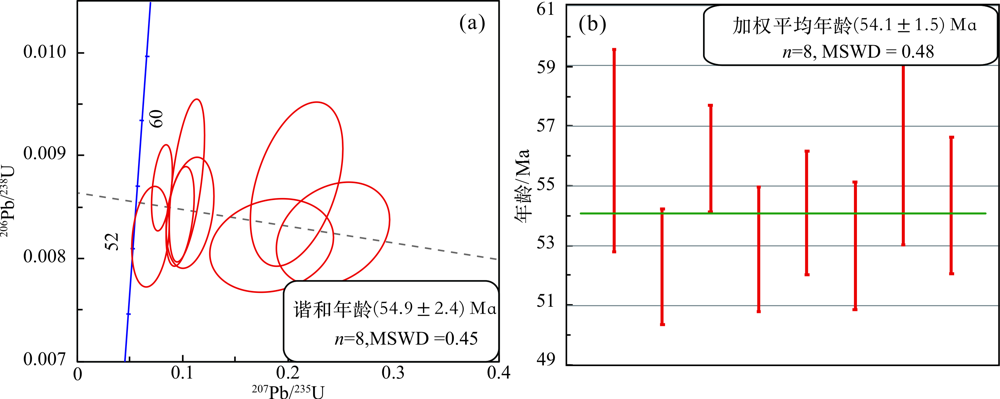
图7 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)锆石U-Pb谐和年龄(a)和加权平均年龄(b)
Fig.7 Zircon U-Pb concordia plot (a) and weighted-mean age plot(b) of the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)
| 点号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | F | Cl | Cr2O3 | P2O5 | Al/(Ca+ Na+K) | K2O+ Na2O+CaO | An | Ab | Or |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pl-1 | 60.13 | 0.020 | 24.47 | 0.168 | 0.019 | - | 5.926 | 8.322 | 0.264 | 0.092 | - | - | 0.007 | 1.26 | 14.512 | 27.82 | 70.70 | 1.47 |
| pl-2 | 59.39 | - | 25.75 | 0.203 | 0.027 | 0.008 | 7.112 | 7.598 | 0.189 | 0.050 | - | - | 0.011 | 1.34 | 14.899 | 33.72 | 65.20 | 1.06 |
| pl-3 | 59.86 | 0.025 | 24.82 | 0.336 | 0.034 | - | 6.706 | 7.961 | 0.253 | - | - | 0.005 | 0.022 | 1.27 | 14.920 | 31.31 | 67.27 | 1.40 |
| pl-4 | 60.12 | 0.048 | 24.82 | 0.149 | 0.034 | - | 6.491 | 8.185 | 0.277 | 0.078 | 0.001 | - | 0.019 | 1.26 | 14.953 | 30.00 | 68.46 | 1.52 |
| pl-5 | 60.03 | - | 24.49 | 0.133 | - | 0.024 | 6.349 | 7.803 | 0.270 | - | 0.006 | - | - | 1.29 | 14.422 | 30.53 | 67.91 | 1.54 |
| pl2-1 | 58.20 | - | 25.78 | 0.140 | - | - | 7.565 | 7.453 | 0.186 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.011 | 1.33 | 15.204 | 35.56 | 63.39 | 1.04 |
| pl2-2 | 58.65 | 0.048 | 25.21 | 0.155 | 0.050 | - | 7.047 | 7.563 | 0.224 | 0.050 | 0.003 | - | 0.022 | 1.32 | 14.834 | 33.55 | 65.17 | 1.26 |
| pl2-3 | 57.07 | 0.002 | 26.57 | 0.102 | 0.053 | 0.006 | 8.688 | 6.746 | 0.186 | - | - | - | - | 1.38 | 15.620 | 41.14 | 57.80 | 1.04 |
| pl2-4 | 58.74 | 0.041 | 25.95 | 0.193 | - | 0.006 | 7.778 | 7.369 | 0.172 | 0.100 | - | 0.037 | - | 1.33 | 15.319 | 36.48 | 62.55 | 0.96 |
| pl2-5 | 63.46 | - | 22.51 | 0.073 | - | - | 3.711 | 9.676 | 0.335 | - | - | - | 0.019 | 1.14 | 13.722 | 17.16 | 80.99 | 1.84 |
| pl3-1 | 56.98 | - | 26.76 | 0.235 | 0.011 | - | 8.552 | 6.855 | 0.178 | - | 0.006 | - | - | 1.39 | 15.585 | 40.39 | 58.59 | 1.00 |
| pl3-2 | 55.45 | 0.016 | 25.47 | 0.082 | 0.034 | 0.041 | 7.649 | 7.179 | 0.184 | 0.036 | 0.011 | - | 0.019 | 1.34 | 15.012 | 36.66 | 62.28 | 1.05 |
| pl3-3 | 55.74 | 0.005 | 26.26 | 0.133 | 0.023 | 0.243 | 7.638 | 6.516 | 0.729 | - | 0.007 | - | 0.015 | 1.42 | 14.883 | 37.63 | 58.09 | 4.27 |
| pl3-4 | 57.19 | 0.014 | 25.88 | 0.101 | 0.019 | 0.103 | 7.080 | 6.841 | 0.482 | - | 0.008 | - | - | 1.42 | 14.403 | 35.34 | 61.79 | 2.86 |
| pl3-5 | 64.91 | - | 22.01 | 0.086 | 0.030 | 0.061 | 1.655 | 9.476 | 1.787 | 0.035 | - | 0.057 | - | 1.15 | 12.918 | 7.90 | 81.92 | 10.16 |
表3 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)长石的主量元素(%)分析结果
Table 3 Representative EPMA major element compositions (%) of feldspars from the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)
| 点号 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | F | Cl | Cr2O3 | P2O5 | Al/(Ca+ Na+K) | K2O+ Na2O+CaO | An | Ab | Or |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pl-1 | 60.13 | 0.020 | 24.47 | 0.168 | 0.019 | - | 5.926 | 8.322 | 0.264 | 0.092 | - | - | 0.007 | 1.26 | 14.512 | 27.82 | 70.70 | 1.47 |
| pl-2 | 59.39 | - | 25.75 | 0.203 | 0.027 | 0.008 | 7.112 | 7.598 | 0.189 | 0.050 | - | - | 0.011 | 1.34 | 14.899 | 33.72 | 65.20 | 1.06 |
| pl-3 | 59.86 | 0.025 | 24.82 | 0.336 | 0.034 | - | 6.706 | 7.961 | 0.253 | - | - | 0.005 | 0.022 | 1.27 | 14.920 | 31.31 | 67.27 | 1.40 |
| pl-4 | 60.12 | 0.048 | 24.82 | 0.149 | 0.034 | - | 6.491 | 8.185 | 0.277 | 0.078 | 0.001 | - | 0.019 | 1.26 | 14.953 | 30.00 | 68.46 | 1.52 |
| pl-5 | 60.03 | - | 24.49 | 0.133 | - | 0.024 | 6.349 | 7.803 | 0.270 | - | 0.006 | - | - | 1.29 | 14.422 | 30.53 | 67.91 | 1.54 |
| pl2-1 | 58.20 | - | 25.78 | 0.140 | - | - | 7.565 | 7.453 | 0.186 | - | 0.002 | - | 0.011 | 1.33 | 15.204 | 35.56 | 63.39 | 1.04 |
| pl2-2 | 58.65 | 0.048 | 25.21 | 0.155 | 0.050 | - | 7.047 | 7.563 | 0.224 | 0.050 | 0.003 | - | 0.022 | 1.32 | 14.834 | 33.55 | 65.17 | 1.26 |
| pl2-3 | 57.07 | 0.002 | 26.57 | 0.102 | 0.053 | 0.006 | 8.688 | 6.746 | 0.186 | - | - | - | - | 1.38 | 15.620 | 41.14 | 57.80 | 1.04 |
| pl2-4 | 58.74 | 0.041 | 25.95 | 0.193 | - | 0.006 | 7.778 | 7.369 | 0.172 | 0.100 | - | 0.037 | - | 1.33 | 15.319 | 36.48 | 62.55 | 0.96 |
| pl2-5 | 63.46 | - | 22.51 | 0.073 | - | - | 3.711 | 9.676 | 0.335 | - | - | - | 0.019 | 1.14 | 13.722 | 17.16 | 80.99 | 1.84 |
| pl3-1 | 56.98 | - | 26.76 | 0.235 | 0.011 | - | 8.552 | 6.855 | 0.178 | - | 0.006 | - | - | 1.39 | 15.585 | 40.39 | 58.59 | 1.00 |
| pl3-2 | 55.45 | 0.016 | 25.47 | 0.082 | 0.034 | 0.041 | 7.649 | 7.179 | 0.184 | 0.036 | 0.011 | - | 0.019 | 1.34 | 15.012 | 36.66 | 62.28 | 1.05 |
| pl3-3 | 55.74 | 0.005 | 26.26 | 0.133 | 0.023 | 0.243 | 7.638 | 6.516 | 0.729 | - | 0.007 | - | 0.015 | 1.42 | 14.883 | 37.63 | 58.09 | 4.27 |
| pl3-4 | 57.19 | 0.014 | 25.88 | 0.101 | 0.019 | 0.103 | 7.080 | 6.841 | 0.482 | - | 0.008 | - | - | 1.42 | 14.403 | 35.34 | 61.79 | 2.86 |
| pl3-5 | 64.91 | - | 22.01 | 0.086 | 0.030 | 0.061 | 1.655 | 9.476 | 1.787 | 0.035 | - | 0.057 | - | 1.15 | 12.918 | 7.90 | 81.92 | 10.16 |
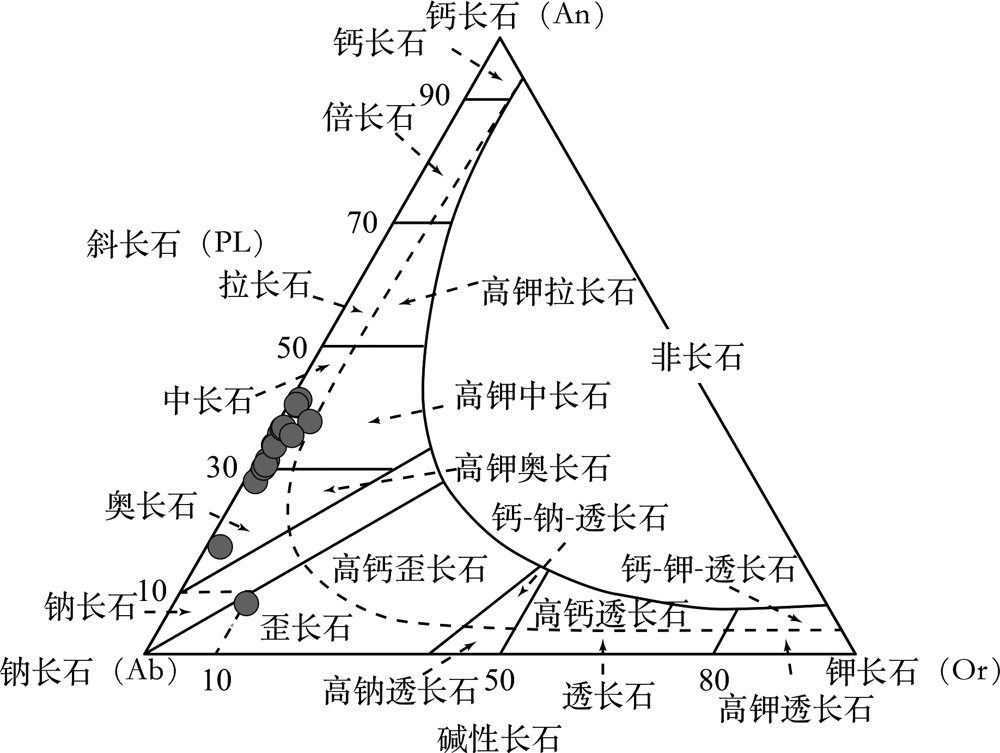
图8 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)长石分类(单位为%,据Deer等[43]修改)
Fig.8 Classification of feldspars from the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)(modified after Deer et al.[43])
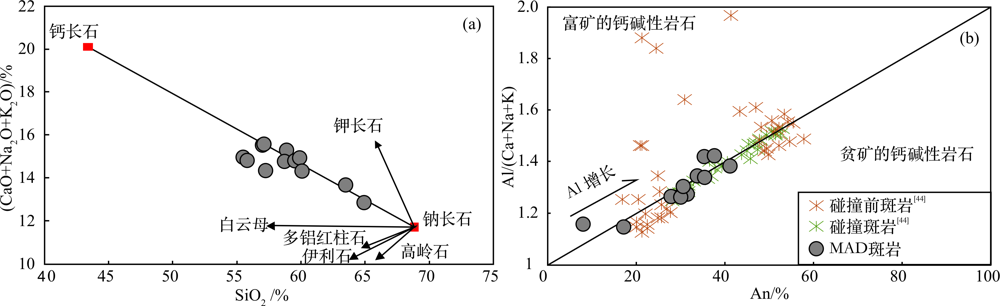
图9 长石SiO2-(CaO+Na2O+K2O)图(a)和An-Al/(Ca+Na+K) 图(b)(据Zarasvandi等[44]修改)
Fig.9 SiO2 vs.(CaO+Na2O+K2O) (a), and An vs. Al / (Ca+Na+K) (b) diagrams of feldspars from the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483) (modified after Zarasvandi et al.[44])
| 编号 | SiO2 | Na2O | K2O | Cr2O3 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | MnO | P2O5 | FeO | TiO2 | NiO | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98.284 | 0.014 | 0.014 | - | - | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.036 | - | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.027 | 98.398 |
| 2 | 99.230 | 0.026 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.021 | - | 0.008 | - | - | - | - | 0.035 | 99.342 |
| 3 | 98.447 | 0.029 | 0.018 | 0.023 | 0.009 | - | 0.010 | - | - | 0.046 | - | - | 98.582 |
| 4 | 98.328 | 0.066 | 0.016 | 0.551 | 0.036 | 0.018 | 0.025 | 0.031 | - | - | - | - | 99.071 |
| 5 | 99.503 | 0.021 | 0.009 | - | 0.030 | - | 0.023 | - | - | - | 0.005 | 0.069 | 99.660 |
| 6 | 99.292 | 0.008 | - | 0.005 | 0.02 | - | 0.013 | - | 0.019 | - | 0.007 | - | 99.364 |
| 7 | 98.809 | - | - | 0.005 | 0.021 | - | - | - | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.020 | 0.017 | 98.913 |
| 8 | 99.059 | 0.015 | 0.007 | - | 0.054 | 0.011 | - | - | - | - | 0.060 | 0.007 | 99.213 |
| 9 | 98.805 | 0.005 | - | - | - | - | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 98.899 |
| 10 | 98.965 | 0.003 | - | 0.041 | 0.071 | - | 0.010 | - | 0.033 | - | 0.061 | - | 99.184 |
表4 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)石英的主量(%)元素分析结果
Table 4 Representative EPMA major element compositions (%) of quartz from the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)
| 编号 | SiO2 | Na2O | K2O | Cr2O3 | Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | MnO | P2O5 | FeO | TiO2 | NiO | 总量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98.284 | 0.014 | 0.014 | - | - | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.036 | - | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.027 | 98.398 |
| 2 | 99.230 | 0.026 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.021 | - | 0.008 | - | - | - | - | 0.035 | 99.342 |
| 3 | 98.447 | 0.029 | 0.018 | 0.023 | 0.009 | - | 0.010 | - | - | 0.046 | - | - | 98.582 |
| 4 | 98.328 | 0.066 | 0.016 | 0.551 | 0.036 | 0.018 | 0.025 | 0.031 | - | - | - | - | 99.071 |
| 5 | 99.503 | 0.021 | 0.009 | - | 0.030 | - | 0.023 | - | - | - | 0.005 | 0.069 | 99.660 |
| 6 | 99.292 | 0.008 | - | 0.005 | 0.02 | - | 0.013 | - | 0.019 | - | 0.007 | - | 99.364 |
| 7 | 98.809 | - | - | 0.005 | 0.021 | - | - | - | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.020 | 0.017 | 98.913 |
| 8 | 99.059 | 0.015 | 0.007 | - | 0.054 | 0.011 | - | - | - | - | 0.060 | 0.007 | 99.213 |
| 9 | 98.805 | 0.005 | - | - | - | - | 0.017 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 98.899 |
| 10 | 98.965 | 0.003 | - | 0.041 | 0.071 | - | 0.010 | - | 0.033 | - | 0.061 | - | 99.184 |
| 编号 | ZrO2 | Ce | Lu | Hf | Ce4+/Ce3+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94.81 | 8.11 | 46.06 | 9 356.71 | 217.45 |
| 2 | 91.12 | 7.79 | 39.15 | 8 914.20 | 197.24 |
| 3 | 91.85 | 8.05 | 43.98 | 8 085.89 | 152.12 |
| 4 | 89.97 | 15.67 | 57.84 | 9 701.81 | 543.19 |
| 5 | 91.74 | 16.01 | 36.09 | 9 968.56 | 433.31 |
| 6 | 93.38 | 10.37 | 47.34 | 9 335.95 | 471.77 |
| 7 | 90.77 | 11.96 | 41.65 | 8 920.27 | 247.08 |
| 8 | 90.30 | 14.09 | 33.20 | 8 615.26 | 496.12 |
| 9 | 94.94 | 31.78 | 103.09 | 10 190.34 | 252.40 |
| 10 | 91.64 | 14.42 | 60.42 | 9 956.50 | 205.69 |
| 11 | 90.89 | 15.00 | 49.37 | 9 846.30 | 481.46 |
| 12 | 91.52 | 12.52 | 44.18 | 10 053.70 | 324.96 |
| 13 | 89.70 | 10.29 | 37.67 | 9 252.59 | 259.83 |
| 14 | 88.98 | 13.53 | 71.74 | 9 965.00 | 469.19 |
| 15 | 94.64 | 15.40 | 58.59 | 9 799.83 | 204.75 |
表5 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)锆石主量(%)和微量(10-6)元素分析结果
Table 5 Representative zircon major (%) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)
| 编号 | ZrO2 | Ce | Lu | Hf | Ce4+/Ce3+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94.81 | 8.11 | 46.06 | 9 356.71 | 217.45 |
| 2 | 91.12 | 7.79 | 39.15 | 8 914.20 | 197.24 |
| 3 | 91.85 | 8.05 | 43.98 | 8 085.89 | 152.12 |
| 4 | 89.97 | 15.67 | 57.84 | 9 701.81 | 543.19 |
| 5 | 91.74 | 16.01 | 36.09 | 9 968.56 | 433.31 |
| 6 | 93.38 | 10.37 | 47.34 | 9 335.95 | 471.77 |
| 7 | 90.77 | 11.96 | 41.65 | 8 920.27 | 247.08 |
| 8 | 90.30 | 14.09 | 33.20 | 8 615.26 | 496.12 |
| 9 | 94.94 | 31.78 | 103.09 | 10 190.34 | 252.40 |
| 10 | 91.64 | 14.42 | 60.42 | 9 956.50 | 205.69 |
| 11 | 90.89 | 15.00 | 49.37 | 9 846.30 | 481.46 |
| 12 | 91.52 | 12.52 | 44.18 | 10 053.70 | 324.96 |
| 13 | 89.70 | 10.29 | 37.67 | 9 252.59 | 259.83 |
| 14 | 88.98 | 13.53 | 71.74 | 9 965.00 | 469.19 |
| 15 | 94.64 | 15.40 | 58.59 | 9 799.83 | 204.75 |
| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63.44 | 0.37 | 14.39 | 1.73 | 0.02 | 2.18 | 3.43 | 3.81 | 4.85 |
| P2O5 | LOI | SUM | Na+K | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr |
| 0.07 | 4.49 | 98.78 | 8.66 | 11.09 | 0.85 | 7.95 | 84.74 | 15.88 |
| Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr |
| 4.91 | 9.97 | 1 957.96 | 61.28 | 14.64 | 111.64 | 702.24 | 5.81 | 106.83 |
| Nb | Sn | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm |
| 8.06 | 0.85 | 1.78 | 1 177.61 | 25.54 | 40.11 | 3.88 | 12.71 | 1.99 |
| Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| 0.66 | 1.37 | 0.18 | 1.05 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 0.09 |
| Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Sr/Y | |||
| 2.67 | 0.46 | 32.99 | 9.78 | 1.83 | 120.78 |
表6 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)全岩主量(%)和微量(10-6)元素分析结果
Table 6 Whole-rock major (%) and trace element (10-6) compositions of the porphyry sample(MAD-13-483)
| SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63.44 | 0.37 | 14.39 | 1.73 | 0.02 | 2.18 | 3.43 | 3.81 | 4.85 |
| P2O5 | LOI | SUM | Na+K | Li | Be | Sc | V | Cr |
| 0.07 | 4.49 | 98.78 | 8.66 | 11.09 | 0.85 | 7.95 | 84.74 | 15.88 |
| Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Zr |
| 4.91 | 9.97 | 1 957.96 | 61.28 | 14.64 | 111.64 | 702.24 | 5.81 | 106.83 |
| Nb | Sn | Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm |
| 8.06 | 0.85 | 1.78 | 1 177.61 | 25.54 | 40.11 | 3.88 | 12.71 | 1.99 |
| Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
| 0.66 | 1.37 | 0.18 | 1.05 | 0.19 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.58 | 0.09 |
| Hf | Ta | Pb | Th | U | Sr/Y | |||
| 2.67 | 0.46 | 32.99 | 9.78 | 1.83 | 120.78 |
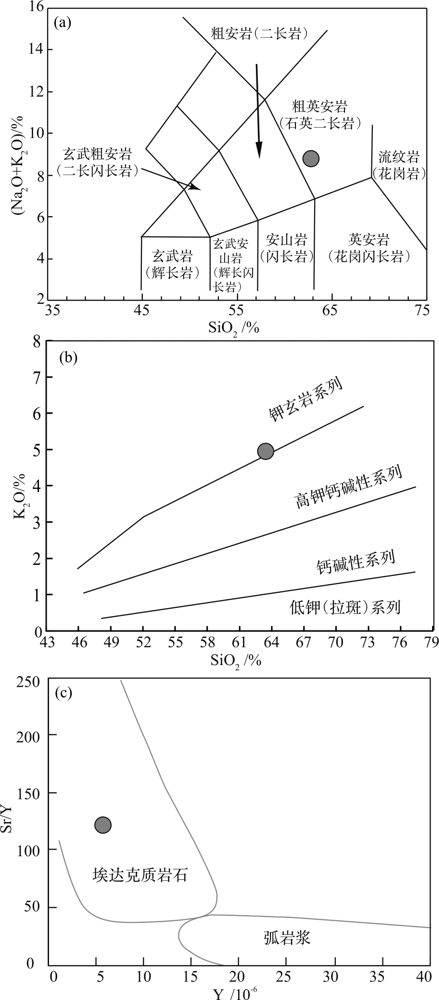
图10 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)TAS分类图解(a)、SiO2-K2O关系图(b)和Y-Sr/Y关系图(c)((a)据Middlemost[46]修改,(b)据Peccerillo和Taylor[47]修改,(c)据Defant等[48]修改)
Fig.10 TAS (a), SiO2 vs. K2O (b), and Y vs. Sr/Y(c)classification diagrams of the porphyry sample (MAO-13-483)((a)modified after Middle-most[46], (b) modified after Peccerillo and Taylor [47],(c) modified after Defant et al.[48])
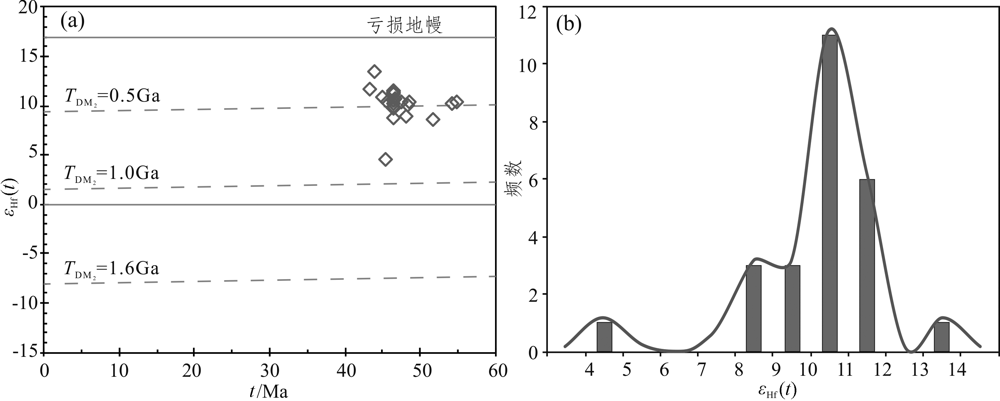
图11 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)锆石t-εHf(t)图(a)和εHf(t)频率图(b)
Fig.11 Zircon U-Pb age vs. εHf(t) isotope data of the Masjed Daghi porphyry(MAD-13-483)(a) and εHf(t) histogram (b)
| 编号 | 年龄/Ma | 176Hf/177Hf(2σ) | 176Lu/177Hf(2σ) | εHf (t) | TDM /Ma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56.16 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.000 82(0.000 02) | 9.95 | 327.79 | 492.38 |
| 2 | 52.30 | 0.283 05(0.000 04) | 0.000 86(0.000 01) | 10.90 | 286.45 | 427.92 |
| 3 | 55.33 | 0.283 03(0.000 03) | 0.000 67(0.000 04) | 10.39 | 308.30 | 463.22 |
| 4 | 63.14 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.001 15(0.000 02) | 10.16 | 327.80 | 484.47 |
| 5 | 55.90 | 0.282 99(0.000 02) | 0.000 98(0.000 01) | 8.87 | 372.20 | 561.78 |
| 6 | 63.85 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.000 86(0.000 01) | 10.31 | 320.33 | 475.28 |
| 7 | 50.23 | 0.283 07(0.000 02) | 0.000 76(0.000 01) | 11.72 | 251.33 | 373.71 |
| 8 | 53.91 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.000 79(0.000 03) | 9.80 | 331.75 | 500.52 |
| 9 | 52.87 | 0.282 87(0.000 07) | 0.001 53(0.000 02) | 4.47 | 553.33 | 841.47 |
| 10 | 60.06 | 0.282 98(0.000 07) | 0.000 84(0.000 01) | 8.52 | 388.31 | 586.92 |
| 11 | 50.92 | 0.283 12(0.000 02) | 0.000 94(0.000 01) | 13.50 | 181.36 | 259.74 |
| 12 | 54.09 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.001 06(0.000 02) | 10.44 | 308.08 | 459.43 |
| 13 | 53.01 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.000 94(0.000 01) | 10.42 | 307.13 | 459.82 |
| 14 | 56.37 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.000 90(0.000 01) | 10.41 | 310.16 | 463.05 |
| 15 | 54.35 | 0.283 04(0.000 03) | 0.000 83(0.000 01) | 10.61 | 299.63 | 448.19 |
| 16 | 54.00 | 0.283 05(0.000 03) | 0.000 62(0.000 04) | 11.13 | 277.45 | 414.72 |
| 17 | 54.00 | 0.282 99(0.000 03) | 0.000 90(0.000 03) | 8.70 | 376.72 | 571.12 |
| 18 | 54.00 | 0.283 04(0.000 03) | 0.001 23(0.000 02) | 10.49 | 307.20 | 456.16 |
| 19 | 54.00 | 0.283 04(0.000 03) | 0.000 56(0.000 01) | 10.53 | 300.85 | 453.21 |
| 20 | 54.00 | 0.283 06(0.000 03) | 0.000 65(0.000 01) | 11.29 | 271.31 | 404.56 |
| 21 | 54.00 | 0.283 07(0.000 03) | 0.000 84(0.000 01) | 11.56 | 261.58 | 387.17 |
| 22 | 54.00 | 0.283 06(0.000 02) | 0.000 91(0.000 02) | 11.43 | 266.99 | 395.22 |
| 23 | 54.00 | 0.283 06(0.000 02) | 0.000 98(0.000 01) | 11.29 | 272.91 | 404.11 |
| 24 | 54.00 | 0.283 01(0.000 02) | 0.001 38(0.000 01) | 9.69 | 340.61 | 507.45 |
| 25 | 54.00 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.001 07(0.000 01) | 10.21 | 317.06 | 473.68 |
表7 马斯杰德达吉斑岩(MAD-13-483)锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 7 Zircon Lu-Hf isotope data of the Masjed Daghi porphyry sample (MAD-13-483)
| 编号 | 年龄/Ma | 176Hf/177Hf(2σ) | 176Lu/177Hf(2σ) | εHf (t) | TDM /Ma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56.16 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.000 82(0.000 02) | 9.95 | 327.79 | 492.38 |
| 2 | 52.30 | 0.283 05(0.000 04) | 0.000 86(0.000 01) | 10.90 | 286.45 | 427.92 |
| 3 | 55.33 | 0.283 03(0.000 03) | 0.000 67(0.000 04) | 10.39 | 308.30 | 463.22 |
| 4 | 63.14 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.001 15(0.000 02) | 10.16 | 327.80 | 484.47 |
| 5 | 55.90 | 0.282 99(0.000 02) | 0.000 98(0.000 01) | 8.87 | 372.20 | 561.78 |
| 6 | 63.85 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.000 86(0.000 01) | 10.31 | 320.33 | 475.28 |
| 7 | 50.23 | 0.283 07(0.000 02) | 0.000 76(0.000 01) | 11.72 | 251.33 | 373.71 |
| 8 | 53.91 | 0.283 02(0.000 02) | 0.000 79(0.000 03) | 9.80 | 331.75 | 500.52 |
| 9 | 52.87 | 0.282 87(0.000 07) | 0.001 53(0.000 02) | 4.47 | 553.33 | 841.47 |
| 10 | 60.06 | 0.282 98(0.000 07) | 0.000 84(0.000 01) | 8.52 | 388.31 | 586.92 |
| 11 | 50.92 | 0.283 12(0.000 02) | 0.000 94(0.000 01) | 13.50 | 181.36 | 259.74 |
| 12 | 54.09 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.001 06(0.000 02) | 10.44 | 308.08 | 459.43 |
| 13 | 53.01 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.000 94(0.000 01) | 10.42 | 307.13 | 459.82 |
| 14 | 56.37 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.000 90(0.000 01) | 10.41 | 310.16 | 463.05 |
| 15 | 54.35 | 0.283 04(0.000 03) | 0.000 83(0.000 01) | 10.61 | 299.63 | 448.19 |
| 16 | 54.00 | 0.283 05(0.000 03) | 0.000 62(0.000 04) | 11.13 | 277.45 | 414.72 |
| 17 | 54.00 | 0.282 99(0.000 03) | 0.000 90(0.000 03) | 8.70 | 376.72 | 571.12 |
| 18 | 54.00 | 0.283 04(0.000 03) | 0.001 23(0.000 02) | 10.49 | 307.20 | 456.16 |
| 19 | 54.00 | 0.283 04(0.000 03) | 0.000 56(0.000 01) | 10.53 | 300.85 | 453.21 |
| 20 | 54.00 | 0.283 06(0.000 03) | 0.000 65(0.000 01) | 11.29 | 271.31 | 404.56 |
| 21 | 54.00 | 0.283 07(0.000 03) | 0.000 84(0.000 01) | 11.56 | 261.58 | 387.17 |
| 22 | 54.00 | 0.283 06(0.000 02) | 0.000 91(0.000 02) | 11.43 | 266.99 | 395.22 |
| 23 | 54.00 | 0.283 06(0.000 02) | 0.000 98(0.000 01) | 11.29 | 272.91 | 404.11 |
| 24 | 54.00 | 0.283 01(0.000 02) | 0.001 38(0.000 01) | 9.69 | 340.61 | 507.45 |
| 25 | 54.00 | 0.283 03(0.000 02) | 0.001 07(0.000 01) | 10.21 | 317.06 | 473.68 |
| [1] |
SILLITOE R H. Porphyry copper systems[J]. Economic Geology, 2010,105:3-41.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
RICHARDS J P. Postsubduction porphyry Cu-Au and epithermal Au deposits: Products of remelting of subduction-modified lithosphere[J]. Geology, 2009,37(3):247-250.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 侯增谦, 郑远川, 杨志明, 等. 大陆碰撞成矿作用:Ⅰ.冈底斯新生代斑岩成矿系统[J]. 矿床地质, 2012,31(4):647-670. |
| [4] | 汪啸风, METCSLFE I, 简平, 等. 金沙江缝合带构造地层划分及时代厘定[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1999,29(4):289-297. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Z Y, XIAO W J, JI W Q, et al. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope for granitoids, NW Sanandaj-Sirjan zone, Iran: Implications for Mesozoic-Cenozoic episodic magmatism during Neo-Tethyan lithospheric subduction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018,62:227-245.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SHAFIEI B, HASCHKE M, SHAHABPOUR J. Recycling of orogenic arc crust triggers porphyry Cu mineralization in Kerman Cenozoic arc rocks, southeastern Iran[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2009,44:265-283.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ASADI S, MOORE F, ZARASVANDI A. Discriminating productive and barren porphyry copper deposits in the southeastern part of the central Iranian volcano-plutonic belt, Kerman region, Iran: A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014,138:25-46.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
IMAMALIPOUR A, MOUSAVI R. Vertical geochemical zonation in the Masjed Daghi porphyry copper-gold deposit, northwestern Iran: implications for exploration of blind mineral deposits[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2017,18:120-131.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ALLEN M B, ARMSTRONG H A. Arabia-Eurasia collision and the forcing of mid-Cenozoic global cooling[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2008,265(1):52-58.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
AGARD P, OMRANI J, JOLIVET L, et al. Zagros Orogeny: A subduction-dominated process[J]. Geological Magazine, 2011,148:692-725.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
AGHAZADEH M, CASTRO A, BADRZADEH Z, et al. Post-collisional polycyclic plutonism from the Zagros hinterland: the Shaivar Dagh plutonic complex, Alborz belt, Iran[J]. Geological Magazine, 2011,148(5/6):980-1008.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
AGARD P, OMRANI J, JOLIVET L, et al. Convergence history across Zagros (Iran): Constraints from collisional and earlier deformation[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2005,94:401-419.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
GOLONKA J. Plate tectonic evolution of the southern margin of Eurasia in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004,381(1/4):235-273.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
RICHARDA J P, SPELL T, RAMEH E, et al. High Sr/Y Magmas Reflect Arc Maturity, High Magmatic Water Content, and Porphyry Cu±Mo±Au Potential: Examples from the Tethyan Arcs of Central and Eastern Iran and Western Pakistan[J]. Economic Geology, 2012,107(2):295-332.
DOI URL |
| [15] | KIRKHAM R V, DUNNE K P. World Distribution of Porphyry, Porphyry-associated Skarn, and bulk-tonnage epithermal deposits and occurrences[R]. Wotawa:The Geological Survey of Canada, 2000: 1-26. |
| [16] | RAZIQUE A, LO GRASSO G, LIVESEY T. Porphyry copper-gold deposits at Reko Diq complex, Chagai Hills Pakistan[M]//9th Biennial Meeting of the Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits. Dublin: SGA, 2007: 125-128. |
| [17] |
JAHANGIRI A. Post-collisional Miocene adakitic volcanism in NW Iran: Geochemical and geodynamic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth sciences, 2007,30(3/4):433-447.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WATERMAN G C, HAMILTON R L. The Sar Cheshmeh porphyry copper deposit[J]. Economic Geology, 1975,70(3):568-576.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
COOKE D R, HOLLINGS P, WALSHE J L. Giant porphyry deposits: characteristics, distribution, and tectonic controls[J]. Economic Geology, 2005,100(5):801-818.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SINGER D A, BERGER V I, MENZIE W D, et al. Porphyry copper deposit density[J]. Economic Geology, 2005,100:491-514.
DOI URL |
| [21] | ZARASVANDI A, LIAGHAT S, ZENTILLI M. Geology of the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad porphyry copper deposits, central Iran[J]. International Geology Review, 2005(6):620-646. |
| [22] |
ZARASVANDI A, LIAGHAT S, ZENTILLI M, et al. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of alteration and petrogenesis of porphyry copper-related granitoids in the Darreh-Zerreshk and Ali-Abad area, central Iran[J]. Exploration and Mining Geology, 2007,16(1/2):11-24.
DOI URL |
| [23] | ZHANG H R, HOU Z Q, SONG Y C, et al. The temporal and spatial distribution of porphyry copper deposits in the eastern Tethyan metallogenic domain: A review[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009,83(12):1818-1837. |
| [24] | SAMANI B. Distribution, setting and metallogenesis of copper deposits in Iran[M]//SAMANI B. Porphyry and Hydrothermal Copper and Gold Deposits: A Global Perspective. Adelaide: PCG Publishing, 1998. |
| [25] | MUTSCHLER F E, LUDINGTON S, BOOKSTROM A A. Giant porphyry-related metal camps of the world-a database[R]. Tulsa: U.S.Geological Survey, 1999: 99-566. |
| [26] |
AGHAZADEH M, HOU Z Q, BADRZADEH Z, et al. Temporal-spatial distribution and tectonic setting of porphyry copper deposits in Iran: Constraints from zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,70:385-406.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
TIEPOLO M, TRIBUZIO R. Petrology and U-Pb zircon geochronology of amphibole-rich cumulates with sanukitic affinity fromHusky Ridge (Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica): Insights into the role of amphibole in the petrogenesis of subduction-related magmas[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2008,49:937-970.
DOI URL |
| [28] | MCINNES B I A, EVANS N J, BELOUSOVA E, et al. Timing of mineralization and exhumation processes at the Sar Cheshmeh and Meiduk porphyry Cu deposits, Kerman belt, Iran[M]//CSIRO.7th Biennial SGA Meeting. Athens: Millpress Science, 2003: 1197-1200. |
| [29] | SHSHSBPOUR J, KRAMERS J D. Lead isotope data from the Sar-Cheshmeh porphyry copper deposit, Iran[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1987,22(4):278-281. |
| [30] | HASSANZADEH J. Metallogenic and tectonomagmatic events in the SE sector of the Cenozoic active continental margin of central Iran (Shahr e Babak area, Kerman Province)[D]. Los Angeles: University of California, 1993: 204. |
| [31] |
TAGHIPOUR N, AFTABI A, MATHUR R. Geology and Re-Os geochronology of mineralization of the Miduk porphyry copper deposit, Iran[J]. Resource Geology, 2008,58(2):143-160.
DOI URL |
| [32] | GHORBANI M. Economic Geology of Iran, Mineral Deposits and Natural Resources of Iran[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2013. |
| [33] | HASSANPOUR Sh. Metallogeny and mineralization of copper and gold in Arasbaran zone (Eastern Azerbaijan)[D]. Shahid: Shahid Beheshti University, Tehran, 2010. |
| [34] |
JAMALI H, MEHRABI B. Relationships between arc maturity and Cu-Mo-Au porphyry and related epithermal mineralization at the Cenozoic Arasbaran magmatic belt[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015,65:487-501.
DOI URL |
| [35] | YADOLLAHI R, KANANIAN A, MAANIJOU M, et al. Genesis of adakitic magmatism in Masjed Daghi region in Julfa, eastern Azarbaijan[J]. Iranian Journal of Crystallography and Mineralogy, 2011,19:297-310. |
| [36] | ROBERT M, JOHANNES M, MARIA O, et al. Major Cu, Au and Mo deposits of the Lesser Caucasus: Products of diverse geodynamic settings[M]//9th Swiss Geoscience Meeting, Mineralogy-Petrology-Geochemistry. Zurich: Swiss Academy of Science, 2011. |
| [37] |
AKBARPOUR A, GHOLAMI N, AZIZI H, et al. Cluster and R-mode factor analyses on soil geochemical data of Masjed-Daghi exploration area, northwestern Iran[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2012,6(9):3397-3408.
DOI URL |
| [38] | FARJANDI F, FAIZIEV A, MOKHTAR F, et al. The application of biogeochemistry for gold exploration in the Masjed-Daghi, Julfa, NW Iran[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2013,7(5):1435-1446. |
| [39] |
ATALOU S, NAZAFATI N, LOYFI M, et al. Fluid inclusion investigations of the Masjed Daghi copper-gold porphyry-epithermal mineralization, east Azerbaijan province, NW Iran[J]. Open Journal of Geology, 2017,7(8):1110-1127.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 彭文世, 刘高魁. 矿物红外光谱图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1982. |
| [41] | 张彦龙, 李兴远. 黄陵花岗岩体长石的XRD、红外光谱特征及其意义[J]. 中山大学研究生学刊(自然科学: 医学版), 2015,36(1):46-56. |
| [42] | 罗军燕, 李胜荣, 杨苏明, 等. 石英傅立叶变换漫反射红外光谱在成矿作用研究中的应用——以山西繁峙义兴寨金矿床为例[J]. 矿物岩石, 2009,29(1):27-34. |
| [43] | DEER W A, HOWIE R A, ZUSSMAN J. An Introduction to the Rock-forming Minerals[M]. London: The Mineralogical Society, 2013: 248-251. |
| [44] |
ZARASVANDI A, HEIDARI M, RAITH J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of collisional and pre-collisional porphyry copper systems in Kerman Cenozoic Magmatic Arc, Iran: Using plagioclase, biotite and amphibole chemistry[J]. Lithos, 2019,326/327:279-297.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHOU Y, XU B, HOU Z Q, et al. Petrogenesis of Cenozoic high-Sr/Y shoshonites and associated mafic microgranular enclaves in an intracontinental setting: Implications for porphyry Cu-Au mineralization in western Yunnan, China[J]. Lithos, 2019,324/325:39-54.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
MIDDLEMOST E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994,37:215-224.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
PECCERILLO A, TAYLOR S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976,58:63-81.
DOI URL |
| [48] | DEFANT M J, XU J F, KEPEZHINSKAS P, et al. Adakites: Some variations on a theme[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2002,18(2):129-142. |
| [49] |
BISSIG T, CLARK A H, LEE J K W , et al. Petrogenetic and metallogenetic responses to Miocene slab flattening: new constraints from the El Indio-Pascua Au-Ag-Cu belt, Chile/Argentina[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003,38(7):844-862.
DOI URL |
| [50] | KAY S M, MPODOZIS C, COIRA B. Neogene magmatism, tectonism, and mineral deposits of the Central Andes (22° to 33° S latitude)[M]//SKINNER B J. Geology and Ore Deposits of the Central Andes. Littleton: Society of Economic Geologists, 1999: 27-59. |
| [51] |
PERELLO J, CARLOTTO V, ZARATE A, et al. Porphyry-style alteration and mineralization of the Middle Eocene to Early Oligocene Andahuaylas-Yauri Belt, Cuzco Region, Peru[J]. Economic Geology, 2003,98(8):1575-1605.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
RICHARDS J P, BOYCE A J, PRINGLE M S. Geologic evolution of the Escondida area, northern Chile: a model for spatial and temporal localization of porphyry cu mineralization[J]. Economic Geology, 2001,96(2):271-306.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
SKEWES M A, STERN C R. Genesis of the giant Late Miocene to Pliocene copper deposits of central Chile in the context of Andean magmatic and tectonic evolution[J]. International Geology Review, 1995,37:893-909.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
KAY R W, KAY M S. Delamination and delamination magmatism[J]. Tectonophysics, 1993,219(1/3):177-189.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
HOU Z Q, ZENG P S, GAO Y F, et al. Himalayan Cu-Mo-Au mineralization in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone: constraints from Re-Os dating of molybdenite[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2006,41:33-45.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
MOUTHEREAU F, LACOMBE O, VERGE S. Building the Zagros collisional orogen: Timing, strain distribution and the dynamics of Arabia/Eurasia plate convergence[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012,532/535:27-60.
DOI URL |
| [57] | ZHANG H R, HOU Z Q, YANG Z M. Metallogenesis and geodynamics of Tethyan metallogenic domain: A review[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2010,29(1):113-133. |
| [58] |
SENGOR A M C, OZEREN M S, KESKIN M, et al. Eastern Turkish high plateau as a small Turkic-type orogen: Implications for post-collisional crust-forming processes in Turkic-type orogens[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2008,90:1-48.
DOI URL |
| [59] | THIEBLEMONT D, STEIN G, LESCUYER J L. Gisements épithermaux et porphyriques: la connexion adakite Epithermal and porphyry deposits: the adakite connection[J]. Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1997,325(2):103-109. |
| [60] | SAJONA F G, MAURY R C. Association of adakites with gold and copper mineralization in the Philippines[J]. Earth and Planetray Sciences, 1998,326(1):27-34. |
| [61] |
OYARZUN R, ALVARO MARQUE Z, LILLO J, et al. Giant versus small porphyry copper deposits of Cenozoic age in northern Chile: adakitic versus normal calc-alkaline magmatism[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2001,36(8):794-798.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
MUNGALL J E. Roasting the mantle: Slab melting and the genesis of major Au and Au-rich Cu deposits[J]. Geology, 2002,30(10):915.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
SUN W, ZHANG H, LING M X, et al. The genetic association of adakites and Cu-Au ore deposits[J]. International Geology Review, 2010,53(5/6):691-703.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
CASTILLO P R, JANNEY P E, SOLIDUM R U. Petrology and geochemistry of Camiguin Island, southern Philippines: insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1999,134(1):33-51.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
MACPHERSON C G, DREHER S T, THIRLWALL M F. Adakites without slab melting: High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006,243(3/4):581-593.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
CHIARADIA M. Adakite-like magmas from fractional crystallization and melting-assimilation of mafic lower crust (Eocene Macuchi arc, Western Cordillera, Ecuador)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009,265(3/4):468-487.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
CHIARADIA M, OTHMAR M, BEATE B, et al. Adakite-like volcanism of Ecuador: lower crust magmatic evolution and recycling[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2009,158(5):563-588.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
GRIFFIN W L, PEARSON N J, BELOUSOVA E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICP-MS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000,64:133-147.
DOI URL |
| [69] | 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007,23(2):185-220. |
| [70] |
TATSUMI Y, HAMILTON D L, NESBITT R W. Chemical characteristics of fluid phase released from a subducted lithosphere and origin of arc magmas: Evidence from high-pressure experiments and natural rocks[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 1986,29(1/4):293-309.
DOI URL |
| [71] | DAVIDSON J P. Deciphering mantle and crustal signatures in subduction zone magmatism[J]. Geophysical Monograph, 1996,96:251-262. |
| [72] |
DE HOOG J C M, MASON P R D, VAN BERGEN M J. Sulfur and chalcophile elements in subduction zones: Constraints from a laser ablation ICP-MS study of melt inclusions from Galunggung Volcano, Indonesia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001,65:3147-3164.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
PEACOCK S M. Large-scale hydration of the lithosphere above subducting slabs[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993,108(1/4):49-59.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
ARCULUS R J. Aspects of magma genesis in arcs[J]. Lithos, 1994,33(1/3):189-208.
DOI URL |
| [75] | RINGWOOD A E. Petrogenesis in Island Arc Systems[M]//Island Arcs, Deep Sea Trenches and Back-Arc Basins. Washington: Advancing Earth and Space Science, 1977: 311-324. |
| [76] |
PERFIT M R, GUST D A, BENCE A E, et al. Chemical characteristics of island-arc basalts: Implications for mantle sources[J]. Chemical Geology, 1980,30:227-256.
DOI URL |
| [77] | PEARCE J A. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins[J]. Destructive Plate Margin Magmas, 1983: 230-249. |
| [78] |
PLANK T, LANGMUIR C H. An evaluation of the global variations in the major element chemistry of arc basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988,90(4):349-370.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
STOLPER E, NEWMAN S. The role of water in the petrogenesis of Mariana trough magmas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994,121:293-325.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
RICHARDS J P. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu (Mo-Au) deposit formation[J]. Economic Geology, 2003,98(8):1515-1533.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
VRY V H, WILKINSON J J, SEGUE J, et al. Multistage intrusion, brecciation, and veining at El Teniente, Chile: evolution of a nested porphyry system[J]. Economic Geology, 2010,105(1):119-153.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
WILLIAMSON B J, HERRINGTON R J, MORRIS A. Porphyry copper enrichment linked to excess aluminum in plagioclase[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2016,9:237-241.
DOI URL |
| [83] | RICHSRDS J P, SHOLEH A. The Tethyan tectonic history and Cu-Au metallogeny of Iran[J]. Society of Economic Geologists, Special Publication, 2016,19:193-212. |
| [84] | 侯增谦, 潘小菲, 杨志明, 等. 初论大陆环境斑岩铜矿[J]. 现代地质, 2007,21(2):332-351. |
| [85] | ROHRLACH B D, LOUCKS R R. Multi-million-year cyclic ramp-up of volatiles in a lower crustal magma reservoir trapped below the Tampakan copper-gold deposit by Mio-Pliocene crustal compression in the southern Philippines[M]//PORTER T M. Super Porphyry Copper and Gold Deposits—A Global Perspective. Adelaide: PCG Publishing, 2005. |
| [86] | LOUCKS R R. Distinctive composition of copper-ore-forming arc magmas[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 2014,61(1):5-16. |
| [87] |
RICHARDS J P. High Sr/Y arc magmas and porphyry Cu±Mo±Au deposits: just add water[J]. Economic Geology, 2011,106(7):1075-1081.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
RICHARDS J P. Magmatic to hydrothermal metal fluxes in convergent and collided margins[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011,40(1):1-26.
DOI URL |
| [89] | NANEY M T. Phase equilibria of rock-forming ferromagnesian silicates in granitic systems[J]. American Journal of Sciences, 1983,283(10):993-1033. |
| [90] |
RIDOLFI F, RENZULLI A, PUERINI M. Stability and chemical equilibrium of amphibole in calc-alkaline magmas: an overview, new thermobarometric formulations and application to subduction-related volcanoes[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010,160(1):45-66.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
BALLHAUS C. Redox states of lithospheric and asthenospheric upper mantle[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1993,114(3):331-348.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
MOORE G, CARMICHAEL I S E . The hydrous phase equilibria (to 3 kbar) of an andesite and basaltic andesite from western Mexico: constraints on water content and conditions of phenocryst growth[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998,130(3/4):304-319.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
MUNTENER O, KELEEMEN P B, GROVE T L. The role of H2O during crystallization of primitive arc magmas under uppermost mantle conditions and genesis of igneous pyroxenites: an experimental study[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2001,141(6):643-658.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
CLAESON D T, MEURER W P. Fractional crystallization of hydrous basaltic “arc-type” magmas and the formation of amphibole-bearing gabbroic cumulates[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2004,147(3):288-304.
DOI URL |
| [95] | 陈文明. 论斑岩铜矿的成因[J]. 现代地质, 2002,16(1):1-8. |
| [96] |
DAVIDSON J, TURNER S, HANDLEY H, et al. Amphibole “sponge” in arc crust?[J]. Geology, 2007,35(9):787-790.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
HOU Z Q, YANG Z M, LU Y J, et al. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones[J]. Geology, 2015,43(3):247-250.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
WANG R, RICHARDS J P, HOU Z Q, et al. Increased magmatic water content-the key to Oligo-Miocene porphyry Cu-Mo-Au formation in the eastern Gangdese belt, Tibet[J]. Economic Geology, 2014,109(5):1315-1339.
DOI URL |
| [99] | 韩吟文, 马振东, 张宏飞, 等. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003: 268-301. |
| [100] |
HOU Z Q, ZHOU Y, WANG R, et al. Recycling of metal-fertilized lower continental crust: Origin of non-arc Au-rich porphyry deposits at Cratonic edges[J]. Geology, 2017,45(7):563-566.
DOI URL |
| [101] | 鲍新尚, 和文言, 高雪. 滇西北衙金矿床富水岩浆对成矿的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2017,33(7):2175-2188. |
| [1] | 张招崇, 王怀洪, 谢秋红, 沈立军, 朱裕振, 吕云鹤, 金博文. “禹城式”矽卡岩型富铁矿的形成机制[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 1-12. |
| [2] | 何云龙, 张国宾, 杨言辰, 冯玥, 孔金贵, 陈兴凯. 锡霍特—阿林造山带那丹哈达地体四平山金矿床成因与构造背景:锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石和流体地球化学制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 128-153. |
| [3] | 刘青占, 蒋孝君, 王果, 李天瑜, 李东鹏. 内蒙古南炮台花岗斑岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年代学、Hf同位素和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 154-168. |
| [4] | 陈耀新, 刘文恒, 王凯兴, 刘晓东, 孙立强, 尹冬华. 甘肃青山堡中牌细粒花岗岩成因与构造环境:锆石U-Pb年龄和全岩元素组成制约[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(01): 169-182. |
| [5] | 杨俊峰, 张娟, 刘新星, 邱佳炜, 王猛, 成嘉伟, 卢克轩, 王瑛雪. 赣南金竹坪钨矿床多期成矿作用特征及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1449-1466. |
| [6] | 宋彦博, 王建平, 沈存利, 车东, 杨文华, 郭海蛟. 内蒙古扎拉格阿木铜矿床成矿岩体地质地球化学及其成矿学意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1482-1494. |
| [7] | 苏惠, 曾认宇, 甘德斌, 严杰. 阿拉善北大山地区花岗斑岩岩石成因及构造启示:元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1580-1596. |
| [8] | 杜俊, 刘洪微, 常洪伦. 斜长石中人工合成流体包裹体的实验研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(06): 1634-1643. |
| [9] | 梁乾坤, 陈岳龙, 王善辉, 于洋, 杨帆. 嫩江河漫滩沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 529-546. |
| [10] | 韩飞, 宋元宝, 张伟, 李道凌, 黄永高, 李应栩, 贾小川, 杨学俊, 杨青松, 宋旭波, 卢柳. 西藏冈底斯南木林地区晚三叠世中酸性岩浆作用及构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 547-561. |
| [11] | 王瑞廷, 李青锋, 秦西社, 张斌, 王博闻, 冀月飞. 南秦岭太白河地区石英二长闪长岩锆石U-Pb同位素年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 562-572. |
| [12] | 鲁浩, 刘欢, 胡峰, 王海波, 王超, 孔祥超. 西昆仑造山带东段中生代碰撞造山事件的记录:来自新疆温泉—胜利达坂一带三叠纪侵入岩年代学、地球化学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 573-585. |
| [13] | 薛仲凯, 范堡程, 黄豪擎, 唐卫东, 葛战林, 李朋伟, 胡建辉, 杨晓奇, 郭永超, 李空. 内蒙古北山地区中基性岩脉年代学和地球化学特征:对塔里木板块北缘构造演化的启示[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 627-644. |
| [14] | 胡子奇, 张德贤, 刘磊. 束斑直径和能量密度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响研究[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(03): 722-732. |
| [15] | 邓科, 王金贵, 董玉杰, 何林武, 袁仁华, 张泽国, 陈守关, 辛堂. 西藏桑耶地区晚白垩世中性侵入岩的成因及对新特提斯板块北向俯冲的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(02): 375-389. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||